Travel Financial Transaction
We have come to the level of development of financial technologies when traditional ideas about the quality of payment services consist of two components: the speed of the transaction and the approval of the payment. And what is new here, you ask? It always has been. But this is only part of the truth.
The result is always the same. But the transaction chain has varied from decade to decade. The number of participants in the process of initiating and approving payment has changed. Here it is worth mentioning the word “processing” not just as data processing, but as a process between initiating a transaction and its final (approval / rejection).
Let's go back to paper checks. When the buyer wrote a check for the services, and the seller went to the bank to submit the signed check.
')
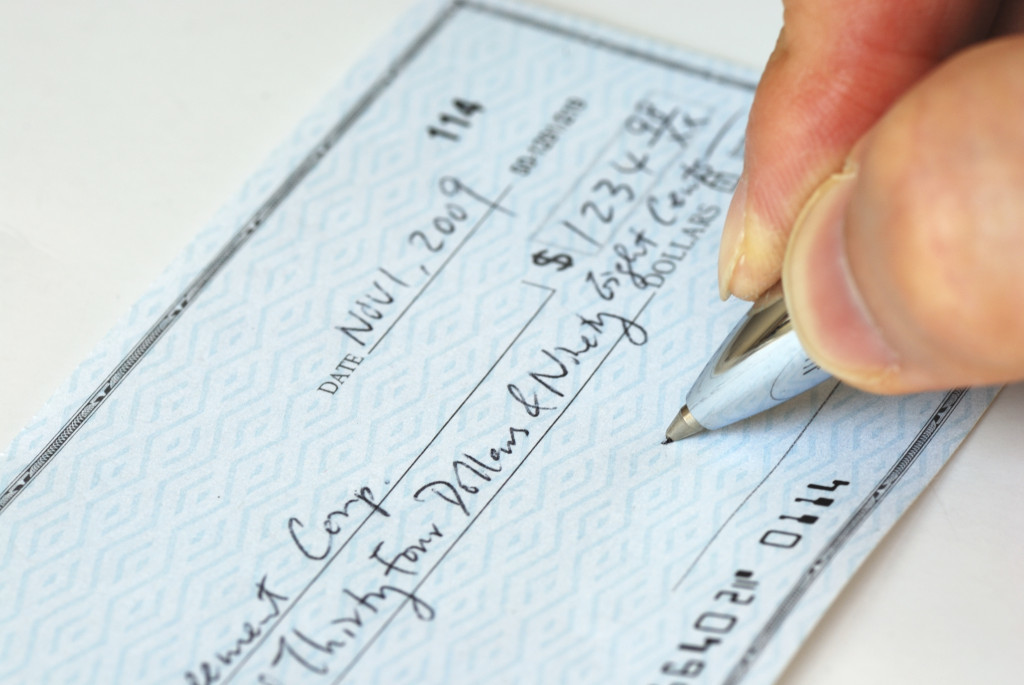

At this stage, everything is quite simple, and we see four participants:
- Buyer services
- Seller Services
- Buyer's financial representative (bank 1)
- Financial representative of the seller (bank 2)
The complete documentary check circulation cycle looked like this:
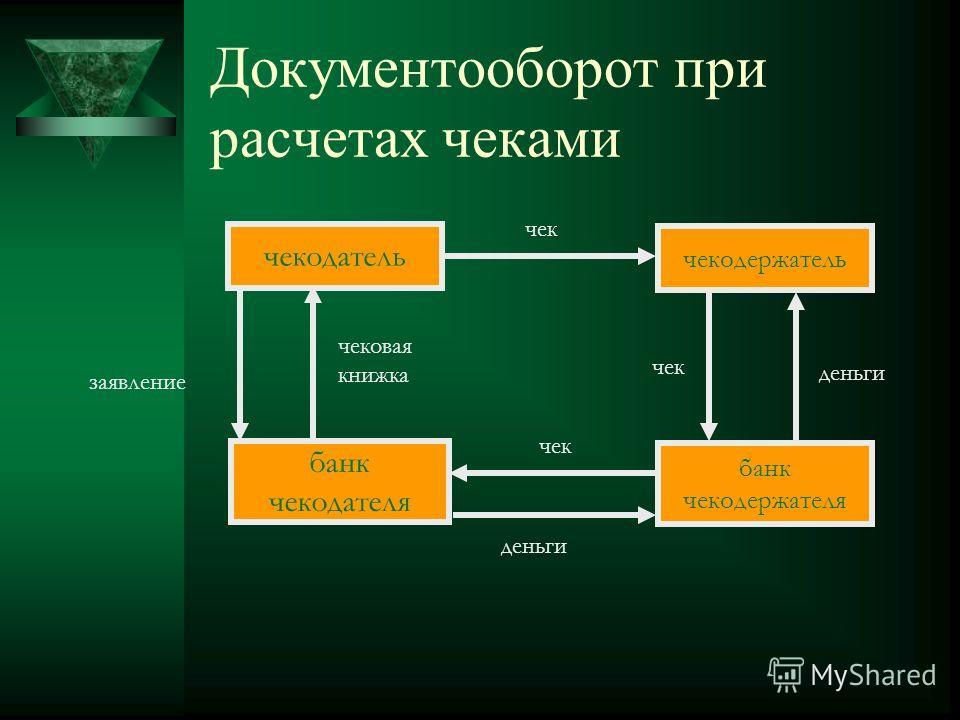
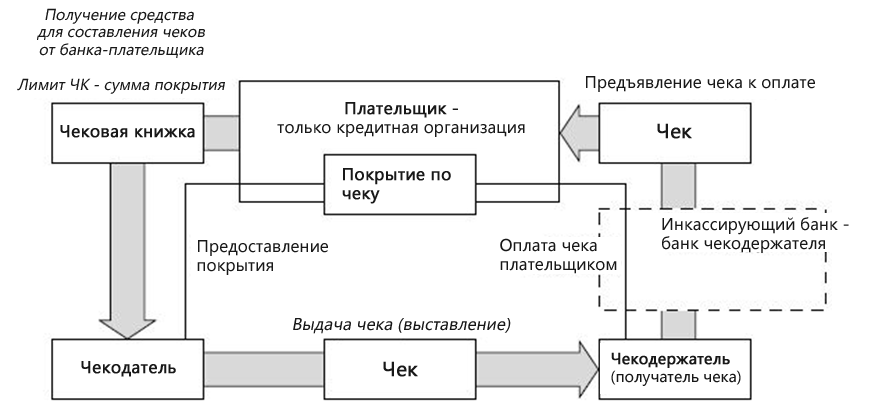
The full financial check circulation cycle looked like this:
Development, and in the 40s - 50s of the twentieth century, payment cards gradually supplanted and replaced checks (Thomas Cook's checks, which were still encountered in the 90s in Russia and other countries, resisted the most).
In detail and with dates about the history of the development of the card business writes the Association of the UK card business.
In Russian, you can read about the history of the development of bank cards here .
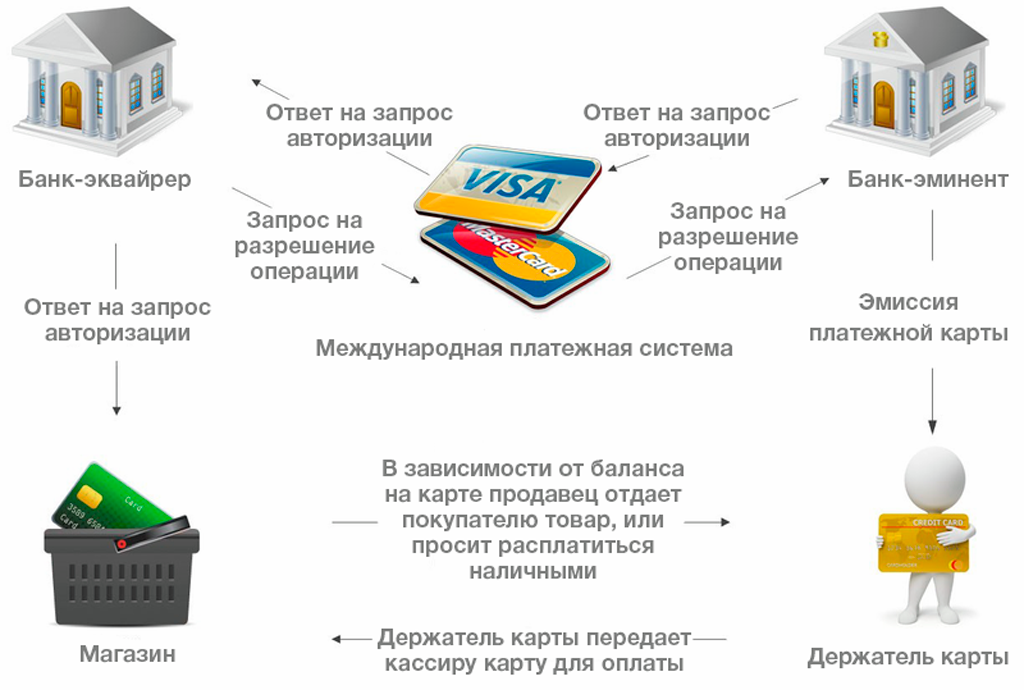
What has changed in the process?
- Service buyer (individual)
- Seller of services (shop, legal entity)
- Buyer's financial representative (bank 1 - card issuer)
- Financial representative of the seller (Bank 2 - payment acquirer)
- The new member is a payment system (Visa / Mastercard / Diners / AmericanExpress) as an intermediary between the issuing bank and the acquiring bank in processing and financial settlements between them. The calculation tool is a plastic card with a magnetic stripe.
The traditional transaction scheme looked like this:
At first, an imprinter served as a tool for making a payment using a card - a machine for rolling a card and receiving an imprint of card data on a slip. A cliché is inserted into the imprinter - a rectangular plate on which the identification data of the receiving point is embossed (or extruded). The plastic card is inserted into the imprinter and put in a slip. On the slip, the identification data of the receiving point (transferred from the cliché) and the identification data of the card (transferred from the card) are imprinted.
Imprinter:

Slip:

Slip in settlements through imprinter has three copies: the buyer, the seller and the bank. Each copy of the slip must be clearly printed with the card details and organization imprinter cliches. In the slip indicate the name of the cardholder, card number, date of purchase, the amount spent, the type of payment system (Visa, Mastercard, etc.), seller's address, etc.
While still very much like checks.
Since the authorization of the transaction was carried out by voice on the phone, it was called “voice”. Before the advent of POS-terminals, it served as a typical method of confirming calculations. According to the instructions of the Ministry of Railways, she was accompanied by a phone call to the Bank Authorization Service (usually located in the bank's processing).
To authorize the card, the cashier contacted the bank by phone. The bank with which the acquiring agreement was concluded, in turn, contacted the card issuing bank and received its permission. As now, this communication was carried out through processing centers, which ensure continuous exchange of information between banks.
With the advent of electronic terminals, voice authorization has been preserved as a method of additional verification during major operations. When making purchases that exceed the limits for the MCC code, the bank has the right to request and launch an additional procedure for checking the client and conduct voice authorization. However, now it will look rather wild.
At this rather long stage, there was a rapid growth of the financial system, and then its stagnation, but this is not our topic today. And now the imprinters were replaced by electronic payment terminals (POS-terminals).
The number of banks and bank clerks grew proportionally, if not always, to the number of clients in the bank, and in the processing centers the workload of the systems and employees was measured by the number of cards issued and transactions processed. Electronics and software developers have advertised their product based on the number of authorizations per minute, the possibilities of matching / reconciliation of authorization and financial message, posting and clearing transactions.
Card business came under the control of interested parties - payment systems (Visa, Mastercard). They formed operational and technological standards, conducted training for bank employees, they also developed reporting forms. Banks quarterly reported on the number of issued simple and more expensive cards, the number of processed transactions and the average amount of authorization in terms of MCC-code (type of services provided).
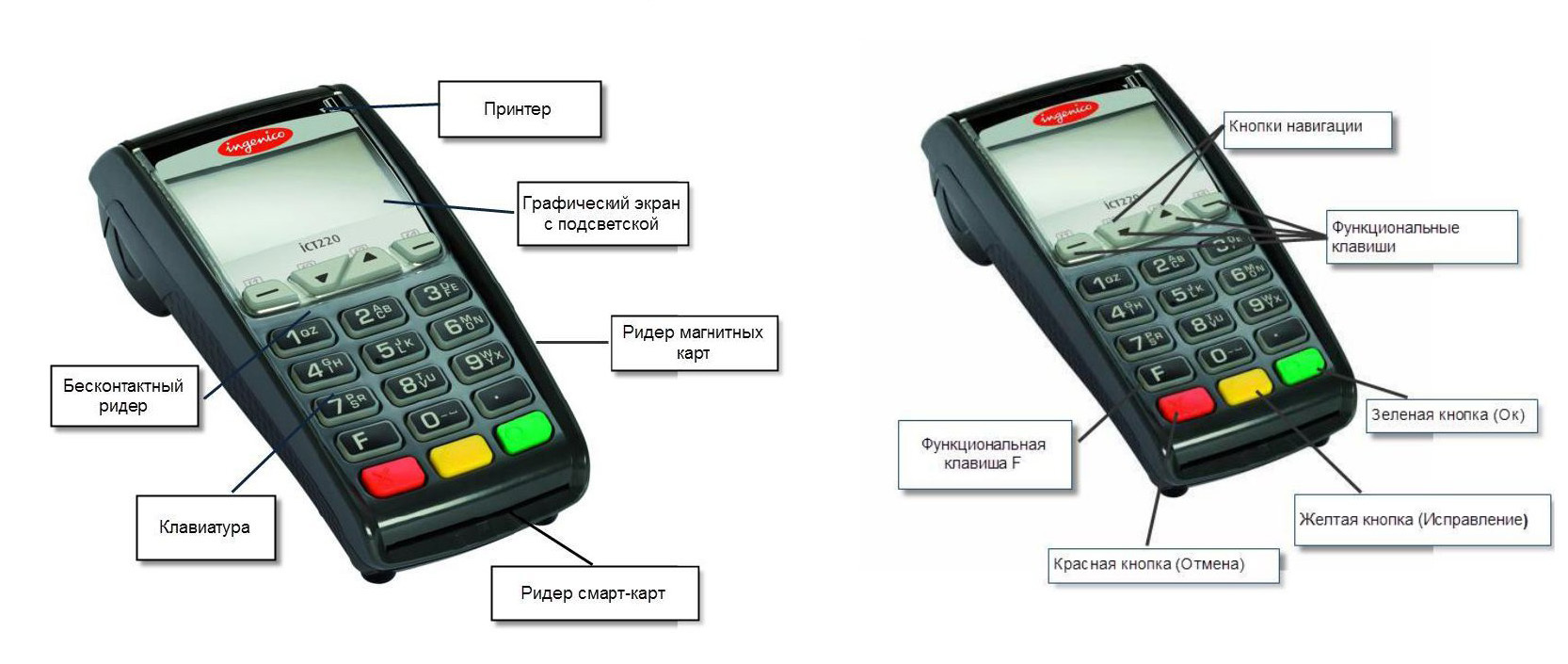
Here is one of the traditional training schemes, known to every employee of the processing, accounting department, and many other departments. This picture is from the primer card.
Plastic card has become loved. It is simple and convenient. At first, the magnetic stripe is integrated into it, and the authorization took place with a voice, then it was not performed at all in order to save phone costs for sublimit transactions.
Very soon, with the improvement of the quality of telephony and communication channels, most of the authorizations took place electronically. And the mandatory 45 seconds have already appeared for a successful transaction from point A to point B. VISA and Mastercard regularly updated the operational requirements and indicated in them, including the time parameters of authorization. It usually looked like this:

Or so:
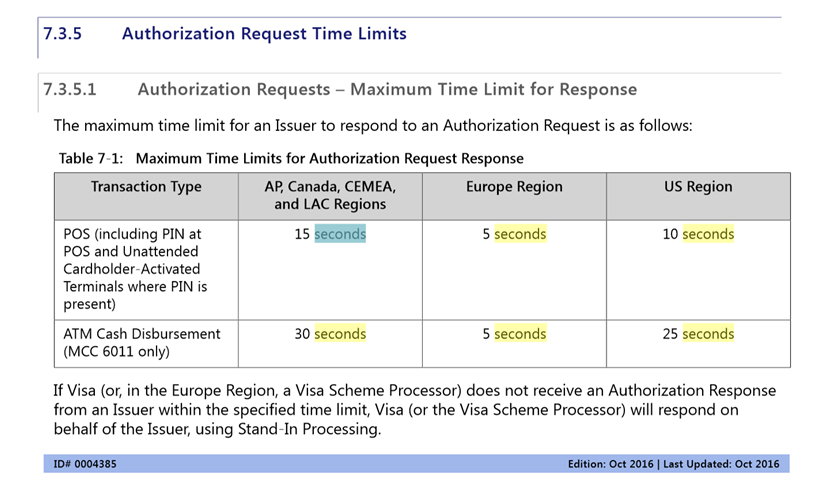
* These are modern requirements of the payment system. Where it is now 30 seconds was given for authorization of a retail transaction, it now takes 5. For ATM transactions, the deadline was shrunk from 15 seconds to 5 too.
The suppliers of financial solutions were responsible for the development and implementation of the process: the payment system as an ideologist, developers (vendors) of processing systems, terminals and ATMs, issuing banks and acquiring banks.
The turn in the development of the end of the 20th - beginning of the 21st century was marked by a change of the magnetic stripe on the chip. At first, the strip and chip were adjacent to the map.
The international payment systems Mastercard, Visa and Europay in 1993 signed a collaboration agreement to develop specifications for the use of smart cards when paying bills with credit and debit cards. The first version of the EMV standard system (Europay, Mastercard, Visa) was released in 1994. In 1998, the next version of the technical specifications became available.
The chip format developed by Eurocard, Mastercard, Visa is called EMV - after the first letters of these companies. More information about the standard chip cards can be read here and here: EMVCo .
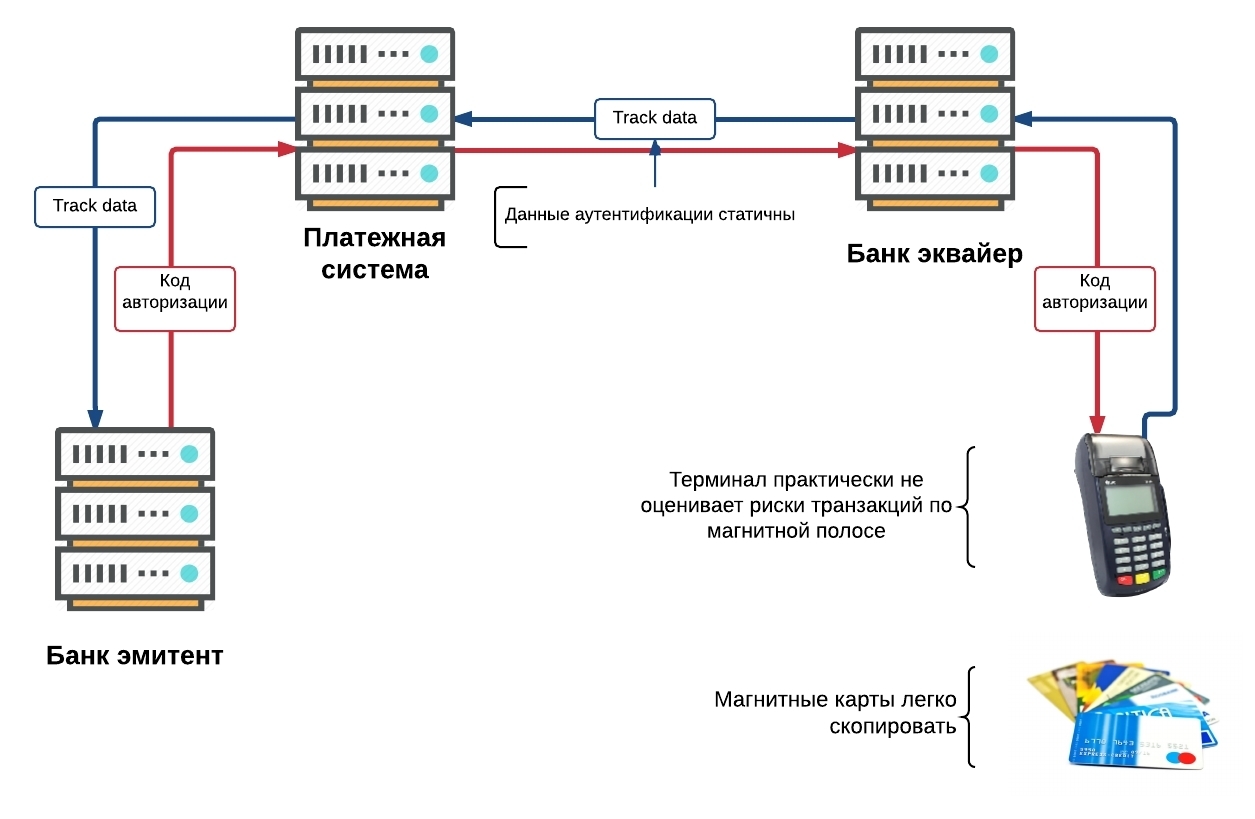
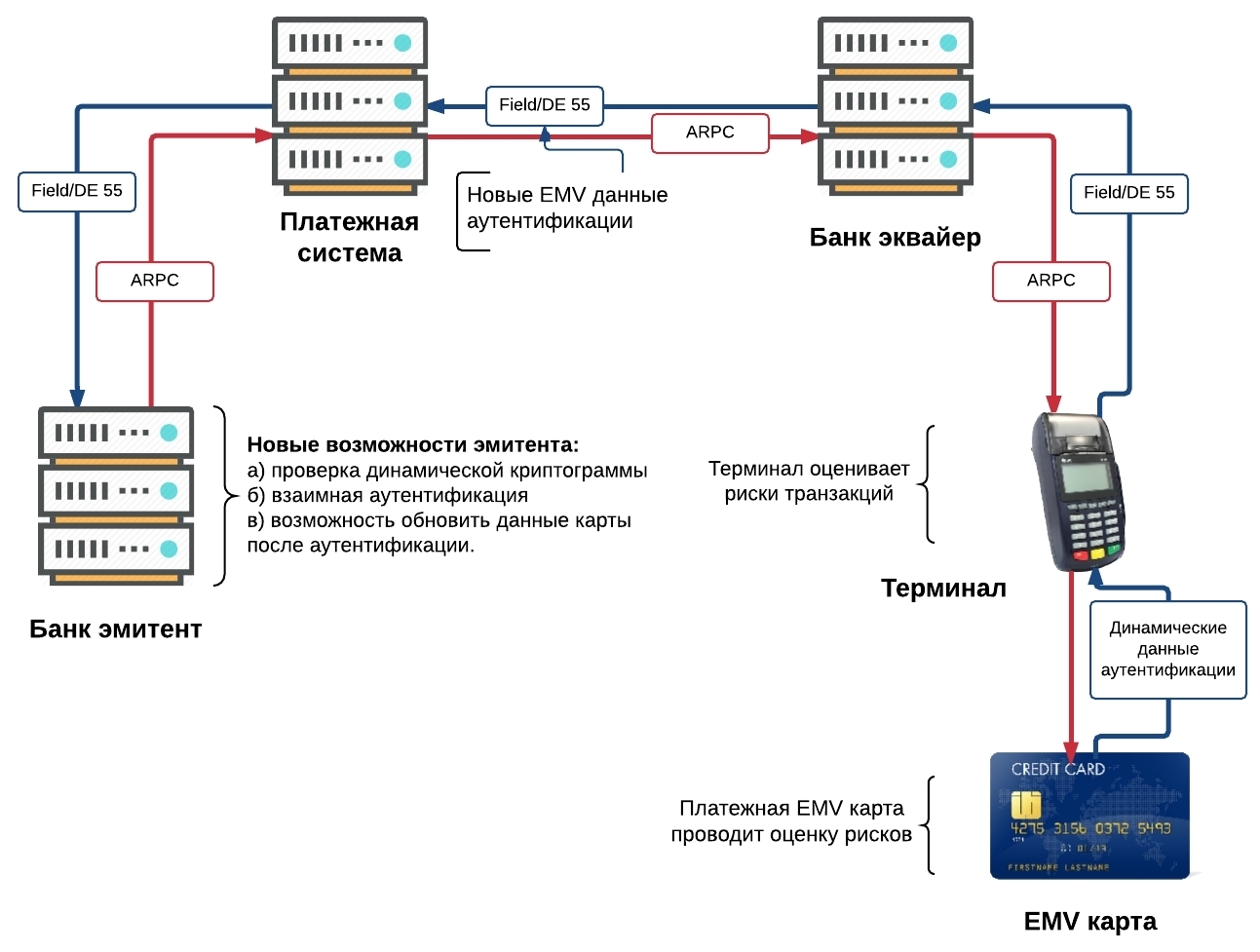
It was assumed that very soon all banks would cope with the simple task of reissuing cards and transferred to chip cards. And then the unexpected happened. Representatives of the IPU (international payment systems) often met with resistance from both issuing banks and acquiring banks. For the first ones, the replacement of plastic turned out to be an expensive idea (the first chips were very expensive), for the second it was necessary to change the card receivers, both in ATMs and in terminals. Probably, it was a golden start for the companies-manufacturers of Gemalto , Oberthur and many others. It was they who stood at the origins of the subsequent explosive growth of technological solutions and further transition from chips to contactless payments. At the moment, according to Michael Finney , the VISA payment system stated that 300 million chip cards have been issued, which can be presented for payment at 1.25 million outlets equipped with EMV terminals.
All smart cards can be divided according to the method of exchange with the reader to:
- contact smart cards with an ISO 7816 interface;
- contact smart cards with USB interface;
- contactless ( RFID ) smart cards.
There are cards that include both contact and contactless interfaces. In terms of functionality, they are of two types:
- memory cards (contain a certain amount of data and a mechanism for restricting access to them)
- smart cards (contain microprocessor and the ability to manage data on the card)
But the change in the payment instrument was made possible by the development and application of cryptographic innovations in the field of payment technologies. Just think, from reading tracks 1 and 2 of the magnetic strip, moving to reading chip cells (and about chip modifications, an increase in the number of cells in a chip that generated an increase in loyalty programs and other applications, tons of materials were written (read once , two , three , ISO / IEC 7816 or ISO / IEC 14443 ), we got to Mastercard Paypass / Visa payWave technologies, contactless payments turned the buyers and sellers in. We spent a few seconds (5 seconds) on the payment itself, it took more time to get to wallet card.
The second decade of the XXI century, and now it is no longer necessary to get the kat from the wallet! New round. We are ready to pay using other devices: phones, bracelets, charms. ApplePay , SamsungPay , AndroidPay , who's next?
Unlike devices from other manufacturers that use only NFC technology, Samsung Pay does not only work with terminals that support contactless payment. The secret is that in addition to NFC, Samsung uses its own technology - MST (from the English. Magnetic Secure Transmission - magnetic secure transmission), which makes it possible to pay for purchases using a smartphone on almost any terminal accepting bank cards. Samsung smartphones that are compatible with the Samsung Pay service and support MST technology can create a magnetic field similar to a magnetic stripe signal of a bank card. Usually, even the sellers themselves do not know that this is possible in their stores, but it really works.
We need simple and intuitive solutions, reliable, more than ever. Protection should be built both at the level of hard and at the level of software. Both in the device and in the payment solution provider. And soon we will not want to go anywhere to pay. Can everything be online? It is possible and necessary for a long time. Briefly, in one click. If it does not work out in one, then at least three: download the application, add a card to it, and everything is ready for payment!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/322736/
All Articles