How to “punch” a person on the Internet: using Google operators and logic
In the next article of our online intelligence series, we will look at how advanced search operators at Google allow us to quickly find the necessary information about a particular person.
In the comments to our first article , readers asked for more practical examples and screenshots, so in this article there will be a lot of practice and graphics. To demonstrate the capabilities of the “advanced” Google search, the personal accounts of the author were chosen as targets. This is done in order not to offend anyone with an excessive interest in his private life. I want to immediately warn you that I have never set myself the goal of hiding my presence on the Internet, so the methods described are suitable for collecting data about ordinary people, and may not be very effective for de-anonymizing fake accounts created for one-time actions. For interested readers, I suggest that you repeat the examples of requests for your accounts and evaluate how easy it is to collect information on them.
Before collecting and analyzing information about a particular person, it is necessary to present the whole picture of what data about a person exist.
Such a map should be detailed to the level required to solve a specific problem. Any search for information begins with some initial data set. In our case it will be the last name, first name and place of work. The rest of the data is somewhere, but we cannot yet link it with the available data. Therefore, we formulate hypotheses and check using search queries.
Sources of information about a person can be:
- himself: accounts in social networks, blog, etc .;
- state: databases of tax, bailiffs, courts, etc. See the links in the article.
- someone else (friends, enemies, media, employer, etc.)
In this article, we consider item 1. - we will calculate the author's accounts in social networks.
Goal number one: usernames
What is a nickname and how do we choose it?
Nick represents our name on the Internet: we choose it by creating our own personal inbox, and then often use it in various services.
We are not limited by the choice of nicknames, but there are favorite algorithms for the formation of our Internet names:
- Games with your name: last name, first name + last name, first name + year of birth, first name + date, initials;
- Games with the names of your favorite characters (tovbender, napoleon);
- A little about yourself: profession, psychology (coolhacker, murmur);
- Demonstration of hobbies: footballer, boxer;
- “So that no one would guess”: a word on the contrary, a Russian word in the English layout, a word in Latin, etc.
If we do not know a nickname, but we know something about a person, we can already make assumptions and test them.
A good way to calculate the nickname of a user is to search and analyze his pages in social networks and search for a personal email address.
You can start searching for information about a specific user with a simple query like the following:
where "daisy" is the name of the company.
At the moment we have to remember that some features of the Google search engine:
- Google reads the query from left to right.
- Google does not distinguish between register: "Earth" and "earth" for him the same thing;
- query length should not exceed 32 words;
- * represents one word in the request;
- You can search for the exact phrase by quoting it;
- there is an invisible logical "AND" between the words in the query;
- Google itself is able to incline words;
- The “-” operator excludes from the output the results that contain an expression placed immediately after the given operator (without a space).
- at the top of the page are pages that Google thinks are the most relevant. Nevertheless, this is his guess, since he does not know how to read our thoughts;
- To clarify the search parameters, you must own advanced search operators.
Now you can enter a similar query by the author of the article and get a lot of pages, among which should be the required pages in social networks:
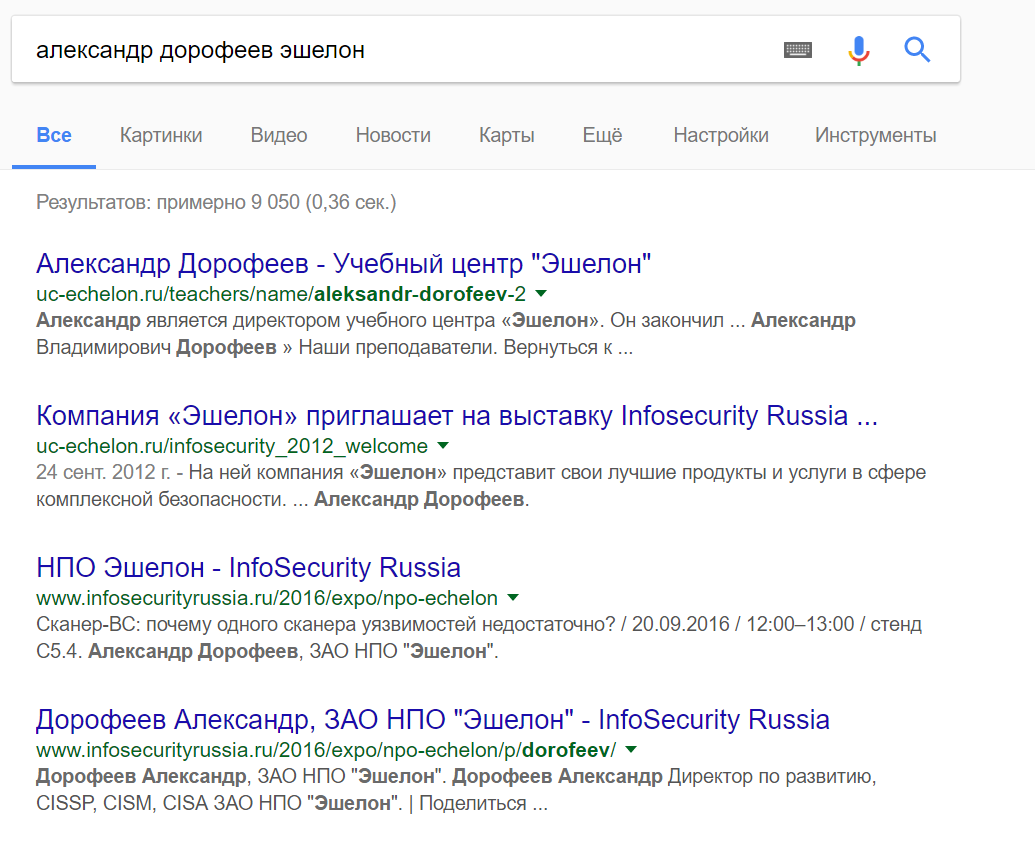
There is a lot of information in search engine search, and in order to find pages on social networks we will have to revise a large number of pages.
Note:
By the way, what to do if we want to find a person from a certain company, but have forgotten his last name? An asterisk operator can help:
* And if we are looking for a person from Romashka LLC, and there are a million such Romashka: both Romashka JSC, Romashka ANO, Romashka Federal State Unitary Enterprise, etc.
Option 1. Search for the full phrase "LLC Romashka".
Option 2. "Minus" unnecessary words: -ANO - JSC-FGUP (but you can "zaminusovat so" and the desired results, for example, if the page says that our "Daisy" has become friends with FSUE "Orange".
Now we need to narrow the issue and find the page of the author of the article in the social network VKontakte. This will allow us to identify one of the user's nicknames, and then calculate the email address. For this, it will be useful to use an operator such as site. It restricts the search to a specific domain of any level.
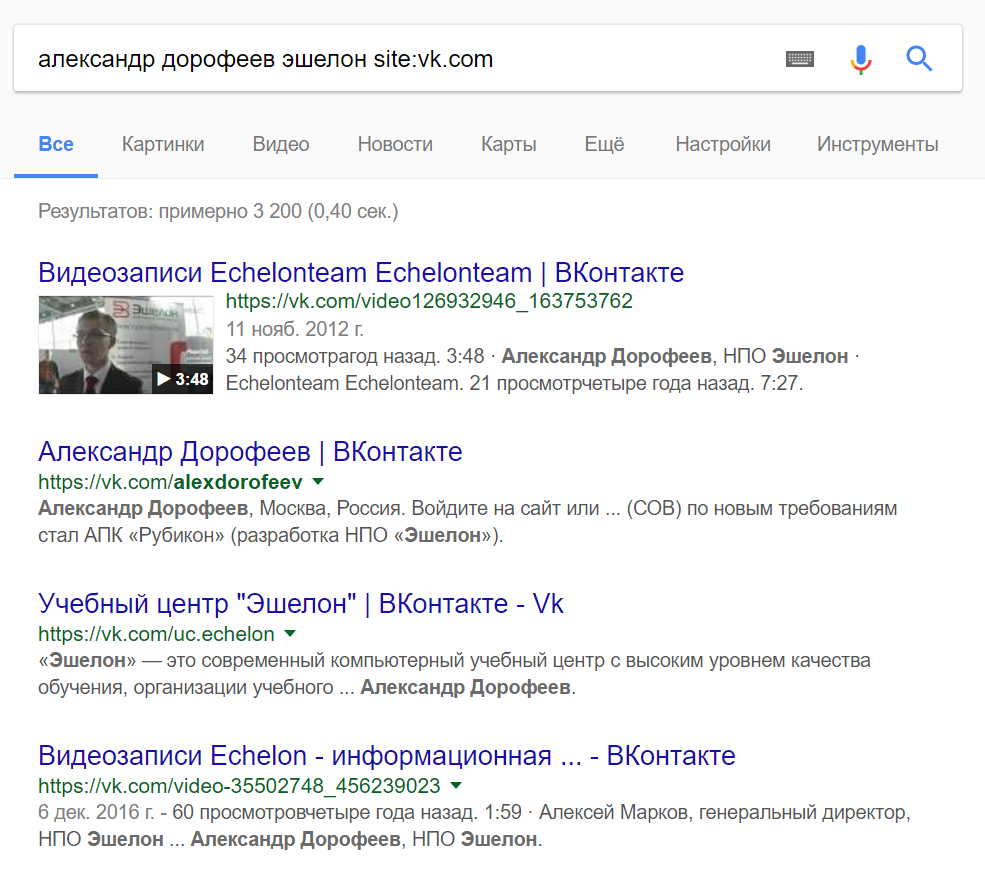
The second link already leads to the author’s article on the VKontakte network. Please note that the author deliberately chose a short nickname: alexdorofeev. Not all Internet resources allow you to set a link to your page, sometimes it is generated automatically, but it may contain a nickname taken from an email address.
Using the extracted information and knowledge, we will try to find a similar page on Facebook.
First, for good luck in the browser, enter the following URL: https://www.facebook.com/alexdorofeev , but unfortunately, we will see that the page belongs to someone else. Then we will use a proven technique and add site: facebook.com to the request.
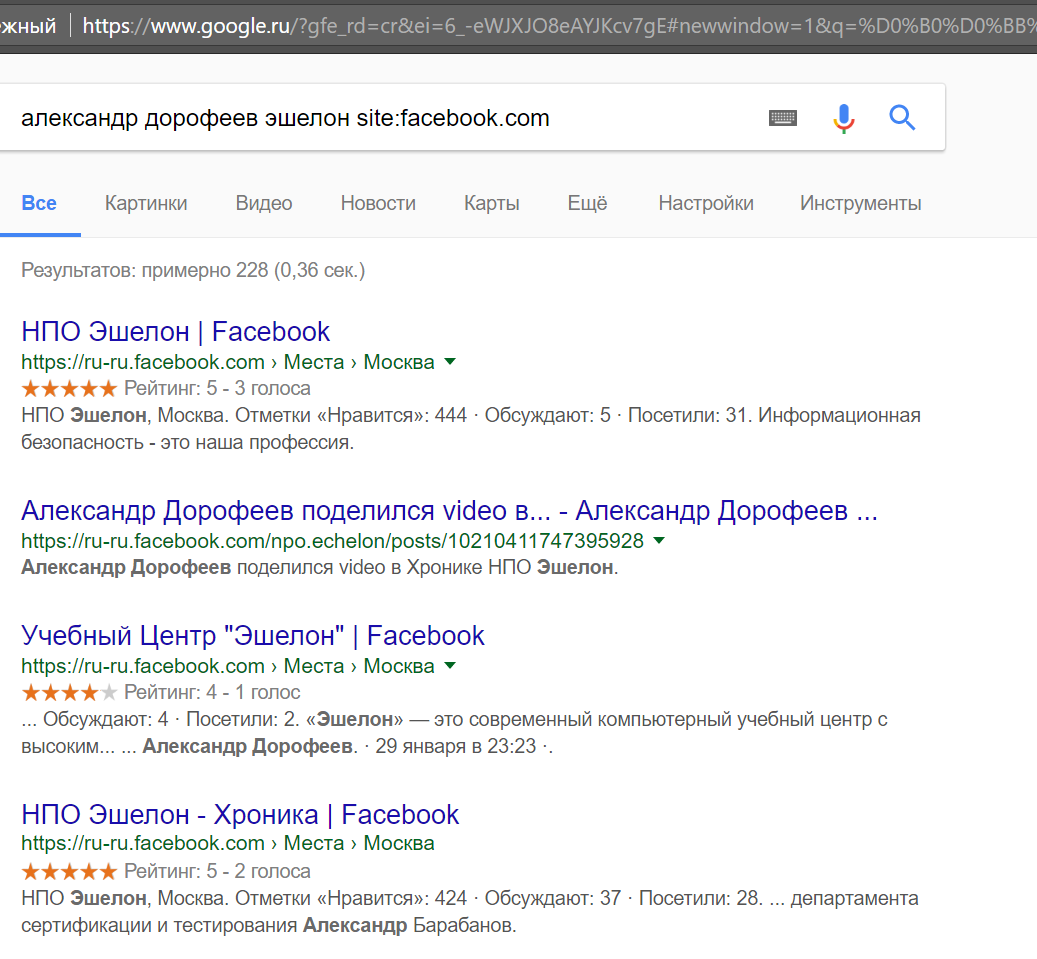
In the results of the issue there is no direct link to the profile that we are looking for, since the user has shown vigilance at one time and has forbidden the “surrender” of his page to search engines.

Here it is necessary to make a small digression again and remember how search engines work, including Google.
What can search engines do and what can't?
Search engines in general work on the following algorithm:
- search engine bots bypass sites;
- page content is indexed;
- At the request of users, links to relevant pages are retrieved.
Search engines cannot:
- index information that can be accessed only by authorized users;
- data that is available after filling out forms, for example, the results of uploading from various databases;
- qualitatively extract information from video, photos, audio materials.
Some more details:
- context: the result of the output depends on the user's request, on the history of his previous requests and on the history of page views by other users;
- the search is performed only in the language in which the user entered his request;
- there is some conflict of interest: search engines make money on advertisements that users click on, because the pages they need are not at the very top of the list;
- there is censorship due to the violation of anyone's rights (copyright, the right to oblivion, etc.).
Facebook belongs to the category of Internet resources that do not really like the indexing of your site and what is directly reported in robots.txt:

In order to detect a hidden user page on Facebook, we will need to log in to this network and use the built-in search functionality. A link to the user’s page can “leak” and appear in the search engine results, but only if the user deliberately published the material behind his authorship for all to see.
Using the search page of the author is easily detected:
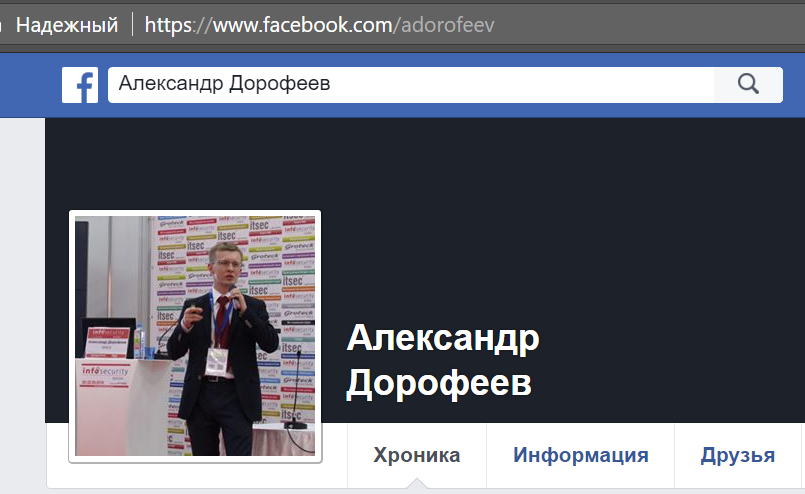
Analyzing the URL of the page, we can determine another user nickname: adorofeev.
Thus, we already got two nicknames: alexdorofeev and adorofeev. Since there are a lot of users on popular resources, a nickname may differ from what a person really likes to use, so his “native” identifier is already occupied by someone. For this reason, the author of the article has a nickname on Habré: alexdorofeeff, although adorofeev likes it more.
Knowing the nickname, we can search for more pages that are potentially associated with the right person.
Here we digress again on Google and remember the following points:
- By default, Google searches for an expression (a word or phrase, quoted) in all parts of the page: in the URL, in the title, in the text, in the text of the links. At the same time, special "advanced" operators allow you to specify exactly where we need it to be the desired text. For this we need to use the operators: inurl :, intext :, intitle :, inanchor :, as well as their counterparts with the prefix all.
- Google understands logical expressions and brackets. AND is a logical "AND", by default it is between the words separated by spaces in the search string. OR or I - logical "OR".
- If we use an operator, then after the colon there should be a search expression without a space.
- Operators with the prefix all allow you to apply them to a series of expressions after the colon, separated by spaces. For the same tasks, you can use operators without all, but with brackets and logical expressions.
Let's play with the inurl operator, which searches for pages that contain the desired word in the page URL. Since we already know a few nicknames of the author, we can make the following query:
inurl:(adorofeev | alexdorofeeff | alexdorofeev) In the results of the issue, we immediately find the pages of the respective accounts and some of the pages will belong to the author. Thus, if we have assumptions about the nicknames used, we can at the very beginning of our research obtain a list of potentially interesting pages.
Closing the topic with nicknames, I want to draw your attention to the services that allow you to quickly find out whether this nickname is used in a number of popular resources. So we can find additional pages of a particular person. An example of such a service: https://namechk.com/
How to find e-mail?
Now, having gotten a set of the user's favorite nicknames, we can try to find out his personal e-mail. Why is it needed? Sometimes you need to find out if a particular e-mail belongs to this person in order to determine the authorship of the letter. Also, e-mail will be useful for finding ads posted by users on forums, etc.
We know the nicknames, but do not yet know the domains of postal services. So let's make assumptions and check. Once a user from Russia, it is likely that he uses one or more of the following services:
- Mail.ru
- Yandex Mail
- Google gmail
- Rambler mail
Accordingly, we can generate addresses (our hypotheses at the moment) with the nicknames adorofeev, alexdorofeev and alexdorofeeff.
How can we verify if such addresses really exist? One of the options: a little "talk" with the mail servers of each service via SMTP:
Step 1. Find a mail server for a specific domain.
nslookup -type=mx " " 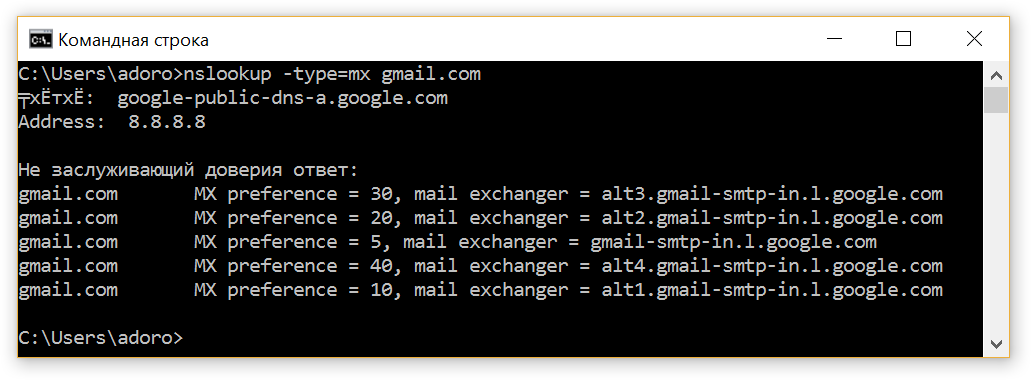
Step 2. Connect to the mail server and simulate the beginning of sending the message. If the server responds to the recipient's name with "OK", then there is such an account.
Option 1: e-mail exists.
telnet gmail-smtp-in.l.google.com 25 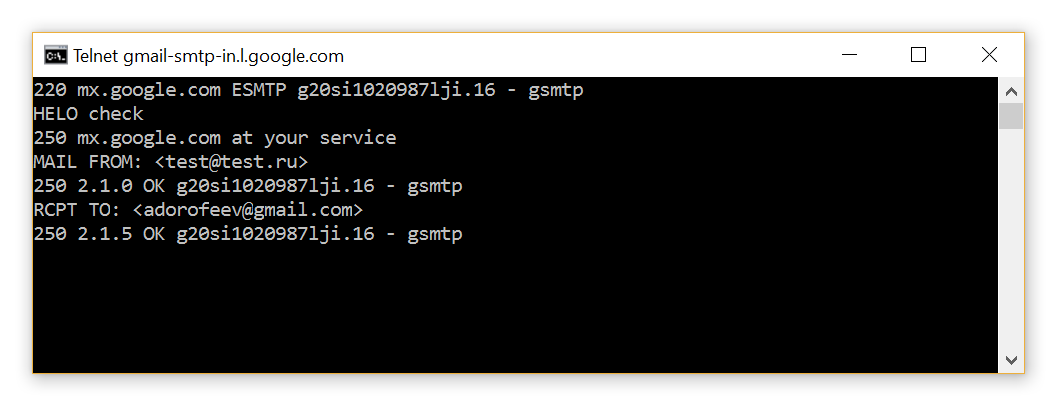
Option 2: e-mail does not exist.
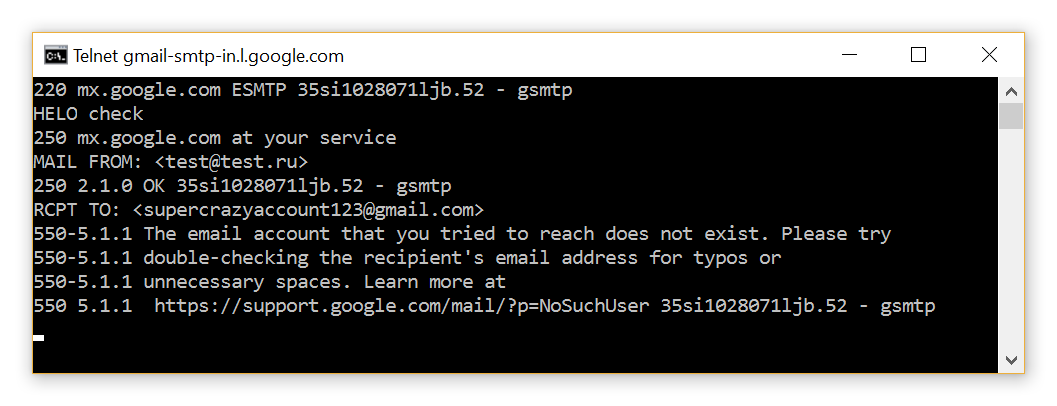
Email Verification
Having determined whether postal addresses exist, we can try to determine whether a particular address is associated with the person we need.
On mail.ru some users create their pages, which can be accessed as follows my.mail.ru/mail/nick/
"Punch" one of the addresses:
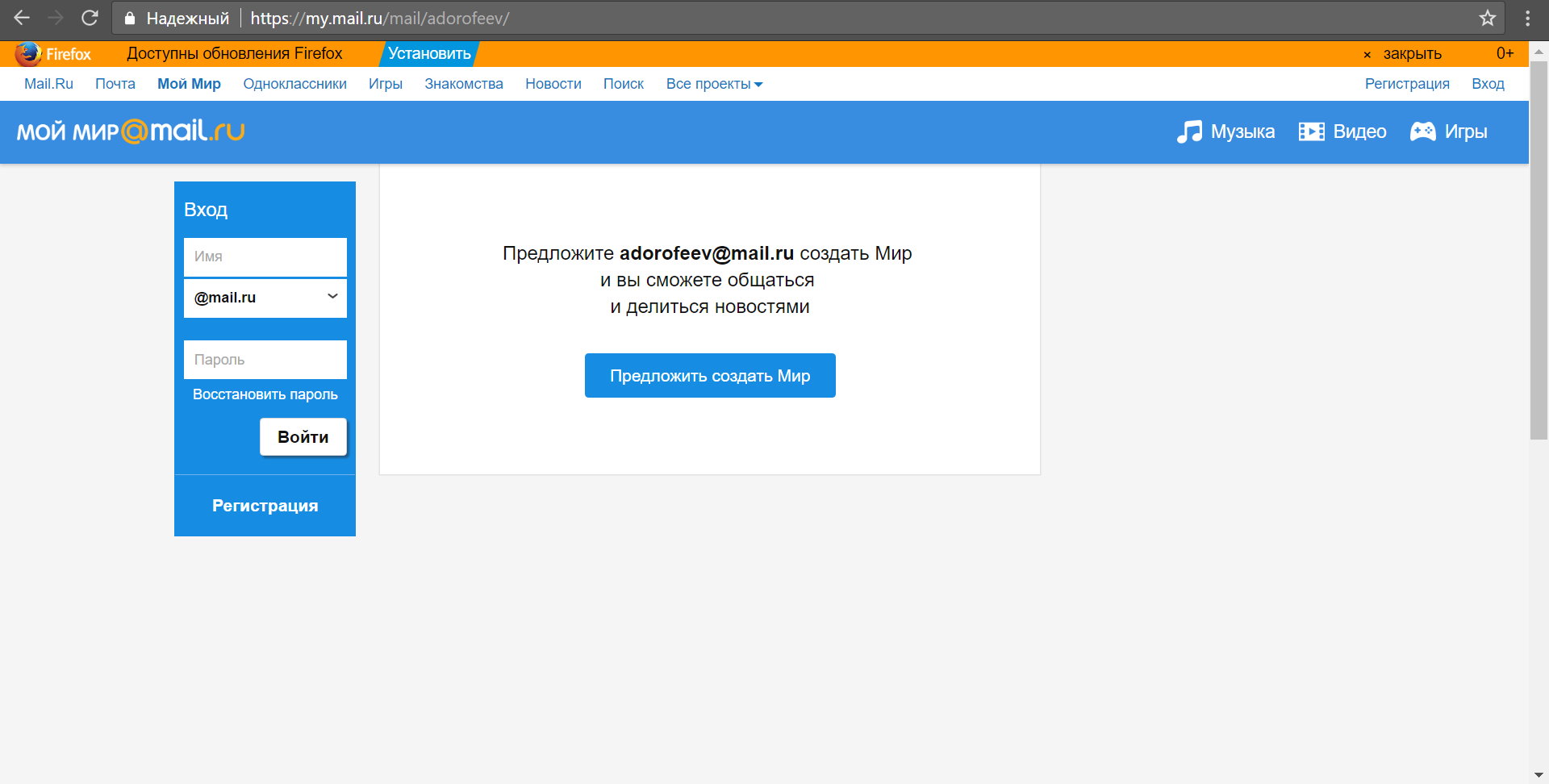
You can also view user pages on all Mail.ru projects using a combination of the inurl: and site: operators already known to us.
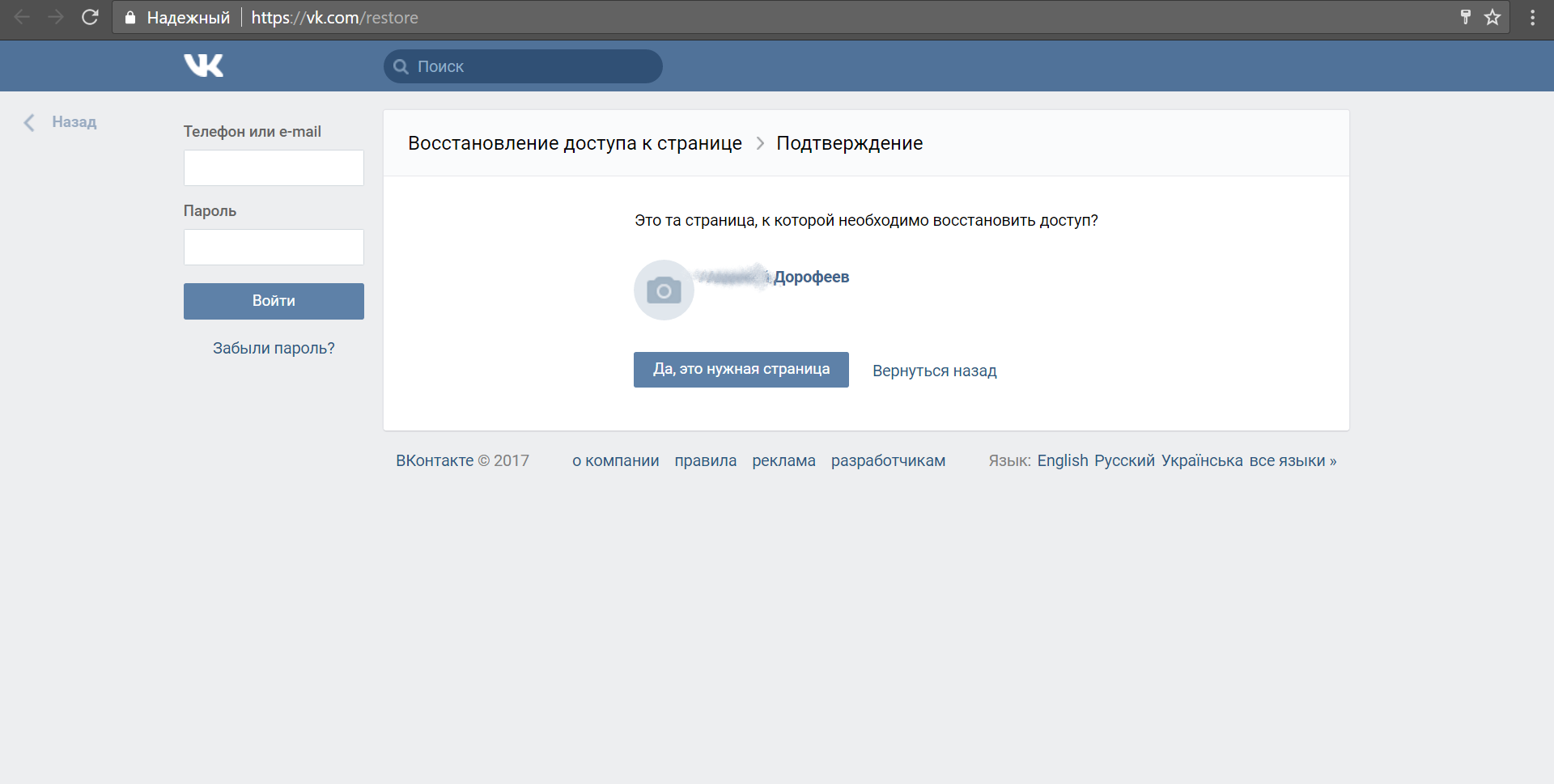
inurl: site:mail.ru If we know what a person looks like, know his name, or even have already found his page on the social network VKontakte (our case), then the task of verifying the ownership of a specific email address is greatly simplified. We can use the mechanism to restore access to the page. We will need luck: the user with such an address should exist, well, and place your photo.
Let's check four variants of addresses for the nickname “adorofeev” and see that for two addresses of the pages does not exist at all, for one - the other name:
But for the corresponding address on Gmail.com we find the author’s page:
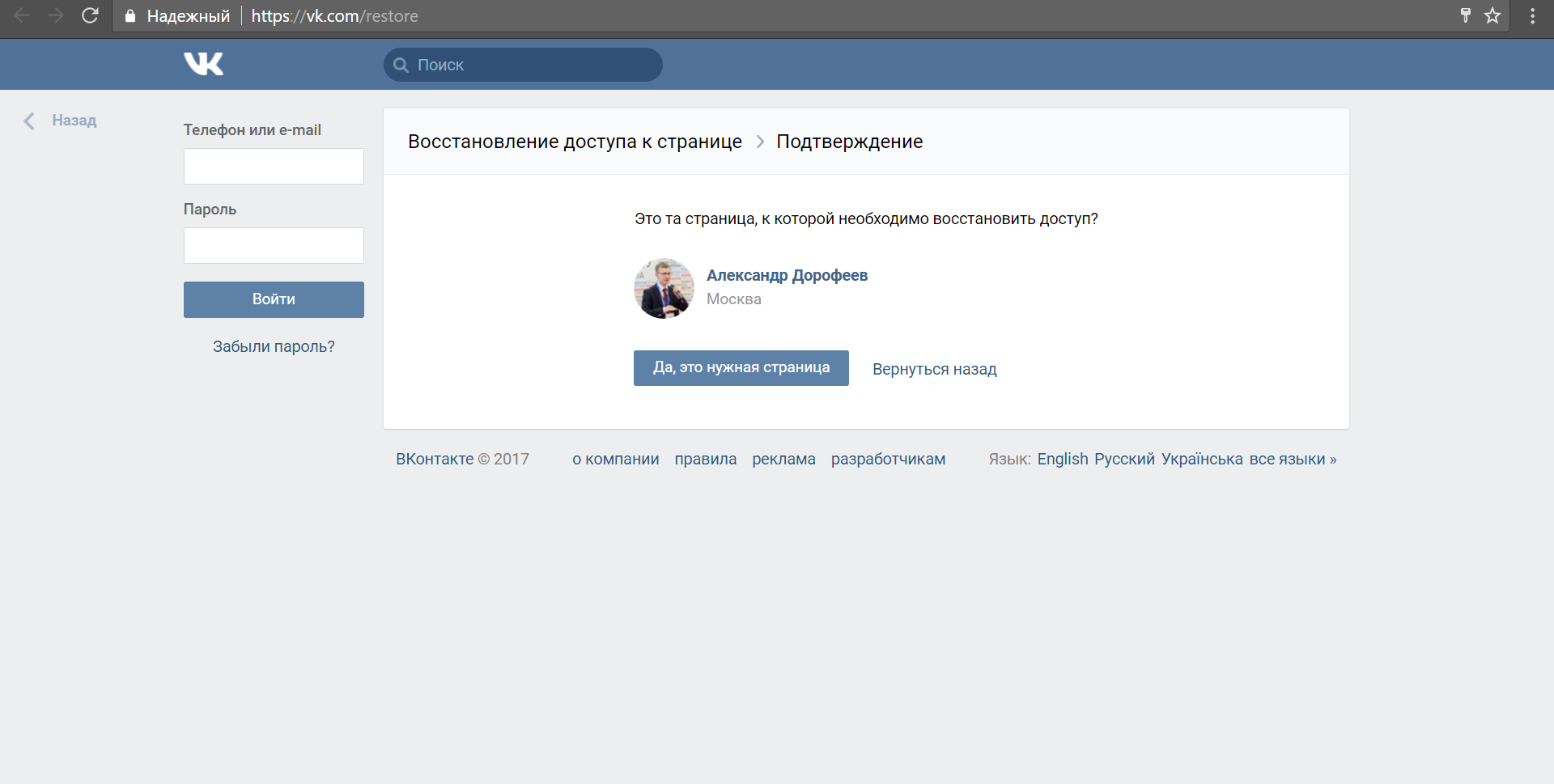
So, we calculated a real personal email address.
How to calculate a corporate email address?
Here the situation is much simpler. The fact is that many organizations have their own rules for forming the names of email accounts, which do not differ in special diversity: initials + last name, first letter of first name + last name, etc. We only need to understand what rule is used in a particular company in order to form the address of the person we need.
We send to Google a request of the following form:
email @ Scrolling through the results of the issue, we find the individual addresses of the employees and everything becomes obvious.
How to calculate user instagram by geo-tags?
Now let's try to calculate the author's account on Instagram. First, we check the most obvious options: https://www.instagram.com/adorofeev/ , https://www.instagram.com/ alexdorofeeff and https://www.instagram.com/a lex dorofeev / We see that this is not those accounts.
Having determined that a person works in a particular company, we can search for photos with an appropriate geo-tag. In our case, this will be the NPO Echelon.
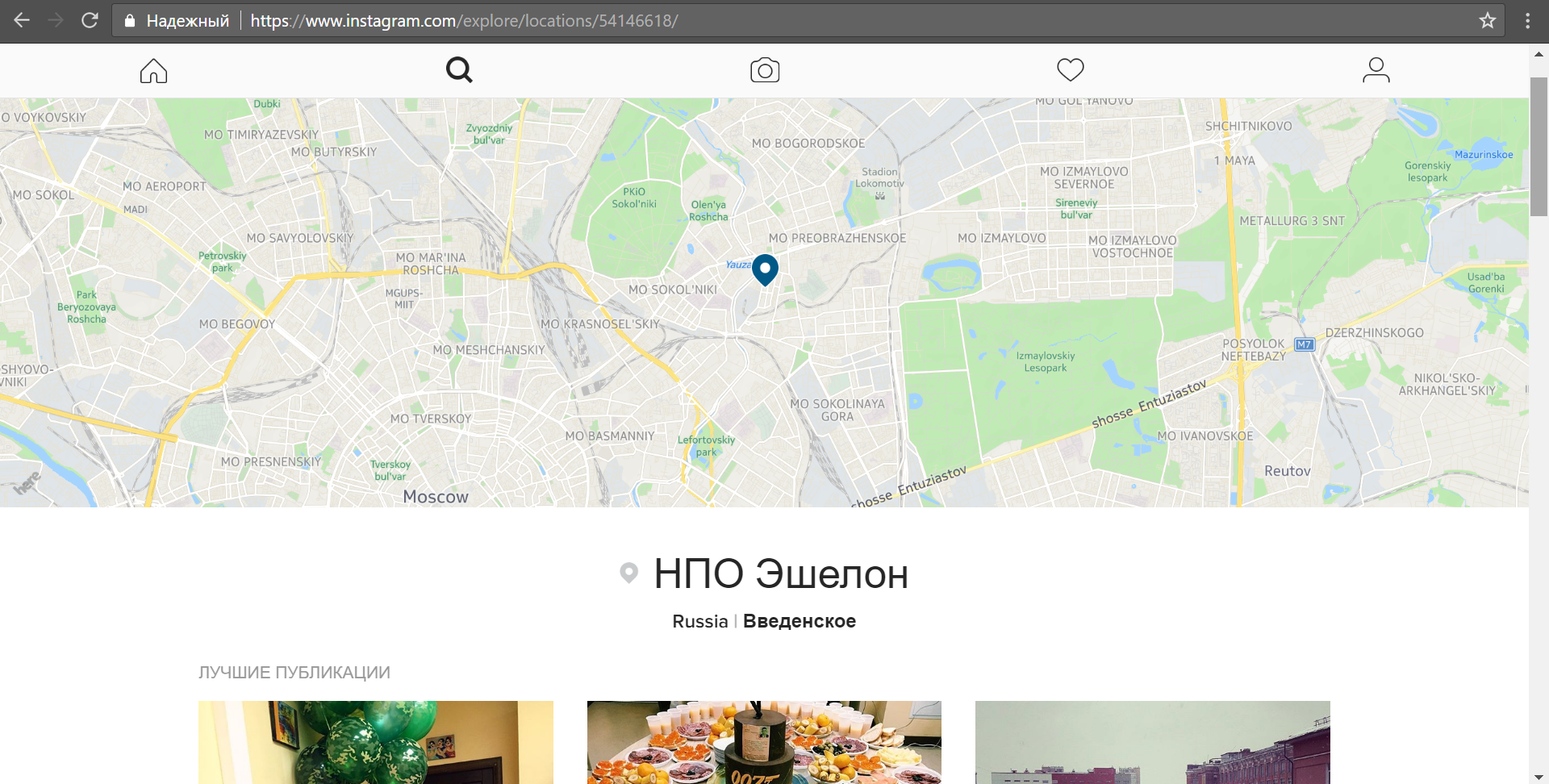
We see that publications with this geo-tag are for the most part made by company employees. It is logical to assume that among the subscribers of many Echelon employees should be the author’s account, which we can easily find:
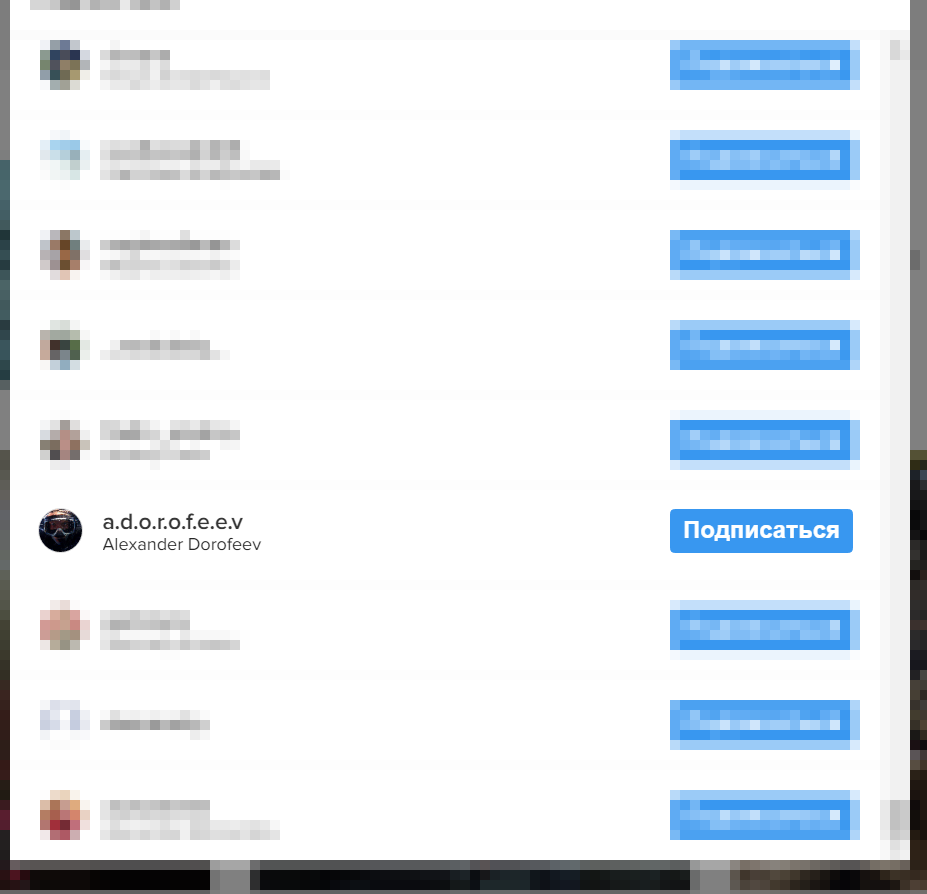
How to use a time machine?
After a similar analysis regarding the account in twitter, you can find that the author led the site adorofeev.ru, which is not available now. What to do in this situation? After all, the materials of the disappeared site may be of real interest. In the practice of the author there was a situation when a similar disappeared site contained published materials of the criminal case, which was interesting to see.
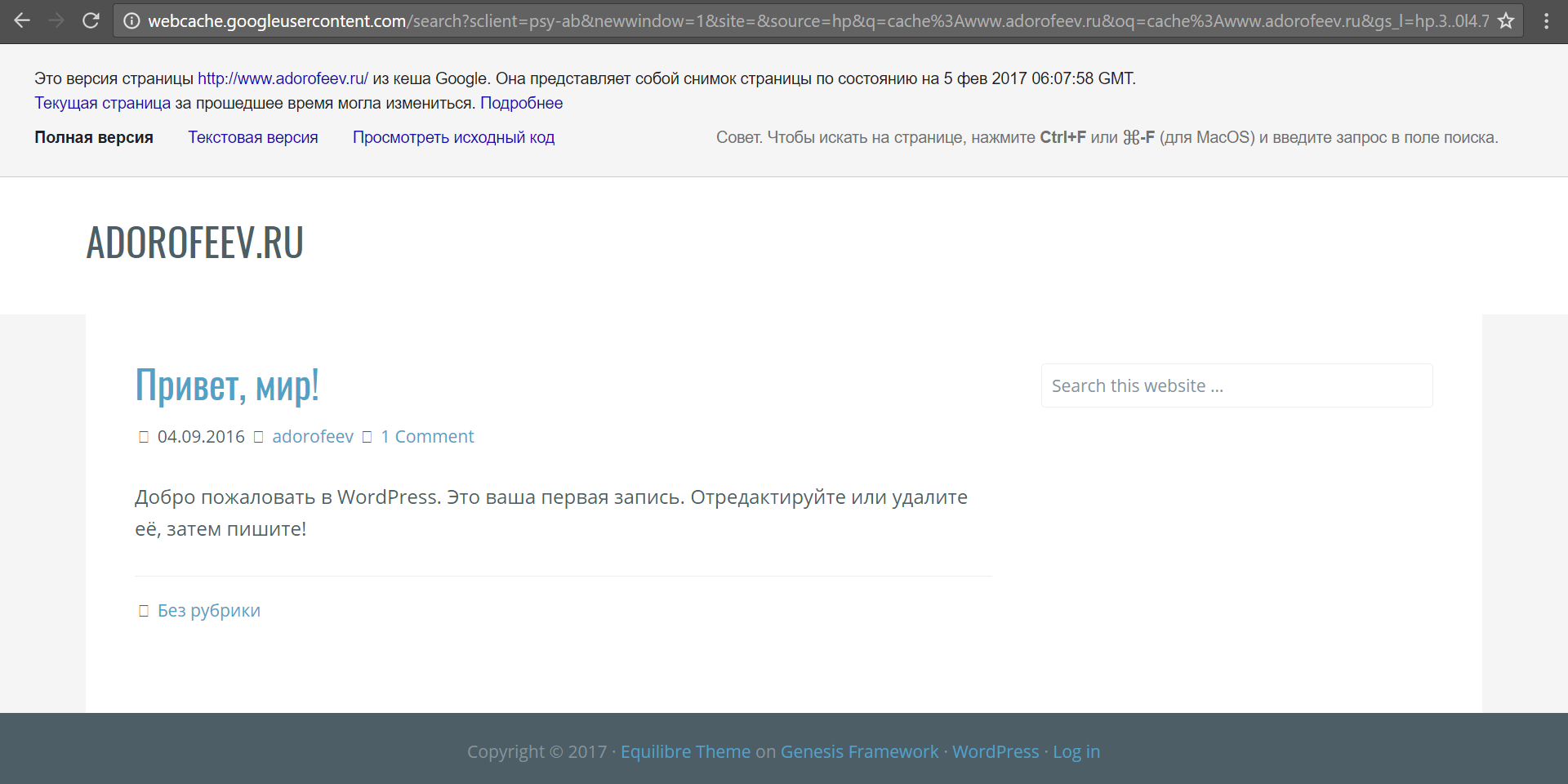
If the site was turned off quite recently, Google can again help us by offering a cache operator: with which you can extract cached pages obtained by a search engine.
cache:www.adorofeev.ru/ We see that the site on February 5th was still included, but did not represent anything interesting from itself.
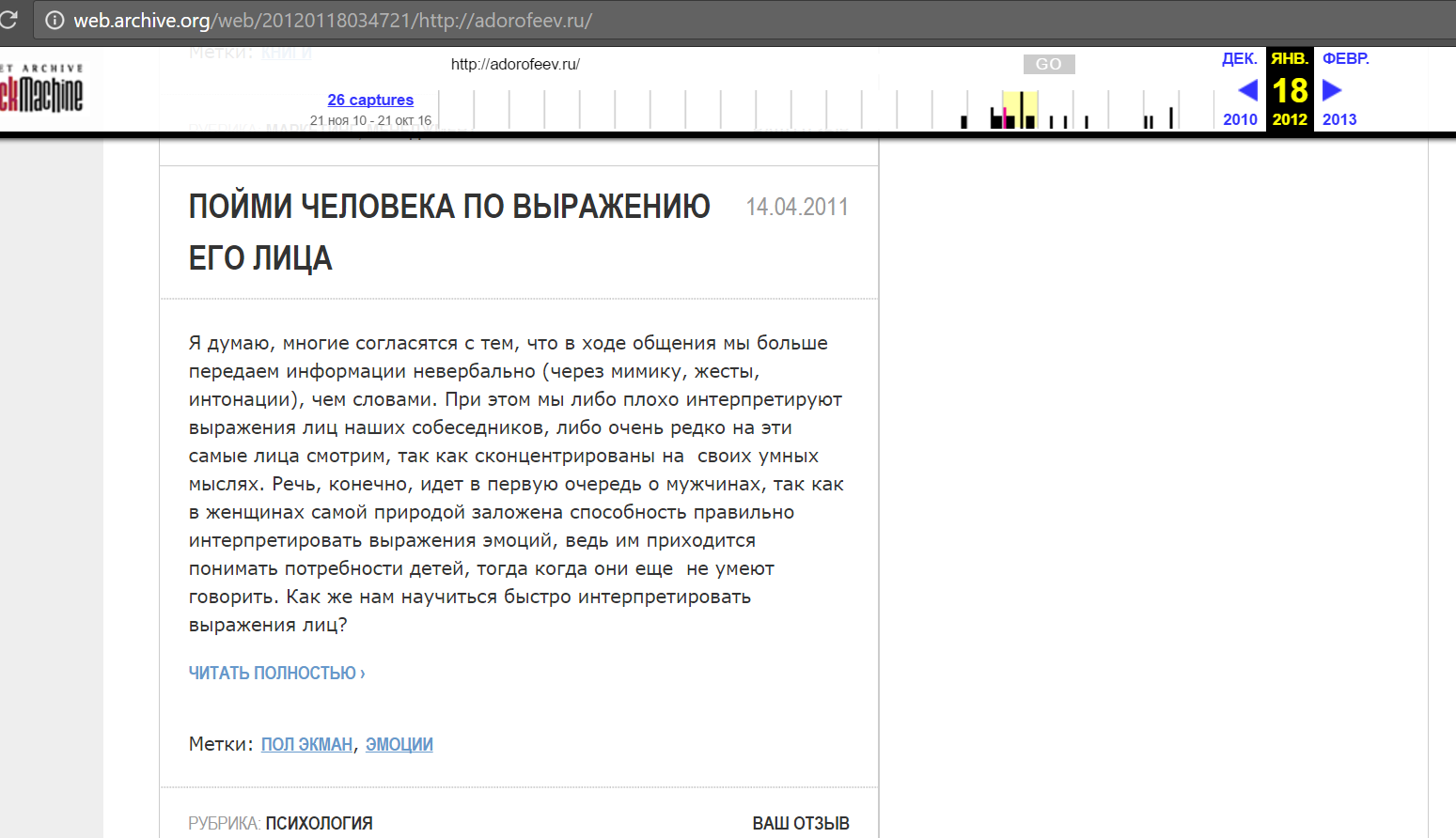
I really want to look into the more distant past - a few years ago. For this, a time machine would be suitable and, oddly enough, it is and is available to any inquisitive user at: https://archive.org/web/
"Punching" the author's site, you can see that in the past there were some materials:
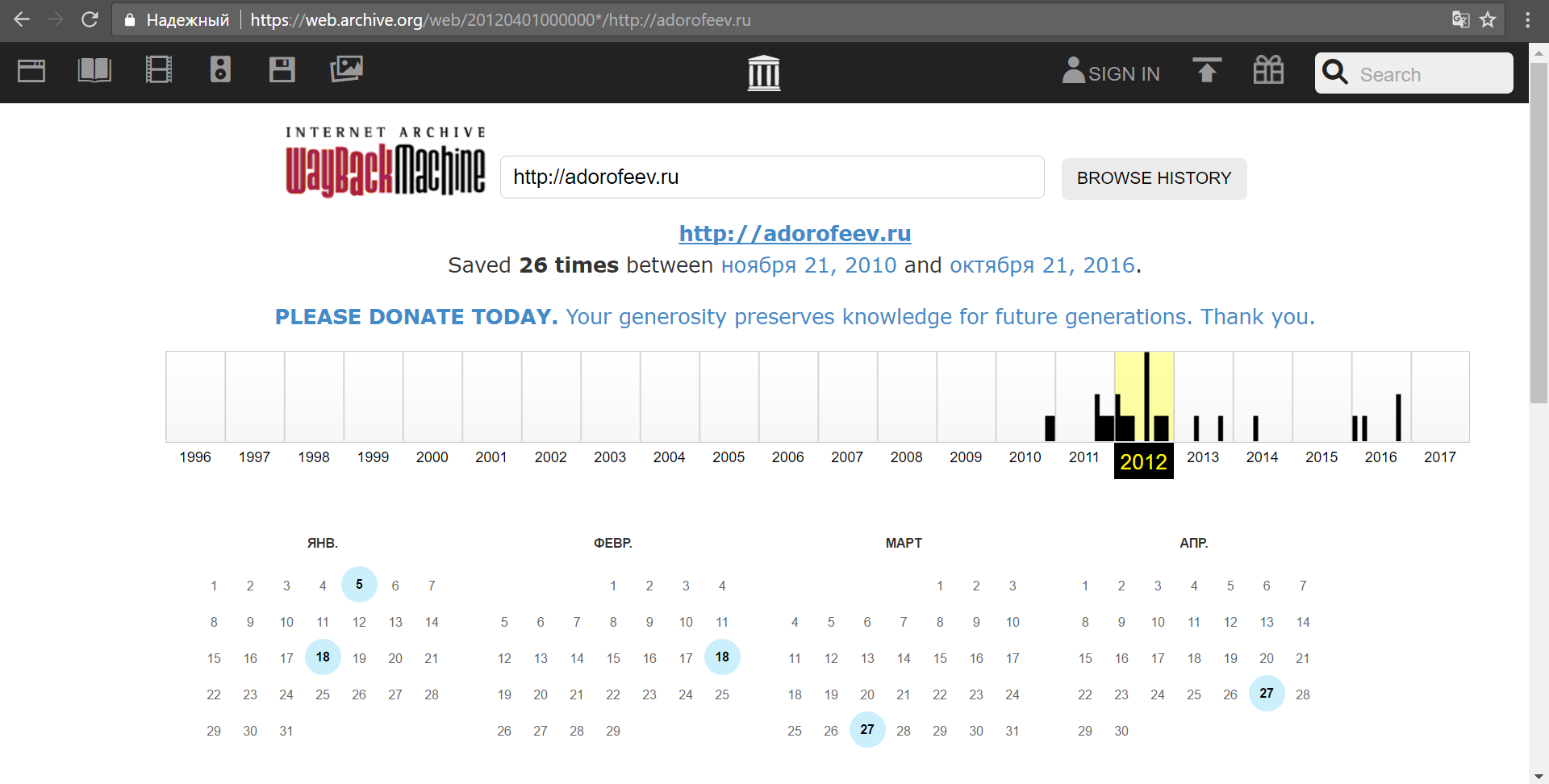
Moreover, selecting certain dates, you can see the content of the site at a particular moment:
Instead of a conclusion: a few words about process automation and other Google operators
Is it possible to automate the process of searching for interesting information using Google? You can, and there are already some good attempts: theHarvester script.
It should be noted that Google is not welcome and is struggling, so the reliability of the results of the use of various scripts will have to be further checked. Even just playing with quite legal operators, which we discussed above, you will constantly see the captcha and prove that you are not a robot.
The article turned out to be quite voluminous and we didn’t consider many other operators of advanced Google search , which can also be useful in Internet intelligence. If the use of operators in a similar way is interesting, then we will definitely continue this topic in one of the following articles.
Literature
- What is in my name to you: how to “pierce” a person on the Internet qualitatively?
- Internet intelligence in action: who is Mr./Ms. Habraman?
- Alexey Markov, Valentin Tsirlov
- Google Hacking for Penetration Testers, Third Edition 3rd Edition by Johnny Long, Bill Gardner, Justin Brown.
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/321754/
All Articles