Second Generation Cloud Computing: CLAVIRE System
Under the cut in this material is a story about what AaaS is, why the Application as a Service model is considered more promising than the familiar SaaS, PaaS and IaaS, and how the developers and scientists of the ITMO University implement such a model as part of the CLAVIRE project.

Torley / Flickr / CC
Today, cloud computing technologies allow the user to get network access to an array of information resources (networks, remote servers, applications and services) that can be quickly reserved and provided by the provider with minimal effort.
')
For developed cloud environments, the integration of various business models is typical, which is associated with a focus on the specific needs of users in different areas of activity. For their classification and analysis, the Cloud Computing Maturity Model (CCMM) cloud computing formation model is used, which includes five levels of development presented in the diagram below.
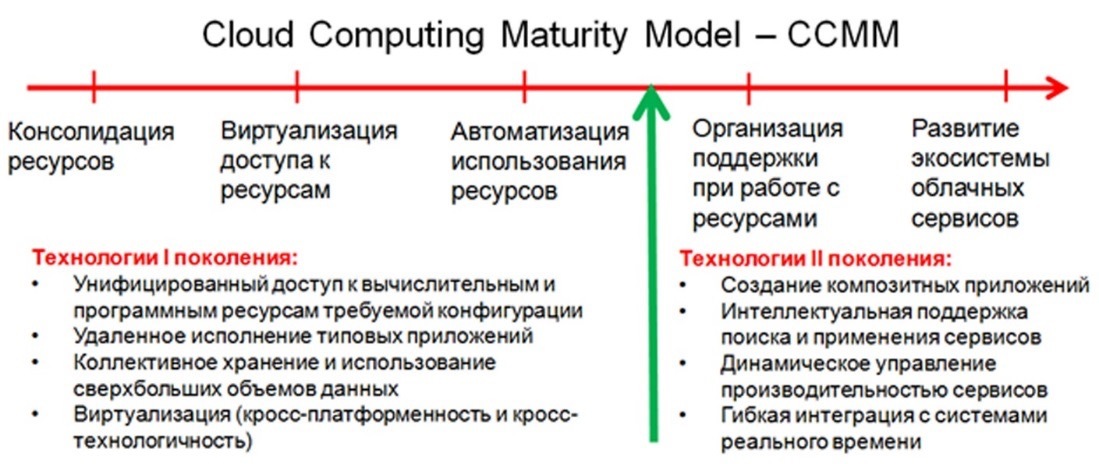
I and II generation cloud technologies in CCMM logic. Source : Second Generation Cloud Computing: Composite Applications, Interactive Systems and Semantic Technologies / A.V. Bukhanovsky, S.V. Kovalchuk
According to CCMM, cloud computing of the first and second generations is distinguished. The first generation technologies correspond to levels I-III and cover three well-known business models - these are IaaS, PaaS, SaaS. Second-generation technologies include levels IV and V and are not only focused on providing users with certain services over the Internet, but also on managing an entire ecosystem of computing, software and information resources.
This allows you to solve complex problems associated with the joint activities of several users. Cloud computing technologies of the second generation implement the promising cloud computing model AaaS (Application as a Service), the main service within which is the development and use of composite applications (this is a set of interacting cloud services aimed at solving one problem).
This concept is embodied in the CLAVIRE (CLoud Application VIRtual Environment) multifunctional instrumental and technological platform (MITP) developed by the Scientific and Research Institute of High-Tech Computer Technologies of the ITMO University as part of a project to implement the Government of the Russian Federation to support the development of cooperation of higher educational institutions and organizations.
The main tasks of the MITP are the effective management of the computing, information and software resources of distributed heterogeneous computing infrastructures, as well as the construction of corporate cloud infrastructures.
The CLAVIRE platform provides access to application packages running on remote computing resources. Currently, the CLAVIRE database includes 65 software systems in such areas as hydrodynamics, nanotechnology and quantum chemistry, analysis and modeling of social systems and transport infrastructure, hydrometeorology, shipbuilding and bioinformatics (this means that a number of complex multi-factor applications can be solved on the CLAVIRE platform tasks in these areas - for example, to predict the likelihood of the onset of flood floods in St. Petersburg).
In addition, CLAVIRE provides multi-purpose calculations in SciLab, WEKA packages (demonstration packages available for public use via CLAVIRE interfaces can be found here ).
Also, the CLAVIRE platform allows you to design composite applications — complexes that interact to solve a common task. The collection of composite applications for various subject areas is provided by experts of the Scientific Research Institute of High-Tech Computer Technologies of NRU ITMO and today contains several models.
Among them, note are the application for calculating the temperature distribution and mass velocities in the volume of the convection layer, the composite application for calculating the vessel’s rolling characteristics and the application for solving the problem of calculating the dynamics of HIV spread.
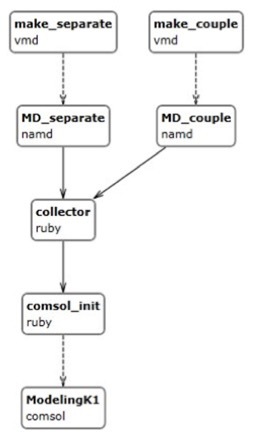
The solution of the problem of calculating the distribution of temperature and mass velocities in the volume of the convection layer is based on modeling the dynamics of nanoparticles in the medium using the molecular dynamics method and numerical simulation of the convection process using the finite element method (packages used: VMD, NAMD, Comsol, MDlogAnalyst, ComsolInitialise, Ruby interpreter)
The calculations themselves are performed at Amazon EC2, OpenStack, using grid computing. Grid computing is a kind of parallel computing that is performed using conventional computer systems connected to a network and combined into a “virtual supercomputer.”
The CLAVIRE system uses the GridNNN project (a grid system for the National Nanotechnology Network , implemented in Russian supercomputer centers). The grid of supercomputers is managed by basic grid services located in the main and backup control centers, whose task is to coordinate the work of the system resources and at the same time be a layer between users and the grid infrastructure.

Computing infrastructure. Source : CLAVIRE Cloud Platform for High Performance Computing / A.V. Bukhanovsky
PBS, Torque, Windows HPC and Condor solutions are used to control the launch of tasks on multiprocessor installations. Access to resources is carried out via SSH or via web services, and Windows and Unix-like systems are used as operating systems. As for virtualization tools, CLAVIRE uses VirtualBox applications and VMware and KVM solutions.
The organization of the process of creating and executing a composite application under the control of MITP is reduced to the sequential formalization of description sets in terms of task flows (WF). At the top level of the application description is meta-WF. In it, separate blocks contain only instructions for performing settlement tasks.
Thus, the MWF is a formal description of a user problem in terms of the subject area, without indicating the conditions for its implementation. In addition to describing the actions and data required for the calculations, the user has the ability to set criteria and set limits on which the selection of resources and specific services will be conducted.
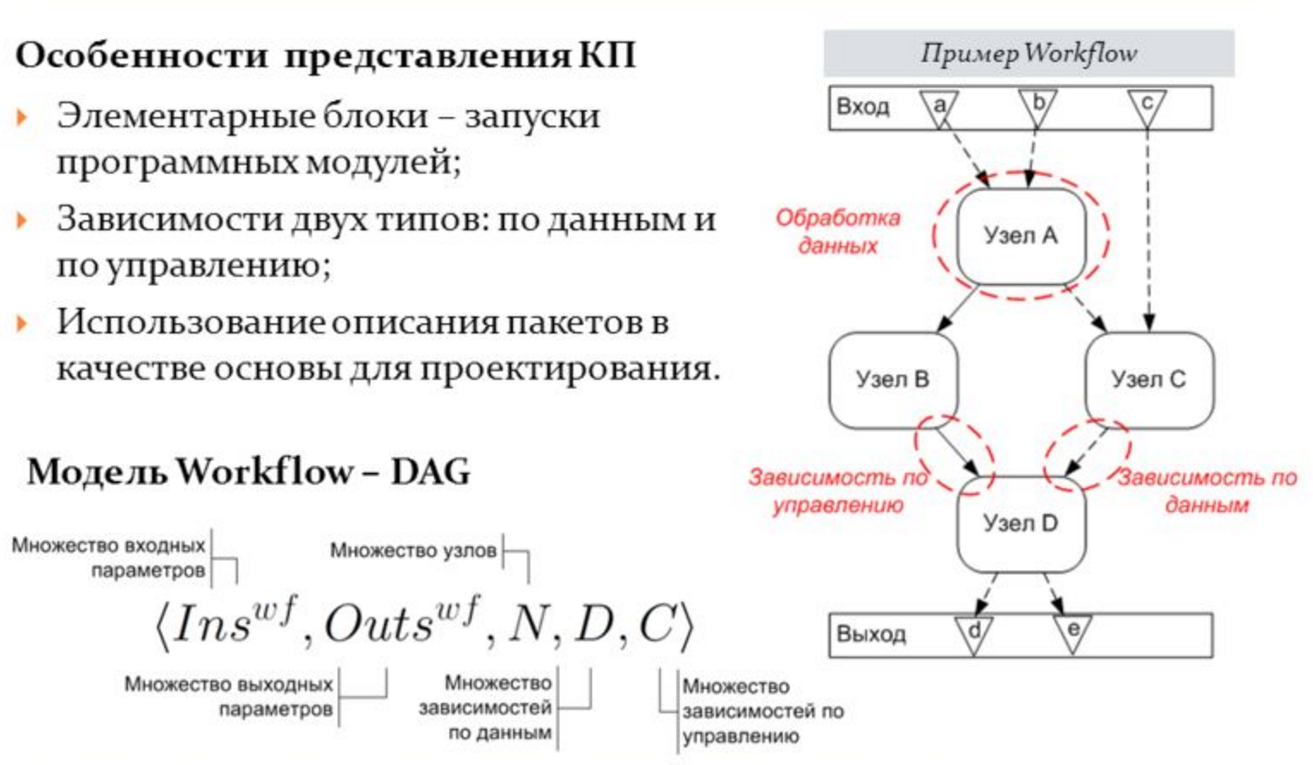
Composite application in the form of WF. Source : Cloud Platform for High Performance Computing / A.V. Bukhanovsky, S.V. Kovalchuk
Designing a composite application for specifying source data is a process of step-by-step refinement of the MWF through the abstract (AWF) and specific WF (CWF) stages, up to the creation of specific service launch scripts in the cloud. At the first stage of designing a composite application, the MWF is formed. The user is able to select classes of services that will be used in the selection of services.
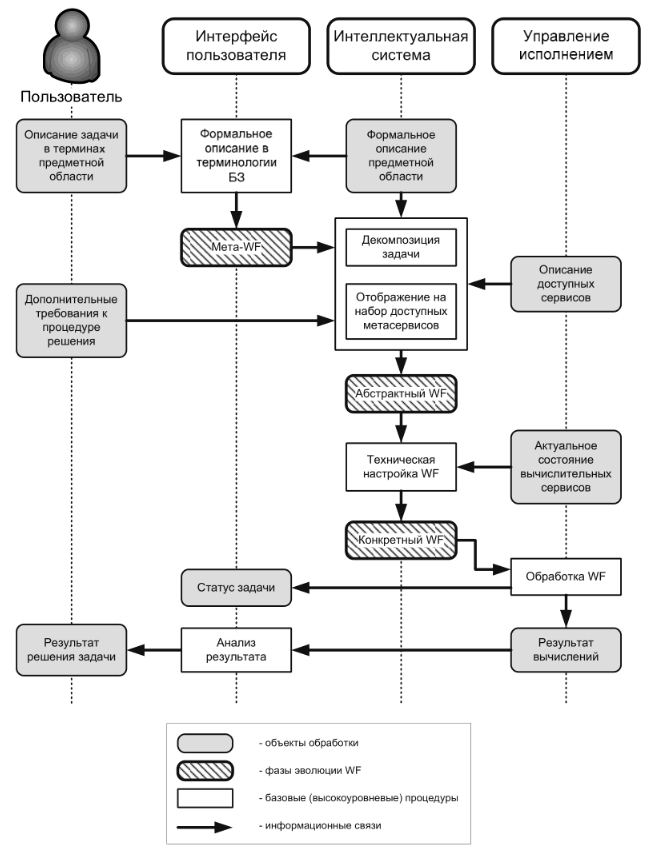
Schematic diagram of the creation and execution of a composite application. Source : CLAVIRE: Second-generation advanced cloud computing technology / A.V. Bukhanovsky, V.N. Vasiliev, V.N. Vinogradov and others.
Next, WF is formed, in which specific implementations of computing services will be fixed. The next design stage is the scheduling and execution script in terms of the CWF. For action blocks, services and nodes are specified for execution, and for data blocks, the specific location of information is indicated.
The figure above shows a schematic diagram of the creation and execution of a composite application under the control of MITP.
As an example of the work of CLAVIRE, one can cite a system that simulates the behavior of a crowd at a stadium during a football World Championship or other mass events. The model takes into account crowd characteristics, such as its social structure, and external factors, such as weather conditions and the political situation. As a result, scientists see a clear picture of the behavior of people in given conditions:
Using the software system, you can recreate any territory and external conditions, and then place a certain group of people in this environment. This opens up tremendous research opportunities. You can, for example, simulate an earthquake in a particular seismically dangerous region during a holiday, when thousands of people are on the streets.
Sergey Ivanov, head of the international laboratory "City Informatics" of ITMO University, explained that the basic work of the models would be enough ordinary surveillance cameras at different points in the territory. This will allow the model to adjust to the real situation, simply by selecting groups of people from the video sequence and projecting them onto the model.
A field study using technology was recently conducted by ITMO University staff together with colleagues from other countries. The object of the study was the religious festival "Kumbh Mela" in India. During the month, researchers observed a pilgrimage of about 70 million people to holy places.
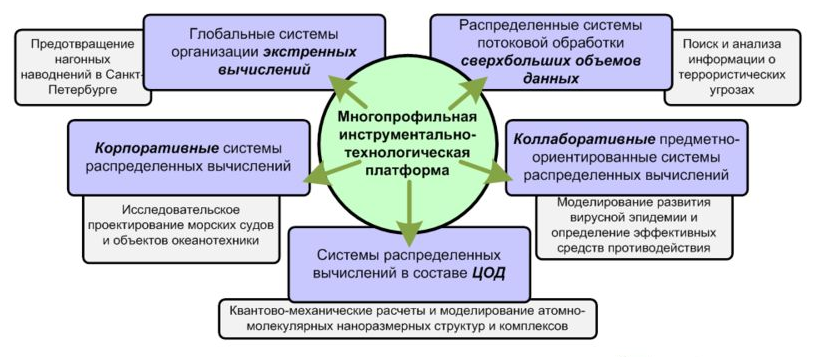
The scope of MITP. Source : Cloud Platform for High Performance Computing / A.V. Bukhanovsky, S.V. Kovalchuk
The complex finds its application in medicine, when its task is to improve the health care system. Decision support systems become program assistants to doctors at all stages of working with patients. They allow you to compile a huge collection of data on best medical practices and to develop more effective methods of treatment and surgery.
PS If you are interested in the system, then a set of technical documentation, methods for using the CLAVIRE complex, software and operational documents, and initial platform skills can be obtained here . You can get acquainted with CLAVIRE and work with the system yourself here .

Torley / Flickr / CC
AaaS: Second Generation Cloud Technologies
Today, cloud computing technologies allow the user to get network access to an array of information resources (networks, remote servers, applications and services) that can be quickly reserved and provided by the provider with minimal effort.
')
For developed cloud environments, the integration of various business models is typical, which is associated with a focus on the specific needs of users in different areas of activity. For their classification and analysis, the Cloud Computing Maturity Model (CCMM) cloud computing formation model is used, which includes five levels of development presented in the diagram below.

I and II generation cloud technologies in CCMM logic. Source : Second Generation Cloud Computing: Composite Applications, Interactive Systems and Semantic Technologies / A.V. Bukhanovsky, S.V. Kovalchuk
According to CCMM, cloud computing of the first and second generations is distinguished. The first generation technologies correspond to levels I-III and cover three well-known business models - these are IaaS, PaaS, SaaS. Second-generation technologies include levels IV and V and are not only focused on providing users with certain services over the Internet, but also on managing an entire ecosystem of computing, software and information resources.
This allows you to solve complex problems associated with the joint activities of several users. Cloud computing technologies of the second generation implement the promising cloud computing model AaaS (Application as a Service), the main service within which is the development and use of composite applications (this is a set of interacting cloud services aimed at solving one problem).
This concept is embodied in the CLAVIRE (CLoud Application VIRtual Environment) multifunctional instrumental and technological platform (MITP) developed by the Scientific and Research Institute of High-Tech Computer Technologies of the ITMO University as part of a project to implement the Government of the Russian Federation to support the development of cooperation of higher educational institutions and organizations.
The main tasks of the MITP are the effective management of the computing, information and software resources of distributed heterogeneous computing infrastructures, as well as the construction of corporate cloud infrastructures.
What can CLAVIRE
The CLAVIRE platform provides access to application packages running on remote computing resources. Currently, the CLAVIRE database includes 65 software systems in such areas as hydrodynamics, nanotechnology and quantum chemistry, analysis and modeling of social systems and transport infrastructure, hydrometeorology, shipbuilding and bioinformatics (this means that a number of complex multi-factor applications can be solved on the CLAVIRE platform tasks in these areas - for example, to predict the likelihood of the onset of flood floods in St. Petersburg).
In addition, CLAVIRE provides multi-purpose calculations in SciLab, WEKA packages (demonstration packages available for public use via CLAVIRE interfaces can be found here ).
Also, the CLAVIRE platform allows you to design composite applications — complexes that interact to solve a common task. The collection of composite applications for various subject areas is provided by experts of the Scientific Research Institute of High-Tech Computer Technologies of NRU ITMO and today contains several models.
Among them, note are the application for calculating the temperature distribution and mass velocities in the volume of the convection layer, the composite application for calculating the vessel’s rolling characteristics and the application for solving the problem of calculating the dynamics of HIV spread.

The solution of the problem of calculating the distribution of temperature and mass velocities in the volume of the convection layer is based on modeling the dynamics of nanoparticles in the medium using the molecular dynamics method and numerical simulation of the convection process using the finite element method (packages used: VMD, NAMD, Comsol, MDlogAnalyst, ComsolInitialise, Ruby interpreter)
How it works
The calculations themselves are performed at Amazon EC2, OpenStack, using grid computing. Grid computing is a kind of parallel computing that is performed using conventional computer systems connected to a network and combined into a “virtual supercomputer.”
The CLAVIRE system uses the GridNNN project (a grid system for the National Nanotechnology Network , implemented in Russian supercomputer centers). The grid of supercomputers is managed by basic grid services located in the main and backup control centers, whose task is to coordinate the work of the system resources and at the same time be a layer between users and the grid infrastructure.

Computing infrastructure. Source : CLAVIRE Cloud Platform for High Performance Computing / A.V. Bukhanovsky
PBS, Torque, Windows HPC and Condor solutions are used to control the launch of tasks on multiprocessor installations. Access to resources is carried out via SSH or via web services, and Windows and Unix-like systems are used as operating systems. As for virtualization tools, CLAVIRE uses VirtualBox applications and VMware and KVM solutions.
The organization of the process of creating and executing a composite application under the control of MITP is reduced to the sequential formalization of description sets in terms of task flows (WF). At the top level of the application description is meta-WF. In it, separate blocks contain only instructions for performing settlement tasks.
Thus, the MWF is a formal description of a user problem in terms of the subject area, without indicating the conditions for its implementation. In addition to describing the actions and data required for the calculations, the user has the ability to set criteria and set limits on which the selection of resources and specific services will be conducted.

Composite application in the form of WF. Source : Cloud Platform for High Performance Computing / A.V. Bukhanovsky, S.V. Kovalchuk
Designing a composite application for specifying source data is a process of step-by-step refinement of the MWF through the abstract (AWF) and specific WF (CWF) stages, up to the creation of specific service launch scripts in the cloud. At the first stage of designing a composite application, the MWF is formed. The user is able to select classes of services that will be used in the selection of services.

Schematic diagram of the creation and execution of a composite application. Source : CLAVIRE: Second-generation advanced cloud computing technology / A.V. Bukhanovsky, V.N. Vasiliev, V.N. Vinogradov and others.
Next, WF is formed, in which specific implementations of computing services will be fixed. The next design stage is the scheduling and execution script in terms of the CWF. For action blocks, services and nodes are specified for execution, and for data blocks, the specific location of information is indicated.
The figure above shows a schematic diagram of the creation and execution of a composite application under the control of MITP.
Where does it work
As an example of the work of CLAVIRE, one can cite a system that simulates the behavior of a crowd at a stadium during a football World Championship or other mass events. The model takes into account crowd characteristics, such as its social structure, and external factors, such as weather conditions and the political situation. As a result, scientists see a clear picture of the behavior of people in given conditions:
Using the software system, you can recreate any territory and external conditions, and then place a certain group of people in this environment. This opens up tremendous research opportunities. You can, for example, simulate an earthquake in a particular seismically dangerous region during a holiday, when thousands of people are on the streets.
Sergey Ivanov, head of the international laboratory "City Informatics" of ITMO University, explained that the basic work of the models would be enough ordinary surveillance cameras at different points in the territory. This will allow the model to adjust to the real situation, simply by selecting groups of people from the video sequence and projecting them onto the model.
A field study using technology was recently conducted by ITMO University staff together with colleagues from other countries. The object of the study was the religious festival "Kumbh Mela" in India. During the month, researchers observed a pilgrimage of about 70 million people to holy places.

The scope of MITP. Source : Cloud Platform for High Performance Computing / A.V. Bukhanovsky, S.V. Kovalchuk
The complex finds its application in medicine, when its task is to improve the health care system. Decision support systems become program assistants to doctors at all stages of working with patients. They allow you to compile a huge collection of data on best medical practices and to develop more effective methods of treatment and surgery.
PS If you are interested in the system, then a set of technical documentation, methods for using the CLAVIRE complex, software and operational documents, and initial platform skills can be obtained here . You can get acquainted with CLAVIRE and work with the system yourself here .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/319688/
All Articles