How smart contracts will change our lives
What are smart contracts, how they work and why the future belongs to them.
Blockchain is a decentralized system that exists thanks to many networked computers. Therefore, one of its main advantages is that you can not pay intermediaries and save your time and nerves.
')
The blockchain has its drawbacks , but it is faster, more reliable and safer than traditional systems, and therefore banks and government organizations are increasingly using this technology for their needs.

In 1994, Nick Sabo, a lawyer and cryptographer, realized that with a decentralized registry, you can make smart contracts, also called self-executable, digital, or smart contracts.
Such contracts can be recorded in the form of a code, saved and duplicated in the system, and their execution will be ensured by a network of computers managing the blockchain. Also, using the registry, you can transfer money to each other and receive goods or services.
Smart contracts allow you to exchange money, property, shares or other assets without resorting to the services of intermediaries.
In order to conclude a normal transaction, you need to go to a lawyer or notary, pay and wait for the paperwork. Smart contracts work like vending machines: you simply throw bitcoins into a machine (that is, the registry), and a third-party contract, driver’s license, or any other service you ordered falls into your account.
In addition, unlike traditional agreements, smart contracts not only contain information about the obligations of the parties and fines for their violation, but also automatically ensure the fulfillment of all contract terms.
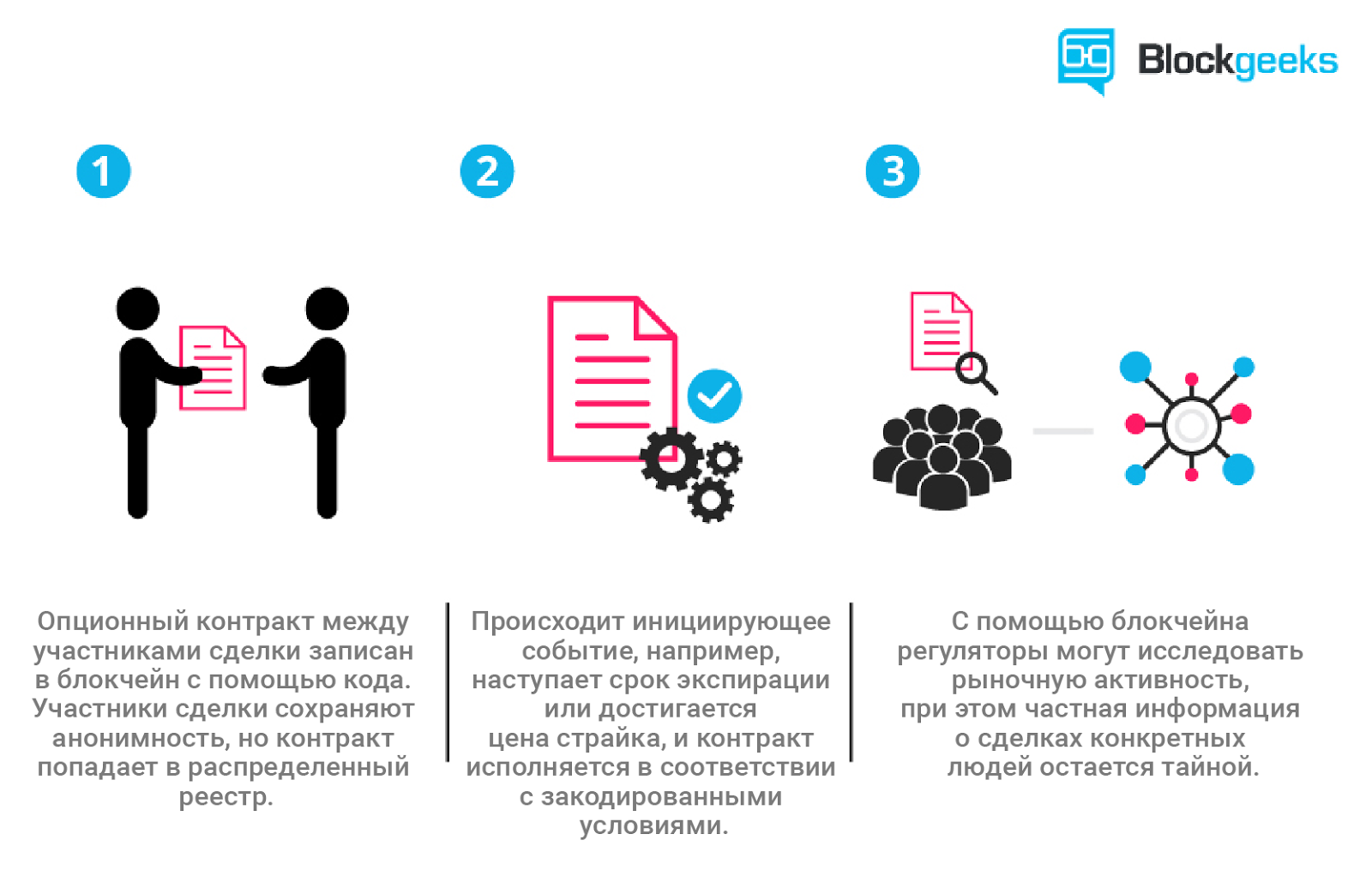
At a recent blockchain summit in Washington, Vitaly Buterin, a 23-year-old programmer from the Ethereum project, explained that in a smart contract, an asset or currency is transferred to a program that monitors compliance with a set of conditions.
At a certain point, this program confirms the fulfillment of the terms of the contract and automatically determines whether the specified asset should go to one of the participants in the transaction or immediately return to the other participant (and maybe the conditions are somewhat more complicated). All this time, the document is stored and duplicated in the decentralized registry, which ensures its reliability and does not allow any of the parties to change the terms of the agreement.
Here is the code written for the usual smart contract on the blockchain platform Ethereum. Contracts can be written in any blockchain, but Ethereum is most popular because it provides unlimited possibilities for writing smart contracts and working with them.

A sample of a smart contract written on the Ethereum platform. Source: www.ethereum.org/token
It says that the contract creator should receive 10 thousand bitcoins. This contract allows anyone who has enough funds in the account to transfer Bitcoins to other people.
Using smart contracts, you can simplify work in many areas of life, including logistics, management, law, and even in elections.
Elections
According to experts, it is almost impossible to falsify the election results, but thanks to clever contracts it is possible to completely exclude the possibility of external interference in the voting system.
In this case, the votes will be placed in a distributed registry, and decoding them will require exceptional computational capabilities. There are no such computers, so it will be impossible to hack this system.
Management
Blockchain not only offers a reliable and transparent general registry, but also helps to avoid misunderstandings when working together or situations where the parties make contracts independently of each other.
Logistics and Supply
Bitcoin Core protocol developer Jeff Garzik says:
“UPS can execute contracts that say:“ If we receive payment for the delivery of the goods, then its manufacturer, who in the supply chain is many links higher, will immediately start creating a new such product, as this has already been delivered to its destination. ”
Procurement too often suffers from bureaucracy, when different forms have to be approved in numerous instances. Because of this, fraudsters get the opportunity to earn money, and companies suffer losses. The blockchain avoids these problems, as each participant in the supply chain gets access to a secure electronic system that controls the execution of work and payments.
Thus, Barclays Corporate Bank uses smart contracts to register the transfer of ownership and automatically transfer payments to other financial institutions.
Cars
Think about the future, where everything will be automated. Google is already building it, creating smart phones, smart glasses and even smart cars. And here smart contracts will come to the rescue.
Take, for example, self-driving or self-parking cars. Smart contracts will determine who is responsible for the accident: the sensor or the driver, as well as help in resolving any other situations. With the help of smart contracts, insurance companies can set the amount of contributions depending on where and under what conditions drivers drive vehicles.
Other areas
Other industries, such as acquiring, lending and accounting, will also use smart contracts — for example, for risk assessment and auditing in real time. Lawyers will be able to move from drawing up traditional contracts to creating standard samples of smart contracts. And on the Blockchain Technologies website, smart contracts have turned into an electronic-paper hybrid: they are confirmed by the blockchain and get material embodiment in the form of a paper copy.
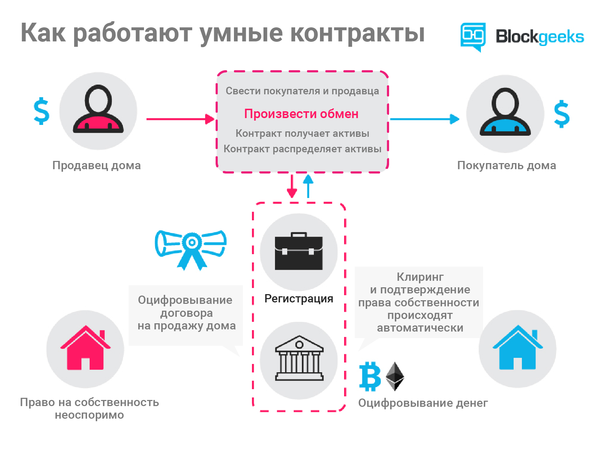
Patrick Hubbard, Senior Specialist and Senior Product Marketing Manager at SolarWinds:
“The Yangon Stock Exchange in Myanmar makes payments using a distributed registry. Of particular interest are those functions of the blockchain, which go beyond the traditional use of technology. So on the Yangon stock exchange it was possible to solve the problem of settlements made at different times in the trading system, which synchronizes trading only twice a day. Due to the fact that smart contracts themselves ensure the execution of transactions, blockchains with their reliable transaction system can be used in situations where complex operations are required, depending on various changing factors. That is why Amazon, Microsoft Azure and IBM Bluemix are paying so much attention to the development of the blockchain-as-a-service cloud technology. ”
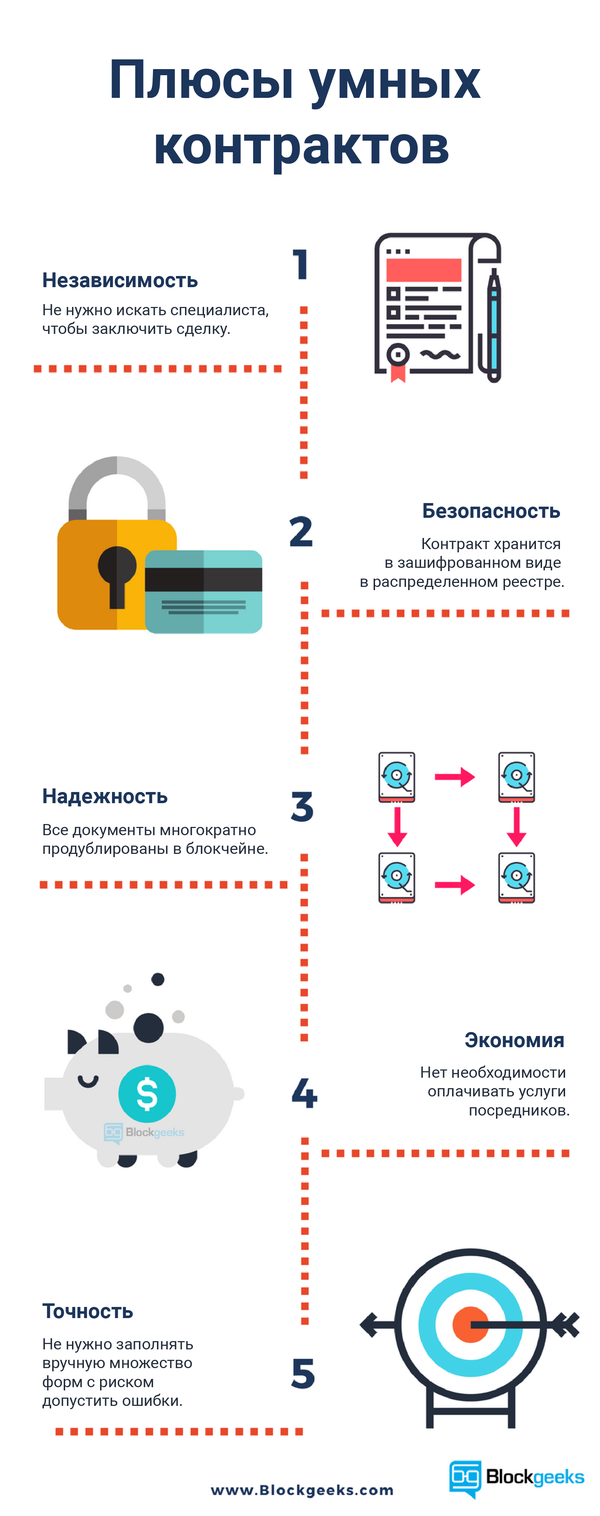
Smart contracts are far from perfect. What if errors get into the code? How should the state regulate these contracts? And how will it levy taxes on such transactions?
The list of possible problems is not limited to this. Specialists are trying to solve all the problems, but such difficulties repel many possible users.
Bitcoin: An excellent blockchain for Bitcoin transactions, but the possibilities for working with documents are limited there.
Side Chains: Another name for blockchains, parallel Bitcoin, which provide several great opportunities to work with contracts.
NXT: This is an open blockchain platform with a limited number of smart contract samples. You can only use what is there; You can not write your code.
Ethereum: An open blockchain platform that is best suited for writing smart contracts and working with them. You can create any program, but you will have to pay for ETH coins with the computing resources of the platform.
Source: Blockgeeks .

Blockchain is a decentralized system that exists thanks to many networked computers. Therefore, one of its main advantages is that you can not pay intermediaries and save your time and nerves.
')
The blockchain has its drawbacks , but it is faster, more reliable and safer than traditional systems, and therefore banks and government organizations are increasingly using this technology for their needs.

In 1994, Nick Sabo, a lawyer and cryptographer, realized that with a decentralized registry, you can make smart contracts, also called self-executable, digital, or smart contracts.
Such contracts can be recorded in the form of a code, saved and duplicated in the system, and their execution will be ensured by a network of computers managing the blockchain. Also, using the registry, you can transfer money to each other and receive goods or services.
What are smart contracts?
Smart contracts allow you to exchange money, property, shares or other assets without resorting to the services of intermediaries.
In order to conclude a normal transaction, you need to go to a lawyer or notary, pay and wait for the paperwork. Smart contracts work like vending machines: you simply throw bitcoins into a machine (that is, the registry), and a third-party contract, driver’s license, or any other service you ordered falls into your account.
In addition, unlike traditional agreements, smart contracts not only contain information about the obligations of the parties and fines for their violation, but also automatically ensure the fulfillment of all contract terms.

At a recent blockchain summit in Washington, Vitaly Buterin, a 23-year-old programmer from the Ethereum project, explained that in a smart contract, an asset or currency is transferred to a program that monitors compliance with a set of conditions.
At a certain point, this program confirms the fulfillment of the terms of the contract and automatically determines whether the specified asset should go to one of the participants in the transaction or immediately return to the other participant (and maybe the conditions are somewhat more complicated). All this time, the document is stored and duplicated in the decentralized registry, which ensures its reliability and does not allow any of the parties to change the terms of the agreement.
Smart Contract Example
Here is the code written for the usual smart contract on the blockchain platform Ethereum. Contracts can be written in any blockchain, but Ethereum is most popular because it provides unlimited possibilities for writing smart contracts and working with them.

A sample of a smart contract written on the Ethereum platform. Source: www.ethereum.org/token
It says that the contract creator should receive 10 thousand bitcoins. This contract allows anyone who has enough funds in the account to transfer Bitcoins to other people.
Practical use of smart contracts
Using smart contracts, you can simplify work in many areas of life, including logistics, management, law, and even in elections.
Elections
According to experts, it is almost impossible to falsify the election results, but thanks to clever contracts it is possible to completely exclude the possibility of external interference in the voting system.
In this case, the votes will be placed in a distributed registry, and decoding them will require exceptional computational capabilities. There are no such computers, so it will be impossible to hack this system.
Management
Blockchain not only offers a reliable and transparent general registry, but also helps to avoid misunderstandings when working together or situations where the parties make contracts independently of each other.
Logistics and Supply
Bitcoin Core protocol developer Jeff Garzik says:
“UPS can execute contracts that say:“ If we receive payment for the delivery of the goods, then its manufacturer, who in the supply chain is many links higher, will immediately start creating a new such product, as this has already been delivered to its destination. ”
Procurement too often suffers from bureaucracy, when different forms have to be approved in numerous instances. Because of this, fraudsters get the opportunity to earn money, and companies suffer losses. The blockchain avoids these problems, as each participant in the supply chain gets access to a secure electronic system that controls the execution of work and payments.
Thus, Barclays Corporate Bank uses smart contracts to register the transfer of ownership and automatically transfer payments to other financial institutions.
Cars
Think about the future, where everything will be automated. Google is already building it, creating smart phones, smart glasses and even smart cars. And here smart contracts will come to the rescue.
Take, for example, self-driving or self-parking cars. Smart contracts will determine who is responsible for the accident: the sensor or the driver, as well as help in resolving any other situations. With the help of smart contracts, insurance companies can set the amount of contributions depending on where and under what conditions drivers drive vehicles.
Other areas
Other industries, such as acquiring, lending and accounting, will also use smart contracts — for example, for risk assessment and auditing in real time. Lawyers will be able to move from drawing up traditional contracts to creating standard samples of smart contracts. And on the Blockchain Technologies website, smart contracts have turned into an electronic-paper hybrid: they are confirmed by the blockchain and get material embodiment in the form of a paper copy.

Patrick Hubbard, Senior Specialist and Senior Product Marketing Manager at SolarWinds:
“The Yangon Stock Exchange in Myanmar makes payments using a distributed registry. Of particular interest are those functions of the blockchain, which go beyond the traditional use of technology. So on the Yangon stock exchange it was possible to solve the problem of settlements made at different times in the trading system, which synchronizes trading only twice a day. Due to the fact that smart contracts themselves ensure the execution of transactions, blockchains with their reliable transaction system can be used in situations where complex operations are required, depending on various changing factors. That is why Amazon, Microsoft Azure and IBM Bluemix are paying so much attention to the development of the blockchain-as-a-service cloud technology. ”

Cons of smart contracts
Smart contracts are far from perfect. What if errors get into the code? How should the state regulate these contracts? And how will it levy taxes on such transactions?
The list of possible problems is not limited to this. Specialists are trying to solve all the problems, but such difficulties repel many possible users.
Blockchains where smart contracts can be made
Bitcoin: An excellent blockchain for Bitcoin transactions, but the possibilities for working with documents are limited there.
Side Chains: Another name for blockchains, parallel Bitcoin, which provide several great opportunities to work with contracts.
NXT: This is an open blockchain platform with a limited number of smart contract samples. You can only use what is there; You can not write your code.
Ethereum: An open blockchain platform that is best suited for writing smart contracts and working with them. You can create any program, but you will have to pay for ETH coins with the computing resources of the platform.
Source: Blockgeeks .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/321548/
All Articles