About spaghetti, or how to explore the business processes of an organization
About spaghetti, or how to explore the business processes of an organization
Many enterprise managers do not have a complete picture of what is happening in their own production units. They are familiar with the organizational structure, activities, general economic indicators. If the result is a profit, then success comes. But are there any enterprises in the market that are held for a long time in a “blind” management mode?

If you leave the allegory, the "twisted spaghetti" in the enterprise is:
- The inability to analyze the cost of production. Even if the accounting system is conducted with detailed specification, these figures have no adequacy. Therefore, profit can be a spontaneous process that does not depend on the actions of management and employees.
- The lack of operational status, and this lack of answers to the questions:
')- At what stage are the orders (customer, production, assembly)?
- What do the staff do?
- What is the performance of the organization? and etc.
- Lack of actual values of inventories, work in progress and finished products.
Evidence from practice. The head of the organization knows that there are 6 technologists and 4 employees in the quality control department. If we divide the total amount of work into the indicated employees, we obtain adequate workloads. After the survey, it turned out that 2 technologists and 1 controller were engaged exclusively in low margin products. Economists and management know about the small profits of this type of production, but they do not know the division of labor in the divisions. In the aggregate of labor costs of staff, production and overhead costs the result for the product category was unprofitable.
Perhaps this is dumping to oust competitors, but the management does not know :)
You can explore the unknown by the direct and inverse method, where in both cases it is necessary to understand the lines of business activity .
The minimum result of the study:
- Classification of business processes of the organization
- Description of each target BP in text form and block diagram.
The most simple and working version of the classification:
Business Process Inspection
Direct method
The direct method corresponds to a co-directed study of processes and the order of procedures in activities.
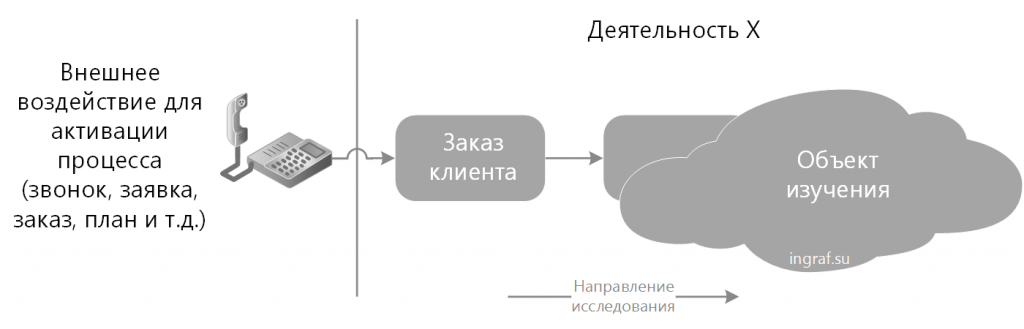
In this case, it is necessary to find an external influence to activate the process. For the absolute majority of enterprises, this is a customer order (in the form of a call, a letter, a schedule). In more rare cases (investment) - this is the decision of the owner of the process. For example, the construction of a shopping center, where there is no external influence, and the decision is based only on the business plan of the project.
The first event, it is the beginning of the process, in our example is a customer order.
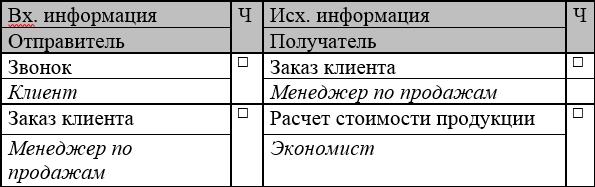
The questionnaire and work with it allows you to describe the steps of the process , identify responsible persons, recipients of information, classify sites.
Reverse method
A feature of the method is the study of the result of the operation (paper or electronic document, file or event) and the search for the author of the document. Further, it is determined who and why formulated this need. The cycle of these actions determines the BP in the reverse order.
For example, the end point of the product sales activity is the transfer to the customer's driver of the “Universal Transfer Document,” TTN, Material Pass. They are created in the program 1C ERP sales manager for vacation products. The signal for their design is the event of payment of the order of the client. Etc.
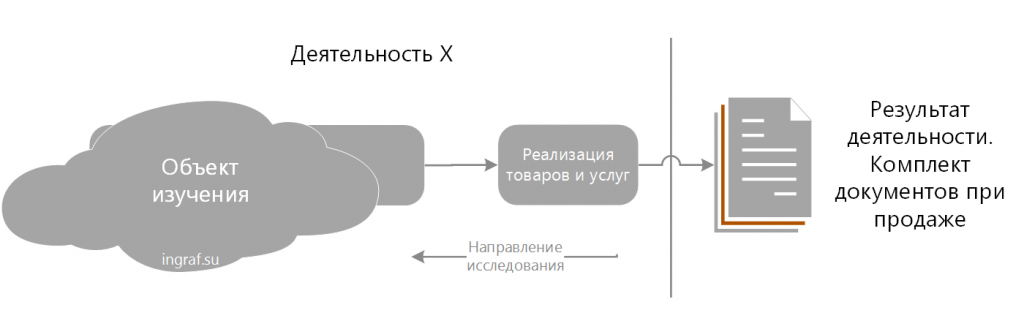
As in the previous example, process descriptions are compiled in the interview questionnaire.
Mixed use
It is worth noting that the direct and inverse methods can be used simultaneously. This is permissible and recommended in a survey of complex processes that are difficult to approach on one side, or in a team study (2 people per BP).
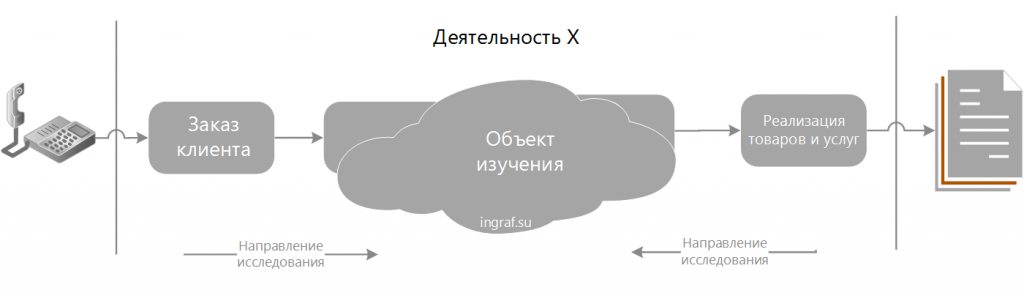
Branching and merging business processes
An operation of a business process can give birth to and terminate a secondary process (subprocess). For example, the operation of placing an order requires the calculation of the cost of production (for unique products), the payment procedure, the formation of an order into production. This is the birth of subprocesses.
This is an example of a real end-to-end BP, affecting several business units.
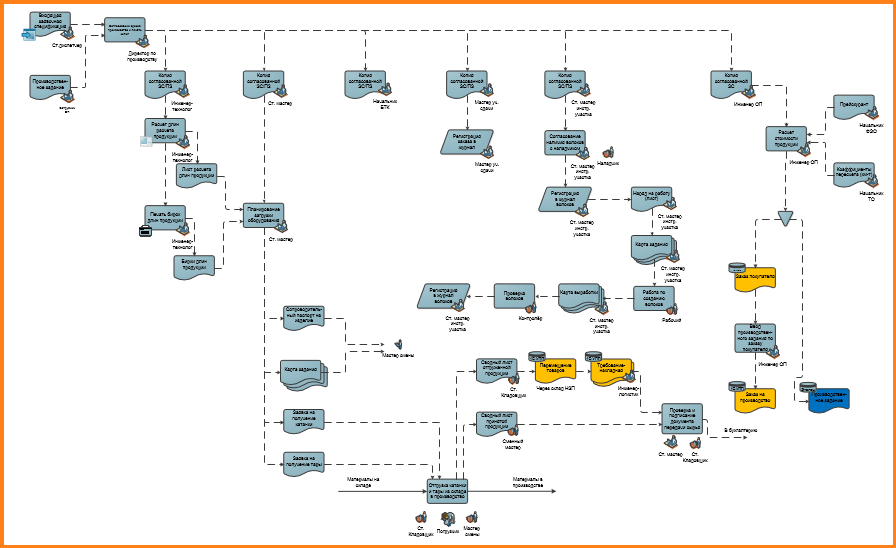
The rule of separation of a process into a separate one is determined by the objectives of the project. If the BP is out of focus of the study, then it can be minimized and described in one procedure. Long schemes are a wow effect, but difficult to read and ineffective in the analysis.
Received a classification, description and flowchart - what to do?
We answer:
- Does this BP operation add value to the product?
- Is your client ready to pay for this procedure?
- Are the resources of an enterprise moving optimally? Do you need this movement?
- What are the longest communication channels and why? What are they needed for?
- The transfer of information between employees is a loss in time and cost. Are there excessive communication channels?
- Where and why is most of the marriage, costs, long waits?
- What regulates the operation of the BP, what is its standard?
+100 questions ...
Sergey Kukanov
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/322448/
All Articles
