How to remotely and centrally manage patches and software updates in the company

Timely updating the software installed at the company and installing the required patches is one of the important tasks, the implementation of which allows you to avoid various software malfunctions, as well as to ensure an adequate level of security. How can you centrally and remotely manage software updates and patches in a company? Consider the example of a cloud RMM-solution Panda Systems Management .
Task: timely software update
Software makers regularly release updates and patches that, by and large, have two goals: on the one hand, they allow to correct existing errors in the program, on the other hand, they cover the detected vulnerabilities or security holes. Therefore, it is not surprising that timely software update is one of the priorities.
')
Accordingly, to solve this problem, it is required to know in a timely manner whether updates / patches are available, as well as to monitor promptly, which devices have already been updated, and which ones have not. Obviously, with the growth of the IT equipment fleet in the company (especially with remote offices), centralized and remote management and control tools are required.
For an automated solution of this task, we invite you to pay attention to RMM solutions designed for remote and centralized monitoring, maintenance and support of corporate networks.
We propose to consider the solution of the patch management problem using the example of one of such solutions, the Panda Systems Management cloud service.
In our previous articles, we talked in detail about how you can quickly implement this service , how to monitor network performance , manage mobile devices , remotely and centrally install software and inventory all of the company's IT assets. Today we will focus on patch management.
By the way, you can register for free Panda Systems Management licenses on the website and together with us set up patch management directly in your network.
So let's go.
What is patch management
In this case, patch management is a set of tools for centralized control, implementation, and installation of patches and software updates. The patch management functions in Panda Systems Management not only make it easier to resolve issues related to regular software updates, but also allow you to perform audits that make it quick and easy to get a list of devices that are not updated or have known vulnerabilities.
As we have said, thanks to patch management, conflicts in the operation of the software can be avoided, as well as an increase in the corporate network security level.
The patch management functions in Panda Systems Management currently support Windows systems and use the Windows Update API, which is present on all Microsoft Windows devices where the agent of this solution is installed.
What patches can I implement / apply?
Panda Systems Management allows you to centrally manage all patches and updates published by Microsoft in its Windows Update. Microsoft publishes updates for all Windows operating systems currently supported, as well as software developed by the corporation:
• Microsoft Office
• Microsoft Exchange
• SQL Server
• Windows Live
• Windows Defender
• Visual Studio
• Zune Software
• Virtual PC
• Virtual Server
• CAPICOM
• Microsoft Lync
• SilverLight
• Windows Media Player
• …other
Implementation and installation of patches
Panda Systems Management offers three complementary patch management methods. Each of them has different functions to adapt all possible needs and / or scenarios.
• Manual patch management
• Windows Updates Policy
• Patch Management Policy
Managing patches using Windows Update and Patch Management are mutually exclusive. It is recommended to disable Windows Updates when using Patch Management policies for updating Windows operating systems, otherwise it may lead to unpredictable consequences.
The procedures described below may conflict with other procedures defined by third-party software vendors, such as the Windows Update policies defined in the GPO. Therefore, it is recommended to disable third-party policies that may interfere with the policies defined in Panda Systems Management.
Comparative table of methods

Method 1: Manual patch management
general description
Manual patch management allows you to individually select the patches you want to install, according to the criteria applied by the administrator. This method allows you to achieve maximum flexibility, because All patches installed on each device, as well as patches awaiting installation, are displayed all the time.
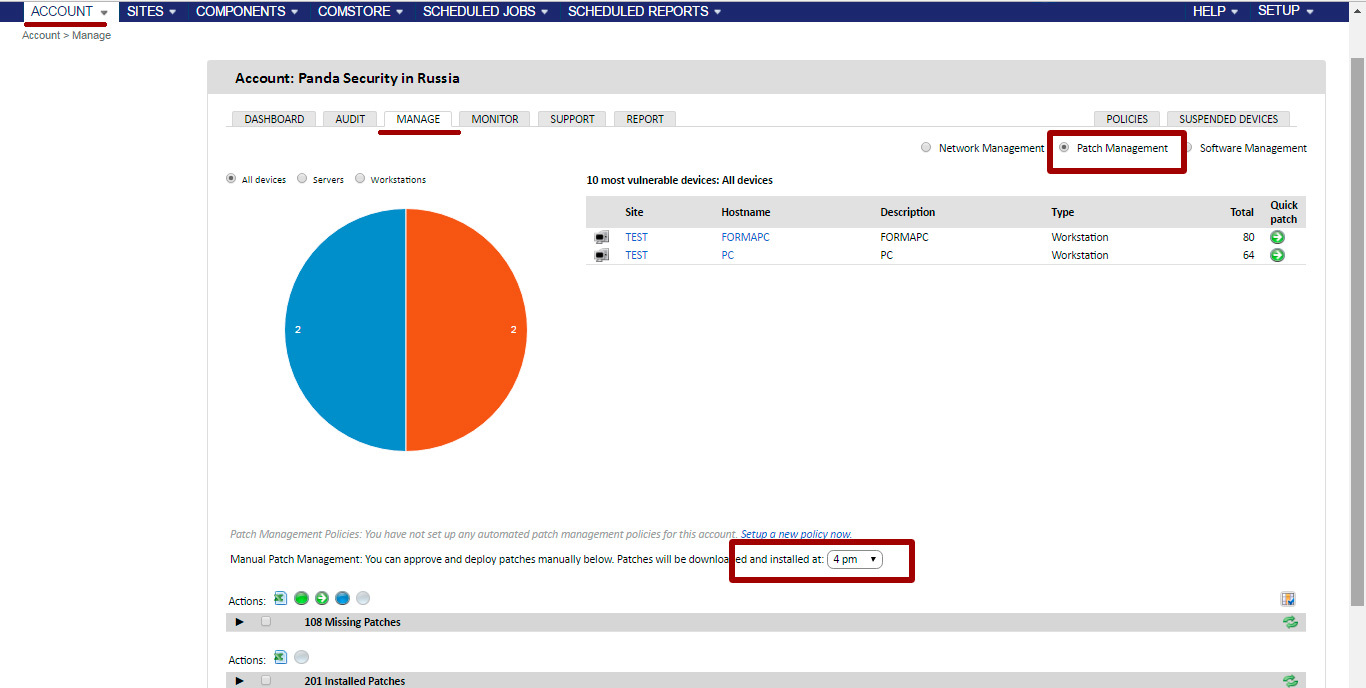
This method can be applied at any level: Account, Site or Device. Thus, you can select patches for a specific device (Device level), for a specific device group or project (Site), or for all devices that are managed by you within your Panda Systems Management (Account) account.
Access to manual patch management
Regardless of the level you choose, the manual method is available when you open the Manage tab.
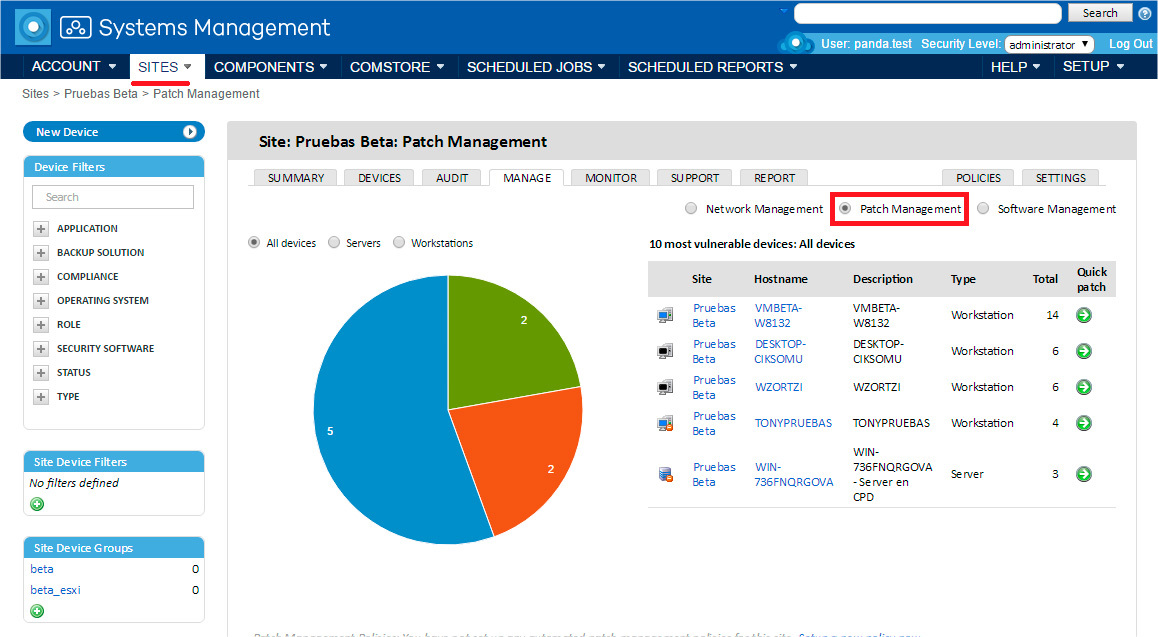
Available actions
The selection of available actions is carried out using icons located in the action bar.
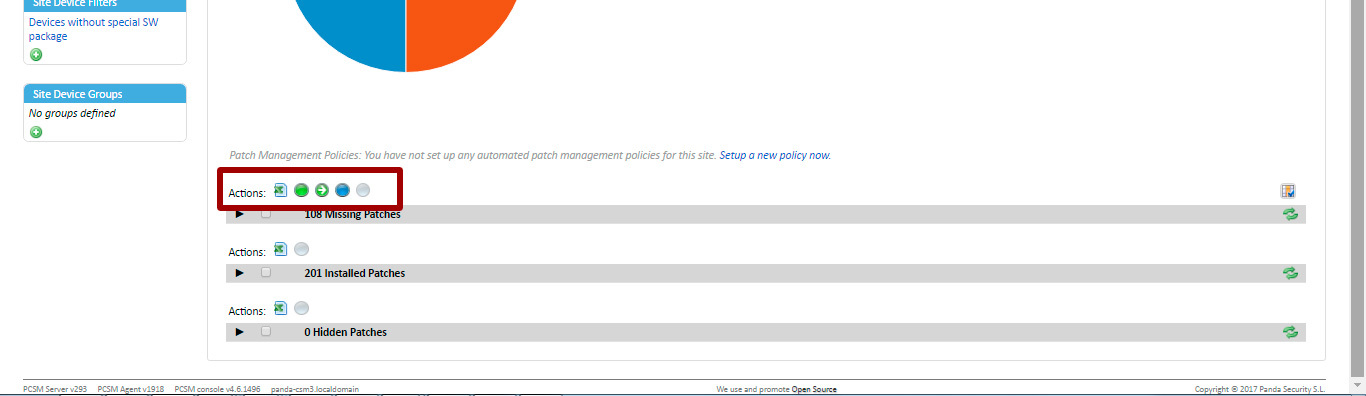
Allow patch (Approve Patch)
Select a patch and click the green icon. As a result, the patch will wait for installation. Manually allowed patches are installed at that time as configured on the Manage tab at the Account level.
Please note that the time for installing manual patches can be configured only at the level of the entire account. Thus, all manually managed patches for all devices within the account will be installed at the same time.
Hide patch
Select a patch and click the blue icon to hide the patch from the list of available patches.
Quick patch installation (Quick patch)
Select a patch and click the green arrow icon to immediately install the patch, without waiting for the time configured to install all manually allowed patches (at the Account level on the Manage tab).
Reset patch selection (Reset patch)
Click the white icon to reset the selection of patches.
View patches
All published patches are grouped into three drop-down lists depending on their status in relation to the device being controlled.

Statuses:
• Missing Patches: Patches that have not yet been installed on devices belonging to this level. At levels above the Device level, the number of devices on which each specific patch has not yet been installed is also shown.
• Installed Patches: Patches that have already been installed at the selected level. At levels above the Device level, the number of devices on which each specific patch has already been installed is also shown.
• Hidden Patches: Patches that the administrator has decided to hide due to the fact that they do not need to be applied and they are not required to receive reminders.
To simplify searches, additional information on patches is available when disclosing each list, and an additional control panel is available for filtering the list of patches.

This additional control panel allows you to easily select from the list those patches that meet the following criteria:
• Severity: allows you to select the degree of patch criticality set by Microsoft: Critical , Important , Moderate , Low , and Unspecified . By the way, it should be noted that Microsoft, as a rule, sets the degree of criticality only for security patches, and therefore the other patches usually have an Unspecified degree.
• Reboot required: if the device needs to be rebooted after applying the patch.
• User input required: if user input is required to apply the patch.
• Category: allows you to select patches that are applied to a specific program.
Panda Systems Management for each record provides the following information:

• Check: checkbox to select a patch.
• Action icon: Displays the icon corresponding to the status of the patch. For those patches that are waiting for installation, this icon will be green, for hidden packages - blue, etc.
• Title: the full name of the patch in accordance with the information from Windows Update.
• Severity: the degree of criticality of the patch for information from Windows Update.
• Reboot: in the event that a device reboot is required after installing the patch, a tick will be displayed in this column.
• User input: a measure of whether user intervention is required to install a patch (dialog boxes to allow installation, EULA, etc.).
When this method is applied
You can use this method if the administrator needs very precise control over the use of patches on managed devices.
Method 2: Windows Update Policy
general description
Windows Update policy allows centralized configuration of Windows Update features on Windows devices on a corporate network. This policy is available at the Account and Site levels.
Access to the Windows Update Policy Method
To use this method, you need to create a Windows Update policy at the Account or Site level. To do this, at the appropriate level on the Policies tab, click the button to add a policy (in the figure below, an example of adding a new policy at the Site level is shown by clicking the New Site Policy button ... ).

After that, in the dropdown box, you must specify the name of the policy and select the type of Windows Update policy.

As a result, a window will open in which you can centrally configure the behavior of Windows Update on all devices to which this policy will be applied. Windows Update policies are configured in the same way as Windows Update resources on each individual Windows device.
Windows Update classifies patches into three categories:
• Important
• Recommended
• Optional (Optional)
Only important and recommended patches can be installed automatically. The remaining patches will be installed manually from the user's device or via Panda Systems Management using other patch management methods.
All settings of this policy are a transposition of the Windows Update functions on Windows devices. Thus, all of these actions relate to devices, and not to the Agent or Management Console.
Although the policy settings are the same for all devices, the behavior of Windows Update on each device may vary slightly depending on the version of the Windows operating system.
So, the policy settings window:
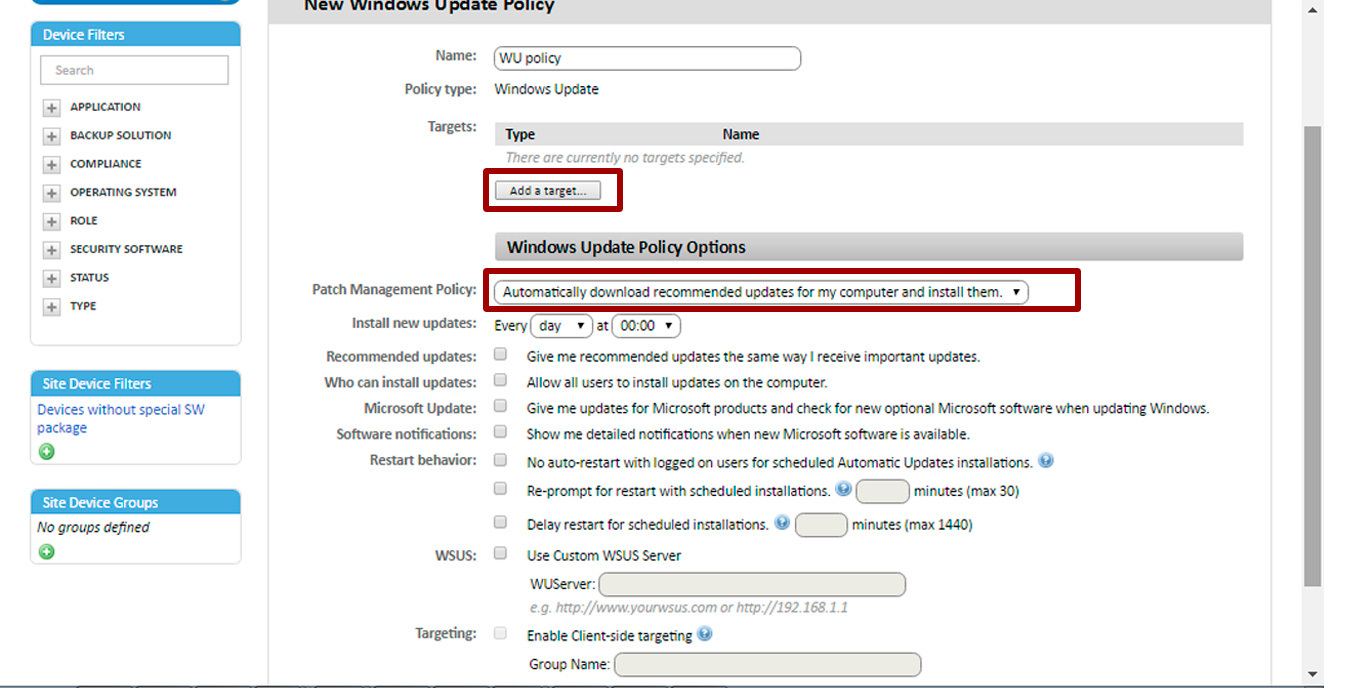
Below is a description of some policy options:
• Add target: allows you to add filters or groups that limit the scope of the policy
• Patch Policy: allows you to specify the main behavior of Windows Update on each device in relation to patches that are classified by Microsoft as “Important”: automatically download and install, manually download and select by the user, notify without downloading, disable Windows Update. At the same time, in order to prevent the intersection of policies in the event that you are already using another patch update method using Panda Systems Management or third-party products, it is recommended to create a Windows Update policy with the value of this parameter “Disable Windows Update”
• Install new updates: specify the frequency of patches
• Give me recommended updates: I apply important updates: applies the policy parameter specified in the Patch Policy option for both important patches and recommended patches.
• Allow all users to install updates on the computer: allows users to manually install patches
• Microsoft software when updating Windows: checks optional patches, basic patches for other Microsoft products.
• Show me detailed notifications when new software is available: shows you detailed notifications when new Microsoft software is available.
• If this option is selected, then after installing the patches, the user is notified that the PC needs to be restarted. If the option is not enabled, then in this case, after installing the patches, the user will be notified that his PC will be restarted after 5 minutes
• Re-prompt for restart with scheduled installations: prompts you to specify how many minutes Windows Update will prompt the user to restart the PC in the event that patches have been installed that require the device to be rebooted
• Delay restart for scheduled installations: determines the number of minutes during which the system will wait for a reboot after installing patches. If not specified, the default time is 15 minutes.
• WSUS: Allows the use of an alternative local or remote Windows Server Update Services server in order to minimize the download of individual patches to each device on the network.
• Enable Client-Side Targeting: if you are using a WSUS server with the Client-Side Targeting option enabled, the groups and devices they contain will be manually defined on the WSUS server. This parameter allows you to specify the groups to which the devices belong to where this policy will be applied (use commas to separate). Moreover, if some or all of the devices on which the Windows Update policy is to be applied do not match those configured in WSUS groups, then the policy will not be applied to such devices.
When this method is applied
• If the administrator needs to ensure that all important patches are automatically installed on all devices on the network, and users cannot prevent this from happening.
• If the administrator does not need to control every patch that is installed and he can delegate the decision to install a patch to Microsoft according to their classification of patches as important or recommended
• Unless you need to automatically install patches classified as optional.
Method 3. Patch Management Policy
general description
Patch Management policies allow the automatic installation of patches in the same way as it is implemented for Windows Update policies. The main difference is in how the patches are grouped, which must be installed. While the manual method allows you to select the application of each individual patch, and the Windows Update policy allows you to apply patches by level (important, recommended, or optional), the Patch Management policy allows you to choose the patches you need to apply, grouping them more flexible. way: by name, description, size, type, etc.
This method is supported at the Account and Site levels.
Access to the Patch Management Policy Method
To use this method, you need to create a new policy with the type of Patch Management at the Account or Site level.
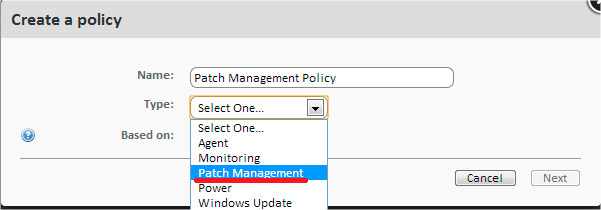
As a result, a window will appear in which you can centrally configure the behavior of the patch management policy for all devices to which this policy will be applied.
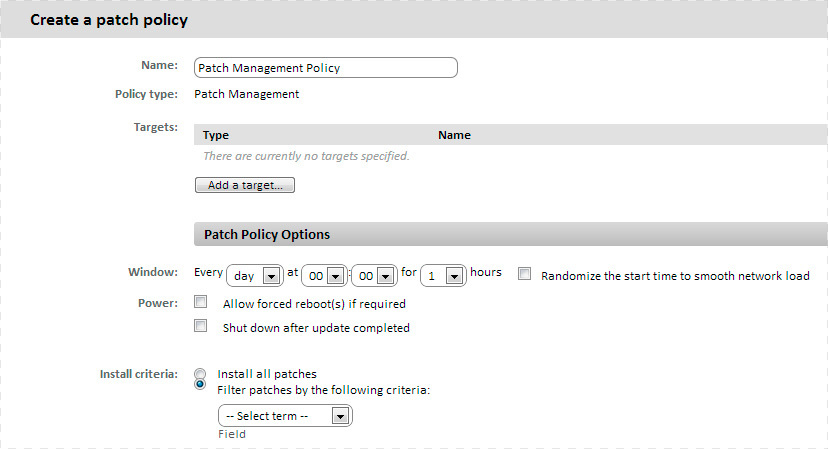
• Add target: allows you to add filters or groups that limit the scope of the policy
• Shedule Options: allows you to specify the time of application of the patches. Click Click to change in the Shedule block to display a form where you can select the patch interval and frequency

In the form that appears on the left, select the frequency, depending on which the right side of the form will change, allowing you to specify the exact date and time when the patches should be installed.
• Install criteria: allows you to select patches to install on the device. There are three options:
- Install all patches: installs all released patches
- Filter patches by: allows you to set up a filter with one or several criteria: category, condition (depending on the selected category) and search object (also depends on the selected category).

You can create complex selection criteria by setting up several categories with AND / OR application logic (corresponding to the position of the AND / OR switch). You can also configure different values for each category using the logical operators AND / OR.
When this method is applied
• If the administrator needs more flexibility than the Windows Update policy.
• If the administrator needs to automatically and centrally install all patches without exception.
Audits
On the Manage tab at the site or account level, you can at a glance assess the status of the entire network in terms of updating applications.
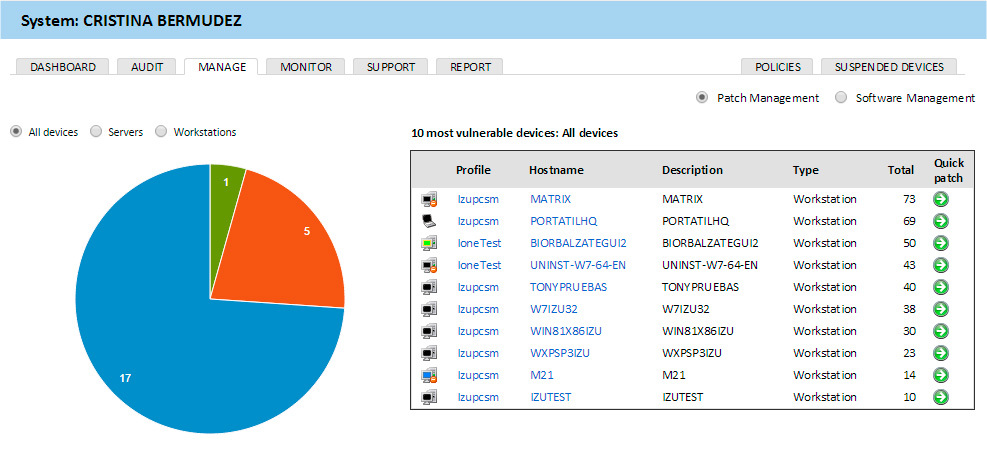
Selection criteria allow you to show information on all devices, only servers or only workstations on the site or within the entire account.
Depending on the selection criteria, relevant statistics will be shown in the pie chart below. In this case, the blue color indicates the number of devices with non-installed non-critical updates, the orange color shows the number of devices with non-installed critical updates, and the green color shows the number of devices that are fully updated.
A list of the 10 most vulnerable devices is displayed to the right of the pie chart, depending on the selection criteria. If you click on the segment you are interested in on a pie chart, this list will be updated, and it will show information only on this segment.
If you click on the name in the Hostname column in this list, you will go to the detailed information on this device in order to see which specific patches on this device were not installed, and allow the required patches.
If you click on the green arrow icon in the Quick patch column in this list, then this device will immediately apply patches according to the selected criteria (critical or non-critical) depending on whether you clicked on the blue or orange segment charts.
Conclusion
Modern integrated RMM-solutions allow you to centrally solve one of the important tasks of any IT department: ensuring timely update of software installed in the corporate network to avoid problems in its work and eliminate known security gaps and vulnerabilities. It is not difficult to understand that the effective solution of an assigned task allows to increase the efficiency of the company's employees, and, therefore, its competitiveness.
By the way, in the second half of February a new version of Panda Systems Management will be available, in which certain changes will be made to patch management, which will make this process even more manageable, simple and effective.
Do more by doing less!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/321302/
All Articles