VPS hosting and cloud hosting: what to choose and what is the difference?
The emergence of the so-called "cloud platforms" has affected a number of industries, and web hosting is no exception. But what is cloud hosting, how is it different from VPS (Virtual Private Server)? VPS hosting and cloud hosting are two similar types of hosting, but there are still differences between them that determine the choice of a particular type of hosting in specific circumstances. We have already talked about different types of hosting - from virtual to physical. Now let's take a closer look at these two.

VPS is a dedicated virtual server. In fact, it is a virtual environment with its own operating system - with dedicated RAM, processor time and disk capacity. The user (owner of the VPS) can install the necessary software on his virtual server and configure it. A virtual server can serve as a platform for hosting Web sites. In this case, the site will not depend on the sites of neighbors in the physical server.

The VPS client receives a virtual environment with allocated disk space or SSD and bandwidth, but the computing resources and host memory are evenly distributed among all the VPS.
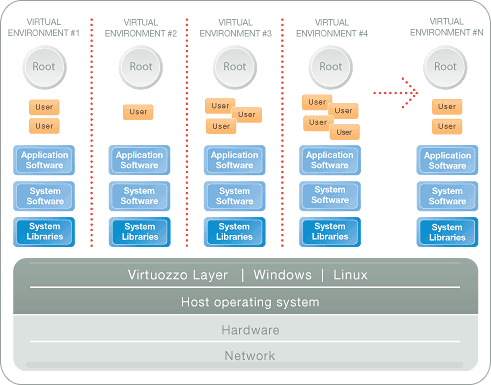
VPS hosting has long been recognized as one of the ways that businesses can reduce costs and improve work efficiency. By isolating applications within a single virtual server, VPS provides a high level of privacy, security and control. However, while the VPS reduces hardware costs and allows multiple operating systems to run simultaneously or sets of programs on separate virtual servers, this solution does not scale well.
')
Cloud hosting is virtual machines (VMs) in the cloud or IaaS (infrastructure as a service). With this hosting, physical servers are combined into a cluster, and storage systems into a storage area network (SAN).
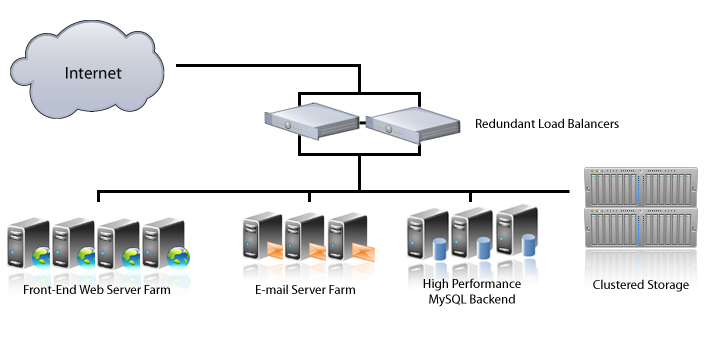
Cloud hosting can be divided into two categories: private (Private) and public (Public). The first is more expensive, but it is better protected and provides more opportunities for self-tuning, control over users and placed data. In the case of a public cloud, a cluster of servers is used by several clients, in the case of a private cloud - one.
Let's compare the key parameters of two types of hosting (scores are given according to besthostingsearch.org):
Let us consider in more detail each of the types of hosting and their properties.

In the case of cloud hosting, a hypervisor typically creates multiple virtual servers on a cluster of physical servers. As with traditional VPS, the user can customize and configure his guest OS, but most of the resources are allocated on request. If a VPS can offer only one operating system, cloud hosting provides freedom of choice.
PS hosting allows you to manage the configuration of a virtual server, the other VPS changes will not affect. VPS hosting service providers usually offer clients dashboard functions like cPanel. On the other hand, the cloud server gives less administration rights.

The cloud platform, as a rule, itself implements the functions of setting up operating systems and applications, and some technologies not provided by the service may be unavailable. These restrictions apply to site security.
Since cloud-based hosting uses a distributed server infrastructure, this makes resource allocation more flexible and increases the fault tolerance of the service, but users ’freedom to choose hosting options is more limited than in the case of VPS. In addition, the configuration of sections may require some knowledge - this is done by experienced application developers. At the same time, with sufficient qualifications, in cloud hosting you can do what is not available in the VPS.

If at VPS-hosting there is already not enough allocated resources, its owner, as a rule, has to change the tariff plan. Cloud hosting is more flexible: users can scale resources in any direction without restarting the server. Yes, and the distribution of resources in the cloud hosting is very fast. VPS customers have to wait. In addition, in the cloud version, resources are used more optimally: customers quickly release unused resources so as not to pay extra money. After all, the payment model is also flexible.
In general, VPS hosting is less efficient, since IT resources are strictly distributed among customers according to their tariff plans, regardless of whether they use these resources or not.
In the cloud, it is possible, if necessary, to connect additional resources: add RAM, disk space or network bandwidth. These resources can be added with a few clicks of the mouse and disabled when they are no longer needed - without financial loss. Thus, cloud hosting is a solution that provides resources on demand. These are virtual machines that are dynamically scalable and customizable according to customer needs.
For example, that with a sharp increase in traffic, you can instantly allocate additional resources to the site. In a cloud-based environment, a Web site uses a pool of resources and can serve all incoming traffic, even if it grows dramatically. This option is useful in the case of Web sites and applications with unpredictable or difficult to predict traffic, load and use of resources.

Information security is one of the most important means of VPS. This hosting has several advantages over cloud hosting. In particular, all your data is stored on one server, and not distributed across several. Root access provides extensive security configuration options. But if the site is subjected, for example, to a DDoS attack, it will affect the remaining VPS on the same host.
With cloud hosting, securing security can be more difficult as the data and resources are distributed across different servers and sites. Most cloud hosting providers provide root access to clients, but you need to understand that data can be physically stored in several places. But in a cloud environment, one client is completely isolated from the files of another - from this point of view, the environment is more secure.

Good VPS hosting is distinguished by high rates of uptime and page load speeds. But in a situation with VPS, if a host falls, or a part of the host “falls off”, then the virtual server will fall: you have to wait until the provider fixes the problem. And if one VPS fails, the rest will work, but you will have to fix the problem and restore the "fallen" - there is no fault tolerance. If the traffic of one VPS rises sharply, this will affect the remaining VPS on the same host.

Like VPS hosting, cloud hosting is characterized by high reliability and speed, but when comparing it turns out that due to the server cluster, the reliability of cloud hosting is much higher. With cloud hosting, any failure causes traffic to be rerouted to another available physical resource. Downtime is minimal. Because each virtual server is independent of others, Web sites in such an environment do not adversely affect others.
Thus, Web sites in the cloud have high availability. They are replicated between cluster servers. With a sharp increase in traffic from one site, requests are routed to a less loaded server in the cloud. If one physical server in a cluster fails, all virtual machines will continue to work. As a result, cloud-based hosting is more stable, since the failure of one component does not affect the operation of the service as a whole.

In most cases, VPS hosting is cheaper than cloud-based hosting with equivalent virtual resources, sometimes more than double. But cloud hosting usually implies not fixed, but flexible payment, for example, a monthly fee for the number of users of applications, traffic and resources. No need to pay for resources that are not really used.
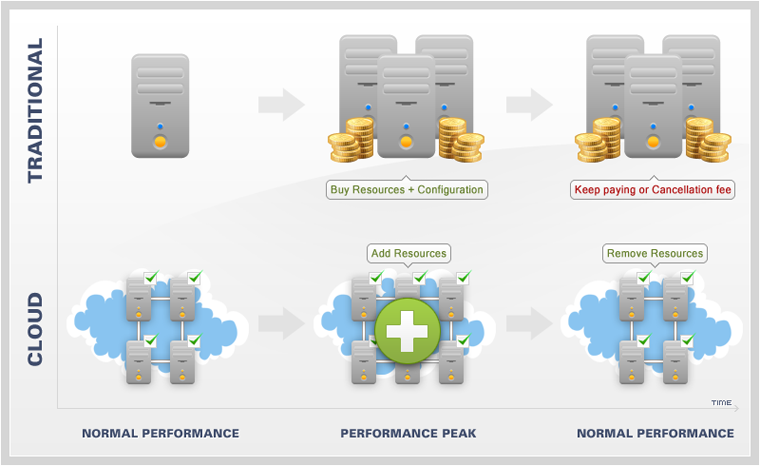
But when VPS-hosting knows in advance how much you have to pay at the end of the month. This option is preferable for websites with predictable traffic and for customers who prefer to receive bills with fixed amounts.

When choosing a hosting you need to take into account a number of parameters . Cloud hosting is a secure environment and the freedom to scale resources.
With a small budget, VPS hosting is recommended: it offers more features and a simple control panel, more IP addresses and more server resources — processor, memory, I / O, storage resources, and an access channel. In fact, the virtual server is similar to the dedicated one - you have full control over it, you can reboot, but it costs much less.
Summarizing, we can say that VPS hosting is low cost, control and security, and cloud hosting means customization capabilities and performance. VPS hosting is preferable for personal use and SMB customers, and cloud hosting is preferred for larger customers.
VPS hosting is a good option for business-critical applications and data, when centralized storage is preferred. However, this does not provide high availability (high-availability), with a failure of the host all VPS will fall. There may be problems with information security. If one of the clients neglects the protection, it may affect the other VPS. System resources are divided between clients: CPU, RAM network bandwidth. If one VPS needs more resources, it can affect other virtual servers. Only one OS can be used on each host.
VPS hosting is not scalable. Resources are limited by the limitations of the physical server. When you have exhausted your maximum of resources allocated for VPS, you will have to change the tariff or consider other options. This can take a lot of time - several hours or days of inactivity.
If you want to get high reliability and powerful functions, then cloud hosting is a good choice. This market has great potential, and the gradual reduction in prices makes cloud hosting more affordable.
VPS is suitable for those who are just interested in hosting a Web site. However, by offering powerful features, VPS hosting does not guarantee the uptime of your site in case of heavy traffic or technical failure.
Cloud hosting is practically unlimited resources, maximum bandwidth, load balancing, no binding to specific hardware components, scalability - you can add at any time (as load increases) or free up resources.
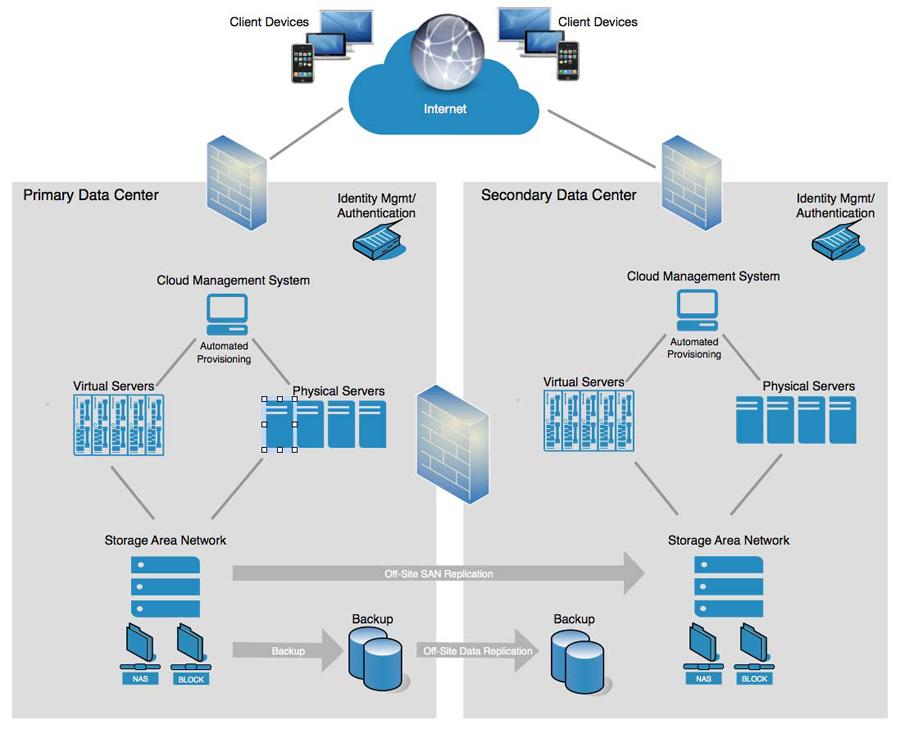
In addition, this hosting provides infrastructure customization options: clients can use special network infrastructure, load balancers, firewalls. Finally, this is high availability: in the event of a physical server failure, VMs migrate to another server without interrupting operation. And a high level of security: during a hacker or virus attack, your data will be protected thanks to the isolation of the virtual server.
In the case of a cloud-based virtual server, you can buy more resources, easily add RAM, processor power, almost unlimited storage resources in the SAN, or even create clones — copies of your server for backing up data.
Cloud hosting is a good choice for fast-growing businesses or companies with seasonal fluctuations in demand. This is an economical way to scale resources and consolidate servers.
Summing up the pros and cons:
VPS
Cloud hosting
VDS / VPS services are widely used and are in demand by site owners who do not need a dedicated physical server. VPS is often used by small companies for hosting sites, developing and testing software and hosting content management systems.
VPS services are provided by many companies that complement their cloud services, management and support services, security, software licensing. Cost is based on a set of support services and administration.
Hosting providers introduce new technologies. This service evolves and acquires the properties of a typical cloud service, along with low cost and convenient management, attracts with simple scalability, when computing resources, memory or storage capacity are added without problems. And gradually, cloud hosting leaves traditional hosting types behind, the line between VPS and IaaS is erased.

VPS is a dedicated virtual server. In fact, it is a virtual environment with its own operating system - with dedicated RAM, processor time and disk capacity. The user (owner of the VPS) can install the necessary software on his virtual server and configure it. A virtual server can serve as a platform for hosting Web sites. In this case, the site will not depend on the sites of neighbors in the physical server.

The VPS client receives a virtual environment with allocated disk space or SSD and bandwidth, but the computing resources and host memory are evenly distributed among all the VPS.

VPS hosting has long been recognized as one of the ways that businesses can reduce costs and improve work efficiency. By isolating applications within a single virtual server, VPS provides a high level of privacy, security and control. However, while the VPS reduces hardware costs and allows multiple operating systems to run simultaneously or sets of programs on separate virtual servers, this solution does not scale well.
')
Cloud hosting is virtual machines (VMs) in the cloud or IaaS (infrastructure as a service). With this hosting, physical servers are combined into a cluster, and storage systems into a storage area network (SAN).

Cloud hosting can be divided into two categories: private (Private) and public (Public). The first is more expensive, but it is better protected and provides more opportunities for self-tuning, control over users and placed data. In the case of a public cloud, a cluster of servers is used by several clients, in the case of a private cloud - one.
Let's compare the key parameters of two types of hosting (scores are given according to besthostingsearch.org):
| Parameter | VPS hosting | Cloud hosting |
| Technology | Single Server Virtualization | Virtualization on a server and SAN cluster |
| Functionality | five | 3 |
| Performance | four | 4.5 |
| Reliability | four | five |
| Extensibility | 3 | five |
| Scalability | Not | Yes |
| Payment model | Monthly or annual subscription | For the actual use of resources |
| Allocation of additional resources | Takes time | Simple and prompt |
| Selection of infrastructure | Not | Yes |
| CPU and RAM resources | Shared | Completely isolated |
| OS selection | Depends on host | Any |
| Web site scale | Small or medium | Large |
| Examples of providers | RUVDS | Amazon cloud |
Let us consider in more detail each of the types of hosting and their properties.

Flexibility
In the case of cloud hosting, a hypervisor typically creates multiple virtual servers on a cluster of physical servers. As with traditional VPS, the user can customize and configure his guest OS, but most of the resources are allocated on request. If a VPS can offer only one operating system, cloud hosting provides freedom of choice.
PS hosting allows you to manage the configuration of a virtual server, the other VPS changes will not affect. VPS hosting service providers usually offer clients dashboard functions like cPanel. On the other hand, the cloud server gives less administration rights.

The cloud platform, as a rule, itself implements the functions of setting up operating systems and applications, and some technologies not provided by the service may be unavailable. These restrictions apply to site security.
Since cloud-based hosting uses a distributed server infrastructure, this makes resource allocation more flexible and increases the fault tolerance of the service, but users ’freedom to choose hosting options is more limited than in the case of VPS. In addition, the configuration of sections may require some knowledge - this is done by experienced application developers. At the same time, with sufficient qualifications, in cloud hosting you can do what is not available in the VPS.

Scalability
If at VPS-hosting there is already not enough allocated resources, its owner, as a rule, has to change the tariff plan. Cloud hosting is more flexible: users can scale resources in any direction without restarting the server. Yes, and the distribution of resources in the cloud hosting is very fast. VPS customers have to wait. In addition, in the cloud version, resources are used more optimally: customers quickly release unused resources so as not to pay extra money. After all, the payment model is also flexible.
In general, VPS hosting is less efficient, since IT resources are strictly distributed among customers according to their tariff plans, regardless of whether they use these resources or not.
In the cloud, it is possible, if necessary, to connect additional resources: add RAM, disk space or network bandwidth. These resources can be added with a few clicks of the mouse and disabled when they are no longer needed - without financial loss. Thus, cloud hosting is a solution that provides resources on demand. These are virtual machines that are dynamically scalable and customizable according to customer needs.
For example, that with a sharp increase in traffic, you can instantly allocate additional resources to the site. In a cloud-based environment, a Web site uses a pool of resources and can serve all incoming traffic, even if it grows dramatically. This option is useful in the case of Web sites and applications with unpredictable or difficult to predict traffic, load and use of resources.

Security
Information security is one of the most important means of VPS. This hosting has several advantages over cloud hosting. In particular, all your data is stored on one server, and not distributed across several. Root access provides extensive security configuration options. But if the site is subjected, for example, to a DDoS attack, it will affect the remaining VPS on the same host.
With cloud hosting, securing security can be more difficult as the data and resources are distributed across different servers and sites. Most cloud hosting providers provide root access to clients, but you need to understand that data can be physically stored in several places. But in a cloud environment, one client is completely isolated from the files of another - from this point of view, the environment is more secure.

Reliability
Good VPS hosting is distinguished by high rates of uptime and page load speeds. But in a situation with VPS, if a host falls, or a part of the host “falls off”, then the virtual server will fall: you have to wait until the provider fixes the problem. And if one VPS fails, the rest will work, but you will have to fix the problem and restore the "fallen" - there is no fault tolerance. If the traffic of one VPS rises sharply, this will affect the remaining VPS on the same host.

Like VPS hosting, cloud hosting is characterized by high reliability and speed, but when comparing it turns out that due to the server cluster, the reliability of cloud hosting is much higher. With cloud hosting, any failure causes traffic to be rerouted to another available physical resource. Downtime is minimal. Because each virtual server is independent of others, Web sites in such an environment do not adversely affect others.
Thus, Web sites in the cloud have high availability. They are replicated between cluster servers. With a sharp increase in traffic from one site, requests are routed to a less loaded server in the cloud. If one physical server in a cluster fails, all virtual machines will continue to work. As a result, cloud-based hosting is more stable, since the failure of one component does not affect the operation of the service as a whole.

Cost of
In most cases, VPS hosting is cheaper than cloud-based hosting with equivalent virtual resources, sometimes more than double. But cloud hosting usually implies not fixed, but flexible payment, for example, a monthly fee for the number of users of applications, traffic and resources. No need to pay for resources that are not really used.

But when VPS-hosting knows in advance how much you have to pay at the end of the month. This option is preferable for websites with predictable traffic and for customers who prefer to receive bills with fixed amounts.

What to choose?
When choosing a hosting you need to take into account a number of parameters . Cloud hosting is a secure environment and the freedom to scale resources.
With a small budget, VPS hosting is recommended: it offers more features and a simple control panel, more IP addresses and more server resources — processor, memory, I / O, storage resources, and an access channel. In fact, the virtual server is similar to the dedicated one - you have full control over it, you can reboot, but it costs much less.
Summarizing, we can say that VPS hosting is low cost, control and security, and cloud hosting means customization capabilities and performance. VPS hosting is preferable for personal use and SMB customers, and cloud hosting is preferred for larger customers.
VPS hosting is a good option for business-critical applications and data, when centralized storage is preferred. However, this does not provide high availability (high-availability), with a failure of the host all VPS will fall. There may be problems with information security. If one of the clients neglects the protection, it may affect the other VPS. System resources are divided between clients: CPU, RAM network bandwidth. If one VPS needs more resources, it can affect other virtual servers. Only one OS can be used on each host.
VPS hosting is not scalable. Resources are limited by the limitations of the physical server. When you have exhausted your maximum of resources allocated for VPS, you will have to change the tariff or consider other options. This can take a lot of time - several hours or days of inactivity.
If you want to get high reliability and powerful functions, then cloud hosting is a good choice. This market has great potential, and the gradual reduction in prices makes cloud hosting more affordable.
VPS is suitable for those who are just interested in hosting a Web site. However, by offering powerful features, VPS hosting does not guarantee the uptime of your site in case of heavy traffic or technical failure.
Cloud hosting is practically unlimited resources, maximum bandwidth, load balancing, no binding to specific hardware components, scalability - you can add at any time (as load increases) or free up resources.

In addition, this hosting provides infrastructure customization options: clients can use special network infrastructure, load balancers, firewalls. Finally, this is high availability: in the event of a physical server failure, VMs migrate to another server without interrupting operation. And a high level of security: during a hacker or virus attack, your data will be protected thanks to the isolation of the virtual server.
In the case of a cloud-based virtual server, you can buy more resources, easily add RAM, processor power, almost unlimited storage resources in the SAN, or even create clones — copies of your server for backing up data.
Cloud hosting is a good choice for fast-growing businesses or companies with seasonal fluctuations in demand. This is an economical way to scale resources and consolidate servers.
Summing up the pros and cons:
VPS
| Behind | Vs |
|
|
Cloud hosting
| Behind | Vs |
|
|
VDS / VPS services are widely used and are in demand by site owners who do not need a dedicated physical server. VPS is often used by small companies for hosting sites, developing and testing software and hosting content management systems.
VPS services are provided by many companies that complement their cloud services, management and support services, security, software licensing. Cost is based on a set of support services and administration.
Hosting providers introduce new technologies. This service evolves and acquires the properties of a typical cloud service, along with low cost and convenient management, attracts with simple scalability, when computing resources, memory or storage capacity are added without problems. And gradually, cloud hosting leaves traditional hosting types behind, the line between VPS and IaaS is erased.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/320880/
All Articles