“What are they eating?”: What is a blockchain?
Blockchain is a multifaceted, young and increasingly popular technology. Its versatility is primarily due to the fact that it stands at the intersection of several scientific disciplines and fields of activity.
For example, distributed computing, macroeconomics, and even game theory - game theory methods are widely used in the mathematical apparatus of cryptocurrencies, stimulating various actions of participants.
In today's article, we will see what the blockchain is, touch on the features of its work and take a brief history.
')
 / image DennisM2 PD
/ image DennisM2 PD
Blockchain is a distributed account of events in the digital world. The key component of the blockchain is the transaction log, and the transactions themselves are the only way to change the state of the registry.
A transaction can be executed either to the end or not executed in any way (the “freezing” of the operation in the intermediate state is unacceptable). In this case, entries in the transaction log can be made only with the consent of the majority of network participants.
An important feature of the transaction log in the blockchain is its immutability. This property means that you can not quietly delete a transaction from the log or add a new one in its middle.
The property of immutability is achieved through the methods of cryptography, and not due to the credibility of the organization or people. The two simplest cryptographic algorithms used in the blockchain are hash functions and electronic signatures that ensure the integrity of transactions and are responsible for authorization.
Although the blockchain is a distributed system, each node can form transactions, this does not mean that all participants of the blockchain network are equal - in almost any implementation of this technology roles are assigned to validators (participants writing transactions in the journal), auditors and light clients. . Moreover, this separation is valid not only for private blockchains, but also for open blockchains, such as Bitcoin.
From a global point of view, the blockchain is a network for processing transactions with a set of rules ("protocol"), following which participants can come to a common vision of the transaction log and set the state of the network at a certain point in time. At the same time, the blockchain is decentralized: even if a substantial part of the nodes fall out of work for a long time or get cracked, the system will continue to work anyway.
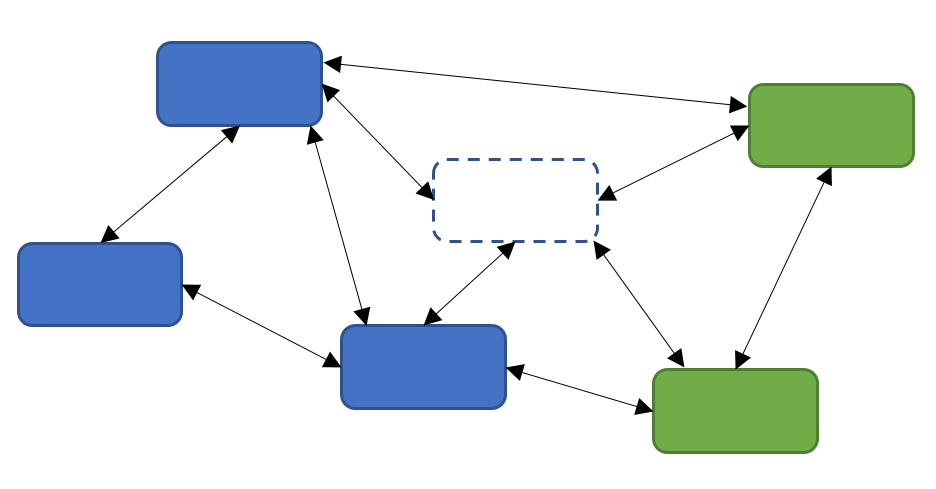
/ The network will continue to work, even if some of the nodes will be hacked
The decentralized, open and mathematically sound nature of the blockchain allows people and organizations to minimize the risks of interaction with each other and conduct P2P transactions, excluding intermediaries. It also has a positive effect on security.
Classical hacker attacks that are capable of causing damage to large centralized banking systems turn out to be unrealizable, or in any case instantly detectable, in a blockchain environment.
If the attacker wants to hack a certain block in the chain, then he will have to crack all the blocks that precede him. In this case, you will have to modify all network logs, the number of which can reach thousands or even millions (if we take into account light clients).

/ It is impossible to change the transaction history without making incorrect all subsequent blocks distributed over the network.
Next, we will look at how the bitcoin blockchain works and how the blocks are processed. To keep track of all ongoing transactions in the network, they are combined into blocks.
Note that the block is a set of digital transactions that were formed in the last 10 minutes (however, it should be added that the inclusion depends on the commission in transactions and other parameters, so the block may not include all transactions in the last N minutes).
The block header includes its own hash, the hash of the previous block, transaction hashes, and additional overhead information. In the bitcoin system, the first transaction in the block always indicates receipt of the commission, which will be the reward to the miner who decided the block.
When solving a transaction block, miners calculate its hash. It is a random sequence of numbers and letters and is a guarantee that if at least one bit changes in a data block, each node can quickly learn about attempting to falsify transaction history. Bitcoin blockchain uses SHA-256 encryption algorithm.
The created block will be accepted by other network members if the numeric value of the header hash is equal to or below a certain number, the value of which is periodically adjusted. The complexity level adapts to the total computing power of the miners. This is done by updating the threshold value every 2016 blocks, which happens about once every two weeks.
Since the hash result (SHA-256 function) is irreversible, the algorithm for obtaining the desired result does not exist - this operation is performed by random search. Usually requires a large number of recalculations.
When an option is found, the node sends the received block to other connected nodes, which check it. If there are no errors, the block is considered to be added to the chain, and the next block includes its hash in its header. Thus, the block chain contains a history of ownership, which can be found, for example, on specialized sites .
The prerequisites for the birth of the blockchain were laid 20–30 years ago. This was facilitated by the emergence of linked time stamps (English linked timestamping ) - collecting transactions into blocks and linking them using hash functions, as well as distributed computing - the principles of building networks that are resistant to falls and malicious behavior of nodes.
The emergence of electronic money played an equally important role when the famous cryptographer David Chaum launched the first practical application DigiCash (although it was not widely used, unlike bitcoin).
The first blockchain is bitcoin cryptocurrency, which still remains the most popular blockchain in terms of economic and technical indicators.
The beginning of the technology was laid by one Satoshi Nakamoto, who published an article in 2008 about the principles of working Bitcoin. The Bitcoin blockchain itself was launched in January 2009.
Bitcoin grew steadily in popularity and led to the emergence of alternative blockchains. Alternatives to the beginning of the 2010s (for example, Litecoin) were built on the basis of the Bitcoin code and differed little from it. Then came the cryptocurrency with a completely new functionality. An example is the privacy of payments for Monero and zCash).
Banks are actively eyeing the blockchain. For example, in the fall of 2016, Bank of America and Microsoft announced the development of a financial blockchain platform.
At the same time, the first real transaction with real money took place - the Israeli company Wave, the British bank Barclays and the Irish dairy producer Ornua held a letter of credit for 100 thousand dollars. The use of blockchain technology has reduced the time of the operation from several weeks to four hours.
In Russia, the blockchain is also used. On December 21 of last year, Alfa-Bank and S7 conducted a letter of credit through the blockchain, and the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, together with major banks in the country, implemented the Masterchain platform, which aims to increase the efficiency of existing financial systems.
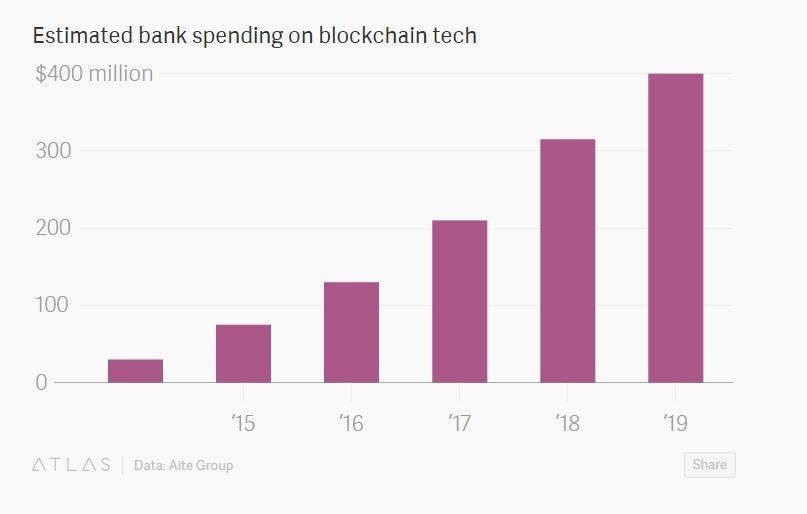
According to the financial and technological consulting firm Aite, in 2015, global banks spent about $ 75 million on blockchain technology. By 2019, this figure promises to grow to 400 million dollars.
Moreover, it became possible to use the blockchain not only for the implementation of electronic money, but also for performing arbitrary distributed computing (smart contracts). The idea is that by running logic on thousands of nodes to it, trust is formed, based on mathematical laws.
Such opportunities opened the way for the blockchain to the corporate environment. IT giants like IBM , Intel and Microsoft have begun to introduce technology into their products. Intra-industry and inter-industry consortia ( R3 , Hyperledger , PTDL Group ), which are involved in the blockchain and distributed registries, are also created.
Researchers who see potential in various fields of activity: finance , healthcare , the Internet of Things have also paid attention to technology. There are more and more new players seeking to popularize the use of the blockchain, for example, the EU Parliament has thought about the implementation of elections to state bodies with its help.
It is safe to say that new projects on the blockchain will be based on its main advantages - openness, security, and security. Therefore, the blockchain will be a good help for any services where users are concerned about the problems of fraud and the safety of personal data.
PS In our next posts we will talk more about the cryptographic algorithms used in blockchains, consensus algorithms, and also consider what smart contracts are and how they are used.
PPS BitFury has been participating in the development of the blockchain since 2011, and we will be happy to share the latest news from the blockchain environment and our own developments. If you're interested, you can pay attention to the following materials:
For example, distributed computing, macroeconomics, and even game theory - game theory methods are widely used in the mathematical apparatus of cryptocurrencies, stimulating various actions of participants.
In today's article, we will see what the blockchain is, touch on the features of its work and take a brief history.
')
 / image DennisM2 PD
/ image DennisM2 PDBlockchain is a distributed account of events in the digital world. The key component of the blockchain is the transaction log, and the transactions themselves are the only way to change the state of the registry.
A transaction can be executed either to the end or not executed in any way (the “freezing” of the operation in the intermediate state is unacceptable). In this case, entries in the transaction log can be made only with the consent of the majority of network participants.
An important feature of the transaction log in the blockchain is its immutability. This property means that you can not quietly delete a transaction from the log or add a new one in its middle.
The property of immutability is achieved through the methods of cryptography, and not due to the credibility of the organization or people. The two simplest cryptographic algorithms used in the blockchain are hash functions and electronic signatures that ensure the integrity of transactions and are responsible for authorization.
Although the blockchain is a distributed system, each node can form transactions, this does not mean that all participants of the blockchain network are equal - in almost any implementation of this technology roles are assigned to validators (participants writing transactions in the journal), auditors and light clients. . Moreover, this separation is valid not only for private blockchains, but also for open blockchains, such as Bitcoin.
From a global point of view, the blockchain is a network for processing transactions with a set of rules ("protocol"), following which participants can come to a common vision of the transaction log and set the state of the network at a certain point in time. At the same time, the blockchain is decentralized: even if a substantial part of the nodes fall out of work for a long time or get cracked, the system will continue to work anyway.

/ The network will continue to work, even if some of the nodes will be hacked
The decentralized, open and mathematically sound nature of the blockchain allows people and organizations to minimize the risks of interaction with each other and conduct P2P transactions, excluding intermediaries. It also has a positive effect on security.
Classical hacker attacks that are capable of causing damage to large centralized banking systems turn out to be unrealizable, or in any case instantly detectable, in a blockchain environment.
If the attacker wants to hack a certain block in the chain, then he will have to crack all the blocks that precede him. In this case, you will have to modify all network logs, the number of which can reach thousands or even millions (if we take into account light clients).

/ It is impossible to change the transaction history without making incorrect all subsequent blocks distributed over the network.
Next, we will look at how the bitcoin blockchain works and how the blocks are processed. To keep track of all ongoing transactions in the network, they are combined into blocks.
Note that the block is a set of digital transactions that were formed in the last 10 minutes (however, it should be added that the inclusion depends on the commission in transactions and other parameters, so the block may not include all transactions in the last N minutes).
The block header includes its own hash, the hash of the previous block, transaction hashes, and additional overhead information. In the bitcoin system, the first transaction in the block always indicates receipt of the commission, which will be the reward to the miner who decided the block.
When solving a transaction block, miners calculate its hash. It is a random sequence of numbers and letters and is a guarantee that if at least one bit changes in a data block, each node can quickly learn about attempting to falsify transaction history. Bitcoin blockchain uses SHA-256 encryption algorithm.
The created block will be accepted by other network members if the numeric value of the header hash is equal to or below a certain number, the value of which is periodically adjusted. The complexity level adapts to the total computing power of the miners. This is done by updating the threshold value every 2016 blocks, which happens about once every two weeks.
Since the hash result (SHA-256 function) is irreversible, the algorithm for obtaining the desired result does not exist - this operation is performed by random search. Usually requires a large number of recalculations.
When an option is found, the node sends the received block to other connected nodes, which check it. If there are no errors, the block is considered to be added to the chain, and the next block includes its hash in its header. Thus, the block chain contains a history of ownership, which can be found, for example, on specialized sites .
A bit of history
The prerequisites for the birth of the blockchain were laid 20–30 years ago. This was facilitated by the emergence of linked time stamps (English linked timestamping ) - collecting transactions into blocks and linking them using hash functions, as well as distributed computing - the principles of building networks that are resistant to falls and malicious behavior of nodes.
The emergence of electronic money played an equally important role when the famous cryptographer David Chaum launched the first practical application DigiCash (although it was not widely used, unlike bitcoin).
The first blockchain is bitcoin cryptocurrency, which still remains the most popular blockchain in terms of economic and technical indicators.
The beginning of the technology was laid by one Satoshi Nakamoto, who published an article in 2008 about the principles of working Bitcoin. The Bitcoin blockchain itself was launched in January 2009.
Bitcoin grew steadily in popularity and led to the emergence of alternative blockchains. Alternatives to the beginning of the 2010s (for example, Litecoin) were built on the basis of the Bitcoin code and differed little from it. Then came the cryptocurrency with a completely new functionality. An example is the privacy of payments for Monero and zCash).
Banks are actively eyeing the blockchain. For example, in the fall of 2016, Bank of America and Microsoft announced the development of a financial blockchain platform.
At the same time, the first real transaction with real money took place - the Israeli company Wave, the British bank Barclays and the Irish dairy producer Ornua held a letter of credit for 100 thousand dollars. The use of blockchain technology has reduced the time of the operation from several weeks to four hours.
In Russia, the blockchain is also used. On December 21 of last year, Alfa-Bank and S7 conducted a letter of credit through the blockchain, and the Central Bank of the Russian Federation, together with major banks in the country, implemented the Masterchain platform, which aims to increase the efficiency of existing financial systems.
According to the financial and technological consulting firm Aite, in 2015, global banks spent about $ 75 million on blockchain technology. By 2019, this figure promises to grow to 400 million dollars.

Moreover, it became possible to use the blockchain not only for the implementation of electronic money, but also for performing arbitrary distributed computing (smart contracts). The idea is that by running logic on thousands of nodes to it, trust is formed, based on mathematical laws.
Such opportunities opened the way for the blockchain to the corporate environment. IT giants like IBM , Intel and Microsoft have begun to introduce technology into their products. Intra-industry and inter-industry consortia ( R3 , Hyperledger , PTDL Group ), which are involved in the blockchain and distributed registries, are also created.
Researchers who see potential in various fields of activity: finance , healthcare , the Internet of Things have also paid attention to technology. There are more and more new players seeking to popularize the use of the blockchain, for example, the EU Parliament has thought about the implementation of elections to state bodies with its help.
It is safe to say that new projects on the blockchain will be based on its main advantages - openness, security, and security. Therefore, the blockchain will be a good help for any services where users are concerned about the problems of fraud and the safety of personal data.
PS In our next posts we will talk more about the cryptographic algorithms used in blockchains, consensus algorithms, and also consider what smart contracts are and how they are used.
PPS BitFury has been participating in the development of the blockchain since 2011, and we will be happy to share the latest news from the blockchain environment and our own developments. If you're interested, you can pay attention to the following materials:
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/326340/
All Articles