The role of the payment service in online transactions
In the first part of the story devoted to the evolution of a financial transaction, we showed the reflection of payments between the seller and the buyer, starting with checks and ending with digital innovations of contactless payments. Entropy increases, and interaction patterns change. A new link appears in the chain - a payment service that performs the functions of processing and routing a transaction from the payer to the recipient. These tasks of business are fulfilled by our payment platform Fondy .

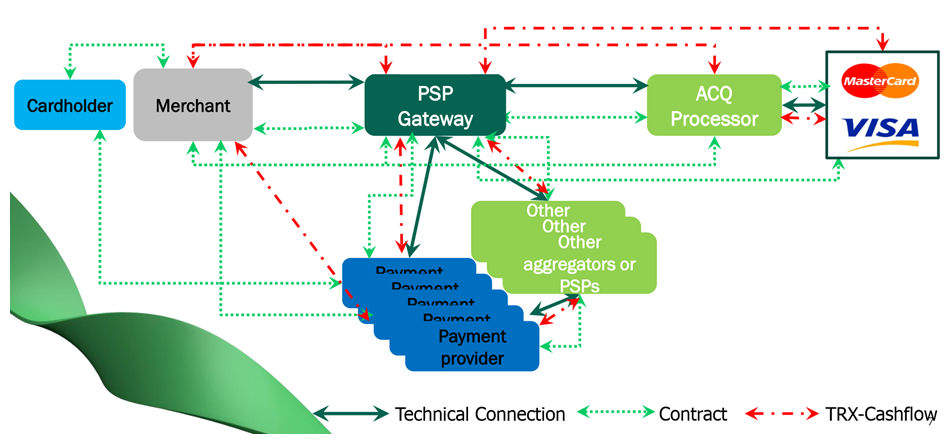
With the advent of a new member online - a payment gateway or PSP Gateway (Payment Service Provider Gateway), the acquiring scheme has become different from the traditional one.
One of the definitions of a payment gateway may sound like this: a payment gateway is a service intermediary that performs processing of electronic transactions and is only a payment router. In technical language, a payment gateway is a software module that routes payments between an online store and various acquirer banks and other Internet acquiring service providers through a single interaction protocol.
')
Thus, it is more logical to call the payment gateway an integrator of payment solutions and remember that there is no financial-accounting function in its activity.
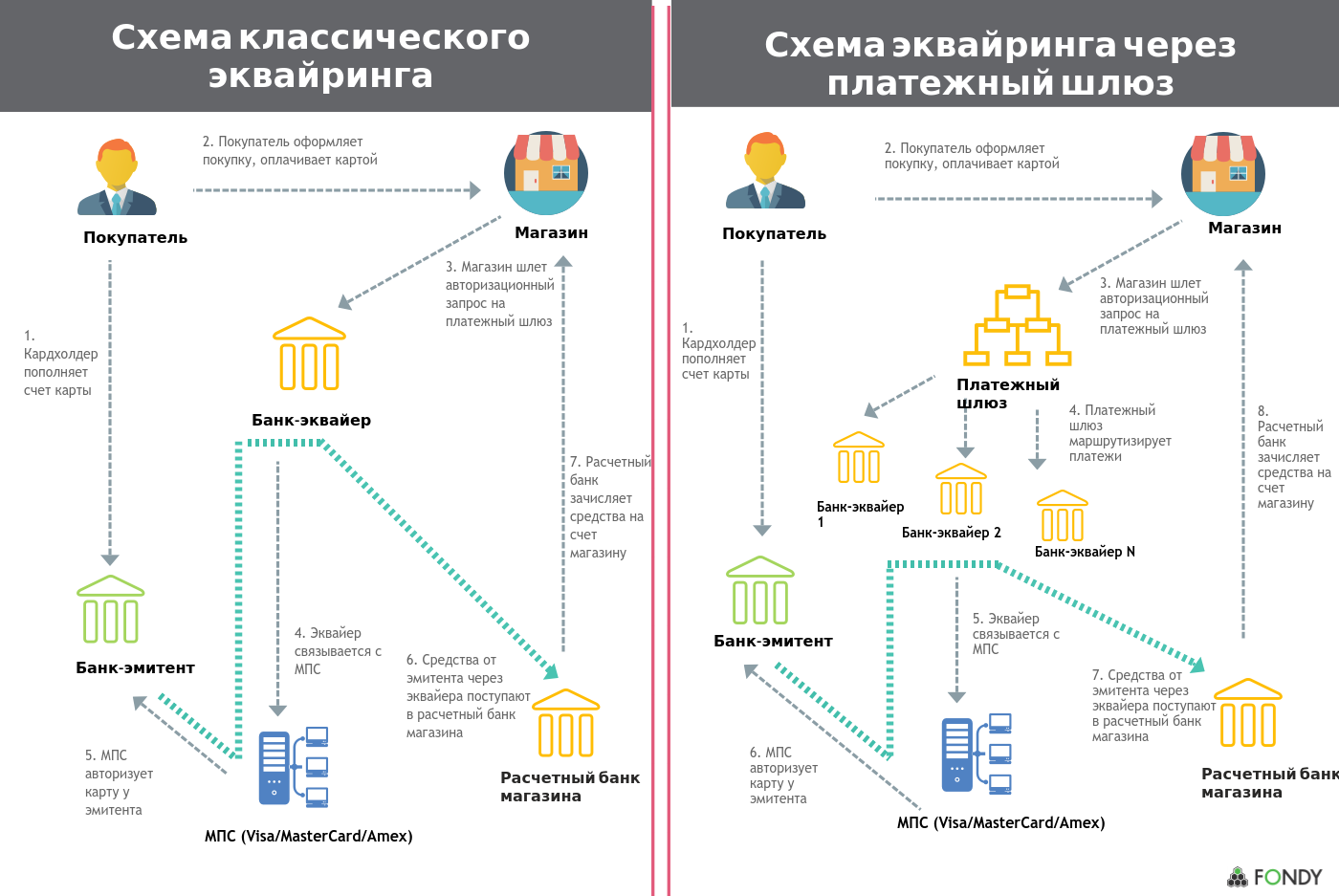
Consider the role of a payment gateway in the entire chain of payment from payer to merchant. The transaction path will consist of the following participants: Cardholder - Shop - Payment gateway - Acquiring processor - MPS (Visa / Mastercard) - Card issuing bank - Issuer processor.
What is changing in modern conditions? The merchant (store), due to integration with the payment gateway, has additional payment channels, new payment providers (payment providers). It is possible that their number will increase as much as the payment gateway can absorb and process requests from possible payment providers.

Here it is necessary to clearly separate the possibilities and areas of activity of integrators and aggregators.
Functions of aggregators: integrate several ways of accepting payments to the seller’s website at once. With this business model, the payment service is forced to pass cash flows through its accounts. Therefore, the aggregators cooperate either with a partner credit organization, or themselves possess a license from a bank or a non-bank credit organization.
What you need to know about PSP providers? How can they be useful for a business and why did they get so quickly involved in payment processing? The answer lies on the surface. They help retailers accept payments online. They offer a single payment interface for one or more than one payment method.
They help merchants in e-commerce to accept traditional payment cards, alternative payment methods (direct debit, electronic bank payments, and purse payments (PayPal, Qiwi, Yandex.Money, Webmoney). But unlike the aggregator interaction model, within the framework of cooperation with the PSP provider, the merchant will have to conclude a separate contract for each method of receiving payments.
The PSP provider works exclusively as a technical integrator, providing a single interface for one or more payment methods. He can connect any store to the processing of the selected acquiring bank. A merchant (shop) must still contact a bank or other financial institution to discuss commission rates and payments.
As an option, a payment integrator can also work according to a payment aggregator model, providing a single interface for one or more payment methods, collecting payments and commissions and contacting banks and financial institutions. But this is not a typical story. To do this, the CSP must enter into an agreement with the payment aggregator, and not directly with the credit organization.
Read more about the difference between aggregators and payment integrators here .
Austrian-English provider Kalixa explains its functions to stores:
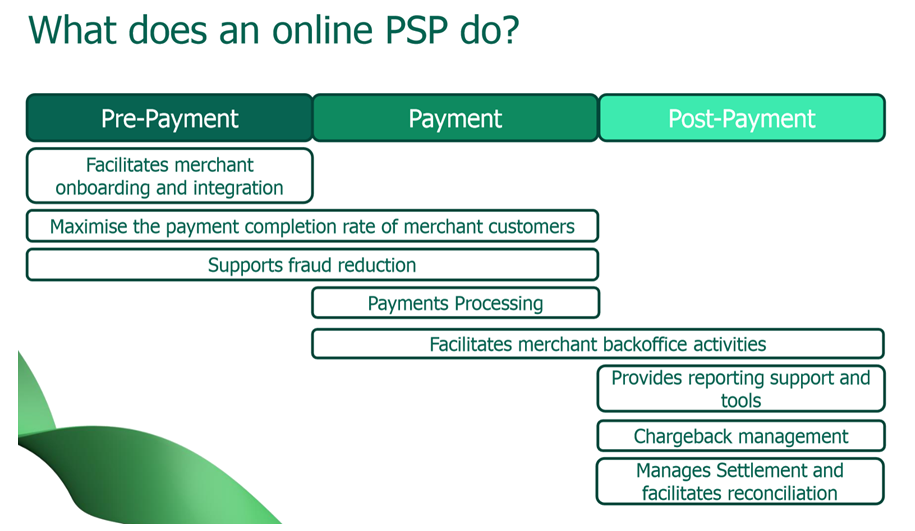
At the expense of prepayments - helps TSP with integration, works to minimize fraud and risk. Make payments. Supports back-office activities.
At the post-payment level provides reports. Dispute management (payment protest). Management of payments and reconciliation.
Thus, there are two models of work in the processing services market:
The first - integration (payment gateway) - consists in passing payments from the payer directly to the online store or through the PC. This is a technological model, not involving the processing of funds. The integrator connects the acquiring bank that the customer indicates. The customer (store) will enter into a contract with the bank and payment systems for settlement services. The execution of the entire operational and financial daily routine lies on the online store.
The second, the aggregator model, in addition to combining all payment acceptance options in a single technological gateway, includes payments to the processing center's account, and only after that the funds go to the online store account.

Major global suppliers of integration payment solutions today:

The Forrester Wave: Global Commerce Payment Providers, Q4 2016 report:

Find Adyen in the Forrester chart in the upper right corner of the chart. And now we will look at Adyen clients in order to understand the scope of their activities, as well as where to aim:

This is the current development. And operating flows here. More than Visa? More than Mastercard? We do not specifically check. But the trend is set, and it is read unequivocally. Cross-platform payments are no longer news, but reality.
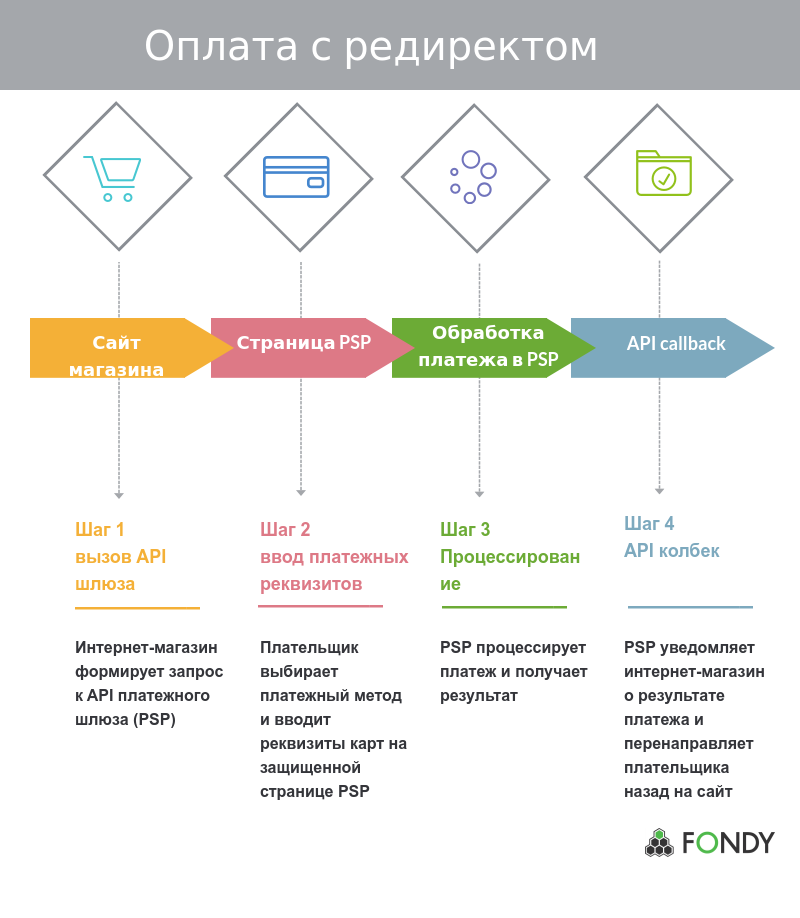
Consider a typical PSP operation when the PSP uses the redirect method. In this case, almost no effort is required from the store for integration. The choice of technical solutions here remains for the PSP.
A PSP technical solution might look like a redirect to the gateway page:
Or with loading the payment page in a JavaScript widget:
A successful financial transaction depends on each segment of the path:
And the main tasks of the PSP here is to provide the basic needs of the business:
The struggle for successfully completed transactions is a business struggle for its sustainability. Each failure leads to a loss of trust on the part of the client, be it a store that has become a client of an aggregator or payment integrator, or a client who has come to the store's page.
A financial transaction is not just an informational message sent from one subject to another. It has the status of a document-guarantor on the transfer of ownership of some entities (goods or money). The importance of a financial intermediary in the process of this exchange cannot be underestimated. The buyer, the seller, the issuing bank and the acquiring bank, and even the payment aggregator, if they participate in the process, all of them trust the selected processing (payment integrator, independent processing center). At the time of confirmation of a successful transaction, the transaction is considered completed.
In order for new technologies, such as blockchain technology, to conquer the minds of users, another round of information-financial system development must occur. From the popular to the well-established method of calculation this method is still far away. Nevertheless, we remember with great difficulty the moments when unique technologies became widespread. Whether a single electronic accounting account (blockchain) will be able to simplify the settlement process is a matter of time. Modern processors, integrators and payment aggregators have good reasons to continue to improve their products for breakthrough innovations.

With the advent of a new member online - a payment gateway or PSP Gateway (Payment Service Provider Gateway), the acquiring scheme has become different from the traditional one.
One of the definitions of a payment gateway may sound like this: a payment gateway is a service intermediary that performs processing of electronic transactions and is only a payment router. In technical language, a payment gateway is a software module that routes payments between an online store and various acquirer banks and other Internet acquiring service providers through a single interaction protocol.
')
Thus, it is more logical to call the payment gateway an integrator of payment solutions and remember that there is no financial-accounting function in its activity.
Consider the role of a payment gateway in the entire chain of payment from payer to merchant. The transaction path will consist of the following participants: Cardholder - Shop - Payment gateway - Acquiring processor - MPS (Visa / Mastercard) - Card issuing bank - Issuer processor.
- Buyer of services (cardholder, individual)
- Seller of services (shop, legal entity)
- Buyer's financial representative (bank 1 - card issuer)
- Financial representative of the seller (Bank 2 - payment acquirer)
- Payment system (Visa / Mastercard / AmericanExpress) as an intermediary between the issuing bank and the acquiring bank in processing and financial settlements between them
- New Member - Payment Gateway

- The buyer enters the payment details / billing information through a web interface.
- Information about the details of the transaction is transmitted to the payment gateway, the payment gateway sends it to the acquiring bank.
- The acquiring bank sends an information (authorization) request to the payment system (Mastercard, VISA, others).
- In the case of receiving a request for authorization, the issuing bank returns an authorization code that allows the payment system to make a transaction.
- This code is returned to the payment gateway, and from there - a report to the seller with the result of authorization.
- If the authorization is positive, the transaction is considered to be completed; the merchant may provide the service or ship the goods. The funds will be debited from the payer's card and refunded to the merchant's account.
What is changing in modern conditions? The merchant (store), due to integration with the payment gateway, has additional payment channels, new payment providers (payment providers). It is possible that their number will increase as much as the payment gateway can absorb and process requests from possible payment providers.

Here it is necessary to clearly separate the possibilities and areas of activity of integrators and aggregators.
Functions of aggregators: integrate several ways of accepting payments to the seller’s website at once. With this business model, the payment service is forced to pass cash flows through its accounts. Therefore, the aggregators cooperate either with a partner credit organization, or themselves possess a license from a bank or a non-bank credit organization.

What you need to know about PSP providers? How can they be useful for a business and why did they get so quickly involved in payment processing? The answer lies on the surface. They help retailers accept payments online. They offer a single payment interface for one or more than one payment method.
They help merchants in e-commerce to accept traditional payment cards, alternative payment methods (direct debit, electronic bank payments, and purse payments (PayPal, Qiwi, Yandex.Money, Webmoney). But unlike the aggregator interaction model, within the framework of cooperation with the PSP provider, the merchant will have to conclude a separate contract for each method of receiving payments.
The PSP provider works exclusively as a technical integrator, providing a single interface for one or more payment methods. He can connect any store to the processing of the selected acquiring bank. A merchant (shop) must still contact a bank or other financial institution to discuss commission rates and payments.
As an option, a payment integrator can also work according to a payment aggregator model, providing a single interface for one or more payment methods, collecting payments and commissions and contacting banks and financial institutions. But this is not a typical story. To do this, the CSP must enter into an agreement with the payment aggregator, and not directly with the credit organization.
Read more about the difference between aggregators and payment integrators here .
What does the payment gateway do?
Austrian-English provider Kalixa explains its functions to stores:

At the expense of prepayments - helps TSP with integration, works to minimize fraud and risk. Make payments. Supports back-office activities.
At the post-payment level provides reports. Dispute management (payment protest). Management of payments and reconciliation.
Thus, there are two models of work in the processing services market:
The first - integration (payment gateway) - consists in passing payments from the payer directly to the online store or through the PC. This is a technological model, not involving the processing of funds. The integrator connects the acquiring bank that the customer indicates. The customer (store) will enter into a contract with the bank and payment systems for settlement services. The execution of the entire operational and financial daily routine lies on the online store.
The second, the aggregator model, in addition to combining all payment acceptance options in a single technological gateway, includes payments to the processing center's account, and only after that the funds go to the online store account.

Major global suppliers of integration payment solutions today:

The Forrester Wave: Global Commerce Payment Providers, Q4 2016 report:

Find Adyen in the Forrester chart in the upper right corner of the chart. And now we will look at Adyen clients in order to understand the scope of their activities, as well as where to aim:

This is the current development. And operating flows here. More than Visa? More than Mastercard? We do not specifically check. But the trend is set, and it is read unequivocally. Cross-platform payments are no longer news, but reality.
Consider a typical PSP operation when the PSP uses the redirect method. In this case, almost no effort is required from the store for integration. The choice of technical solutions here remains for the PSP.
A PSP technical solution might look like a redirect to the gateway page:

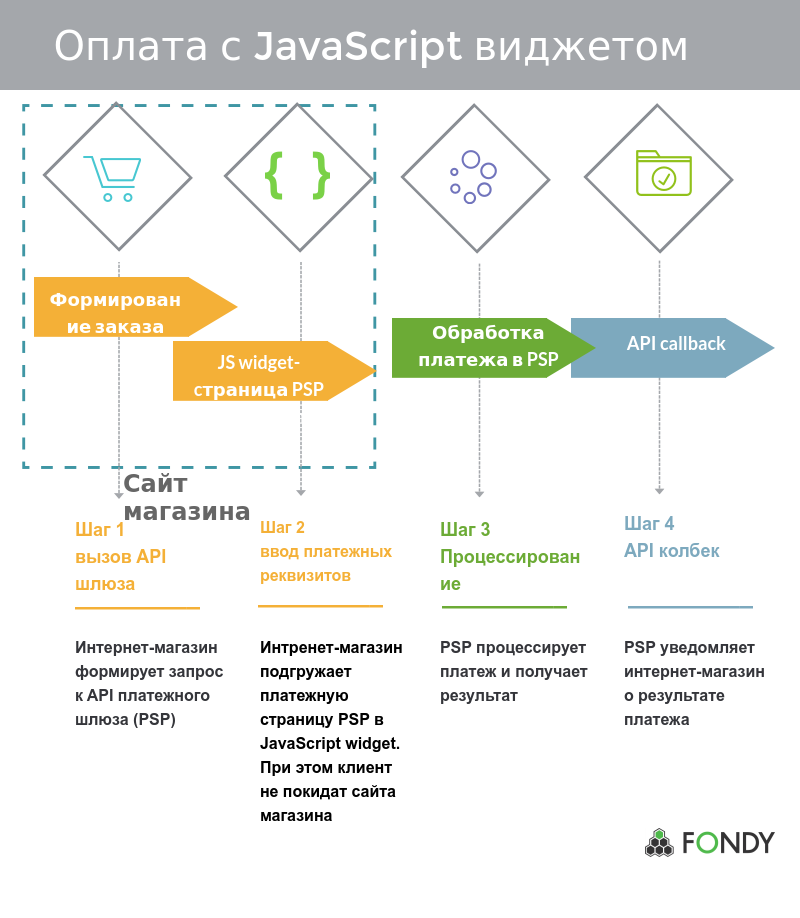
Or with loading the payment page in a JavaScript widget:

A successful financial transaction depends on each segment of the path:
- Choosing a payment method
- Enter payment details
- Payment routing
- Payment authorization
And the main tasks of the PSP here is to provide the basic needs of the business:
- reliability: the level of service (SLA) and% conversion of payments into successful purchases at a level higher than a single acquirer bank or payment provider can provide
- Protection: Blocking fraudulent payments using an antifraud system without lowering the conversion level
- convenience for the payer: an adaptive payment page for any devices with a high level of usability
- Accounting: Analytics, Reports, Reconciliation Acts Required by an Internet Enterprise
The struggle for successfully completed transactions is a business struggle for its sustainability. Each failure leads to a loss of trust on the part of the client, be it a store that has become a client of an aggregator or payment integrator, or a client who has come to the store's page.
A financial transaction is not just an informational message sent from one subject to another. It has the status of a document-guarantor on the transfer of ownership of some entities (goods or money). The importance of a financial intermediary in the process of this exchange cannot be underestimated. The buyer, the seller, the issuing bank and the acquiring bank, and even the payment aggregator, if they participate in the process, all of them trust the selected processing (payment integrator, independent processing center). At the time of confirmation of a successful transaction, the transaction is considered completed.
In order for new technologies, such as blockchain technology, to conquer the minds of users, another round of information-financial system development must occur. From the popular to the well-established method of calculation this method is still far away. Nevertheless, we remember with great difficulty the moments when unique technologies became widespread. Whether a single electronic accounting account (blockchain) will be able to simplify the settlement process is a matter of time. Modern processors, integrators and payment aggregators have good reasons to continue to improve their products for breakthrough innovations.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/322738/
All Articles