Trends and events in the world of web technologies in 2016

Photo: Flickr / Dennis Skley / CC
The beginning of the year is an excellent occasion to talk again about the interesting events of the recent past. But we are not interested in everything, but how our favorite industry has evolved - the web. So, we present to your attention a selection of key events and trends that took shape in 2016 and will influence what the Internet will become in the near future.
')
Major releases of the year
Talking about the most important events in the world of the web cannot be started without a brief overview of the major releases of important products for the industry - and the year was rich in new launches.
Large-scale news last year - release of the release candidate Webpack 2.2. The significance of this release is somewhat degrading to the not entirely clear numbering - in fact, this is not a small update “2.2”, but a full-fledged large version 2.0, which includes updates and bug fixes that were contained in previous releases.
Grunt 1.0 was also released (and then release candidate 1.0.1 ). In addition to the narrowly focused thematic changes, there are also more noticeable ones - like new products in the API and changes in the work of npm-scripts. The jQuery developers who presented version 3.0 also pleased their users. A big deal, considering that work on it has been going on since 2014.
Google and its developers, who finally presented the final release of Angular 2.0, are not far behind their colleagues. The new version of the framework is aimed at improving the support of modern browsers and facilitating mobile development ( review of innovations ). In addition, Angular developers recommend application creators to use Microsoft's TypeScript product.
Speaking of TypeScript: a beta version 2.0 was introduced in July 2016, and its final release in September. In the publication devoted to release 2.0, the developers told about new features of the language - according to them, the main goal was to increase the productivity of development, to implement the compliance of the product with evolving ECMAScript and to support a wide range of JavaScript libraries and tools. Among the most striking innovations are the unions tagged , the type never , the types this and glob support in
tsconfig .Security and Availability
Mozilla's Observatory project has been launched - it helps developers, administrators and security specialists analyze the level of site security and enhance it.
One of the most talked about browsers of the year was Edge from Microsoft. In the course of various tests, he showed the best results in blocking information security threats. Edge, among other things, is the first browser to support all HTML5 accessibility features.
In addition, Google Chrome browser - starting with the 56th version - has learned to identify pages that may carry potential threats to information security. Now users will be warned that the page on which they are located is transmitting data in an insecure way - these can also be passwords with bank details. The project team has noted in its blog that in the future it plans to mark all HTTP sites as unsafe - it is reported that some users are already seeing new markings.
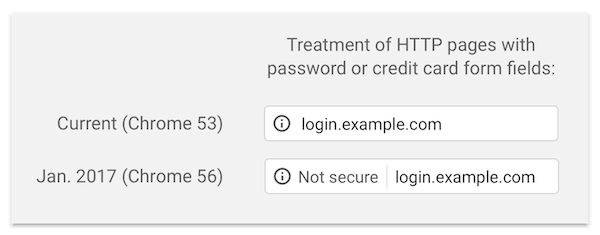
How potentially insecure pages were shown in old and new versions of Chrome
In turn, the developers Safari talked about the implementation of the updated security policy (Content Security Policy 2). Among the important innovations - a more rigorous approach to the connected content.
Changes occurred not only at the level of specific projects, but also in the area of standards. First of all, was published a document Content Security Policy 3 , improvements which have already started. For example, among the novelties in the draft that distinguish it from the previous version of the document are the return of the frame-src directive (imposes a restriction on what URLs can be loaded into the
iframe ) and the appearance of the directive worker-src (it imposes restrictions on what URLs can boot as Worker , SharedWorker , ServiceWorker ).Javascript update
The past year was a turning point in the distribution of a new version of JavaScript, called ES2015 (formerly ES6). In particular, its support appeared in WebKit-browsers . Safari developers were the first to implement 100% support - the level of support for ES2015 by different browsers is presented in the table .
ES2015 includes a variety of language enhancements and useful new features , while maintaining the usual JS syntax - unlike CoffeeScript or TypeScript.
The rapid development of CSS
This news allows us to understand what a big path the CSS technology actually went: this December turned into 20 years of the first recommendation of CSS 1. And the development is still very active (the events below are in confirmation of this thesis).
Published version of the candidate in the recommendations of the CSS Grid Layout. Despite not the fastest development of technology (the first draft was written in 2011, and the implementation was available in IE 10), experts agree that it will have a powerful influence on the development of the web and working with CSS in the coming years.
The methodology of web development originated in the depths of “Yandex” and the set of BEM libraries and frameworks (Block-Element-Modifier) is also successfully developing. Smoothes it, as it seems to some, shortcomings, which include long class names. However, experiments show that there is no need to minimize the BEM code: it does not allow for greater compactness and only makes the code more confusing.
Of the other good news: the
position: sticky CSS attribute returned to the Google Chrome browser, which allows you to capture an element in the viewport, hanging-punctuation: first appeared in WebKit due to the hanging-punctuation: first property, and interactive form validation was implemented in Safari. In addition, CSSO came out of the coma: the project has a new maintainer Roman Dvornov, who released the version of the CSSO optimizer 1.6 . It includes code cards, understandable errors, and also works “at least 2 times faster,” according to the developers.As for the development of standards, there are interesting events here. For example, the CSS Level 2 Revision 2 (CSS 2.2) Specification was published . In addition, a new
max-lines property is described in the draft CSS Overflow document: it can be used to break a block into fragments by the number of lines.But perhaps the main news on this background is that the W3C has published the CSS specification of the Flexible Box Layout Module Level 1 as a candidate recommendation. Experts immediately noted a more logical approach to working with existing implementation bugs - in many cases they became “features,” such as the behavior of table cells in a Flex container in Chrome.
HTTP / 2 conquers the web
In 2015, an important event occurred in the world of web technologies: a new version of the HTTP protocol was approved and standardized. It received the name HTTP / 2. Its support is implemented in widely used Apache, Nginx, IIS web servers and most popular browsers.
Using the new version of the protocol is growing rapidly. If in the middle of 2015, the percentage of websites and web services that switched to it was only 0.4%, by the beginning of 2016 it was already 6.5%, and in January 2017, 11.2% of all sites use HTTP / 2. It is obvious that every day this percentage will grow.
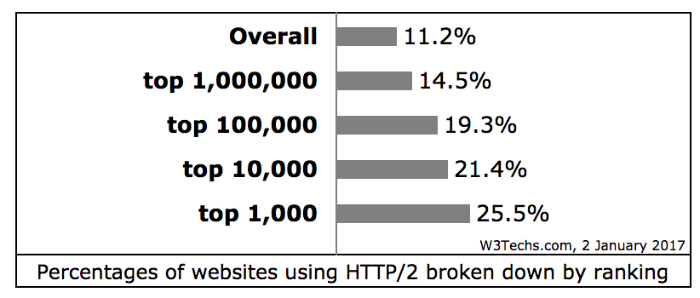
Statistics at the beginning of January 2017
More API for god API
The past year has become a real “year of new APIs”: a breathtaking number of new useful interfaces has appeared. And this is good.
Here are some useful interfaces that appeared in the past year:
- gyroscope ;
- magnetometer ;
- accelerometer ;
- API for outputting web content to external devices (projectors, screens, televisions).
The developers of Chromium have formulated a description of the new API, the purpose of which is to make DOM operations asynchronous. For this, the functions asyncAppend, finish, cancel are presented.
In addition, Dev.Opera published an introduction to the Web Bluetooth API - this technology is used to interact with various devices via Bluetooth directly from the browser - without having to install many applications for each gadget.
There are new (and old) interesting editors.
Visual Studio developers introduced the free and open VS Code editor. In fact, this is the online editor of Visual Studio Online (code name - Monaco), which is made cross-platform with the help of the GitHub Electron framework. The output was a fast and efficient environment for web developers.
It looks like VS Code
"Resurrection" of the year: from the "dead" rose the famous Dreamweaver. Once one of the most popular editors for web developers in recent years has lost its audience: the product has become less and less convenient for this category of users. However, in 2016, the project team seems to have decided to rectify the situation. Dreamweaver received a new engine, a redesigned editor interface, integration with Git, the possibility of preview code. The project is now frankly unpopular, but there are already positive reviews about the update.

New Dreamweaver interface
Icon fonts live the last days
The evolution of the web continues - in addition to the emergence of new technologies and approaches, this means the decline of old ones. One of such representatives of the world of the “warm, lamp web” living the last days is icon fonts. The events of the past year make it clear that they have little time left to live.
An eloquent fact: GitHub refused to use icon fonts in favor of SVG icons.
At the same time, web typography does not stand still: new interesting concepts appear. For example, at one of the core conferences, representatives of Adobe, Microsoft, Apple and Google implemented support for variable fonts on the web using OpenType.

Sunset Flash continues
Not only iconic fonts are not doing very well - they continue their way to the dustbin of history and Flash. More and more development companies are abandoning this technology. So, at the end of the summer, Google Chrome developers announced that, starting from December 2016, HTML5 would be the “default” choice - with the exception of those sites that only support Flash, but these are now a clear minority. Background Flash is blocked even earlier - in September.
Mozilla also supported the general trend towards abandoning Flash - in Firefox, Flash content was blocked for security for a long time, and since the summer, content that has no value to the user has been blocked. According to the developers, this not only improves user safety, but also allows for improved performance and reduced energy consumption.
HTML5 evolves
The HTML5 standard continues to evolve. Last year, its specification version 5.1 received the status of the official recommendation of the W3C.
Now the attention of the developers of the standard is focused on the future, so work has begun on the specification of HTML 5.2, which now has the status of a working draft (Working Draft), published for discussion by the professional web community. The document contains many interesting innovations and recommendations - for example, its developers insist that you should not disable viewport scaling.
Results
The developers of the basic technologies of the modern web update their products, more and more attention is paid to security and accessibility, the number of useful APIs for solving various problems is constantly growing, outdated technologies and approaches are finally falling out of use, and CSS and HTML5 are developing most actively.
Everything suggests that the evolution of the web will continue in 2017 - which means that soon we will see more new products, APIs, technologies and standards.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/319458/
All Articles