The reverse side of the operation of payment technologies based on NFC and MST
According to the results of issuing Yandex, the main question of users on the topic of NFC is “What is NFC and how to learn to use it?”. This contrasts strongly with the same Google, where the question is another. They already know what NFC is - there is an NFC in every household there. The question is how to apply what is given? What can I do using NFC? What should an ordinary non-advanced user do with near-field technology?
First, here is a list of several smart devices compatible with NFC: Nexus 6 , Sony Xperia Z3 , iPhone 6/7 , Samsung Galaxy Note 4 , LG G3 , HTC One M9 . For those who like to study and compare devices, here is the complete list .
Very soon, NFC chips will be built into the smartphones of all manufacturers, and even fitness trackers will work on the basis of NFC. Apple uses this technology in the Apple Watch, and now you can pay for goods through Apple Pay with a wave of the hand.
')
This is how reading a card with an EMV chip looks like:
What was the excursion to EMV for? In order to clearly show that with the advent of NFC, almost all previous steps (actions) had to be somehow repeated, replicated, transferred to a phone or other contactless device.
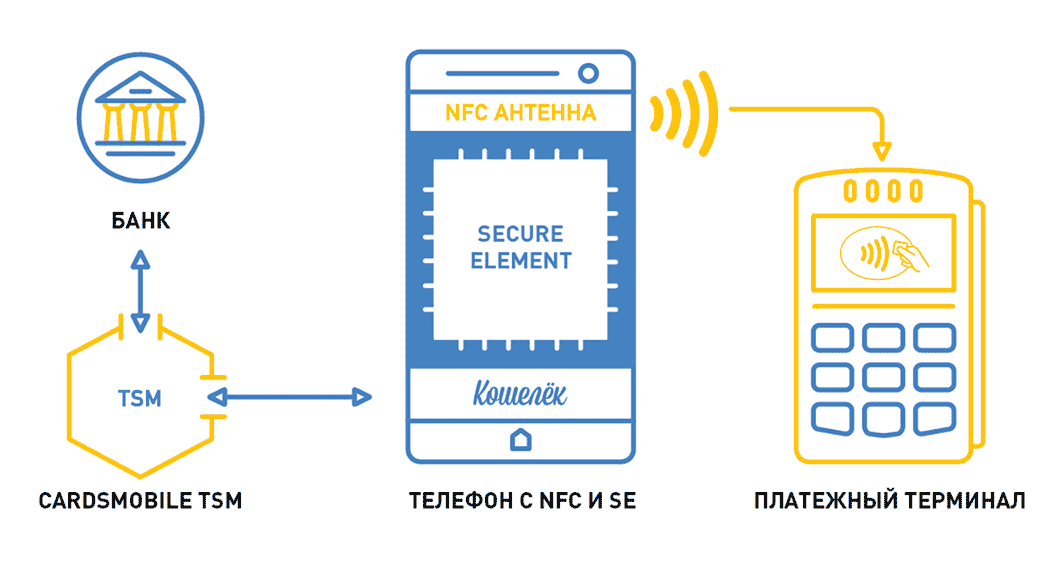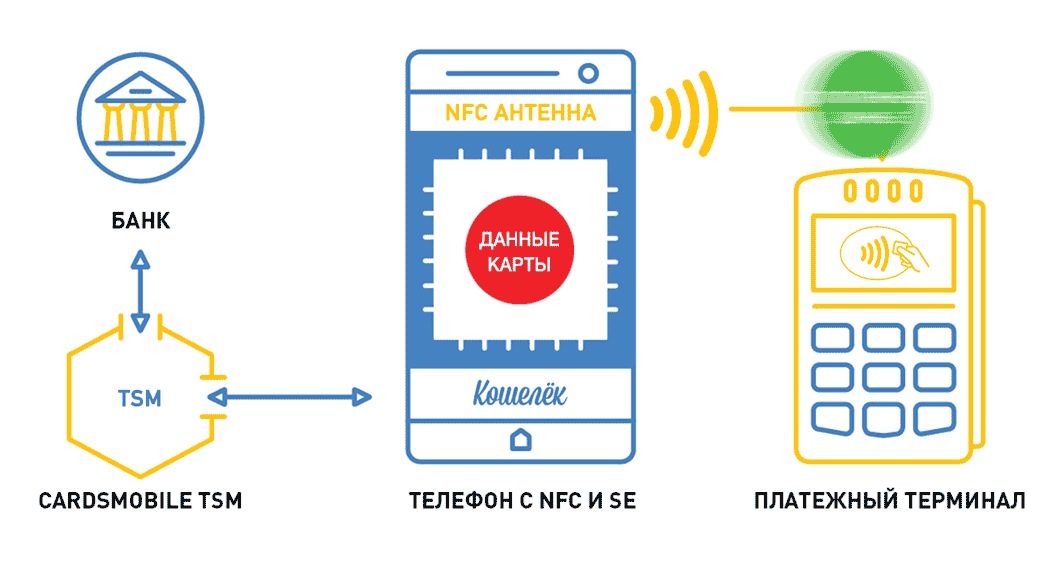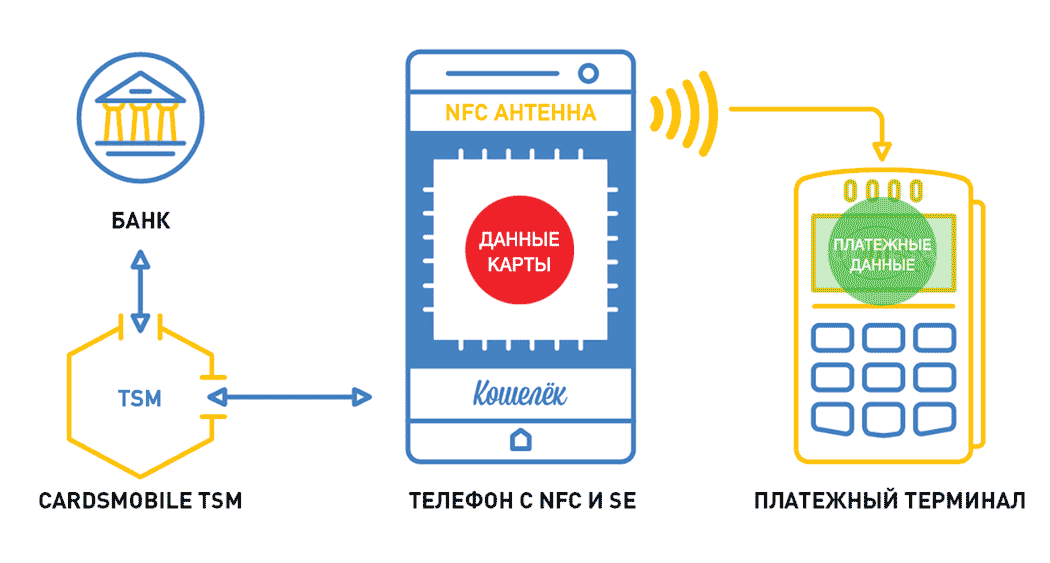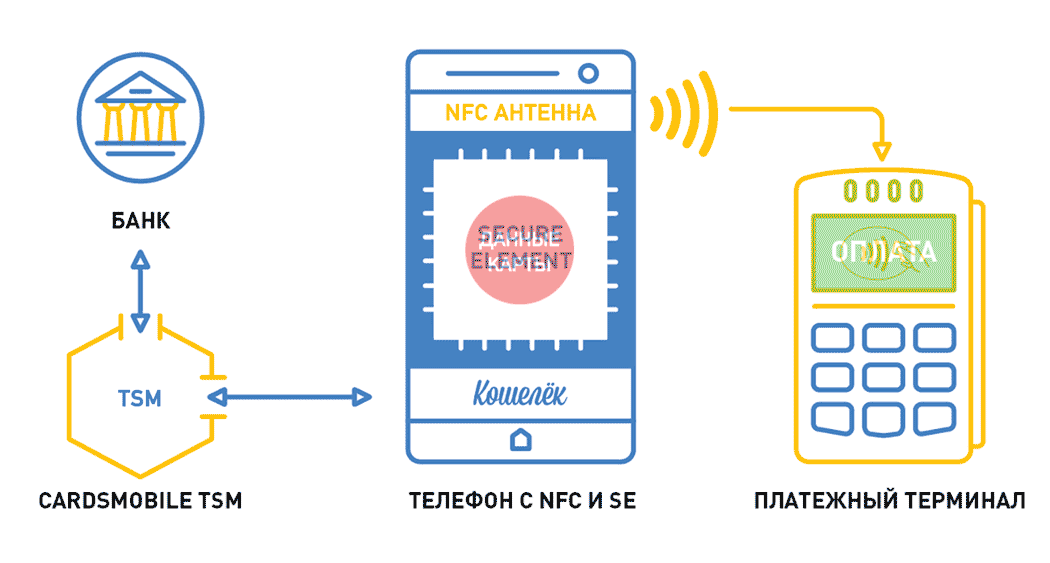
Next we'll talk about what TSM and SecureElement are, which make NFC transactions more secure. After all, if the card is not emulated in the phone using HCE (HostCardEmulation), then the data must be stored somewhere. SecureElement is just busy solving this problem.
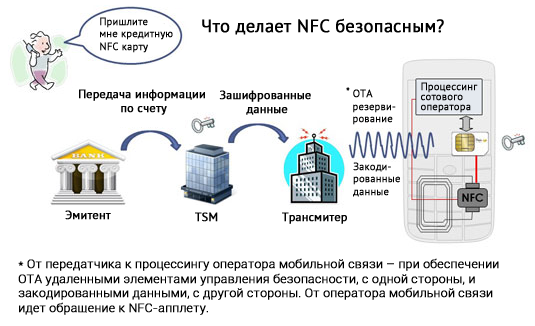
OTA - remote control of security elements.
TSM - TrustedServiceManager is a unique intermediary that owns the keys. This is a hardware and software complex that provides technological relations between telecom operators and service providers.
Key services of a trusted third party include secure download and content management of the security element, performed when interacting with mobile service providers. These can be banks, transport companies, service providers and aggregators. Remote control of applications, usually performed using wireless cellular technologies (over-the-air, OTA), includes installation and personalization of applications in the mobile phone security element, as well as further maintenance of installed applications throughout their life cycle, as well as service support Read more about the role and place of TSM in the NFC ecosystem here .
SecureElement is a secure item in an NFC device — data stored in the device’s wallet. This is a separate microprocessor responsible for the safe storage and operability of Mastercard Mobile PayPass / VisaPayWave payment applications. Either it is made built-in (installed on the motherboard of the phone), or it is placed on a detachable module: UICC SIM card / SD memory card.
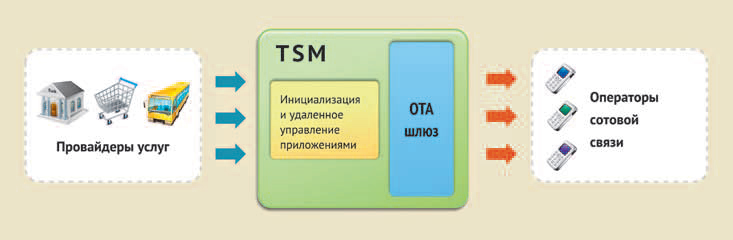
For a clearer understanding of the daily use of the TSM platform, we quote an excerpt from the MTS March 3, 2014 press release :
“With the advent of the TSM platform, the last infrastructure constraint on the way of mass development of NFC services in Russia is removed - we will get a link in the NFC ecosystem, a single“ entry point ”for quick connection of a wide range of service providers ... For the user, our new technical complex allows and secure download “by air” directly to the SIM card of an electronic image of bank and transport cards, travel tickets, loyalty cards, passes. Soon, the MTS subscriber will only need to receive an NFC-enabled SIM card in the MTS salon once, in order to process duplicate plastic bank cards in the future without visiting the bank or buying travel tickets, receiving discount coupons without contacting points of sale. And all this will fit in one smartphone surrounded by a friendly interface with complete information about all available contactless cards. ”
Now you can check the clock and see how the plans were justified. Technologically very justified. It was possible to embody a lot.
NFC chips are already so popular that even the news about their subcutaneous implantation is not new to people.
Prior to Evgeny Chereshnev (2 years ago, a Russian implanted a NFC-biochip in his hand, “which will open doors, store data, pay in cafes and much more”) was Martin Vismeyer, known as MrBitcoin. He implanted two NFC chips to store the cryptocurrency. Moscow engineer Vlad Zaitsev sewed in himself a chip from the Moscow transport card "Troika": now with the help of his hand, he pays the fare in transport, and also opens the door of the office.
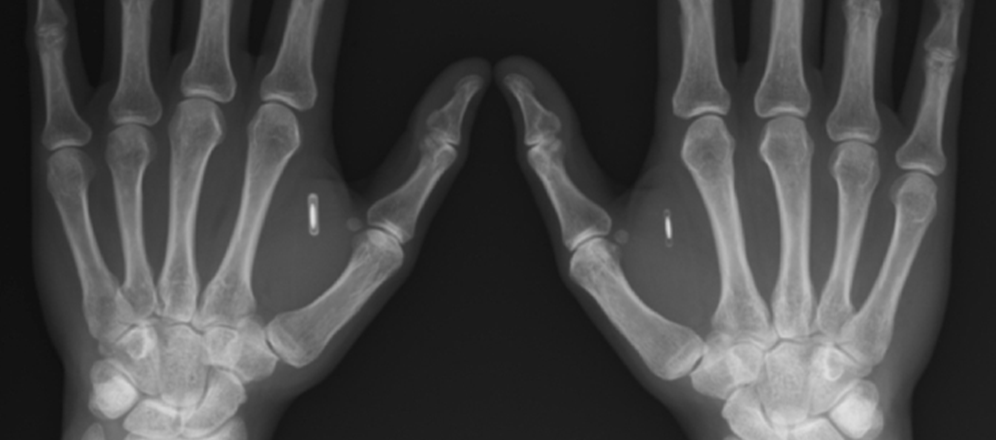
NFC chips in the photo are sewn into the hands. But there are other NFC devices, such as a payment ring: medical titanium, embedded chip (read mode, write support, business card transfer), keychain, sticker on the gadget, case for smartphones, NFC-watch - all these The devices will support data transmission provided that an NFC device is inserted into them, which will serve to transmit financial or other informational data.
If earlier, to protect the card and the transaction relied on encryption of data on the magnetic stripe of the card, and then all hopes were connected with the applets of the chip itself, now the security of payment transactions is associated with tokenization. As the NFC technology strengthened and simultaneously simplified the data transfer method, so tokenization through NFC greatly enhanced the security of card transactions.
Yevgeny Chereshnev, who visited TED in New York, published his reflections on the topic of modern biochips (and the NFC chip, embedded subcutaneously, is biochip) on Facebook.
A person who has successfully lived with a biochip under the skin for more than two years, based on his experience, introduces a new term “digital DNA”. Against such a background, will not the familiar NFC seem like a relic and technological rudiment? However, so far far away.
For now, it is important to continue working on security in the area of financial transactions, including NFC transactions. Tokenization is an indispensable companion of NFC transactions.
Tokenization is the method of protecting your card's data, in which the card number (PAN) is replaced with a virtual (token), a unique and randomly generated set of numbers. The tokens themselves can be both disposable and reusable. This technology derives from NFC technology.
Tokenization allowed the user to tie their cards to mobile wallets, while not informing the merchants of the real card number, and replacing it with a tokenized one. Thus, it is safe to send transactions from the phone or pay for the purchase using the phone, using tokenization.
Replacing the details of payment cards with randomly selected symbols / numbers (tokens) that will be stored in the database of stores where the user makes a payment is convenient for further purchases - with just one touch of a finger you make a payment. In addition, for each online store can be formed its own set of characters. For example, the VISAToken service initially worked only on iOS devices (Apple Pay became the first platform for experimentation), but later on tokenization was supported on other NFC devices.
How is data exchanged when using a token?
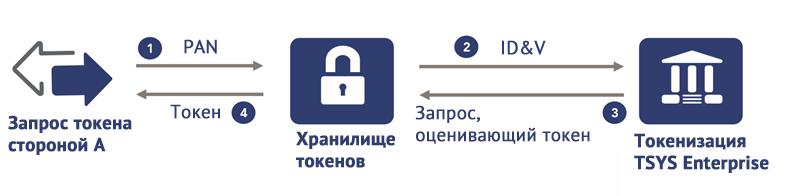
And this is how the authorization request looks like:
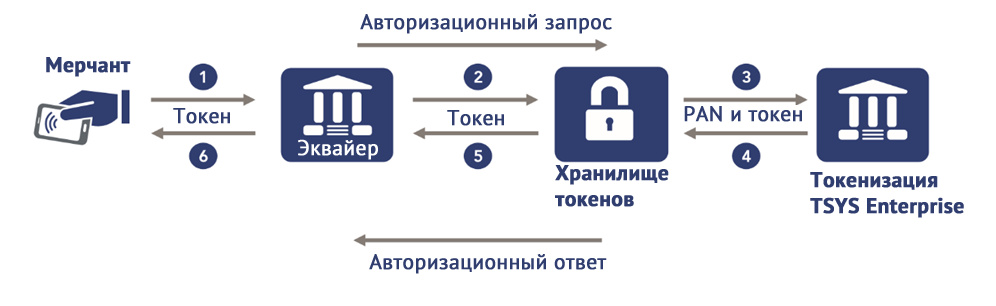
Already developed tokenized payment gateway, for example, Rambus Bell ID. It is a software platform that manages all transactions made through tokens (keys) between issuers and "multichannel" providers of tokenized services through a single payment gateway. The PSP (payment service providers) are being replaced by TSP (tokenized service providers).
VISA payment system introduced the Visa Token Service for European banks. The main platform on which VTS will work will be Apple Pay. However, all devices with an NFC chip can support this system. In 2015, Mastercard launched the Digital Enablement Express (Express) platform to accelerate the provision of additional features to millions of buyers when making secure electronic payments. The Express service accelerates the process of digital conversion and tokenization using Mastercard cards through the Mastercard Digital Enablement Service (MDES) platform. This technology will allow you to turn any accessory, gadget or household appliances into a device with the function of payment.
Apple Pay payment system uses NFC. Samsung, building up its payment system, relies on both NFC technology and MST (Magnetic Secure Transmission) technology - a magnetic-safe transmission. If the first device must be equipped with an NFC receiver, the MST simulates the transmitted magnetic field using an induction loop built into the device, which creates a magnetic field easily readable by the MAG terminal, as if an ordinary card transaction had been made.
According to the market, both technologies suffer from user neglect. If NFC transactions suffer from the fact that only 10% of terminals are equipped with the same receiver, then with MST the picture is better, but also strange: it is likely that up to 10% of receiving devices will not be able to read MST transactions. Meanwhile, both the first and second technologies are completely reliable: both use tokenization and protect the card number from others eyes, both support NFC to transmit information on the card. Samsung took a step forward by offering MST, but the user is too lazy and conservative to appreciate it now.
Contactless payments received the name "cash 2.0", and meanwhile, from the Bank 2.0 all long ago rushed to the Bank 3.0. “The bank today is not the place where you go, but what you are doing.” Brett King writes quickly, but news from the world of financial technology is becoming obsolete and becoming commonplace even faster. When King’s next masterpiece is published, most likely tokenization, MST, NFC, RFID tags - all this will become the classic toponymy of Bank 3.0.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/322822/
All Articles