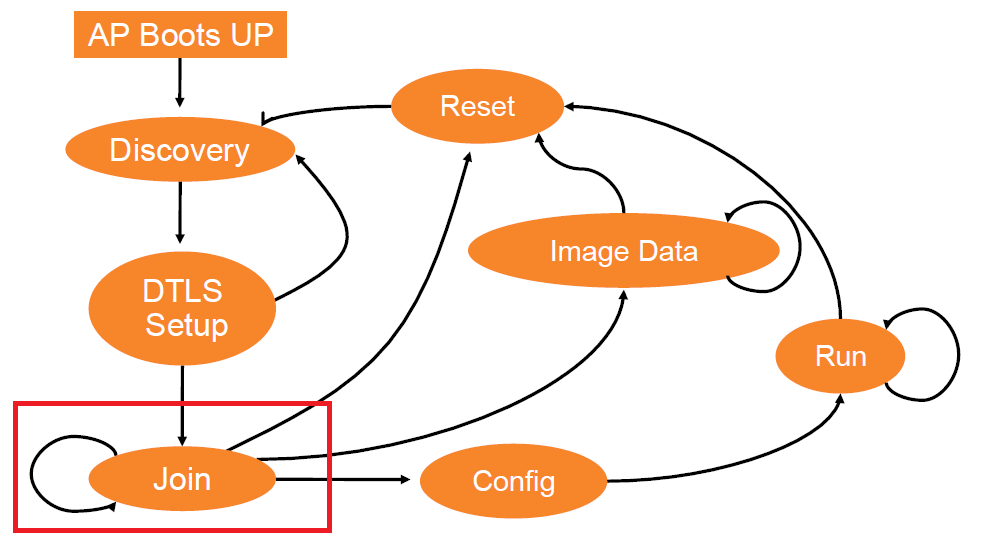
CAPWAP State Machine in the Cisco Unified Wireless Implementation: Join State
After searching the point with all available methods of controllers, sending them a Discovery request, receiving a Discovery response, a list of controllers (controller list) is formed, after which it is decided which controller to try to connect (send a Join Request).
How does the access point choose which controller to connect to?
CAPWAP Join Phase IPv4 (WLC Selection process) on Cisco Wireless AireOS
The following information is returned from the controller to the Discovery response.
- Ap-Manager interface of the controller (the access points are connected to it, it can be the same IP logical interface as the Management);
- controller sysname;
- controller type;
- the number of connected points (to the AP-Manager interface) and the free capacity of the controller (how many more access points can be connected);
- Master Controller Mode flag.
The access point sends a Join Request in the following order, sequentially (only to those from which Discovery response received, that is, which are present in the controller list):
- The access point attempts to send a Join Request to the Primary Controller. Sysname in discovery response and registered on the access point must match!
- If there is no controller in the controller list that is registered as Primary, then the access point tries to send a Join Request to the next, Secondary Controller
- If there are no controllers in the controller list that are registered as Primary, Secondary, then the access point tries to send a Join Request to the Tertiary controller.
- Controller with the Master Controller Mode flag set
- If the access point failed to connect in step 1-4, then it selects the controller with the largest free capacity from the remaining list. Thereby, access points are balanced between controllers (AP-Manager) interfaces of the controller (s).
How to configure Primary, Secondary and Tertiary controllers, as indicated in the previous article .
Master Controller through the CLI is configured (by default, this mode is disabled) using the command
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/325274/
All Articles