Internet counterintelligence in action: create a personal information security management system
In previous articles, we considered intelligence methods of obtaining information about a person on the Internet, but never touched on the topic of protection against such actions by our ill-wishers. Now the time has come, and we will do it. Before diving into today's topic, a small disclaimer:
All events and participants are fictional. Any matches are random. The author is not responsible for any negative consequences in the event of the introduction of the countermeasures in question, including physical injuries resulting from an uncontrollable attack of jealousy arising from your second half. Remember: increased security measures may attract unnecessary attention and raise suspicions.
To consider the logic of creating an effective personal information security management system, we will have to create a whole range of actors with their own motives, competencies and threats.
Characters
Ivan Dobroglyuk - a programmer from the city of N, a big fan of Habr, fits well into the portrait of an average habrovtz, which we calculated in the article Internet intelligence in action: who is Mr./Ms. Habraman? . Ivan is a developer at the young innovative IT company Matryoshka Production. Lives with his girlfriend Masha Easy, which has already made an offer.
Masha Easy - loves Ivan very much and is jealous of all girls. Reads Habr. Studies on the 5th year at the Faculty of Information Technology at the N-th Polytechnic University.
Misha Kosyak is an administrator in the provider Shustrine, a former classmate of Masha Light. Passively in love with Masha, considers Ivan his natural enemy.
Angela Suchkova (emphasis on the second syllable) - Ivan's colleague. Works as a programmer in the RnD-department. Angela likes Ivan, and she was very upset to hear about his engagement. Angela leads a double life. At night, she goes online under the nickname badgirl314 and earns additionally a hacker. Specializes in hacking personal computers, “punching” people on the Internet , sometimes penetrates into the computer networks of organizations. Strong and independent girl.
Identifying information assets
Early Saturday morning, Ivan woke up in a cold sweat. He dreamed that someone had hacked his computer and deleted a folder with photos that he carefully collected from school. This sign made our hero take a firm decision to protect his data from possible threats.
Ivan conducted an inventory of all data of value, and determined where they are stored and processed:
| No | Data | Storage |
|---|---|---|
| one | Passwords to Internet services: mail, social networks, cloud data storage, etc. | own head, passwords.txt file on the desktop on a laptop, some passwords are recorded in notes on the iPhone |
| 2 | Financial information: income / expense | mailbox (email alerts from the bank), iPhone (sms) |
| 3 | Correspondence with friends | mailbox, mail client on a laptop, instant messengers on the iPhone, instant messengers on personal pages on social networks. |
| four | Personal data: contacts, biography, psychological profile | social networks, activity data on the Internet (laptop, sites) |
| ... | ||
| N | Photo Collection Folder | laptop hard drive |
Now Ivan will be able to clearly form a list of personal information assets. Ivan remembered that an asset is information and means of its processing, respectively, it can be any kind of data, software and hardware, information systems, etc.
Ivan compiled the following list on a napkin:
A laptop;
Smartphone;
E-mail account;
Account in the social network "VKontakte";
Facebook account;
...
Detection of threats
After Ivan realized that he needed to be protected, he would try to determine what threats he needed to be considered. To do this, he will use the information about the assets recorded above, as well as his assumptions about the sources of threats.
Ivan, after some thought, formed lists of threats, grouping by sources.
His bride Masha Easy can:
peep a password;
read messages from friends and girlfriends;
read messages from the bank about the flow of funds and expenses.
Masha's motives: control over the bridegroom. She doesn't want any fans, unwanted friends, or stashes from her.
Ivan knew from the words of Masha about her strange admirer, Misha Kosyak, and he knew that he was working on an Internet provider that provided them with access to the Internet.
Misha Kosyak can:
intercept Internet traffic Ivan;
follow his activity on social networks.
The main motives of Misha: curiosity and intoxication with his unrequited love for Masha.
Our Ivan also guesses about the possibilities of her colleague Angela Suchkova, as she recently witnessed how the contents of her purse happened to be on the office floor, and his sharp eye highlighted the new Wi-Fi adapter Alfa AWUS051NH, which hackers like to use among various female stuff. for hacking Wi-Fi-networks.
Angela Suchkova can:
try to hack Ivan's computer;
try to get access to his accounts on social networks, e-mail, etc.
The threats of social engineering coming from Angela, our Ivan immediately excludes. He truly loves Masha, so Angela’s red miniskirt doesn’t evoke a tide of emotion.
Angela's motives: to upset Ivan's wedding, finding compromising information on any of the loving couples, as well as “feel out” for Ivan’s financial capabilities.
When compiling the list of threats, Ivan does not forget about threats to physical security and the environment, such as:
theft / loss of a laptop / smartphone;
malfunctions of the laptop / smartphone.
Let's pay attention to the fact that the identified threats are not very detailed, but not very abstract. Excessive detailing can lead to a large amount of unnecessary information that we can not cope with, for example, describing what might break in a laptop. Maximum abstraction can lead to a “separation” from reality and the inability to obtain specific assessments, for example, for each asset only abstract threats of breach of confidentiality, integrity and availability are considered, without being tied to specific attackers, scenarios, etc.
Information Security Risk Assessment: Methodology
Understanding threats is in itself very useful, but we need a tool that will allow us to assess them so that we can “process” them in a timely manner. Such a tool is risk assessment.
What is risk, we all understand at an intuitive level: this is the probability of something bad. Accordingly, risk is a combination of the probability of a threat and the consequences of its realization, and we can derive the following simple formula:
R = P * I,
where R is a risk assessment, P is a probability, I is a consequence.
Our Ivan forms the following criteria for assessing the consequences:
| I | Finance | Image | Relationship with Masha |
|---|---|---|---|
| H | Loss up to 10 000 rubles | Up to 10 people will learn something bad about Ivan | Masha scolds |
| WITH | Loss from 10,000 rubles to 100,000 rubles | 10 to 100 people will learn something bad about Ivan | Masha can be offended and in the evening she will say that she has a headache. |
| AT | Loss of more than 100 000 rubles | Something bad about Ivan learns the entire Internet | Ivan and Masha will part |
A similar table is formed to assess the level of probability of the threat:
P | Statistics | Exposure to threat | Motivation intruder |
|---|---|---|---|
| H | Ivan faces a threat once a year. | Low There are no vulnerabilities. There are effective remedies. | Low The threat will be realized in case of favorable circumstances. Potentially low gain |
| WITH | Ivan faces the threat once a month. | Average. There are vulnerabilities. Remedies are not fully implemented. | Average. There are signs of preparation by the attacker for the realization of the threat. Potentially average win. |
| AT | Ivan faces the threat once a week. | High. There are many vulnerabilities. No security features. | High. There is confidence in the preparation of the attacker to implement the threat. Potentially high gain. |
To determine the final risk value, Ivan forms the following table:
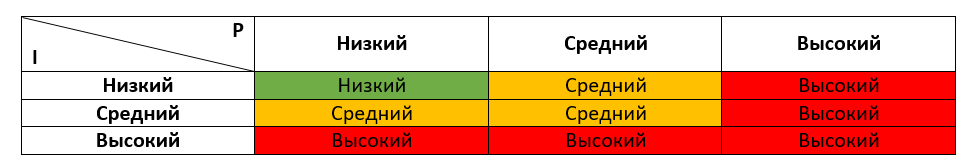
Evaluation of own security
For most of the criteria, you can almost immediately understand where we fall with a specific threat, but it’s better to evaluate the level of probability by the criterion related to the presence / absence of vulnerabilities and protection measures based on the results of a qualitative survey (audit).
How to assess the security of their assets from the identified threats? Professional auditors never disdain such a tool as a checklist, in which points are worth checking out. Ivan decided not to reinvent the wheel and downloaded checklists for Windows 10, Google Chrome and iOS 10 from the Center of Internet Security site.
Windows 10
The checklist from CIS for Windows 10, which includes 931 pages, impressed Ivan so much that he had to adopt such an auditing method as selective testing of countermeasures. He checked only some settings: updates, privacy, Wi-Fi networks (respectively, in the search you need to type “privacy”, ”updates”, “Wi-Fi”).
Ivan additionally checked the system updates level using the systeminfo command, obtaining a list of installed fixes:
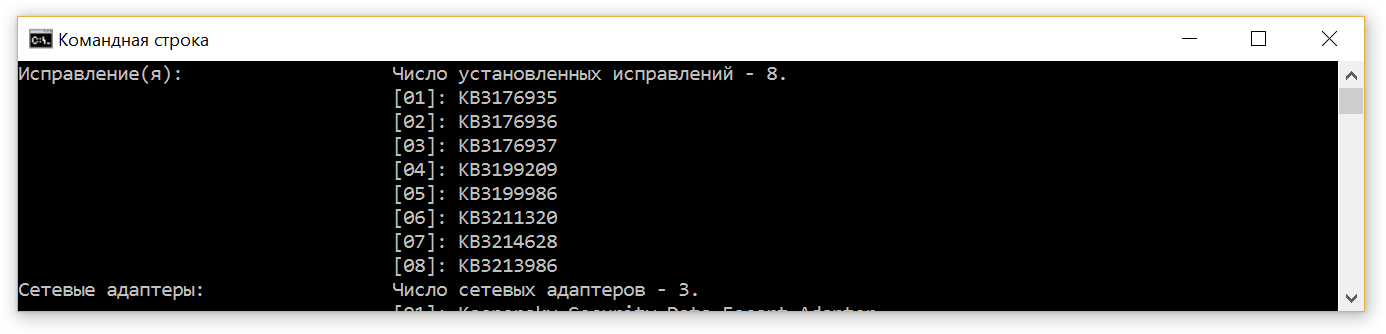
Going to the Microsoft website: https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/4000825/windows-10-and-windows-server-2016-update-history Ivan saw that a couple more updates were released after the last KB3213986 installed by him:
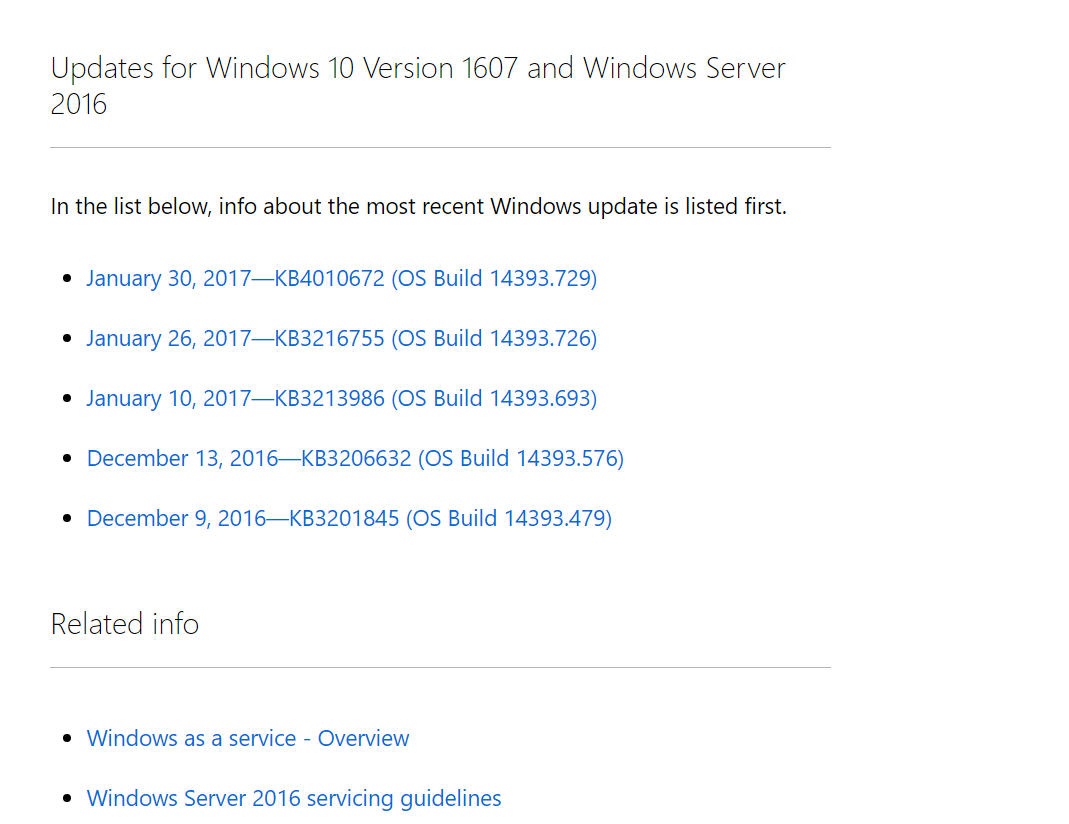
After reviewing the description of the missing updates, our hero made sure that there are no security-related fixes, and concluded that the update level of the operating system is quite decent.
As a result of the analysis, Ivan found only that the laptop can “merge” unnecessary information, since it has enabled the location service and a number of monitoring functions for the user's activity.
Google chrome
On his own experience, Ivan knew that it was not good when browsers kept their browsing history, remembered passwords, used outdated versions of plug-ins, and they themselves were not updated.
Ivan also decided to manually review the Google Chrome browser settings with a CIS checklist on his knee ( chrome: // settings / ), and additionally use a couple of online services:
Browser security check: https://browsercheck.qualys.com/
Checking the browser for "draining" extra information to curious sites: http://webkay.robinlinus.com/ and https://browserleaks.com/
As a result, Ivan found that:
passwords are stored in the browser for access to the social networks VKontakte and Facebook;
the browser does not block data and cookies from third-party sites (Settings-> Advanced settings-> Content settings), respectively, overly curious sites can track in which social networks it is authorized.
iOS 10
Similarly, Ivan checked the settings and his iPhone, finding several flaws:
erasing all data on the phone after 10 attempts of selection is not activated;
synchronization of notes with iCloud is turned on, and as we remember, Ivan wrote down some passwords in them and was sure that they remain only on the phone;
The option to send the “Do not track” header in the Safari browser settings is disabled.
Social networks
Guided by logic, Ivan made 6 points, by which he checked his accounts in the networks of VKontakte and Facebook:
Friends should include only trusted people, since friends, as a rule, have greater access to data;
Privacy settings should adequately distinguish between what is visible to all, and that only to friends;
Published data (including posts) contain only the information that we want to share;
It is necessary to check whether there is superfluous information on the published photos (car numbers, addresses, phone numbers, coordinates, etc.);
Correspondence with contacts does not contain personal information;
Among authorized applications, only those that are really needed.
The creators of Facebook recently created the Privacy Check feature, which allows you to conduct an express audit of basic privacy settings.
Also through the menu item "Quick privacy settings" you can view and change other settings. Ivan did not forget about account security settings: https://www.facebook.com/settings?tab=security
In contact with
The interface of the Russian social network is more convenient and you just need to select the “Settings” menu https://vk.com/settings?act=security and see the options in the “Security”, “Privacy” submenus, as well as application settings.
As a result of this analysis, Ivan found that:
among his friends in social networks there are little familiar personalities who show no activity, but perhaps follow everything that he publishes, and it can be assumed that one of these personalities hides Misha Kosyak known to us;
over the years of its presence in social networks, a whole mass of third-party applications have accumulated, with access to its contact information and not only.
Gmail
Having logged in to your Gmail account, our hero was upset because he discovered:
mail account turned into a real trash he never cleaned. In this case, it was possible to find very sensitive things in this garbage: personal correspondence, information on receipt and withdrawal of funds, passwords for access to various accounts;
Smart Lock was enabled for passwords https://passwords.google.com , which gathered a lot of passwords for various sites.
Identify possible incidents
In addition to assessing your security, it is also a good idea to see if there are any signs that someone has taken advantage of our carelessness and is already reading our correspondence on social networks or in the same Gmail. Now it is quite easy to do this, since this functionality has been implemented in all the considered services:
Gmail
control device connections: https://myaccount.google.com/device-activity
Gmail connection history: go to Gmail.com and in the lower right corner click on "More Information".
In contact with
https://vk.com/setting?act=security
https://www.facebook.com/settings?tab=security§ion=sessions&view
Windows logs can be viewed in the Event Viewer by typing eventvwr on the command line.
During the test, Ivan discovered that in the list of devices from which connections were made to his account, there is a foreign computer running Linux. He immediately thought of Angela Suchkova. Sadness added to Ivan the fact that the tracking of his actions was enabled ( https://myactivity.google.com/myactivity ), and Angela probably found out about the sites Ivan visited and about his secret passion for interesting photos.
Information Security Risk Assessment: Results
Understanding information security threats and existing vulnerabilities, Ivan applied the risk assessment methodology he developed. For each asset, Ivan formulated risks and recorded possible sources of threat.
Risk assessment was conducted approximately as follows:
“Masha can find my valuable photo archive on a laptop. She may understand everything wrong, think that something is wrong with me and, perhaps, even give up ... How can she get access? It may come up with the camera turned on on the smartphone and record how I enter the password ... Or I will forget to lock the screen. Angela can throw a trojan and go through the entire disk. The probability is high, the consequences are at least moderate. The risk, of course, is high. ”
Ivan records an information security risk assessment:
| No | Assets | Risk statement | Source of threat | Probability | Effects | Risk assessment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| one | A laptop | Theft | Unknown | H | AT | AT |
| 2 | A laptop | Failure with data loss | Nature | H | AT | AT |
| 3 | A laptop | Traffic interception | Misha | AT | WITH | AT |
| four | A laptop | Windows password compromise | Masha | AT | WITH | AT |
| five | A laptop | Unauthorized file access | Masha, Angela | AT | WITH | AT |
| 6 | A laptop | Malware infection | Angela | WITH | AT | AT |
| 7 | Smartphone | Theft | Unknown | WITH | WITH | WITH |
| eight | Smartphone | Failure | Nature | H | WITH | WITH |
| 9 | Smartphone | Unauthorized access to messages | Masha | AT | WITH | WITH |
| ten | Social Network Accounts | Unauthorized access to correspondence with contacts | Masha, Angela | WITH | WITH | WITH |
| eleven | Social Network Accounts | Leakage of sensitive information | Misha, Masha, Angela | WITH | WITH | WITH |
| 12 | Email account | Unauthorized access to e-mails | Masha, Angela | WITH | AT | AT |
| 13 | Passwords | Unauthorized access to passwords | Misha, Masha, Angela | WITH | WITH | WITH |
Choosing and implementing countermeasures
Ivan assessed risks not just for the sake of art, but in order to then select the appropriate risk treatment methods.
There are only four risk treatment options:
minimization - the introduction of countermeasures;
avoidance - changing the process in such a way that the risk ceases to be relevant;
transfer - transfer of risk to a third party (for example, outsourcing);
acceptance - consciously accepting the possibility of realizing the threat and its consequences.
The most common risk management principle is the following: assess the risks, then take the low immediately, and high and medium to minimize the risks through the introduction of countermeasures, and take the low residuals.
Our Ivan has 13 risks and all of them need to be minimized. He sits down again at Excel and begins to think about what measures will allow risks to be minimized:
| No | Assets | Risk statement | Countermeasures |
|---|---|---|---|
| one | A laptop | Theft |
|
| 2 | A laptop | Failure with data loss |
|
| 3 | A laptop | Traffic interception |
|
| four | A laptop | Windows password compromise |
|
| five | A laptop | Unauthorized file access |
|
| 6 | A laptop | Malware infection |
|
| 7 | Smartphone | Theft |
|
| eight | Smartphone | Failure |
|
| 9 | Smartphone | Unauthorized access to messages |
|
| ten | Social Network Accounts | Unauthorized access to correspondence with contacts |
|
| eleven | Social Network Accounts | Leakage of sensitive information |
|
| 12 | Email account | Unauthorized access to e-mails |
|
| 13 | Passwords | Password compromise (unauthorized access, guessing, etc.) |
|
Having received a list of countermeasures, our hero began to look for appropriate solutions. Since he secretly saved up Masha for her wedding gift, he was guided by free means of information protection or those that require minimal expenses.
Consider the implementation of several key measures.
Hard Disk Encryption
Ivan carefully studied the list of solutions published on Wikipedia https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comparison_of_disk_encryption_software and chose VeraCrypt
Our hero was well aware of the reverse side of using data encryption: if something goes wrong and the integrity of the crypto-container is broken, it will most likely be impossible to restore something.
Guaranteed data destruction on the hard disk
Ivan knew that it’s not so easy to delete a file. Even deleting from the recycle bin does not deprive attackers who have received physical access to the computer from being able to restore it with the help of special utilities for working with hard disks.
On the Internet, Ivan found the Eraser project and installed the utility. Now he started working with files containing critical information for him as follows: the file is created and stored in a crypto container created using VeraCrypt, if the file is outside the crypto container, then after working with it, it is deleted using Eraser. Ivan also planned a daily cleanup of the “Downloads” folder, in which garbage always accumulates, among which you can find files with information that is interesting to attackers.
Encryption network traffic
Encryption of data transmitted over the network can be provided in various ways and for different services.
Web traffic: we all know that HTTPs is used to hide it from prying eyes. To automatically switch to HTTPs (where possible), Ivan decides to use a special plugin for Chrome: HTTPS Everywhere .
Mail traffic: to access mail servers, SSL protocols are required.
Ivan decides for himself that he will protect critical correspondence with public-key cryptography. To do this, he will need an email client, for example, Thunderbird , a Gpg4win encryption software package and a plugin for Thunderbird called Enigmail . Ivan generates a pair of public / private key. Open informs your friends, and closed keeps in a safe place.
Ivan is thinking to encrypt all his traffic passing through the untrusted provider, in which Misha works. Our hero is considering options for VPN services, such as https://torguard.net/pcmag-vpn-discount.php or https://www.hidemyass.com , is also thinking, not whether to rent him an external server on which to raise the proxy and OpenVPN, but so far it does not, as it is costly, and he saves money for the gift of his beloved Masha.
Malware Protection
Even from school, Ivan knows that it is not safe to go on the Internet without a good antivirus. Therefore, he did not regret the money and bought a reliable antivirus. Ivan also knows that even his favorite antivirus will not provide a 100% guarantee of protection, and therefore just in case he creates virtual machines with Linux and Windows to work with potentially dangerous data. For example, if a letter arrives that can contain both “malware” and interesting information with equal probability, Ivan starts the virtual machine from snapshot and loads the data, then disconnects the network for the virtual machine and opens the file. If there was a malware instead of useful information, then nothing terrible will happen - after all, the original snapshot remained.
Passwords
There is no worse vulnerability than a weak password. A modern person is constantly overloaded with information, and here you also need to remember the passwords to numerous services. How to be? In fact, there is no need to remember a large number of passwords. You can remember only two passwords: the password from your main mailbox, to which all services are tied, and the password from the password database, which stores all other passwords generated according to all best practices: long, with special characters, with characters in different registers. This password database can be maintained using the free KeePass utility. The password database itself is of course encrypted, but for additional protection you can write it to a reliable external medium and work with the data only on it. Your passwords will be stored in just two places - in your pocket and in your head.
Our hero did.
Threats are beginning to be realized
Having created a personal information security management system, Ivan began to sleep much calmer, because now his valuable photo archive is stored in encrypted form, and also in duplicate. Periodically, Ivan conducted an assessment of security, looked at the logs, thought about new risks and, if necessary, adjusted his information protection measures.
Several months passed, the wedding day of Ivan and Masha was approaching. In desperation, Angela decided on the last spurt: Ivan received a letter from her to her almost abandoned box, located on the mail server of the known provider Shustrinet. The subject of the letter: "My photos in your collection." Intuition suggested to Ivan that it would be better not to open the letter, but curiosity got the upper hand: suddenly it will turn out to be replenished with new materials. Ivan with all precautions launched a special virtual machine sandbox and opened the received files. Troyan, prepared by Angela, started, but did not find anything interesting in the empty virtual machine and could not even inform its owner about the negative result, as there was no access to the Internet. Ivan disappointedly found in the letter intimate photos of Angela and was convinced of the correctness of his choice in favor of Masha.
Misha Kosyak has long been intercepting letters that came to the box of his enemy on the server controlled by him, but lately it happened very rarely, so Ivan used mail on Gmail and turned on encryption. Misha opened the intercepted letter with interest and saw in the photographs the girl of his dreams. He immediately forgot about his love for Masha the Light.
Angela Suchkova was looking forward to the incoming connection from a skillfully trained Trojan, and here is the luck: there is a contact. Angela looked through the contents of the disc of a compromised computer and realized that this was not Ivan’s laptop. She sent a command so that the installed camera would take a photo of the person sitting behind the monitor. After receiving the photo, she realized that it was her fate. I launched Misha notepad remotely on the computer and spent the whole evening discussing Japanese poetry in it.
Both couples soon married, and they began a happy and carefree life. On the first wedding night, Ivan opened up to Masha and showed his collection of UFO photos. Masha found this hobby very interesting.
Instead of concluding with a couple of words about ISO 27001
The considered case may seem a little frivolous to us, but in fact we have just considered the principles of the information security management system (ISMS). In serious organizations, the ISMS is being implemented on the basis of the international standard ISO / IEC 27001: 2013, which describes the steps that the organization must take to build an effective management system. These steps correspond to the well-known Shewhart-Deming cycle Plan-Do-Check-Act. . , , , British Standards Institution (, ISO 27001). - , : / . ed. ... .: , 2017. 224 .
, , «» !
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/322996/
All Articles