Economy of ideas. Composable infrastructure. HPE Synergy
In a modern business environment with a high level of competition, it has become much easier to offer new innovative solutions - everything that helps to manage resources more efficiently and get faster returns will take root very well. Cloud and mobile computing combined with the growing popularity of social networks have opened up unprecedented opportunities for businesses to reach new customers with innovative products and services.

This is called the "Economy of Ideas" (Idea Economy). It allows new businesses and new projects to quickly occupy their niche in the industry, while often their better-known competitors have to make significant efforts to maintain their positions. Success in the era of the economy of ideas is due to the ability not only to design configurations according to specifications or implement business projects, but to implement the ideas themselves, and do it faster than competitors. Under these conditions, great responsibility falls on the shoulders of IT managers, who are forced to work in two completely different and conflicting directions.
The first direction - ensuring the continuous operation of the enterprise. This is the traditional responsibility of the IT department manager, which involves managing applications such as enterprise resource planning, collaboration tools, databases, etc. The goal is to ensure high availability of systems and minimize costs and risks. In a traditional information system, everyone is usually comfortable with everything when applications are working properly, nothing breaks, and the department’s expenses fit into a predetermined budget framework.
')
However, in an era of radical change in the industry, advanced enterprises set higher goals for their IT departments. Business units place high demands on IT managers, which come down to providing full support for new applications and services. These are mobile, cloud applications, social networking applications and the Internet of Things (Internet of Things, IoT). All of these solutions take into account location, work in real time, have a personalized approach to customers and are focused on making a profit. In these new economic conditions, successful management of both traditional components of the IT system and new profit-oriented services is the basis for sustainable development.
The problem for untrained IT managers is that these two different directions of development require different approaches to infrastructure.
The traditional approach implies the work of traditional applications in a stable, unchanging environment. Applications work in a complex, fragmented structure that is usually optimized for specific applications. Scattered infrastructure components are often abundant, but resources are usually scarce. Few changes are made to maintain reliability and stability, this is done infrequently and is usually accompanied by lengthy inspections, procurement and deployment cycles. Making changes usually takes weeks or even months.
As for the economics of ideas, it cannot exist without a dynamic environment in which changes occur constantly, and solutions are implemented in a matter of hours or several days. Business units are looking for opportunities to quickly, without interrupting workflows, to deploy new applications and updates. To meet this demand, development and operations (DevOps) teams must deploy new infrastructures instantly. The problem is that traditional infrastructure does not provide this opportunity. In the new environment with new requirements, the IT department risks losing trust from the enterprise, since it is not able to meet the business needs fast enough. Their managers often find themselves in a situation where business units that have not achieved a dynamic service of a corporate data center from their IT, use the services of a public cloud to get the necessary capacity and flexibility. This leads to new problems, and IT directors lose control over the budget and often can no longer guarantee the safety and security of company data.
Most enterprises today have already invested heavily in traditional IT-models, which to some extent still ensure the continuity of business processes, but they can not provide the flexibility and speed needed to support the economy of ideas.
One of the alternatives is the cloud approach, which implies the use of internal resources to support traditional applications and external resources of the public cloud - to support new-style applications. "Cloud giants" offer attractive alternative solutions with low initial costs and the ability to increase or decrease the number of resources in accordance with the demand.
However, many enterprises have already experienced shock from the prices that they have requested to process and store large amounts of data in the cloud. In addition, almost every enterprise has confidential applications or data that they would not want to transmit to the public cloud. As mobile and cloud-based applications evolve from “engagement systems” that facilitate initial customer acquisition, into “accounting systems” used to store ever-increasing amounts of sensitive data from businesses and customers, the need for a more secure and secure alternative to the public cloud is only growing.
And here the concept of a two-tier model comes to the aid of IT departments, in which one level of infrastructure is used to ensure reliability and stability of developed applications and the second level - to ensure the flexibility and speed of mobile and cloud applications. Some analysts suggest that the two-tier model is the future of any information system, but this approach increases complexity and is not consistent with another requirement that most IT managers face: simplifying operations and reducing the total cost of ownership of an information system. Of course, IT departments would be happy to provide corporate data centers with the flexibility that the cloud can give them. However, this is hampered by the requirement to reduce operational complexity and costs. A new architecture is required that supports both models, an architecture that ensures the reliability of stable traditional environments, cloud flexibility, and the ability for DevOps to define the infrastructure as code. And all this should be combined in a single local infrastructure of the enterprise.
The infrastructure corresponding to both of these models should ensure the reliability and stability inherent in traditional environments, and at the same time the flexibility and dynamism inherent in the public cloud. It is these needs and solves the new concept of architecture.
Composable Infrastructure gives IT departments the ability to instantly provide infrastructure for each specific workload. It allows you to instantly allocate physical and virtual resources for applications, regardless of the style of applications or the type and amount of resources. Composable infrastructure has a unique feature - it is not limited to any computing paradigm, because it supports virtual machines, and deployments from scratch, and containers, and cloud applications.

Compatibility is not only a consistent improvement in server design or management software. This is a qualitatively new approach to infrastructure, a new architecture for the data center from the first to the last level, offering the enterprise a new concept of doing business. Composable infrastructure includes hardware and software that form a single infrastructure, reducing the complexity of operating traditional loads, and increasing the flexibility and speed of issuing new generations of applications and services.
In order to meet these high requirements, the composable infrastructure must have at least these three basic properties:
• Adaptable flexible resource pools — available computational, switching, and storage resources that are ready to support any physical or virtual workload from the time they are loaded and are instantly assembled to support specific applications and services;
• Software-defined management environment — tools for automating workloads based on templates for quickly introducing changes through software tools to ensure smooth operation;
• Unified interface - an open application programming interface (API) that provides one line of code to abstract each element of the infrastructure in accordance with the “infrastructure as code” model.
It is the combination of all these attributes that determines composability. In the absence of one of the attributes, some composability characteristics may occur, but all the advantages of a single composable infrastructure will not be available.
Composable infrastructure can be thought of as a set of flexible building blocks that can be quickly and automatically assembled and disassembled in accordance with changing workload requirements. That's what Frost & Sullivan’s latest information document says about this: “This infrastructure resembles the Lego building kit, in which, if necessary, blocks can be reproduced and programmed, today creating the Ninja temple from them, and tomorrow a racing car.” (How the Right Infrastructure Can Prepare Your Data Center for Business Disruptors, Frost & Sullivan 2015, h20195.www2.hpe.com/V2/getpdf.aspx/4AA6-2190ENW.pdf?ver=2 ).
Computing resources can be linked at the physical, virtual or container levels. Composite services for data processing can be defined at the level of blocks, files or objects - it all depends on the needs of the application. Using simple software commands and repeated patterns, resources are provided in the appropriate state (BIOS settings, firmware, drivers, protocols, etc.) and with the image of the operating system. Thanks to this, logical infrastructures are created almost instantly. Now, using a single line of code, IT professionals gain access to the computing capacity, memory, and storage resources needed for a particular application. Equipment can operate on virtually any workload base, and when this workload is not needed, resources are returned to the resource pool.
Composable infrastructure is a unique solution that helps to implement the concept of DevOps continuous service delivery. In a composable infrastructure environment, developers can use resource allocation patterns based on workloads, as well as a unified API that allows them to instantly and at the program level to provide resources from the available pool. At the same time, specialists do not need to thoroughly understand the elements of the basic physical equipment. Developers can deploy pure-hardware based applications, virtual machines, and containers using single application code. The Infrastructure as Code model provides DevOps with the following advantages:
• Shorter and simpler deployment cycles - a programmable infrastructure increases the efficiency of cooperation between developers and operation specialists;
• Acceleration and automation of the construction and integration processes - confident implementation of its own cloud infrastructure on a “pure hardware” using templates and a unified interface;
• Accelerate and automate testing - a unified API simplifies the deployment of multiple test environments by providing a recurring development process.
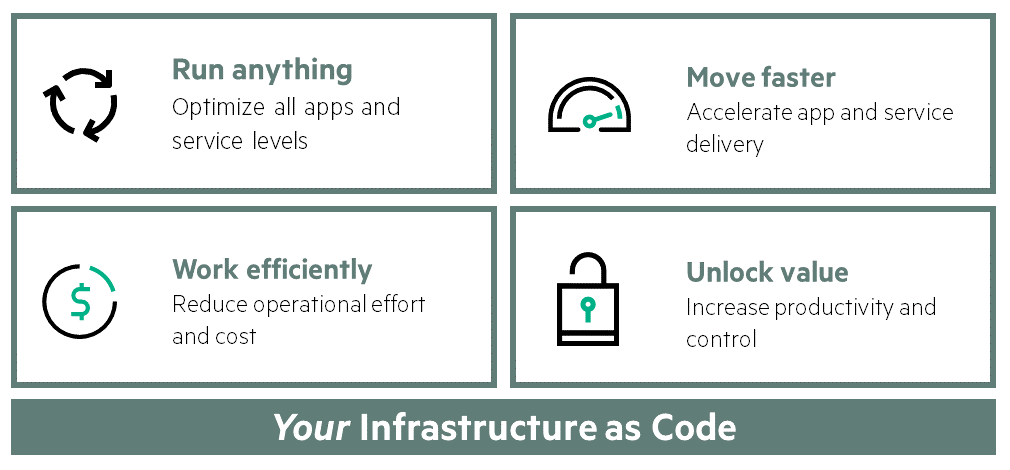
Composite infrastructure enables IT managers to more quickly, efficiently and cost-effectively deliver services, since they do not require the formation of two separate infrastructure environments to support both traditional and innovative applications:
• Run any workloads — optimize any application and store data based on a single infrastructure using adaptable pools of physical and virtual resources for computing, storage and switching
• Dynamic - accelerated provision of applications and services through a single interface that allows you to accurately and almost instantly assemble logical infrastructures;
• Efficient work - reduction of financial and labor costs due to internal software-defined analytics and impeccable template-based work;
• Realizing value - increasing productivity and increasing control over the operation of the data center by integrating and automating operations and applications in the infrastructure using a unified API.
For CIOs who need a more efficient way to support traditional applications, composable infrastructure will simplify day-to-day operations with easier deployment of physical and virtualized resources using repetitive patterns. And the provision of resources on demand will make it possible to eliminate their excessive allocation and “attachment”. Composable infrastructure is a way to protect investment in infrastructure in the future, it is a step towards successful competition in the era of the economy of ideas.
To IT department managers who need their own Internet resources or resources with cloud capabilities, the composable infrastructure allows you to maintain a two-tier infrastructure model without creating two separate infrastructures. For the IT departments of enterprises, this is the best alternative, providing reliable and stable support for traditional applications and at the same time providing the DevOps teams with the infrastructure for continuous development.
For IT directors, in organizations whose business units use external IT services, such as a public cloud, composable infrastructure, is a source of funds that fundamentally change the role of IT managers in meeting business needs. Such an infrastructure is a great alternative and, at the same time, a reliable and secure proprietary solution capable of supporting the work of innovative applications and services in enterprises.
HPE Synergy, the first and so far the only platform in the world that was originally designed for composable infrastructure, allows you to create a unified infrastructure that simplifies the management of traditional workloads and increases the speed of new applications and services. Using a single interface, HPE Synergy assembles physical and virtual pools of computing resources, data storage systems and a switching network in any configuration, for any application.

HPE Synergy Frame 12000 Chassis
Being an extensible platform, it allows the use of a wide range of applications and operating models, from virtualization to a hybrid cloud, and also fully supports DevOps - the concept of continuous integration and application and service development.
HPE Synergy's fully programmable interface is compatible and seamlessly integrates with many other popular and familiar management tools such as Microsoft Systems Center, Red Hat, and VMware vCenter, so you can continue to use your favorite tools to manage virtualized resources. HPE OneView will also protect your investment in the future, as it seamlessly integrates with open source-based automation tools and DevOps tools such as Chef, Docker, and OpenStack, fully supporting the infrastructure-based code environment.
Composable infrastructure allows IT professionals to easily perform their traditional duties and more effectively support business processes, while providing new mobile and cloud applications and services that improve customer service and create new opportunities for profit. With a composable infrastructure, IT departments successfully manage workflows based on a single data center architecture.
As mentioned above, composability is defined by three elements: adaptable resource pools, software-defined analytics, and a unified API that abstracts each element of the infrastructure. This combination of three elements, working in close relationship and creating the basis of a single composable infrastructure, takes the work of IT departments to a completely new, better and more efficient level.
CIOs can operate their data centers more efficiently. Operating engineers are easier to solve the problem of automating and speeding up internal work processes. , . , -, , .
Hewlett Packard Enterprise , . HPE , , , , , .

This is called the "Economy of Ideas" (Idea Economy). It allows new businesses and new projects to quickly occupy their niche in the industry, while often their better-known competitors have to make significant efforts to maintain their positions. Success in the era of the economy of ideas is due to the ability not only to design configurations according to specifications or implement business projects, but to implement the ideas themselves, and do it faster than competitors. Under these conditions, great responsibility falls on the shoulders of IT managers, who are forced to work in two completely different and conflicting directions.

The first direction - ensuring the continuous operation of the enterprise. This is the traditional responsibility of the IT department manager, which involves managing applications such as enterprise resource planning, collaboration tools, databases, etc. The goal is to ensure high availability of systems and minimize costs and risks. In a traditional information system, everyone is usually comfortable with everything when applications are working properly, nothing breaks, and the department’s expenses fit into a predetermined budget framework.
')
However, in an era of radical change in the industry, advanced enterprises set higher goals for their IT departments. Business units place high demands on IT managers, which come down to providing full support for new applications and services. These are mobile, cloud applications, social networking applications and the Internet of Things (Internet of Things, IoT). All of these solutions take into account location, work in real time, have a personalized approach to customers and are focused on making a profit. In these new economic conditions, successful management of both traditional components of the IT system and new profit-oriented services is the basis for sustainable development.
The problem for untrained IT managers is that these two different directions of development require different approaches to infrastructure.
The traditional approach implies the work of traditional applications in a stable, unchanging environment. Applications work in a complex, fragmented structure that is usually optimized for specific applications. Scattered infrastructure components are often abundant, but resources are usually scarce. Few changes are made to maintain reliability and stability, this is done infrequently and is usually accompanied by lengthy inspections, procurement and deployment cycles. Making changes usually takes weeks or even months.
As for the economics of ideas, it cannot exist without a dynamic environment in which changes occur constantly, and solutions are implemented in a matter of hours or several days. Business units are looking for opportunities to quickly, without interrupting workflows, to deploy new applications and updates. To meet this demand, development and operations (DevOps) teams must deploy new infrastructures instantly. The problem is that traditional infrastructure does not provide this opportunity. In the new environment with new requirements, the IT department risks losing trust from the enterprise, since it is not able to meet the business needs fast enough. Their managers often find themselves in a situation where business units that have not achieved a dynamic service of a corporate data center from their IT, use the services of a public cloud to get the necessary capacity and flexibility. This leads to new problems, and IT directors lose control over the budget and often can no longer guarantee the safety and security of company data.
Most enterprises today have already invested heavily in traditional IT-models, which to some extent still ensure the continuity of business processes, but they can not provide the flexibility and speed needed to support the economy of ideas.
One of the alternatives is the cloud approach, which implies the use of internal resources to support traditional applications and external resources of the public cloud - to support new-style applications. "Cloud giants" offer attractive alternative solutions with low initial costs and the ability to increase or decrease the number of resources in accordance with the demand.
However, many enterprises have already experienced shock from the prices that they have requested to process and store large amounts of data in the cloud. In addition, almost every enterprise has confidential applications or data that they would not want to transmit to the public cloud. As mobile and cloud-based applications evolve from “engagement systems” that facilitate initial customer acquisition, into “accounting systems” used to store ever-increasing amounts of sensitive data from businesses and customers, the need for a more secure and secure alternative to the public cloud is only growing.
And here the concept of a two-tier model comes to the aid of IT departments, in which one level of infrastructure is used to ensure reliability and stability of developed applications and the second level - to ensure the flexibility and speed of mobile and cloud applications. Some analysts suggest that the two-tier model is the future of any information system, but this approach increases complexity and is not consistent with another requirement that most IT managers face: simplifying operations and reducing the total cost of ownership of an information system. Of course, IT departments would be happy to provide corporate data centers with the flexibility that the cloud can give them. However, this is hampered by the requirement to reduce operational complexity and costs. A new architecture is required that supports both models, an architecture that ensures the reliability of stable traditional environments, cloud flexibility, and the ability for DevOps to define the infrastructure as code. And all this should be combined in a single local infrastructure of the enterprise.

The infrastructure corresponding to both of these models should ensure the reliability and stability inherent in traditional environments, and at the same time the flexibility and dynamism inherent in the public cloud. It is these needs and solves the new concept of architecture.
Composable Infrastructure gives IT departments the ability to instantly provide infrastructure for each specific workload. It allows you to instantly allocate physical and virtual resources for applications, regardless of the style of applications or the type and amount of resources. Composable infrastructure has a unique feature - it is not limited to any computing paradigm, because it supports virtual machines, and deployments from scratch, and containers, and cloud applications.

Compatibility is not only a consistent improvement in server design or management software. This is a qualitatively new approach to infrastructure, a new architecture for the data center from the first to the last level, offering the enterprise a new concept of doing business. Composable infrastructure includes hardware and software that form a single infrastructure, reducing the complexity of operating traditional loads, and increasing the flexibility and speed of issuing new generations of applications and services.
In order to meet these high requirements, the composable infrastructure must have at least these three basic properties:
• Adaptable flexible resource pools — available computational, switching, and storage resources that are ready to support any physical or virtual workload from the time they are loaded and are instantly assembled to support specific applications and services;
• Software-defined management environment — tools for automating workloads based on templates for quickly introducing changes through software tools to ensure smooth operation;
• Unified interface - an open application programming interface (API) that provides one line of code to abstract each element of the infrastructure in accordance with the “infrastructure as code” model.
It is the combination of all these attributes that determines composability. In the absence of one of the attributes, some composability characteristics may occur, but all the advantages of a single composable infrastructure will not be available.
Composable infrastructure can be thought of as a set of flexible building blocks that can be quickly and automatically assembled and disassembled in accordance with changing workload requirements. That's what Frost & Sullivan’s latest information document says about this: “This infrastructure resembles the Lego building kit, in which, if necessary, blocks can be reproduced and programmed, today creating the Ninja temple from them, and tomorrow a racing car.” (How the Right Infrastructure Can Prepare Your Data Center for Business Disruptors, Frost & Sullivan 2015, h20195.www2.hpe.com/V2/getpdf.aspx/4AA6-2190ENW.pdf?ver=2 ).
Computing resources can be linked at the physical, virtual or container levels. Composite services for data processing can be defined at the level of blocks, files or objects - it all depends on the needs of the application. Using simple software commands and repeated patterns, resources are provided in the appropriate state (BIOS settings, firmware, drivers, protocols, etc.) and with the image of the operating system. Thanks to this, logical infrastructures are created almost instantly. Now, using a single line of code, IT professionals gain access to the computing capacity, memory, and storage resources needed for a particular application. Equipment can operate on virtually any workload base, and when this workload is not needed, resources are returned to the resource pool.
Composable infrastructure is a unique solution that helps to implement the concept of DevOps continuous service delivery. In a composable infrastructure environment, developers can use resource allocation patterns based on workloads, as well as a unified API that allows them to instantly and at the program level to provide resources from the available pool. At the same time, specialists do not need to thoroughly understand the elements of the basic physical equipment. Developers can deploy pure-hardware based applications, virtual machines, and containers using single application code. The Infrastructure as Code model provides DevOps with the following advantages:
• Shorter and simpler deployment cycles - a programmable infrastructure increases the efficiency of cooperation between developers and operation specialists;
• Acceleration and automation of the construction and integration processes - confident implementation of its own cloud infrastructure on a “pure hardware” using templates and a unified interface;
• Accelerate and automate testing - a unified API simplifies the deployment of multiple test environments by providing a recurring development process.
Composite infrastructure enables IT managers to more quickly, efficiently and cost-effectively deliver services, since they do not require the formation of two separate infrastructure environments to support both traditional and innovative applications:
• Run any workloads — optimize any application and store data based on a single infrastructure using adaptable pools of physical and virtual resources for computing, storage and switching
• Dynamic - accelerated provision of applications and services through a single interface that allows you to accurately and almost instantly assemble logical infrastructures;
• Efficient work - reduction of financial and labor costs due to internal software-defined analytics and impeccable template-based work;
• Realizing value - increasing productivity and increasing control over the operation of the data center by integrating and automating operations and applications in the infrastructure using a unified API.
For CIOs who need a more efficient way to support traditional applications, composable infrastructure will simplify day-to-day operations with easier deployment of physical and virtualized resources using repetitive patterns. And the provision of resources on demand will make it possible to eliminate their excessive allocation and “attachment”. Composable infrastructure is a way to protect investment in infrastructure in the future, it is a step towards successful competition in the era of the economy of ideas.
To IT department managers who need their own Internet resources or resources with cloud capabilities, the composable infrastructure allows you to maintain a two-tier infrastructure model without creating two separate infrastructures. For the IT departments of enterprises, this is the best alternative, providing reliable and stable support for traditional applications and at the same time providing the DevOps teams with the infrastructure for continuous development.
For IT directors, in organizations whose business units use external IT services, such as a public cloud, composable infrastructure, is a source of funds that fundamentally change the role of IT managers in meeting business needs. Such an infrastructure is a great alternative and, at the same time, a reliable and secure proprietary solution capable of supporting the work of innovative applications and services in enterprises.
HPE Synergy, the first and so far the only platform in the world that was originally designed for composable infrastructure, allows you to create a unified infrastructure that simplifies the management of traditional workloads and increases the speed of new applications and services. Using a single interface, HPE Synergy assembles physical and virtual pools of computing resources, data storage systems and a switching network in any configuration, for any application.

HPE Synergy Frame 12000 Chassis
Being an extensible platform, it allows the use of a wide range of applications and operating models, from virtualization to a hybrid cloud, and also fully supports DevOps - the concept of continuous integration and application and service development.
HPE Synergy's fully programmable interface is compatible and seamlessly integrates with many other popular and familiar management tools such as Microsoft Systems Center, Red Hat, and VMware vCenter, so you can continue to use your favorite tools to manage virtualized resources. HPE OneView will also protect your investment in the future, as it seamlessly integrates with open source-based automation tools and DevOps tools such as Chef, Docker, and OpenStack, fully supporting the infrastructure-based code environment.
Composable infrastructure allows IT professionals to easily perform their traditional duties and more effectively support business processes, while providing new mobile and cloud applications and services that improve customer service and create new opportunities for profit. With a composable infrastructure, IT departments successfully manage workflows based on a single data center architecture.
As mentioned above, composability is defined by three elements: adaptable resource pools, software-defined analytics, and a unified API that abstracts each element of the infrastructure. This combination of three elements, working in close relationship and creating the basis of a single composable infrastructure, takes the work of IT departments to a completely new, better and more efficient level.
CIOs can operate their data centers more efficiently. Operating engineers are easier to solve the problem of automating and speeding up internal work processes. , . , -, , .
Hewlett Packard Enterprise , . HPE , , , , , .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/319300/
All Articles