Hyper-Converged Platforms: From Exotic to Mainstream
Hello! It so happened that my article is the first in the blog of the group of companies LANIT on Habré. I am very pleased with this opportunity, I realize the responsibility and I hope that the materials of our blog will be interesting for you.
So, to the point. Hyper-converged systems are now becoming one of the main decisions in the field of building an enterprise-class IT infrastructure. In this article, I will briefly talk about what these systems are and in what cases they can be useful when deploying IT infrastructure. I will also share the results of a comparison of the technical capabilities of a number of hyperconvergent platforms that we studied when planning the development of the IT infrastructure of the OnCloud.ru cloud of Onlanta .

IT infrastructure is the basis of the activities of various organizations and business structures. But its creation and maintenance is an expensive thing that seriously eats up the resources of the IT service.
')
Cost-effective solution for the deployment of IT infrastructure are modular hyperconvergent systems, which are characterized by:
By definition, Forrester Research, hyperconvergence is an approach to creating an IT infrastructure that combines servers, storage systems, network functions, and software responsible for creating a pool of IT resources in one modular solution, which is quick and easy to reconfigure without requiring special training. .
Such systems can simplify and accelerate the commissioning of IT resources, reduce management costs and the total cost of ownership of the IT infrastructure, including through deep automation and self-service.
According to the Gartner forecast, the HCI (Hyper-Converged Infrastructure) market will increase annually by 68% and in 2019 will reach 5 billion dollars. Similar expectations and IDC analysts.

Source: IDC Hyperconverged Systems 2015-2019 Forecast, February, 2016
According to IDC, in 2015, hyperconvergent systems accounted for 10.9% of the market for convergent systems, and in 2016 their sales in the world will be almost $ 2 billion and more than double by 2019.
Hyper-converged systems are sometimes considered as a solution for small and medium-sized enterprises, however, most HCI vendors consider them to be the target segment of the data center and really hyper-convergent systems are suitable for this.
Finally, they were originally created with the expectation of supporting virtual environments, which opens the way to the construction of software-configured data centers (SDDC) with advanced management and automation tools.

Source: IDC's Converged Systems Survey, December 2015
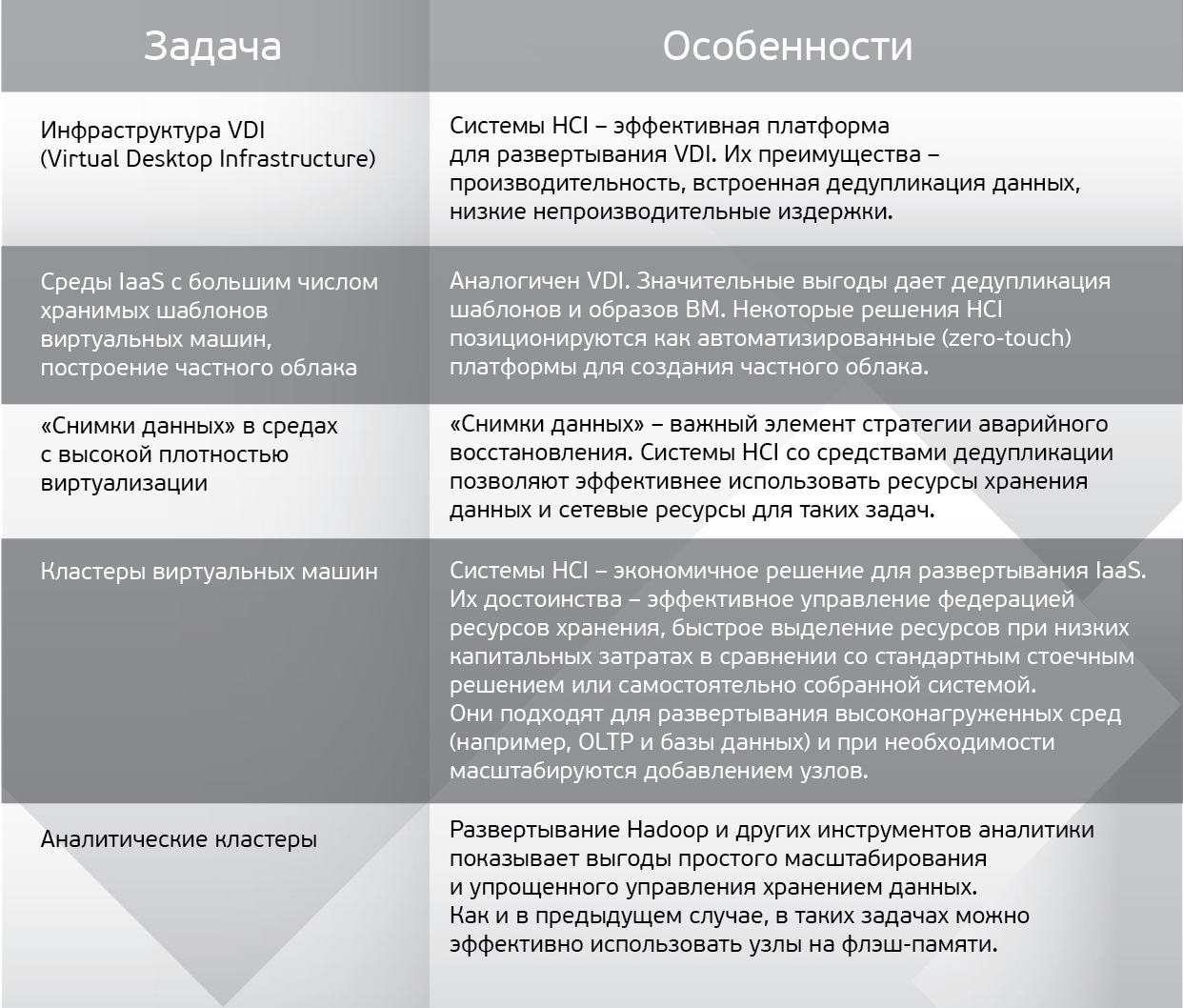
According to Forrester analysts, HCI solutions have extremely wide applications. They can be used almost everywhere where fast resource allocation is required (table 1).
Table 1. Typical scenarios for using HCI
Hyper-converged systems usually consist of several modules, combined into a horizontally-scalable cluster, containing, as a rule, from 4 to 64 nodes. Each of them includes a computational core, storage resources, network components, and usually a hypervisor.
A distinctive feature of hyperconvergent systems is the presence of preinstalled software for solving problems of resource allocation and scaling control.
But it must be borne in mind that scaling at the level of individual elements entering into the HCI nodes (processors, memory, disks) can be associated with certain costs. For example, you need to increase disk capacity, and processors and memory are not needed. However, you still have to add a node that contains all the elements. There will be no difficulties with adding, but processors and memory will not be involved "right now", therefore this local solution is not economically most efficient. However, with the further development of the infrastructure, memory and processors will “go to work” and will be used in virtual machines.

Figure 1. Hyper-Converged Infrastructure:
To some extent, hyperconvergent systems - return at a new level to the DAS (Direct-Attached Storage) paradigm with direct connection of the storage subsystem to the x86 server. However, this does not lead to the formation of isolated storage media. Each node has access to storage resources on other nodes due to the use of software-configured memory (Software-Defined Storage, SDS), which allows pooling the required storage resources into a common pool and providing them to the cluster. At the same time automation simplifies management.
Software for HCI can be offered separately or in a pre-installed form. These are two fundamentally different architectural approaches. Proponents of the first offer users to build the necessary infrastructure themselves, without limiting themselves in the choice of server hardware, although boxed solutions are also possible. In this case, you can choose hardware, as opposed to ready-made devices with pre-installed software, but most often customers buy it already pre-installed on servers (appliance), which is what OEMs of developers or integrators do. The main part of hyperconverged solutions offered on the market is made up of completely ready HCI systems.
Another approach is to use the reference architecture for constructing HCI for a particular task. This option is offered, in particular, by the developers of the EVO platform : RAIL .
The system from Green IT Glob also uses external storage connected to InfiniBand MicroBlade servers. The system allows the use of various processors, including low-cost versions of Intel Xeon. The use of a larger number of smaller blades has its advantages: in the event of the failure of such a node, it will be necessary to restart fewer virtual machines on neighboring nodes.
Another interesting solution is the Huawei FusionCube , built on the base of the E9000 chassis and offering the choice of blades — compute and half-length storage nodes with SSD, SAS HDD or SATA HDD. Huawei's HCI solution based on conventional rack-mount servers is used, in particular, in the data center built by Huawei for Akado.
Ericsson's Hyperscale system is designed for telecom companies that are very demanding in terms of equipment reliability. It is deployed, for example, in AT & T, where it provides fault tolerance in the "five nines". However, this solution is somewhat heavy on the software used, in particular, there is a complete set of OpenStack, as well as additions from Ericsson. A third-party solution is used to implement SDS, and another Ericsson product is used as a managing orchestrator. Such a motley software stack can cause some problems in operation.
There is another architectural difference. In some cases, instead of SDS used traditional storage system. This is done, for example, in NetApp FlexPod . Note that this system refers to convergent, not hyperconvergent solutions, but since the line between such solutions is very thin, it also participated in the comparison (Table 2). When expanding the storage system capacity in this solution, it will not be necessary to acquire extra computational resources, but its total cost is higher than that of systems with SDS. Buying a node with a storage system and processors can cost less than a new storage shelf of a similar capacity. Plus, in this case, we lose the possibility of quick and easy implementation of the system and its expansion due to the need to configure the individual components of the system.
The remaining solutions in Table 2 are distinguished by a less flexible architecture. Their closeness affects the amount of objective information freely available. The attachment of some solutions to specific hardware also affects its cost. Unfortunately, in the open access there is no information about the experience of building large systems on these solutions. Usually installations are limited to 4 nodes. If you have information on building larger solutions, we will be happy to hear from you.
In today's market, many players offer hyperconvergent solutions. Here is a comparative analysis of the main.
Table 2. Comparison of hyper-convergent decisions of major players

* 1 - Also known as Dell XC
Of course, the list of hyper-convergent solutions is not limited to those listed in Table 2. Among other well-known developments:

Forrester analysts identify 12 leading vendors of HCI, but half of them are not represented in Russia.
Most of the HCI proposals are aimed at solving a wide range of tasks:
In fact, they can be used for any virtualized applications. For example, VxRail systems are designed and optimized for VMware environments and use VMware vSphere and VMware VSAN software. Among their targets are:
However, special configurations are offered for each of them. So, for graphics, these are VxRail platforms with PowerEdge R730 servers and graphic accelerators (GPU) from NVIDIA and AMD, for branch offices - a three-node entry-level configuration with simplified management when deployed at several remote sites.
Meanwhile, applications such as ERP and CRM may require optimization to work in a distributed environment. For a narrower class of loads, vendors also offer reference architectures or specialized solutions.
Today, hyperconvergent systems are one of the rapidly developing solutions in the field of building corporate IT infrastructures. The market of hyperconvergent systems continues to show an increase in the number of players, sales are growing at double-digit rates, the target audience and areas of application are expanding. Many companies are interested in taking advantage of the cloud model in their corporate infrastructure, and HCI systems offer such an opportunity, while ensuring high application performance.
I hope that the data provided in the article will be useful to you. I would appreciate comments, and, if possible, please share your experience with hyperconvergent solutions. In the next article I will talk about our experiments with Software Define Storage.
So, to the point. Hyper-converged systems are now becoming one of the main decisions in the field of building an enterprise-class IT infrastructure. In this article, I will briefly talk about what these systems are and in what cases they can be useful when deploying IT infrastructure. I will also share the results of a comparison of the technical capabilities of a number of hyperconvergent platforms that we studied when planning the development of the IT infrastructure of the OnCloud.ru cloud of Onlanta .

IT infrastructure is the basis of the activities of various organizations and business structures. But its creation and maintenance is an expensive thing that seriously eats up the resources of the IT service.
')
Cost-effective solution for the deployment of IT infrastructure are modular hyperconvergent systems, which are characterized by:
- ease of scaling,
- unified management software interface.
By definition, Forrester Research, hyperconvergence is an approach to creating an IT infrastructure that combines servers, storage systems, network functions, and software responsible for creating a pool of IT resources in one modular solution, which is quick and easy to reconfigure without requiring special training. .
Such systems can simplify and accelerate the commissioning of IT resources, reduce management costs and the total cost of ownership of the IT infrastructure, including through deep automation and self-service.
Applications and Use Cases
According to the Gartner forecast, the HCI (Hyper-Converged Infrastructure) market will increase annually by 68% and in 2019 will reach 5 billion dollars. Similar expectations and IDC analysts.

Source: IDC Hyperconverged Systems 2015-2019 Forecast, February, 2016
According to IDC, in 2015, hyperconvergent systems accounted for 10.9% of the market for convergent systems, and in 2016 their sales in the world will be almost $ 2 billion and more than double by 2019.
Hyper-converged systems are sometimes considered as a solution for small and medium-sized enterprises, however, most HCI vendors consider them to be the target segment of the data center and really hyper-convergent systems are suitable for this.
- They solve the problems of productivity growth, complexity, scaling of the IT infrastructure.
- Allow to reduce the cost of IT infrastructure as business expands.
- Reduced number of managed systems.
- Scaling is simplified.
- Increased productivity through the use of flash drives.
- The software and hardware collaboration platform is optimized.
Finally, they were originally created with the expectation of supporting virtual environments, which opens the way to the construction of software-configured data centers (SDDC) with advanced management and automation tools.

Source: IDC's Converged Systems Survey, December 2015
According to Forrester analysts, HCI solutions have extremely wide applications. They can be used almost everywhere where fast resource allocation is required (table 1).
Table 1. Typical scenarios for using HCI

Basic architectural solutions
Hyper-converged systems usually consist of several modules, combined into a horizontally-scalable cluster, containing, as a rule, from 4 to 64 nodes. Each of them includes a computational core, storage resources, network components, and usually a hypervisor.
A distinctive feature of hyperconvergent systems is the presence of preinstalled software for solving problems of resource allocation and scaling control.
But it must be borne in mind that scaling at the level of individual elements entering into the HCI nodes (processors, memory, disks) can be associated with certain costs. For example, you need to increase disk capacity, and processors and memory are not needed. However, you still have to add a node that contains all the elements. There will be no difficulties with adding, but processors and memory will not be involved "right now", therefore this local solution is not economically most efficient. However, with the further development of the infrastructure, memory and processors will “go to work” and will be used in virtual machines.

Figure 1. Hyper-Converged Infrastructure:
- Computing, network and storage resources are virtualized using software.
- Standard x86 server nodes are used.
- Horizontal scaling of the system is done by adding nodes.
- Technical improvements to the standard architecture are used with the benefits of the “x86 economy”.
- Direct connection of flash arrays allows for maximum performance.
- Unification simplifies resource allocation and management.
To some extent, hyperconvergent systems - return at a new level to the DAS (Direct-Attached Storage) paradigm with direct connection of the storage subsystem to the x86 server. However, this does not lead to the formation of isolated storage media. Each node has access to storage resources on other nodes due to the use of software-configured memory (Software-Defined Storage, SDS), which allows pooling the required storage resources into a common pool and providing them to the cluster. At the same time automation simplifies management.
Software for HCI can be offered separately or in a pre-installed form. These are two fundamentally different architectural approaches. Proponents of the first offer users to build the necessary infrastructure themselves, without limiting themselves in the choice of server hardware, although boxed solutions are also possible. In this case, you can choose hardware, as opposed to ready-made devices with pre-installed software, but most often customers buy it already pre-installed on servers (appliance), which is what OEMs of developers or integrators do. The main part of hyperconverged solutions offered on the market is made up of completely ready HCI systems.
Another approach is to use the reference architecture for constructing HCI for a particular task. This option is offered, in particular, by the developers of the EVO platform : RAIL .
The system from Green IT Glob also uses external storage connected to InfiniBand MicroBlade servers. The system allows the use of various processors, including low-cost versions of Intel Xeon. The use of a larger number of smaller blades has its advantages: in the event of the failure of such a node, it will be necessary to restart fewer virtual machines on neighboring nodes.
Another interesting solution is the Huawei FusionCube , built on the base of the E9000 chassis and offering the choice of blades — compute and half-length storage nodes with SSD, SAS HDD or SATA HDD. Huawei's HCI solution based on conventional rack-mount servers is used, in particular, in the data center built by Huawei for Akado.
Ericsson's Hyperscale system is designed for telecom companies that are very demanding in terms of equipment reliability. It is deployed, for example, in AT & T, where it provides fault tolerance in the "five nines". However, this solution is somewhat heavy on the software used, in particular, there is a complete set of OpenStack, as well as additions from Ericsson. A third-party solution is used to implement SDS, and another Ericsson product is used as a managing orchestrator. Such a motley software stack can cause some problems in operation.
There is another architectural difference. In some cases, instead of SDS used traditional storage system. This is done, for example, in NetApp FlexPod . Note that this system refers to convergent, not hyperconvergent solutions, but since the line between such solutions is very thin, it also participated in the comparison (Table 2). When expanding the storage system capacity in this solution, it will not be necessary to acquire extra computational resources, but its total cost is higher than that of systems with SDS. Buying a node with a storage system and processors can cost less than a new storage shelf of a similar capacity. Plus, in this case, we lose the possibility of quick and easy implementation of the system and its expansion due to the need to configure the individual components of the system.
The remaining solutions in Table 2 are distinguished by a less flexible architecture. Their closeness affects the amount of objective information freely available. The attachment of some solutions to specific hardware also affects its cost. Unfortunately, in the open access there is no information about the experience of building large systems on these solutions. Usually installations are limited to 4 nodes. If you have information on building larger solutions, we will be happy to hear from you.
Product Examples
In today's market, many players offer hyperconvergent solutions. Here is a comparative analysis of the main.
Table 2. Comparison of hyper-convergent decisions of major players

* 1 - Also known as Dell XC
Of course, the list of hyper-convergent solutions is not limited to those listed in Table 2. Among other well-known developments:
- enterprise market and data center products: Cisco HyperFlex, Gridstore HyperConverged Appliance, HPE HC250 / HC380 and HP ProLiant DL380, Lenovo Converged HX Series, Pivot3 HyperConverged Infrastructure, Oracle SuperCluster M7, Scale Computing HC Series,
- developments that can be used in small and medium business: Atlantis HyperScale CX-4, Lenovo HX2000 + Nutanix Xpress, Nutanix Acropolis, ZeroStack Cloud Platform,
- A number of solutions are the result of the cooperation of vendors with Nutanix and SimpliVity startups, which offer the HCI software option.

Forrester analysts identify 12 leading vendors of HCI, but half of them are not represented in Russia.
Target tasks
Most of the HCI proposals are aimed at solving a wide range of tasks:
- Deploy private clouds and VDI (this is the main application)
- analytical applications, OLTP systems,
- support for business-critical applications
- server consolidation and data center upgrades.
In fact, they can be used for any virtualized applications. For example, VxRail systems are designed and optimized for VMware environments and use VMware vSphere and VMware VSAN software. Among their targets are:
- workloads that actively work with storage resources: such as big data analytics and Microsoft Exchange;
- loads with high demands on graphics, CAD, scientific applications and development packages;
- environments of remote offices and branches.
However, special configurations are offered for each of them. So, for graphics, these are VxRail platforms with PowerEdge R730 servers and graphic accelerators (GPU) from NVIDIA and AMD, for branch offices - a three-node entry-level configuration with simplified management when deployed at several remote sites.
Meanwhile, applications such as ERP and CRM may require optimization to work in a distributed environment. For a narrower class of loads, vendors also offer reference architectures or specialized solutions.
Today, hyperconvergent systems are one of the rapidly developing solutions in the field of building corporate IT infrastructures. The market of hyperconvergent systems continues to show an increase in the number of players, sales are growing at double-digit rates, the target audience and areas of application are expanding. Many companies are interested in taking advantage of the cloud model in their corporate infrastructure, and HCI systems offer such an opportunity, while ensuring high application performance.
I hope that the data provided in the article will be useful to you. I would appreciate comments, and, if possible, please share your experience with hyperconvergent solutions. In the next article I will talk about our experiments with Software Define Storage.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/320954/
All Articles