3CX technical support responds: Plug and Play auto-tuning of IP phones does not work
Quite often we get the following question: a supported 3CX IP phone is used, however, when you first turn on the phone does not appear in the 3CX control interface. Accordingly, it cannot be configured (tied to the user) automatically by Plug and Play technology.
In order for 3CX to intercept a multicast request from an IP phone, due to which the phone appears in the system interface, the following conditions must be met:
- 3CX server must use SIP port 5060
- 3CX must be connected to multicast group
- The IP phone must be on the same IP subnet as the 3CX server.
- The switch must broadcast multicast traffic
- Phone firmware must support PnP auto-tuning.
Consider these conditions in more detail.
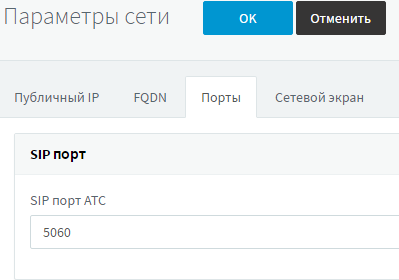
3CX server must use SIP port 5060
In the 3CX interface, go to Settings - Network - Ports tab and make sure that the PBX uses SIP port 5060.
3CX server must participate in multicast group
Depending on the binding of networks to the network interface, 3CX may not “listen” to multicast requests. First of all, it is recommended to disable all unused network interfaces, including Wi-Fi and Bluetooth. After that, make sure that 3CX "intercepts" multicast requests:
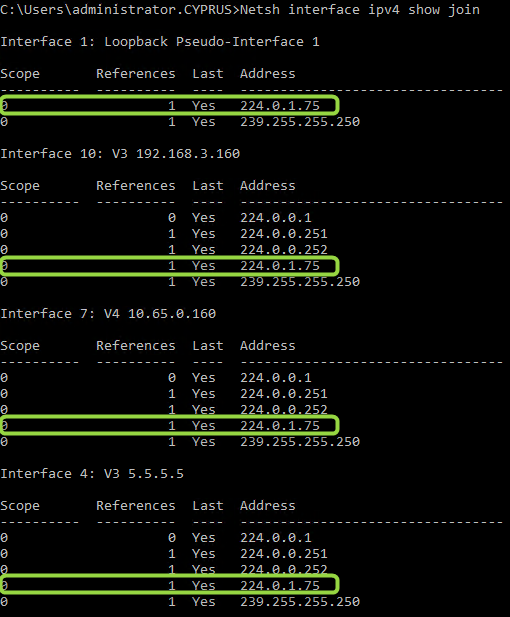
- Open a command prompt and enter netsh interface ipv4 show join
You will see which networks the 3CX interfaces are tied to. The example shows a system with 4 interfaces that are members of the multicast group 224.0.1.75 .
If the multicast group is not in the list of attached networks, 3CX will not “hear” requests from IP phones. To solve the problem in Windows, go to Control Panel - Network and Internet - Network Connections - Advanced - Advanced Settings
')

Set the priority of the interfaces so that the system interface that you specified during the 3CX installation comes first. In other words, the first must be the interface that is used by 3CX to receive SIP requests.

After setting the priority, restart the computer and make sure that the interface is connected to the multicast group.
The IP phone must be on the same IP subnet as the 3CX server.
The auto configuration mechanism uses multicast requests, so PnP-connected IP phones and the 3CX server must be on the same IP subnet.
For example, this configuration will work:
- PBX IP address: 192.168.0.1, subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
- IP address of the phone: 192.168.0.28, subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
And this will not happen:
- PBX IP Address: 192.168.0.1, Mask: 255.255.255.0
- IP address of the phone: 192.168.1.28, mask: 255.255.255.0 (another subnet)
Attention: if you use 3CX SBC (Session Border Controller) to connect phones from a remote network, 3CX SBC will intercept multicast PnP requests and redirect them to the central 3CX server via a 3CX Tunnel connection.
The switch must broadcast multicast traffic
The cost and class of the switch (switch) do not particularly affect the ability to broadcast multicast traffic. On the contrary, expensive managed switches often require additional configuration in order to broadcast multicast traffic. At the same time, simple unmanaged switches broadcast it without problems. However, if for some reason such a switch does not broadcast it, you cannot configure it in any way. Sometimes it helps to update the firmware, if provided. In any case, refer to the technical specifications of the switch.
In general, in most cases, you should have no difficulty with the switch, but these features should be remembered.
Phone firmware must support PnP auto-tuning.
Of course, the IP phone itself must support sending special PnP auto-tuning requests. However, outdated versions of firmware either do not support it at all, or they support it, but not in full. Therefore, if all the above conditions are met, and requests from the phone do not come, you will have to manually update the phone firmware to the latest supported version.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/323754/
All Articles