Power supply without interruption
With the increasing dependence of business on IT and the increasing requirements of information systems for power supply, the need for uninterruptible power systems becomes more and more obvious.

Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) are widely used to protect IT equipment from power outages and poor-quality power supplies. This is an additional equipment designed to power IT systems or other devices in the event of a short (up to several tens of minutes) disconnecting the main power supply, as well as to protect against disturbances and surges in the power supply network and to maintain the power parameters within acceptable limits. That is, UPSs can also be used to improve power quality.

By design, the UPS can be divided into desktop, floor and rack (19 "). The main purpose of any UPS is to protect the load from possible problems in power supply circuits. According to statistics, each PC is exposed to about 120 emergency situations associated with power problems every month. among them:
Thus, the UPSs smooth out small and short-circuited power surges, filter the supply voltage, but their main task is to feed the load for some time after the voltage drops in the network. Many models can automatically shut down IT equipment with the help of software when there is a continuous absence of power in the supply network, and also restart it when power is restored or by timer. Some UPSs include monitoring and recording of power supply parameters (such as temperature, battery charge level and other indicators), display of voltage parameters and frequencies, output voltage and power, warning of emergency situations, etc. When there is a power failure, any UPS switches load on battery power, but there are important differences.
')
 Today, 95% of all uninterruptible power supplies are manufactured using lead-acid batteries as a constant current source.
Today, 95% of all uninterruptible power supplies are manufactured using lead-acid batteries as a constant current source.
Meanwhile, some vendors have already announced the beginning of the transfer of several models of uninterruptible power devices from lead-acid batteries to lithium-ion. Their initial cost is still higher than lead-acid, but over the past few years, the price gap has narrowed significantly.
According to Schneider Electric, depending on the scope of use of lithium-ion batteries in the total cost of ownership during their service life can be achieved savings of 10-40% compared with traditional batteries.

Lithium-ion batteries (Li-ion) accumulate much more energy in a smaller volume. So, in comparison with lead-acid batteries with valve control (VRLA) of equal power, they take up three times less space. And due to the long service life, the amount of work and the cost of replacing them is significantly reduced.
Meanwhile, the vast majority of UPSs are still equipped with lead-acid batteries, known for their reliability, high quality and optimal price characteristics.
By the principle of operation, UPSs are divided into three main classes: backup UPS (off-line), linear-interactive (line-interactive) and UPS with double conversion (on-line). The type of UPS is determined by the ratio of parameters at the input and output of the device. The first frequency and voltage at the output are determined by the frequency and voltage at the input; the second stabilize the output voltage when the frequencies coincide, and double-conversion UPS convert the alternating voltage to DC and again generate an alternating (sinusoidal) voltage at the output, the characteristics of which do not depend on the parameters at the UPS input.
In standby (or passive) UPSs, the load is powered directly from the mains, usually via an anti-interference filter. In the event of a power failure, the load is switched to backup power from the battery-powered inverter. Such UPSs are simple and inexpensive, have high efficiency, but do not stabilize the voltage and frequency of the power grid, and switching to battery power occurs within a few milliseconds. Their power is usually small - from 220 to 2000 VA.
Standby UPS:
A typical field of application for backup UPS is the protection of a PC or ancillary equipment, where the importance of stored information or operations performed is relatively small. This topology is not suitable in the case of frequent outages or low-quality power supply.
The operation scheme of the simplest backup UPS is shown below.

UPS backup type: normal operation (rectifier - rectifier, inverter - inverter, SPD - power filter, bypass - bypass).

UPS backup type: emergency operation .
For the protection of more important equipment, such as entry-level servers, network and telecommunications equipment, it is better to use line-interactive UPS. They provide stabilization of the supply voltage in a given range and reduce the effect of transients on the performance of the protected equipment.
Line-interactive UPSs maintain the power supply and synchronously transfer the load to the inverter when it is lost. In them, the inverter is connected in parallel to the mains, it regulates and stabilizes the output voltage, while charging the battery. Sometimes UPSs are supplemented with autotransformers, which allows extending the voltage regulation range without switching to a battery.
The advantages of this technology are voltage stabilization, shorter switching times for batteries and a well-approximated sinusoidal voltage form at the output of the UPS. There are also cheaper versions of linear-interactive UPS with a “stepped” sinusoid.

Line-interactive UPS: normal operation.

Line-interactive UPS: emergency mode.
Line Interactive UPS:
Line-interactive UPSs can be used to protect professional workstations, mid-level servers, switches, routers, and other network equipment, but they are not suitable for protecting complex and expensive equipment that is sensitive to electromagnetic interference, supply voltage fluctuations and power frequency instability, for example, medical.
Line-interactive UPSs are not suitable for the protection of continuous technological processes, as well as for building centralized systems of guaranteed power supply, where it is important to ensure complete independence of the electrical parameters at the output of the UPS from the parameters at the input.
A variety of linear-interactive systems - UPS with delta-voltage conversion. Thanks to the improved feedback, the voltage at the load is regulated smoothly, not stepwise, and the frequency of the output voltage is stabilized.
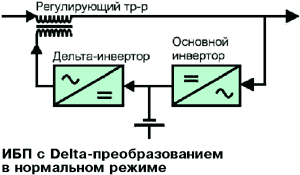
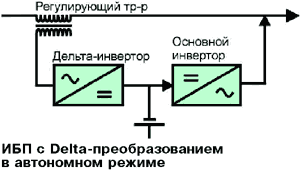
UPS with delta conversion in normal and autonomous modes.
The main advantage of UPS with delta-conversion is high efficiency. However, it is achieved when the mains voltage parameters correspond to the nominal values, the input impedance of the load has only the active component, and the UPS itself is loaded at full power. Otherwise, the load on the main and delta inverters increases, or the efficiency of use of the input transformer decreases, which deteriorates the efficiency. In addition, the effect of expanding the range of input voltages for normal operation. As a result, having an efficiency advantage (2-3%) in ideal conditions, delta-conversion UPSs lose linear-interactive under real conditions.
Delta Transform UPS:
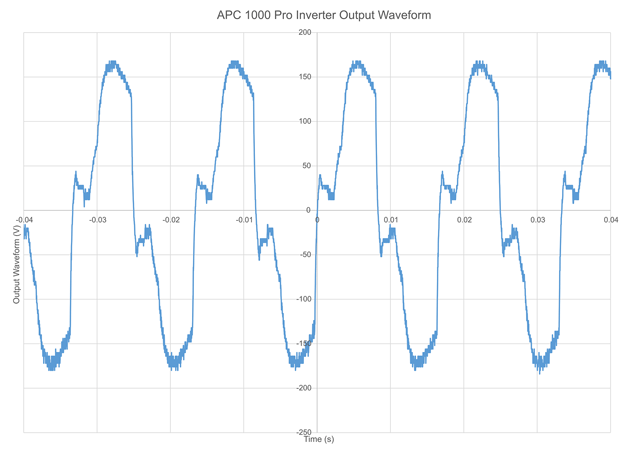
Line-interactive UPS APC BR1000G gives the output is not quite pure sinusoid, but this approximation is enough for most devices.
The most technically advanced class of uninterruptible power supply systems - double conversion systems - guarantee output electrical characteristics close to ideal, both in voltage and frequency. For this you have to pay complication and cost of construction.
Dual conversion systems provide very short battery switching times and have high electrical output characteristics. Such UPSs are suitable for mission-critical applications, protecting powerful servers and clusters, telecommunications equipment, and local area networks. They have high efficiency in the double conversion mode (95-96%) and a sinusoidal output voltage.
In the Russian market there are more than two dozen models of double-conversion UPS. About half of these devices are designed for rack mounting. The double conversion technology ensures maximum protection against power outages.
In such UPSs, the input AC voltage is converted by the rectifier into DC, and then by the inverter back into AC. Even with large deviations of the input voltage, the UPS supplies the load with a pure sinusoidal stabilized voltage. The inverter is connected in series with the main source of electricity and is always in the on state. When the input voltage is lost, it switches to battery power.
In normal mode, when powered from the mains, electricity is supplied through a rectifier and an inverter, simultaneously charging the battery. In the event of a power failure or power failure at the UPS input, the inverter is powered by rechargeable batteries. Switching occurs without using a static switch, so switching to battery operation is instantaneous. The static key in this scheme is used only to switch to the automatic bypass mode to power the load in the event of a significant failure of the UPS.

Double-conversion UPS features reliable power protection for the load.

Double conversion UPS: emergency mode, battery powered.
In a double conversion UPS, precise voltage and frequency regulation at the output of the UPS is maintained, and a bypass is smoothly transferred. The manual bypass can be used for maintenance and hot-swappable batteries and the UPS itself.
Such UPSs are distinguished by constant voltage and frequency stabilization, output voltage phase continuity, no influence of the load on the network, and complete power filtering. But there are also negative sides - the complexity of the design and the high price, relatively low efficiency. The power range of manufactured devices is very wide - from 600 VA to several hundred kVA.
Double conversion UPS:
Brief comparison of different classes of UPS
Meanwhile, the industry has long needed a more accurate classification of UPS. According to the IEC 32040 standard, three letter designations are entered: VFI, VI and VFD.
Here is how it relates to the UPS topology:
The classification also takes into account the degree of non-sinusoidal output voltage of the UPS in normal (when running on line) and offline (when running on battery). The first letter corresponds to the characteristic shape of the voltage for the normal mode, the second - for autonomous.
Finally, the dynamic characteristics of the UPS are taken into account - fluctuations in the amplitude of the output voltage when the operating mode changes and a 100% abrupt change in the load value. The first symbol in this classification is the output voltage fluctuation when the UPS changes its operating mode (normal, autonomous, bypass).
The second symbol characterizes fluctuations in the output voltage at a 100% change in linear load. Testing is carried out in normal and autonomous modes, the worst indicator is selected. The third symbol characterizes fluctuations in the output voltage at a 100% change in non-linear load. Of course, UPS has other characteristics, and there are plenty of them.
We briefly list the main characteristics of the UPS ^
Some PC power supplies use the PFC function and do not always work correctly with an approximate, not “clean” power supply sine wave. This can lead to periodic system reboot.
UPS power may be indicated in volt-amperes (VA) or in watts (W). VA represents the maximum theoretical output power of the UPS, however, the available power in watts is less - 60% of the nominal value in VA. That is, a 1000 VA UPS corresponds to a 600 W UPS.
Do not overload the UPS. For example, to protect a load of 300 W, it is better to use a 400-600 W UPS. This option is more reliable and provides longer battery life. Also note that battery capacity drops over time. And do not connect equipment with peak power consumption to the UPS that could overload the power source, such as laser printers. Some UPSs have overload protection.
The task of power supply with a long absence of voltage is usually solved by installing gasoline or diesel generators. But often noise, exhaust gases, the need for periodic maintenance, as well as high demands on the quality of the power supply make the use of a generator unacceptable. In such cases, it is recommended to use specialized UPS with an external large capacity battery pack.
Interruptions in information systems often lead to large financial losses, so you have to take into account the threat of poor-quality power supply, possible interruptions and even long-term power outages.
In the world, more than 40% of the sold uninterruptible power systems is used to protect servers, storage systems, network equipment. About 60% of UPS consumption accounts for local networks, telecommunications and data centers, a significant amount is used in industry, since many manufacturing processes require high-quality power supplies.
About a quarter of the world's UPS sales account for devices with a capacity of less than 1 kVA, and about half of sales for devices with a capacity of up to 5 kVA. Usually they are used to protect PCs and entry-level servers. In Russia, no more than 15% of users protect their PCs with the help of UPS - most are content with a network filter.
The increase in the popularity of laptops is also not conducive to the demand for UPSs, however servers of any class and network equipment, office PBXs still need similar protection.
Unlike powerful UPSs (over 20 kVA), whose life cycle reaches 20 years, low-power power supplies are designed for a five-year service life, but a replaceable battery pack (the most short-lived part of the device) allows them to extend their operation.
In small offices, backup or line-interactive UPSs are commonly used. The latter are relatively inexpensive, have acceptable functionality and a sufficient class of protection. More than half of manufacturers produce UPS of small and even medium power in South-East Asia under OEM contracts.
For low-cost “simple” UPSs, the development trend has been to bring them closer in functionality and efficiency (such as maintenance bypass for hot-swappable or equipment repair, controlled sockets and extended equipment) to “big” UPS.
When choosing a UPS, you should consider the warranty period for the device itself and its components, for example, batteries. Give preference to well-known manufacturers who specialize in the manufacture of such equipment. Decide on the maximum number and type of outlets for the connected devices. In cases where, in addition to periodic outages, there are problems with power supply parameters, it is necessary to install linear-interactive devices.
In general, do not follow the battery life, it usually takes up to 5 minutes at 100% load. It is better to choose a model with additional battery modules or buy a generator. It is cheaper than spent on sealed, maintenance-free batteries.
Uninterruptible power supplies protect computer equipment from power outages. A good UPS will reliably protect electronic devices from overloads, will allow you to save all the data and shut down the system correctly in the event of a power outage. It is better not to save on the price of the device, and to buy at least a linear-interactive UPS, and to protect critical systems use a double-conversion UPS.
Interruptions in the work of the data center seriously damage their customers and the image of the companies themselves. Therefore, it is important for owners to find effective solutions to improve the power supply reliability of their data centers. Global manufacturers of uninterruptible power systems for data centers offer their options for the implementation of UPS.
What are the main requirements for the "UPS for data center"? This is high reliability (taking into account the system recovery time, i.e. the availability factor is not the MTBF parameter); high efficiency at partial load (50-80%), which directly affects the heat generation and efficiency of the equipment; support of parallel operation with capacity increase or increase in the degree of redundancy; scalability; high input and output power factor and low harmonic distortion of the input current, which is especially important when organizing backup power from the diesel generator set.
Other important factors are compactness of systems, support for parallel operation, low heat generation, intelligent battery charge management, simple maintenance and support, improved server shutdown capabilities (there are software versions that allow correct shutdown of virtual machines), management / monitoring tools, including remote, the possibility of simple and intuitive switching to the external bypass with protection from incorrect personnel actions, good support with side of the equipment manufacturer.
In the absence of a backup power supply system from DGU, the battery life can be increased by using external battery cabinets. Among the mandatory functions of high-end UPSs are intelligent battery charge management systems, equipment warning equipment about low battery power. The use of energy-efficient UPSs in the data center helps to reduce power consumption, while the power and reliability of uninterruptible power supplies remain unchanged.
Double-conversion UPSs provide the highest degree of protection against various power outages, since IT systems are completely immune to the effects of the power supply and are powered from the UPS directly. When using such a UPS, the equipment is protected from problems associated with voltage drops, power failure and other possible power failures. For this reason, double-conversion UPSs are used to provide power to servers, network-sensitive equipment, and other critical devices on which data center operation depends. In addition, double-conversion UPSs have a large arsenal of functions as well as flexible scalability.
FSP Group some time ago caught the trends of the growing data center market and began to produce specialized equipment, which is designed to provide telecom service providers with the necessary energy sources. FSP's CUSTOS 9X double conversion uninterruptible power supplies cover a power range from 1K to 10K.
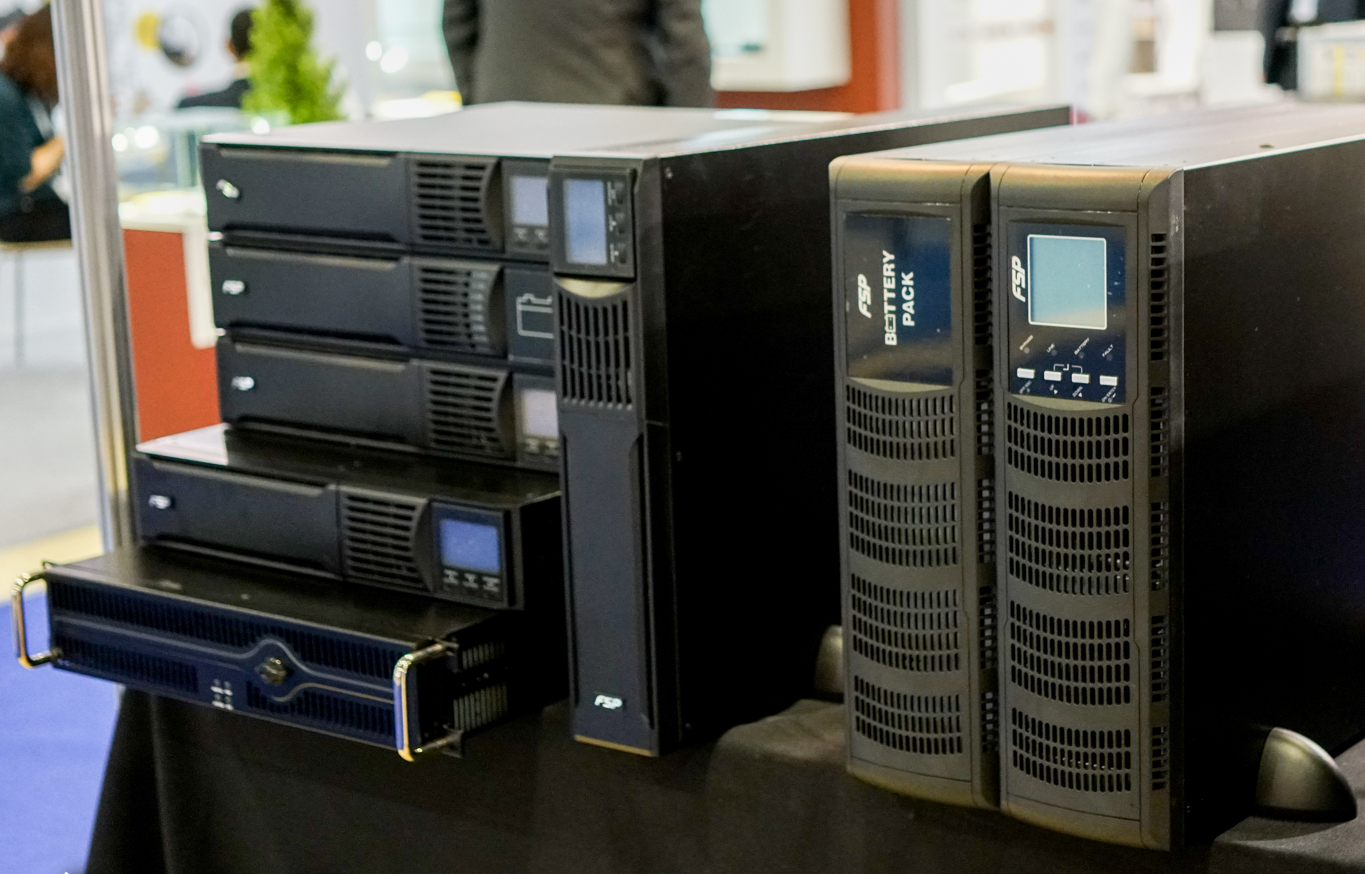

Double-conversion UPS FSP Custos 9X + 10K.
For example, UPS Custos 9X + 10K has the following design features:
The package with the UPS includes ViewPower software with the support of the Russian language, which allows you to remotely monitor the parameters of the uninterruptible power supply, set the schedule of switching on and off, and receive notifications of alarm events by mail or SMS.
UPS with dual voltage converter FSP Custos 9X + series can be used in conjunction with additional battery packs, there is the possibility of hot-swappable power supplies.
These are the UPSs who use the hosting provider RUVDS to ensure the smooth operation of the equipment in their data center .. Its uninterrupted power supply system is built according to the classical scheme. The data center is powered by two substations that power the data center via two independent lines. The facility has a set of UPS and DGS (redundancy scheme - N + 1).
Each physical server is connected to an uninterruptible power supply. If these components suddenly fail, then diesel generators will be put into operation, which will provide the data center with electricity until the substation problems are resolved. This is an important component of high reliability VPS-hosting.

Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) are widely used to protect IT equipment from power outages and poor-quality power supplies. This is an additional equipment designed to power IT systems or other devices in the event of a short (up to several tens of minutes) disconnecting the main power supply, as well as to protect against disturbances and surges in the power supply network and to maintain the power parameters within acceptable limits. That is, UPSs can also be used to improve power quality.

By design, the UPS can be divided into desktop, floor and rack (19 "). The main purpose of any UPS is to protect the load from possible problems in power supply circuits. According to statistics, each PC is exposed to about 120 emergency situations associated with power problems every month. among them:
| Voltage spikes | Increases voltage by more than 10% for more than 20 ms. |
| High voltage power surges | Short pulses with voltage up to 6000 V and duration up to 10 ms. |
| Power failures | Short-term reduction in voltage to less than 80-85% of nominal. |
| High frequency interference | Interference of electromagnetic or other origin. |
| Frequency run | Frequency drift by more than 3 Hz from nominal (50 Hz). |
| Voltage sweep | The voltage drop in the network for a long time. |
| Voltage drop | No voltage in the mains for more than 40 ms. |
Thus, the UPSs smooth out small and short-circuited power surges, filter the supply voltage, but their main task is to feed the load for some time after the voltage drops in the network. Many models can automatically shut down IT equipment with the help of software when there is a continuous absence of power in the supply network, and also restart it when power is restored or by timer. Some UPSs include monitoring and recording of power supply parameters (such as temperature, battery charge level and other indicators), display of voltage parameters and frequencies, output voltage and power, warning of emergency situations, etc. When there is a power failure, any UPS switches load on battery power, but there are important differences.
')
Batteries: an alternative to lead acid batteries
 Today, 95% of all uninterruptible power supplies are manufactured using lead-acid batteries as a constant current source.
Today, 95% of all uninterruptible power supplies are manufactured using lead-acid batteries as a constant current source.Meanwhile, some vendors have already announced the beginning of the transfer of several models of uninterruptible power devices from lead-acid batteries to lithium-ion. Their initial cost is still higher than lead-acid, but over the past few years, the price gap has narrowed significantly.
According to Schneider Electric, depending on the scope of use of lithium-ion batteries in the total cost of ownership during their service life can be achieved savings of 10-40% compared with traditional batteries.

Lithium-ion batteries (Li-ion) accumulate much more energy in a smaller volume. So, in comparison with lead-acid batteries with valve control (VRLA) of equal power, they take up three times less space. And due to the long service life, the amount of work and the cost of replacing them is significantly reduced.
Meanwhile, the vast majority of UPSs are still equipped with lead-acid batteries, known for their reliability, high quality and optimal price characteristics.
UPS Classes
By the principle of operation, UPSs are divided into three main classes: backup UPS (off-line), linear-interactive (line-interactive) and UPS with double conversion (on-line). The type of UPS is determined by the ratio of parameters at the input and output of the device. The first frequency and voltage at the output are determined by the frequency and voltage at the input; the second stabilize the output voltage when the frequencies coincide, and double-conversion UPS convert the alternating voltage to DC and again generate an alternating (sinusoidal) voltage at the output, the characteristics of which do not depend on the parameters at the UPS input.
In standby (or passive) UPSs, the load is powered directly from the mains, usually via an anti-interference filter. In the event of a power failure, the load is switched to backup power from the battery-powered inverter. Such UPSs are simple and inexpensive, have high efficiency, but do not stabilize the voltage and frequency of the power grid, and switching to battery power occurs within a few milliseconds. Their power is usually small - from 220 to 2000 VA.
Standby UPS:
| Virtues | disadvantages |
| - Compactness, low weight, economy, relative cheapness. | - There is no stabilization of the output voltage; - Incomplete filtering of the mains voltage from interference and emissions; interference generated by the load is passed back to the network; - Abrupt change in voltage, frequency and shape of the output voltage when switching to battery power (switching time> 5 ms); - Rectangular output voltage instead of sinusoidal. |
A typical field of application for backup UPS is the protection of a PC or ancillary equipment, where the importance of stored information or operations performed is relatively small. This topology is not suitable in the case of frequent outages or low-quality power supply.
The operation scheme of the simplest backup UPS is shown below.

UPS backup type: normal operation (rectifier - rectifier, inverter - inverter, SPD - power filter, bypass - bypass).

UPS backup type: emergency operation .
For the protection of more important equipment, such as entry-level servers, network and telecommunications equipment, it is better to use line-interactive UPS. They provide stabilization of the supply voltage in a given range and reduce the effect of transients on the performance of the protected equipment.
Line-interactive UPSs maintain the power supply and synchronously transfer the load to the inverter when it is lost. In them, the inverter is connected in parallel to the mains, it regulates and stabilizes the output voltage, while charging the battery. Sometimes UPSs are supplemented with autotransformers, which allows extending the voltage regulation range without switching to a battery.
The advantages of this technology are voltage stabilization, shorter switching times for batteries and a well-approximated sinusoidal voltage form at the output of the UPS. There are also cheaper versions of linear-interactive UPS with a “stepped” sinusoid.

Line-interactive UPS: normal operation.

Line-interactive UPS: emergency mode.
Line Interactive UPS:
| Virtues | disadvantages |
| - Compact, economical; - Step stabilization of the input voltage; - Almost sinusoidal output voltage; - Low cost. | - They are more expensive than backup; - Lack of real isolation of the load from the power distribution network; - Lack of adjustment and stabilization of the input frequency; - Relatively weak stabilization of the output voltage, especially during transients or in the case of step-by-step load changes; - Low efficiency when feeding non-linear loads. |
Line-interactive UPSs can be used to protect professional workstations, mid-level servers, switches, routers, and other network equipment, but they are not suitable for protecting complex and expensive equipment that is sensitive to electromagnetic interference, supply voltage fluctuations and power frequency instability, for example, medical.
Line-interactive UPSs are not suitable for the protection of continuous technological processes, as well as for building centralized systems of guaranteed power supply, where it is important to ensure complete independence of the electrical parameters at the output of the UPS from the parameters at the input.
A variety of linear-interactive systems - UPS with delta-voltage conversion. Thanks to the improved feedback, the voltage at the load is regulated smoothly, not stepwise, and the frequency of the output voltage is stabilized.


UPS with delta conversion in normal and autonomous modes.
The main advantage of UPS with delta-conversion is high efficiency. However, it is achieved when the mains voltage parameters correspond to the nominal values, the input impedance of the load has only the active component, and the UPS itself is loaded at full power. Otherwise, the load on the main and delta inverters increases, or the efficiency of use of the input transformer decreases, which deteriorates the efficiency. In addition, the effect of expanding the range of input voltages for normal operation. As a result, having an efficiency advantage (2-3%) in ideal conditions, delta-conversion UPSs lose linear-interactive under real conditions.
Delta Transform UPS:
| Virtues | disadvantages |
| - High efficiency (with ideal input voltage parameters); - High input power factor (no need for corrective filters). | - Increased complexity due to the use of bidirectional inverters and, consequently, lower reliability; - A lower degree of load protection in normal operation against sudden changes in input voltage due to the inertia of the feedback circuit; - The lack of load protection in normal operation from the frequency deviations of the input voltage; - Lack of integrated electrical isolation between input and output. |

Line-interactive UPS APC BR1000G gives the output is not quite pure sinusoid, but this approximation is enough for most devices.
The most technically advanced class of uninterruptible power supply systems - double conversion systems - guarantee output electrical characteristics close to ideal, both in voltage and frequency. For this you have to pay complication and cost of construction.
Dual conversion systems provide very short battery switching times and have high electrical output characteristics. Such UPSs are suitable for mission-critical applications, protecting powerful servers and clusters, telecommunications equipment, and local area networks. They have high efficiency in the double conversion mode (95-96%) and a sinusoidal output voltage.
In the Russian market there are more than two dozen models of double-conversion UPS. About half of these devices are designed for rack mounting. The double conversion technology ensures maximum protection against power outages.
In such UPSs, the input AC voltage is converted by the rectifier into DC, and then by the inverter back into AC. Even with large deviations of the input voltage, the UPS supplies the load with a pure sinusoidal stabilized voltage. The inverter is connected in series with the main source of electricity and is always in the on state. When the input voltage is lost, it switches to battery power.
In normal mode, when powered from the mains, electricity is supplied through a rectifier and an inverter, simultaneously charging the battery. In the event of a power failure or power failure at the UPS input, the inverter is powered by rechargeable batteries. Switching occurs without using a static switch, so switching to battery operation is instantaneous. The static key in this scheme is used only to switch to the automatic bypass mode to power the load in the event of a significant failure of the UPS.

Double-conversion UPS features reliable power protection for the load.

Double conversion UPS: emergency mode, battery powered.
In a double conversion UPS, precise voltage and frequency regulation at the output of the UPS is maintained, and a bypass is smoothly transferred. The manual bypass can be used for maintenance and hot-swappable batteries and the UPS itself.
Such UPSs are distinguished by constant voltage and frequency stabilization, output voltage phase continuity, no influence of the load on the network, and complete power filtering. But there are also negative sides - the complexity of the design and the high price, relatively low efficiency. The power range of manufactured devices is very wide - from 600 VA to several hundred kVA.
Double conversion UPS:
| Virtues | disadvantages |
| - Maximum filtering of the mains voltage from interference and emissions; interference generated by the load is not passed back to the network; - Power supply with a “clean” sinusoidal power supply, stabilized in magnitude, frequency, and voltage form, when operating from the mains and from batteries; - Switching to batteries occurs instantly, with no transients. | - Relative complexity and higher cost; - Additional energy consumption for double voltage conversion, reducing efficiency; - Low power factor at the input (to increase it, an additional element is required - THD filter). |
Brief comparison of different classes of UPS
| Reserve | Line Interactive | Double conversion | |
| UPS power | less than 1.5 kVA | less than 4 kVA | not limited |
| Network mode | |||
| Voltage stabilization | not | stepped | full |
| Frequency stabilization | not | Not | there is |
| Interference filtering | weak | average | maximum |
| Battery mode | |||
| Conversion frequency | frequent | average | rare |
| Battery Transit Time | 5-15 ms | 2-6 ms | not |
| Sinusoid shape | often trapezoidal | sinusoidal | sinusoidal |
| bypass mode | not | not | there is |
| galvanic isolation | Not | not | is possible |
Meanwhile, the industry has long needed a more accurate classification of UPS. According to the IEC 32040 standard, three letter designations are entered: VFI, VI and VFD.
- Class VFI (Voltage & Frequency Independent) - the output voltage and frequency of the UPS do not depend on the input parameters.
- Class VI (Voltage Independent) - the output frequency coincides with the input, the output voltage is regulated within the specified limits.
- Class VFD (Voltage & Frequency Dependent) - the output voltage and frequency coincide with the input.
Here is how it relates to the UPS topology:
| UPS topology | Specification | Typical power | Typical application |
| Spare | Voltage & Frequency Dependent (VFD) | 1500 VA | Small office, home PCs and other non-critical environments |
| Line Interactive | Voltage Independent (VI) | 5000 VA | Small business, web sites, branch servers |
| Double conversion | Voltage and Frequency Independent (VFI) | 1000 kVA | Data centers |
The classification also takes into account the degree of non-sinusoidal output voltage of the UPS in normal (when running on line) and offline (when running on battery). The first letter corresponds to the characteristic shape of the voltage for the normal mode, the second - for autonomous.
- S corresponds to a sinusoidal output voltage with a non-linear distortion factor (SOI) of less than 8% for both linear and non-linear loads.
- X corresponds to a non-sinusoidal signal with a SOI of more than 8% with a non-linear load.
- Y corresponds to a non-sinusoidal signal at any load, SOI exceeds the limits set in IEC 61000-2-4.
Finally, the dynamic characteristics of the UPS are taken into account - fluctuations in the amplitude of the output voltage when the operating mode changes and a 100% abrupt change in the load value. The first symbol in this classification is the output voltage fluctuation when the UPS changes its operating mode (normal, autonomous, bypass).
The second symbol characterizes fluctuations in the output voltage at a 100% change in linear load. Testing is carried out in normal and autonomous modes, the worst indicator is selected. The third symbol characterizes fluctuations in the output voltage at a 100% change in non-linear load. Of course, UPS has other characteristics, and there are plenty of them.
UPS characteristics
We briefly list the main characteristics of the UPS ^
| The input voltage change range at which the UPS does not switch to batteries. | The larger it is, the smaller the number of transitions to the battery, which increases its service life. This is especially true for power grids in the Russian regions, where voltage drops are not uncommon. |
| The change in output voltage when the input is changed. | The UPS must provide output voltage for normal operation of the equipment. Failure to exceed the allowable range may cause malfunction of the equipment or even damage it. |
| The parameters of the output voltage during battery operation. | These parameters determine the quality of power provided by the UPS. |
| The process of switching the UPS to the battery and back. | For the protected equipment, all transients must be “invisible”, performed quickly and correctly. |
| UPS behavior when overloaded. | When overloaded in battery mode, the UPS shuts down, that is, if the mains voltage drops, the equipment will be de-energized. Some UPSs provide indication (including audible) overload and / or overload protection. |
| The presence of a "cold" start. | The ability to turn on the UPS in the absence of mains voltage may be useful, for example, if during a long power outage it is necessary to turn on the computer for a short time or to test the system. |
| Stabilization of the frequency of power. | Some types of equipment require a stable frequency power supply. |
| Software support and interface for PC connection. | "Intelligent" UPS support programmable shutdown of the least critical loads in moments of overload. Many modern UPSs are also supplied with special programs that allow saving the statistics files of the device operation. |
| Output power measured in volt-amperes (VA) or watts (W). | Power is considered one of the main characteristics. If the total capacity of the load exceeds the capacity of the UPS, then this may lead to the last failure, or constant reloads. You need to know how much power your PC consumes and all devices connected to it. The active power of the UPS should be at least 10-15% more than the sum of the capacities of the PC power supply and the monitor. |
| The battery life at power load. | It is determined by the capacity of the batteries and the capacity of the equipment connected to the UPS. Most office UPSs are 4-15 minutes. |
| Battery life | Usually lead batteries significantly lose their capacity after 3-4 years. Their lifespan depends on the battery charging circuit. In modern UPSs, technical solutions are applied that prolong the life of the battery and allow its replacement. UPSs of low power with ten-year batteries of 9–18 Ah capacity (which actually work for five to seven years) instead of five-year ones (which actually serve three years) appear. |
| The number of power connectors (sockets). | It is necessary to calculate how many devices require power protection. Along with uninterruptible power connectors, UPSs often have additional sockets simply with protection from power surges. Consider the type of outlets — Euro (CEE 7/4) or computer (C-13 or C-14). |
| Indication mode of operation. | UPSs can not only sound signals in the case of mode switching, but also provide information using LEDs or display it on an LCD screen, where up to 20 different states can be displayed, as well as complemented by management tools (for example, via SNMP). Some models are able to inform about the need to replace the battery. |
| The shape of the output voltage. | The shape of the output voltage can be sinusoidal or approximated. PC power supplies with active PFC are “poorly friendly” with UPSs, which have a stepped approximation of a sinusoid. On the other hand, the sinusoidal signal inverter is more complex, has a lower efficiency. |
| AVR | A UPS with good performance of an automatic voltage regulator (AVR) is needed for those who have unstable mains voltage. |
| Power filter. | The correct power filter consists of four capacitors and two chokes, in the filter it is easier to replace the chokes with a resistor or special jumpers. In some UPSs there is no filter - they are supplied only with a varistor limiter. Although the filter is not a necessity for modern technology, if it is not, then it is worthwhile to take a closer look at the chosen model. Perhaps the manufacturer saves not only the filter. |
| Acoustic noise. | All UPSs make noise when running on battery, but some also when charging batteries. In general, it is better to choose a UPS without a fan if it will not be installed in the server room. |
| Battery charge. | The charging circuit of the UPS must ensure optimum fast charging of the battery to the desired voltage. However, too fast charging, as well as charging to an overvoltage, leads to premature battery wear, and slow charging does not ensure timely re-availability of the UPS. |
Some PC power supplies use the PFC function and do not always work correctly with an approximate, not “clean” power supply sine wave. This can lead to periodic system reboot.
UPS power may be indicated in volt-amperes (VA) or in watts (W). VA represents the maximum theoretical output power of the UPS, however, the available power in watts is less - 60% of the nominal value in VA. That is, a 1000 VA UPS corresponds to a 600 W UPS.
Do not overload the UPS. For example, to protect a load of 300 W, it is better to use a 400-600 W UPS. This option is more reliable and provides longer battery life. Also note that battery capacity drops over time. And do not connect equipment with peak power consumption to the UPS that could overload the power source, such as laser printers. Some UPSs have overload protection.
The task of power supply with a long absence of voltage is usually solved by installing gasoline or diesel generators. But often noise, exhaust gases, the need for periodic maintenance, as well as high demands on the quality of the power supply make the use of a generator unacceptable. In such cases, it is recommended to use specialized UPS with an external large capacity battery pack.
Under the protection of the UPS
Interruptions in information systems often lead to large financial losses, so you have to take into account the threat of poor-quality power supply, possible interruptions and even long-term power outages.
In the world, more than 40% of the sold uninterruptible power systems is used to protect servers, storage systems, network equipment. About 60% of UPS consumption accounts for local networks, telecommunications and data centers, a significant amount is used in industry, since many manufacturing processes require high-quality power supplies.
About a quarter of the world's UPS sales account for devices with a capacity of less than 1 kVA, and about half of sales for devices with a capacity of up to 5 kVA. Usually they are used to protect PCs and entry-level servers. In Russia, no more than 15% of users protect their PCs with the help of UPS - most are content with a network filter.
The increase in the popularity of laptops is also not conducive to the demand for UPSs, however servers of any class and network equipment, office PBXs still need similar protection.
Unlike powerful UPSs (over 20 kVA), whose life cycle reaches 20 years, low-power power supplies are designed for a five-year service life, but a replaceable battery pack (the most short-lived part of the device) allows them to extend their operation.
In small offices, backup or line-interactive UPSs are commonly used. The latter are relatively inexpensive, have acceptable functionality and a sufficient class of protection. More than half of manufacturers produce UPS of small and even medium power in South-East Asia under OEM contracts.
For low-cost “simple” UPSs, the development trend has been to bring them closer in functionality and efficiency (such as maintenance bypass for hot-swappable or equipment repair, controlled sockets and extended equipment) to “big” UPS.
When choosing a UPS, you should consider the warranty period for the device itself and its components, for example, batteries. Give preference to well-known manufacturers who specialize in the manufacture of such equipment. Decide on the maximum number and type of outlets for the connected devices. In cases where, in addition to periodic outages, there are problems with power supply parameters, it is necessary to install linear-interactive devices.
In general, do not follow the battery life, it usually takes up to 5 minutes at 100% load. It is better to choose a model with additional battery modules or buy a generator. It is cheaper than spent on sealed, maintenance-free batteries.
Uninterruptible power supplies protect computer equipment from power outages. A good UPS will reliably protect electronic devices from overloads, will allow you to save all the data and shut down the system correctly in the event of a power outage. It is better not to save on the price of the device, and to buy at least a linear-interactive UPS, and to protect critical systems use a double-conversion UPS.
UPS in data center
Interruptions in the work of the data center seriously damage their customers and the image of the companies themselves. Therefore, it is important for owners to find effective solutions to improve the power supply reliability of their data centers. Global manufacturers of uninterruptible power systems for data centers offer their options for the implementation of UPS.
What are the main requirements for the "UPS for data center"? This is high reliability (taking into account the system recovery time, i.e. the availability factor is not the MTBF parameter); high efficiency at partial load (50-80%), which directly affects the heat generation and efficiency of the equipment; support of parallel operation with capacity increase or increase in the degree of redundancy; scalability; high input and output power factor and low harmonic distortion of the input current, which is especially important when organizing backup power from the diesel generator set.
Other important factors are compactness of systems, support for parallel operation, low heat generation, intelligent battery charge management, simple maintenance and support, improved server shutdown capabilities (there are software versions that allow correct shutdown of virtual machines), management / monitoring tools, including remote, the possibility of simple and intuitive switching to the external bypass with protection from incorrect personnel actions, good support with side of the equipment manufacturer.
In the absence of a backup power supply system from DGU, the battery life can be increased by using external battery cabinets. Among the mandatory functions of high-end UPSs are intelligent battery charge management systems, equipment warning equipment about low battery power. The use of energy-efficient UPSs in the data center helps to reduce power consumption, while the power and reliability of uninterruptible power supplies remain unchanged.
Double-conversion UPSs provide the highest degree of protection against various power outages, since IT systems are completely immune to the effects of the power supply and are powered from the UPS directly. When using such a UPS, the equipment is protected from problems associated with voltage drops, power failure and other possible power failures. For this reason, double-conversion UPSs are used to provide power to servers, network-sensitive equipment, and other critical devices on which data center operation depends. In addition, double-conversion UPSs have a large arsenal of functions as well as flexible scalability.
FSP Group some time ago caught the trends of the growing data center market and began to produce specialized equipment, which is designed to provide telecom service providers with the necessary energy sources. FSP's CUSTOS 9X double conversion uninterruptible power supplies cover a power range from 1K to 10K.

Double-conversion UPS FSP Custos 9X + 10K.
For example, UPS Custos 9X + 10K has the following design features:
- Output power factor 0.9
- Informative and clear LCD display with interchangeable orientation
- Rack / Tower version
- Programmable outputs
- 50 / 60Hz frequency conversion mode
- ECO and Advanced ECO power saving modes
- Emergency Power Off (EPO)
The package with the UPS includes ViewPower software with the support of the Russian language, which allows you to remotely monitor the parameters of the uninterruptible power supply, set the schedule of switching on and off, and receive notifications of alarm events by mail or SMS.
UPS with dual voltage converter FSP Custos 9X + series can be used in conjunction with additional battery packs, there is the possibility of hot-swappable power supplies.
These are the UPSs who use the hosting provider RUVDS to ensure the smooth operation of the equipment in their data center .. Its uninterrupted power supply system is built according to the classical scheme. The data center is powered by two substations that power the data center via two independent lines. The facility has a set of UPS and DGS (redundancy scheme - N + 1).
Each physical server is connected to an uninterruptible power supply. If these components suddenly fail, then diesel generators will be put into operation, which will provide the data center with electricity until the substation problems are resolved. This is an important component of high reliability VPS-hosting.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/319588/
All Articles