Sandbox technology. Check Point SandBlast. Part 1

I am sure that everyone who is interested in information security issues is familiar with the expressions: " Targeted (targeted) attack ", " Zero-day vulnerability ", " 0-day " or even Advanced Persistant Threats (ATP) . These topics can be called the main trend in the field of information security. The same cryptographers are one of the subtypes of these threats. To date, Sandboxes (Sandbox) are the only means that allow you to fight the above threats. Most of the leaders in the field of information security ( CheckPoint , Fortinet , PaloAlto, FireEye, TrendMicro , etc.) have already acquired solutions of the “network sandboxes” class. And if a couple of years ago, many regarded these solutions as something exotic, now most people admit that Sandboxes are almost mandatory for any secure network. However, in RuNet, there is quite a bit of information about such products and the principles of their work. In this regard, we decided to share our own video course, where we briefly consider the main points. As an example, we will in practice show the capabilities of the CheckPoint SandBlast solution, its features and differences from other solutions.
The course consists of three parts. The first part will be devoted to a review of the current situation in the IS world, after which we will draw some conclusions regarding the effectiveness of traditional remedies. And in order not to be unfounded, in practice we will consider an example of the process of infecting a victim’s computer (using Kali Linux ). The text will be quite a lot of pictures from the presentation and if you are too lazy to read, you can watch the video at the end of the article. All interested welcome under the cat ...
Introduction
The first thing I would like to start with is a small statistic on Information Security.
Many still perceive IS as something mythical. But this is a misconception. If you look at the statistics kindly provided by CheckPoint, Cisco, Garnter, you can select the following figures for 2016:
')

And what is most interesting, the situation with information security is getting worse every year. This is due primarily to the motivation of hackers. There are more of them. The question is why? To answer this question, it is enough to analyze the market of cybercrime lately:

At the same time, it is becoming increasingly difficult to figure out a hacker, even if it is a regular student.
- Using Bitcoin you can safely accept payments from their victims.
- TOR anonymous networks allow you to safely enter the malware market. You can buy a ready-made virus and start your malicious activity almost immediately.
- And given the success of modern attacks (for example, cryptographers), the hacker starts earning almost immediately. The average price for the purchase of information is 300-500 dollars.
Those. you need to understand that cybercrime is a real market where you can earn real money . In this case, the profession of a hacker becomes easier and, accordingly, more popular. Thus, when it comes to Information Security, you should not approach this topic with the question " If I am hacked, then ... ". A more correct question would be " When I am hacked, then ... " because if you do not respond adequately to ever-growing threats, then you will definitely be hacked. Accept this fact and try to calculate the cost of the consequences.
Means of protection
What are the remedies we have today?

Many still use Traditional Firewalls. This is either stateful inspection, or even port based. This firewall is not applicable at all on the perimeter of the network. Most modern attacks are carried out within the allowed network connections (tcp, http, smtp, etc.). Classic ME just does not see all these threats.
For a modern network, we need comprehensive protection. For example, NGFW or UTM devices, which are essentially the answer to modern needs. In fact, here we have a huge selection. You can choose UTM solutions, you can use specialized narrowly focused solutions, such as Anti-Spam, Aplication Firewall, DDoS Protector, SIEM, etc.).
However, it is worth noting that almost all the most significant players of information security with their decisions are fighting for 2-5% in the tests conducted. Otherwise, everything goes more or less on a par. This can be seen in the various quadrants of Gartner:
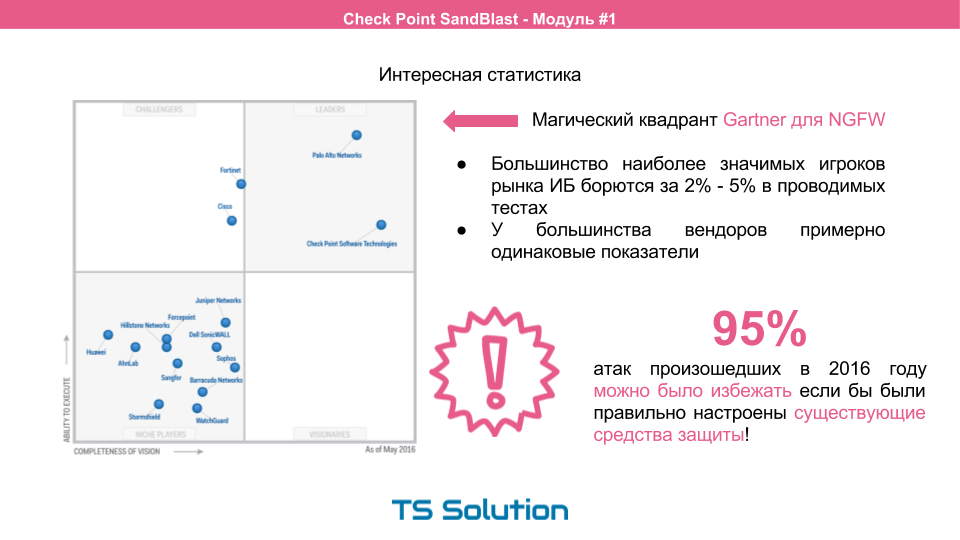
But here's an interesting thing. According to the report of the same Gartner, 95% of all attacks in the past year could have been prevented if existing security tools were properly configured (regardless of the vendor chosen).
This 95% is the so-called fool attack. Take known viruses or trojans and are scattered wherever possible. At the same time there is a very interesting statistics. In the New Year and summer periods the number of attacks increases significantly. What do you think it is connected with? And this is due to the fact that a large number of schoolchildren and students go on vacation and begin to have fun imagining themselves in the role of a hacker. And as mentioned above, due to the poor tuning of existing tools, a rather large percentage of “childish” attacks are successful. This sad statistics does not end there. Most of these malware remain in the network of companies for a long time, they simply cannot be noticed.
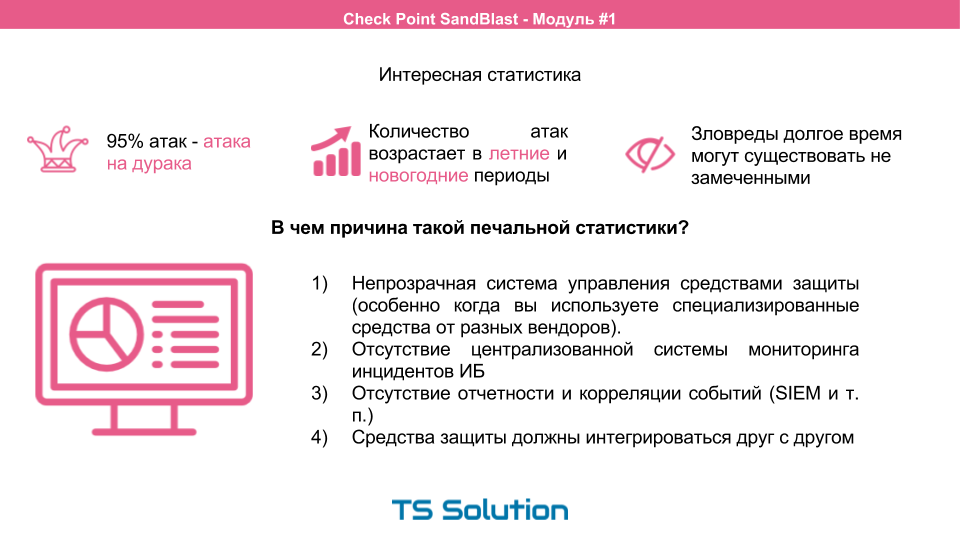
What is the reason? As a rule, it all comes down to an opaque control system of protective equipment. This is especially pronounced if you use specialized tools from different vendors. The lack of a centralized monitoring system and event correlation system (i.e. SIEM) also negatively affects the time of detection of information security incidents. The ideal option is when security tools are integrated with each other. In this regard, UTM devices benefit from specialized, narrowly targeted means. Moreover, it is much easier to study and exploit them, even if it is done by one person.
Why checkpoint?
And yet, why did we decide to check CheckPoint? As I said earlier, most often the difference in the effectiveness of remedies is only a few percent. We will not discuss them, although in this case, CheckPoint shows the best results.
One of the main advantages of CheckPoint is the control system!

It is a quality management system that is the key to effective protection. The CheckPoint control system has been a recognized leader in the information security market for a long time. This is actually the "gold standard". And just recently a new version was announced - the R80. However, our course is not about that. But we will definitely discuss this in a new course.
To summarize all of the above, we can conclude that today, one of the most important aspects when choosing remedies is a comprehensive and at the same time easily manageable protection system that will allow even one person to monitor and analyze everything that happens in the network. So to say, keep your finger on the pulse.
Modern methods of attack
Now let's consider the modern methods of attacks and the myths associated with them:

- Contrary to popular belief, you can get infected not only on adult sites. The erroneous opinion is that if you close all entertainment sites on a proxy server, then users will be safe. Far from it. Hackers can infect quite well-known sites and then the malware can be “picked up” even on a news portal, forum or social. networks.
- Mail is also a favorite hacker tool. But the infected letter can come not only in the form of spam. In a literal sense, a virus can be received by mail from its boss; an attacker simply needs to change the address or send a letter from a similar domain.
- It is also believed that if the virus does get to the computer, then nothing bad will happen and the antivirus will cope with it later. This is fundamentally not true. A few seconds are enough for modern malware to significantly spoil your mood. Antivirus will not have time to react. A prime example is cryptographers who, when launched, begin to encrypt your data. And even if the antivirus subsequently detects this activity, the data will already be encrypted.
Ciphers ... This is a prime example of the possibility of zero-day attacks. At best, you picked up the old cryptographer that you accidentally downloaded from a public site that was hacked by a careless student. Then there is the opportunity to find the key on the Internet, which are periodically published on the network. But there is an option that you picked up something new, still unexplored, the hacker servers have not yet been compromised and there are no keys in the access.
Ciphermakers are probably the most long-playing malware of all. In this case, you do not have the slightest chance to recover your data and you have to pay.
Those. In this situation, classic security tools like IPS, AntiVirus, AntiBot, which work with known signatures, will not save you. Signature analysis will die soon.

The signature concept itself implies that a successful attack has already been noticed. And this first attack could be a computer on your network. Signatures just make no sense. Some viruses or infected files were seen only once. At the same time, a new malware is created in just a few clicks. Or one team, as shown in the figure above.
Zero day attacks
Here we are moving smoothly to targeted attacks, or zero-day attacks. Targeted or targeted attacks are the most dangerous type of attack. Often they are called zero-day attacks, because previously they were unknown. Here is a small statistic:

Such a zero-day attack is being developed for a specific company and even for a specific person. Preparing to attack can even include elements of social engineering.
Malicious software can be hosted on a site that the victim trusts. Quite often, hacking a site is much easier than the victim’s infrastructure. It can also be delivered by mail in a tricky way. In this case, hackers very rarely repeat. Which also greatly complicates their capture.
The whole attack process itself is as follows:

How to deal with intruders if traditional remedies are no longer effective? The answer to this question is provided by the CheckPoint SandBlast technology, to which this mini course will be devoted.

But first things first and foremost, we will do some laboratory work.
Video Course on the first part
As mentioned above, the entire theoretical part of this post can be viewed in video format:
If you are interested in seeing how easy it is to “hack” the victim’s computer, you can familiarize yourself with the records of laboratory work.
1) In the first laboratory, we will test the following scenario:
- We will infect the user's computer by clicking on the link in the letter. For this, metasploit will be used, with which we will exploit the adobe flash vulnerability.
- Get remote access using the Kali Linux distribution. Reverse TCP is used for this.
- We study the logs for suspicious activity (in fact, we will not see anything ...).
- We draw conclusions about the use of traditional firewalls.
2) In the second laboratory work we will repeat the experiment, but only this time we activate additional software blades to see what happens at the moment of infection:
- Configure additional blades on Check Point (Identity Awareness, IPS, AntiVirus, AntiBot, Threat Prevention).
- Enable the detect mode.
- Re-infect the victim's computer.
- We study the logs for suspicious activity.
- Activate the prevent mode.
- We block remote access.
This concludes the first part of the course. In the next two modules, we will consider the work of sandboxes in practice.
PS If you hear about Check Point for the first time, we recommend that you read this article .
PSS After completing this course, we will continue to review the Check Point setup process for conducting a Security CheckUP free audit.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/325246/
All Articles