New features of the product SCAT DPI 6.0 “Sevastopol” from VAS Experts
At VAS Experts, we are creating services for analyzing and controlling traffic and present a new version of SCAT DPI 6.0 “Sevastopol” solution . The system received several corrections based on the experience of developing previous versions of the product, and also acquired new features, which will be discussed below.
 / Flickr / Alexxx Malev / CC
/ Flickr / Alexxx Malev / CC
In the new version of the product, the ability to connect NAT for users who simultaneously use white and gray addresses has been added. To do this, several IP addresses are combined on one login, and then policies are assigned to it and services are connected. This feature is convenient for corporate customers who buy blocks of addresses from an operator.
')
Here is an example of a command to combine addresses into one login:
In this case, I would like to note that the CG-NAT function requires the inclusion of a backup device in the scheme. This is due to the fact that by installing the SCAT system “into the gap” the bypass card does not help, therefore, the platform’s failure stops issuing addresses. Thus, the recommended wiring diagram looks like this:
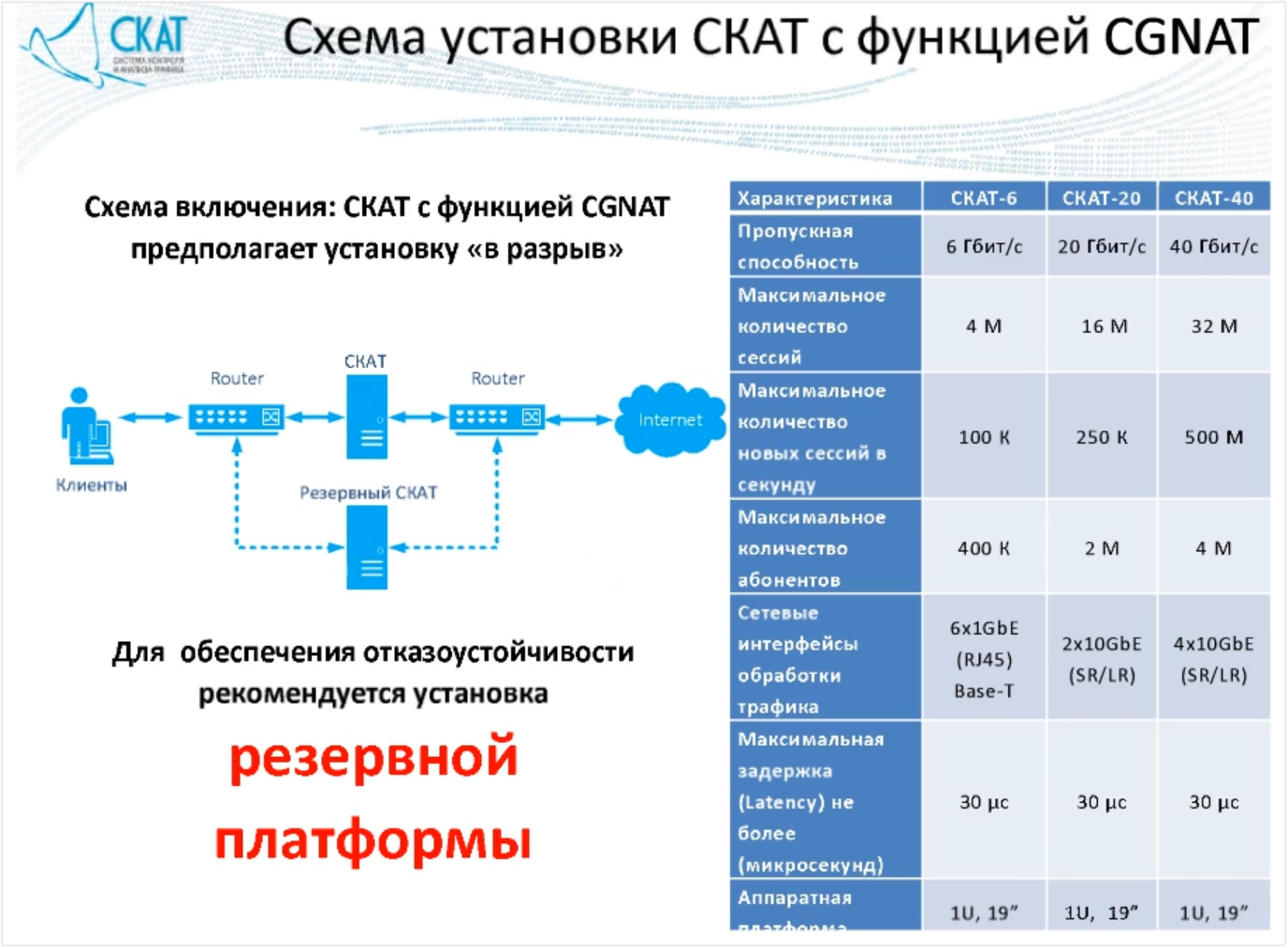 Installation scheme SCAT with CGNAT function (Source: webinar )
Installation scheme SCAT with CGNAT function (Source: webinar )
As for the IPFIX protocol, it allows transferring analytical data from SCAT to both the internal storage system of the server and external aggregators. In its new incarnation, IPFIX received two new features. The first is the export of the resource blocking flag: for example, if the resource is blocked by blacklists, then the corresponding value will appear in the LOCKED field. The second is the export of the host name for the HTTPS and QUIC protocols.
 IPFIX development (Source: webinar )
IPFIX development (Source: webinar )
Note that one of the most popular ways to analyze information from the DPI platform is a bunch of nfcapd daemon collector, nfdump dump and NfSen visualizer, which is a graphical interface for nfdump data. To collect information in the IPFIX format, any universal IPFIX collector that understands patterns or the IPFIX Receiver utility is suitable. After accumulating data at least in one day, NfSen builds graphs by protocols, traffic volume, etc.

In addition to graphs, using NfSen, you can build reports for arbitrary periods by protocols and directions. At the same time, we would like to note that the visualizer is not recommended to be installed on the server where the DPI solution is deployed - the preparation of reports loads the CPU heavily, and this may adversely affect the performance of the DPI platform.
The BRAS service gateway is a new feature of the SCAT traffic monitoring and analysis system. Part of its capabilities were presented in SCAT 5.0. In the new version, the authorization of IPoE sessions on radius appeared, which expanded the range of operator's possibilities in the area of controlling subscriber access to the Internet, as well as when working with additional tariff options (L3 operation and client identification by IP or Q-in-Q tag).
Note that SCAT with the BRAS function is embedded in the operator’s network “into the gap”, however with the use of additional components: SCAT PCRF, radius server and billing server. How to configure the function L3 BRAS read in one of our materials, which you will find on the link .
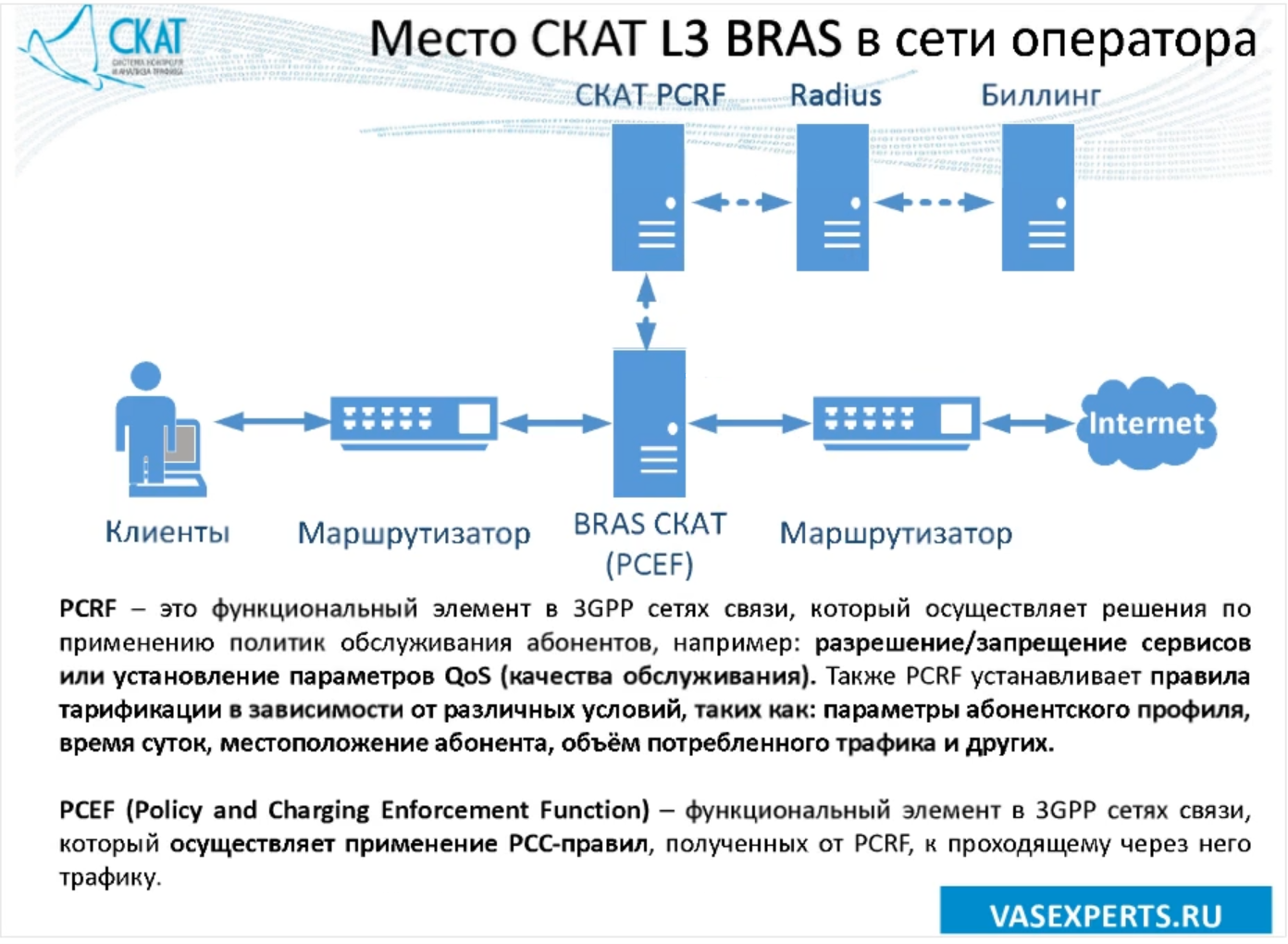 SCAT L3 BRAS location in the operator’s network (Source: webinar )
SCAT L3 BRAS location in the operator’s network (Source: webinar )
The SCAT system with the BRAS function has several applications, among which it is worth highlighting the subscriber access control at zero balance, so that the user can go to the payment system page and replenish the account, manage the total channel bandwidth (tariff plans, QoS), and also identify subscribers in Wi-Fi-network (for example, by phone number).
As for the last point, the work on identification of the user takes place on the equipment of the telecom operator. To do this, the operator must have a standard set of devices (switches, routers, etc.), as well as a DPI system, a DHCP server for arranging the issuance of addresses to subscribers, VMs with an Apache web server, and NAT with a broadcast log entry.
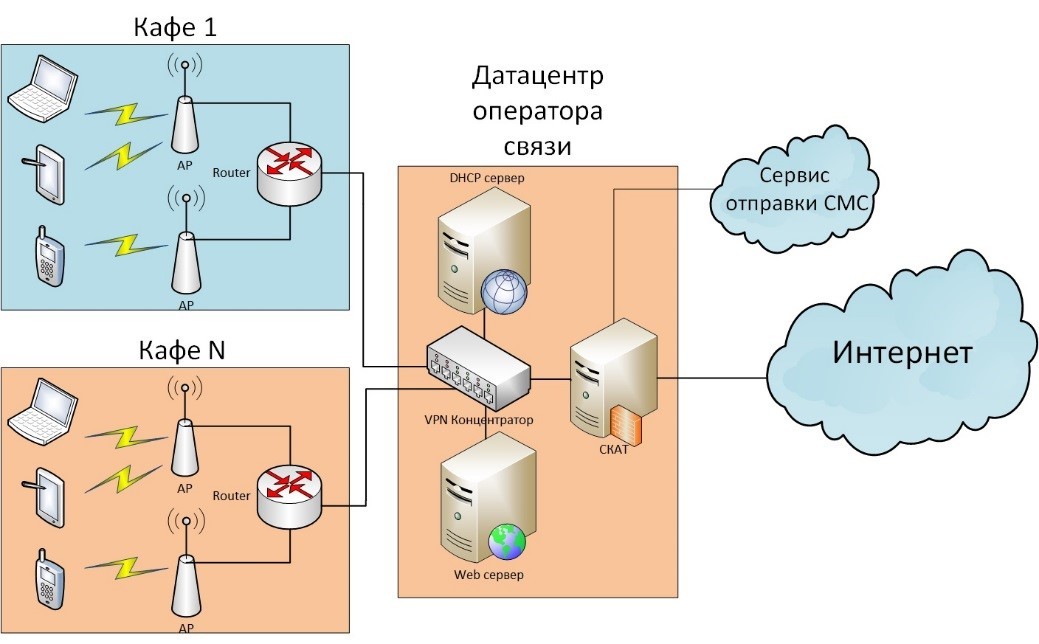 Access to the Internet through a point of access
Access to the Internet through a point of access
The system works as follows. The subscriber's device connects to a Wi-Fi router, which, in turn, “asks” a new IP from a DHCP server. The latter sends data back to the router and calls a shell script that activates a tariff with access restrictions in SCAT DPI.
Then, when the user enters the URL he needs, the web server receives a request for an identification page, where the user enters a phone number followed by a request for an access code. The server generates a random sequence of numbers and sends it to the user via SMS. When the code is confirmed, the new shell script sets the Wi-Fi access rate and forwards the client to the requested URL.
To implement the above scheme, it is necessary to configure the operator’s equipment: a DPI system, a DHCP server, a web server. Instructions for setting up you can find in one of our materials .
The PCRF server can be located on a separate device and manage multiple PCEFs or be part of the SCAT DPI system. The fdpi_pcrf service performs the BRAS role for fastdpi — for outgoing client traffic, fdpi_pcrf requests authorization from the radius server, the tariff plan profile and the list of services provided. To ensure the fault tolerance of the system, it is possible to implement a master-slave redundancy scheme.
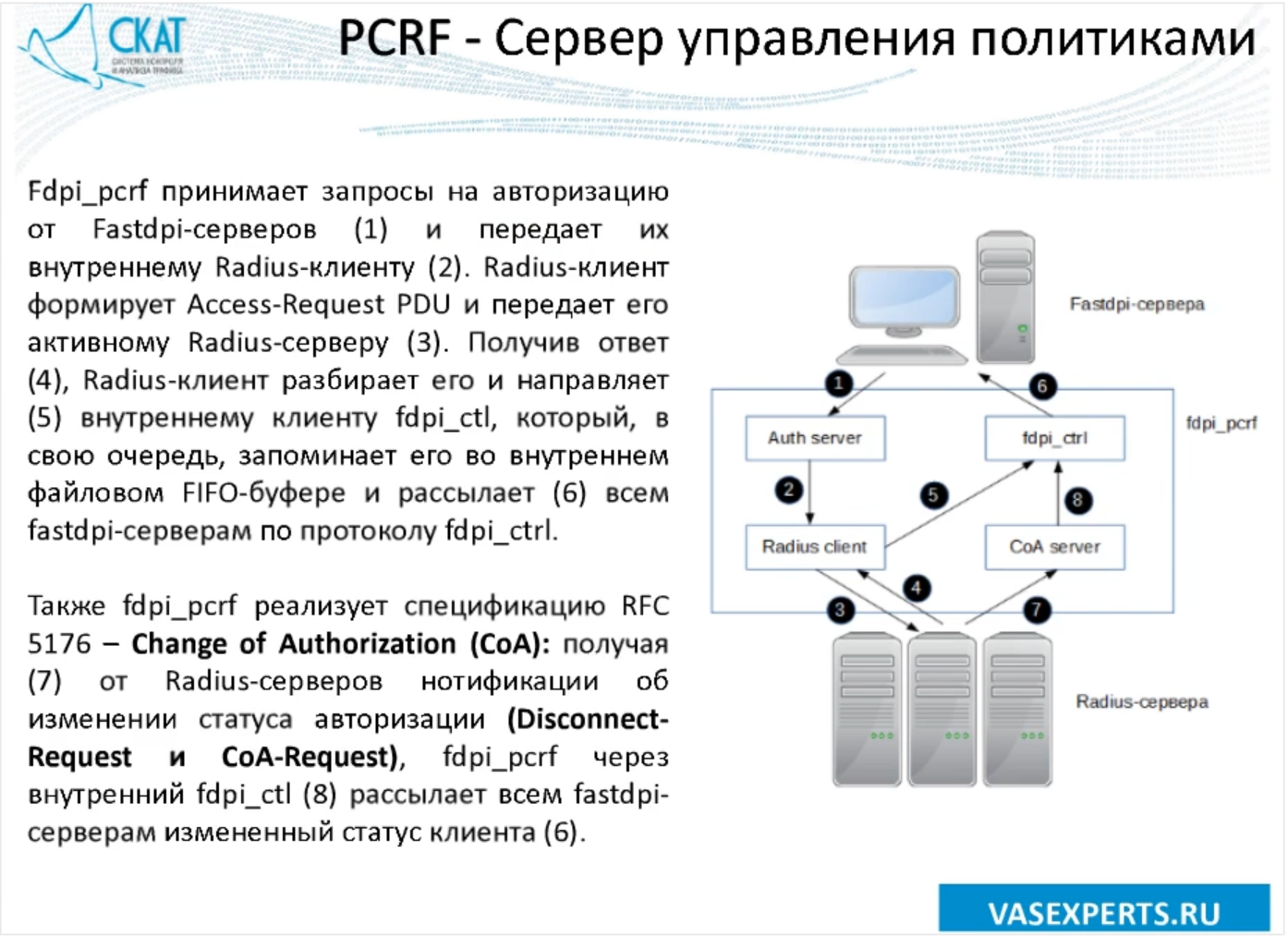 Policy Management Server Operation (Source: webinar )
Policy Management Server Operation (Source: webinar )
The fdpi_pcrf server itself is integrated with fastdpi and has three components. The first is the fastdpi authorization module, which analyzes outgoing traffic from local clients. If there is no client authorization, the module sends a TCP request to fdpi_pcrf. The second is the fdpi_pcrf server, which accepts authorization requests from fastdpi using an internal protocol and processes them. Well, the third is the fastdpi control module, which receives the results of fdpi_pcrf using the fdpi_ctrl protocol and writes them to the client database.
You can learn more about the SCAT DPI 6.0 “Sevastopol” system from our presentation presented above. Part of the video is devoted to the Q & A section - questions were asked by the participants of the webinar online.
PS Other materials from our blog:
 / Flickr / Alexxx Malev / CC
/ Flickr / Alexxx Malev / CCDevelopment of NAT and IPFIX
In the new version of the product, the ability to connect NAT for users who simultaneously use white and gray addresses has been added. To do this, several IP addresses are combined on one login, and then policies are assigned to it and services are connected. This feature is convenient for corporate customers who buy blocks of addresses from an operator.
')
Here is an example of a command to combine addresses into one login:
fdpi_ctrl load –bind_multi –user _: ip___ In this case, I would like to note that the CG-NAT function requires the inclusion of a backup device in the scheme. This is due to the fact that by installing the SCAT system “into the gap” the bypass card does not help, therefore, the platform’s failure stops issuing addresses. Thus, the recommended wiring diagram looks like this:

As for the IPFIX protocol, it allows transferring analytical data from SCAT to both the internal storage system of the server and external aggregators. In its new incarnation, IPFIX received two new features. The first is the export of the resource blocking flag: for example, if the resource is blocked by blacklists, then the corresponding value will appear in the LOCKED field. The second is the export of the host name for the HTTPS and QUIC protocols.

Note that one of the most popular ways to analyze information from the DPI platform is a bunch of nfcapd daemon collector, nfdump dump and NfSen visualizer, which is a graphical interface for nfdump data. To collect information in the IPFIX format, any universal IPFIX collector that understands patterns or the IPFIX Receiver utility is suitable. After accumulating data at least in one day, NfSen builds graphs by protocols, traffic volume, etc.

In addition to graphs, using NfSen, you can build reports for arbitrary periods by protocols and directions. At the same time, we would like to note that the visualizer is not recommended to be installed on the server where the DPI solution is deployed - the preparation of reports loads the CPU heavily, and this may adversely affect the performance of the DPI platform.
Feature Set to work as a L3 BRAS
The BRAS service gateway is a new feature of the SCAT traffic monitoring and analysis system. Part of its capabilities were presented in SCAT 5.0. In the new version, the authorization of IPoE sessions on radius appeared, which expanded the range of operator's possibilities in the area of controlling subscriber access to the Internet, as well as when working with additional tariff options (L3 operation and client identification by IP or Q-in-Q tag).
Note that SCAT with the BRAS function is embedded in the operator’s network “into the gap”, however with the use of additional components: SCAT PCRF, radius server and billing server. How to configure the function L3 BRAS read in one of our materials, which you will find on the link .

The SCAT system with the BRAS function has several applications, among which it is worth highlighting the subscriber access control at zero balance, so that the user can go to the payment system page and replenish the account, manage the total channel bandwidth (tariff plans, QoS), and also identify subscribers in Wi-Fi-network (for example, by phone number).
As for the last point, the work on identification of the user takes place on the equipment of the telecom operator. To do this, the operator must have a standard set of devices (switches, routers, etc.), as well as a DPI system, a DHCP server for arranging the issuance of addresses to subscribers, VMs with an Apache web server, and NAT with a broadcast log entry.

The system works as follows. The subscriber's device connects to a Wi-Fi router, which, in turn, “asks” a new IP from a DHCP server. The latter sends data back to the router and calls a shell script that activates a tariff with access restrictions in SCAT DPI.
Then, when the user enters the URL he needs, the web server receives a request for an identification page, where the user enters a phone number followed by a request for an access code. The server generates a random sequence of numbers and sends it to the user via SMS. When the code is confirmed, the new shell script sets the Wi-Fi access rate and forwards the client to the requested URL.
To implement the above scheme, it is necessary to configure the operator’s equipment: a DPI system, a DHCP server, a web server. Instructions for setting up you can find in one of our materials .
PCRF Policy Management Server Support
The PCRF server can be located on a separate device and manage multiple PCEFs or be part of the SCAT DPI system. The fdpi_pcrf service performs the BRAS role for fastdpi — for outgoing client traffic, fdpi_pcrf requests authorization from the radius server, the tariff plan profile and the list of services provided. To ensure the fault tolerance of the system, it is possible to implement a master-slave redundancy scheme.

The fdpi_pcrf server itself is integrated with fastdpi and has three components. The first is the fastdpi authorization module, which analyzes outgoing traffic from local clients. If there is no client authorization, the module sends a TCP request to fdpi_pcrf. The second is the fdpi_pcrf server, which accepts authorization requests from fastdpi using an internal protocol and processes them. Well, the third is the fastdpi control module, which receives the results of fdpi_pcrf using the fdpi_ctrl protocol and writes them to the client database.
You can learn more about the SCAT DPI 6.0 “Sevastopol” system from our presentation presented above. Part of the video is devoted to the Q & A section - questions were asked by the participants of the webinar online.
PS Other materials from our blog:
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/319636/
All Articles