What to do if the cables have ears, or a steganographic proxy
Good afternoon. Today I will tell you about one type of paranoia associated with the latest trends in the state protection of the population from information, and the method of its treatment.

The fact is that recently the active distribution of Roskomnadzor, SORM, gold shields, root certificates, black FBI vans and other methods of interception / restriction / substitution of traffic on everyone’s favorite Internet began.
Against this background, many began to have a disease, beautifully described by the phrase "the walls have ears." And it would have been without a reason - but all your data goes through routes that are unknown to you, through black boxes that do not belong to you, servers that you do not control, and soon all this will also be saved. Well, how can you not get nervous?
')
They say encryption will save everyone. But is it? By omitting the problems of classical and modern cryptography, one way or another, encrypted traffic can always be relatively easy to detect and tritely cover the transmission channel. And here steganography comes to the rescue.
To penetrate and understand why we need it, let's look at the classical scheme of transferring traffic from Alice to Bob on the Internet:

We take into account that the Internet and communication channels in it are beyond our control and vulnerable by design. Moreover, between Alice and Bob, there is someone who controls the transmission medium and restricts ( listening to / inserting her word) their message exchange.
In fact, transmission via data via the Internet increasingly resembles the problem of prisoners.
And the scheme looks like this:

Where Willy is not a gardener, as it seems at first glance, but a security guard, restricting the transfer of any messages to Bob. Alice is a free man (or a prisoner in another cell), with whom Bob wants to communicate bypassing the guard.
Accordingly, the task of steganography is that the security guard simply does not notice the exchange of messages. And who exactly is the guard - pkn or FBI van - special cases.
Depending on the situation, between Alice and Bob can be both a controlled communication channel by Willy, his (channel) may not be in principle. For the sake of truth, it is worth noting that few people completely cut off communication channels, and even behind a great firewall you can, if you wish, sit on Facebook. So this case will be the first and easiest option.
The steganographic channel will then be created simply on top of the previously known channel controlled by Willy. Consider as an example the implementation using ordinary sockets.
A stegokanal is created by connecting Bob to Alice via a socket on a pre-set port.
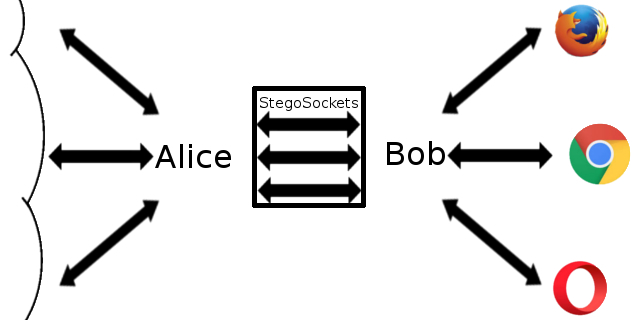
The resulting scheme is simple and reliable. But, this is not exactly steganography. For Willy, it is quite obvious that the exchange of pictures on non-standard ports is no accident. Partially, you can reduce the level of suspicion using standard ports and protocols. For example, file sharing via FTP. In general, one of the fastest and most convenient options. You can use it as long as the degree of inadequacy and suspicion on the part of Willy is not very high.
Then, to create a steganographic tunnel (a channel without a direct link), a shared resource is needed. A classic example is social networks - accessible from most points of the world, public. Ideal for the exchange of steganograms, not quite suitable for proxies due to the need for a large flow of information. However, sekyurnost requires sacrifice. In this case, the victim will fall speed, but more on that later. Consider the implementation using the VC as a public medium of exchange:
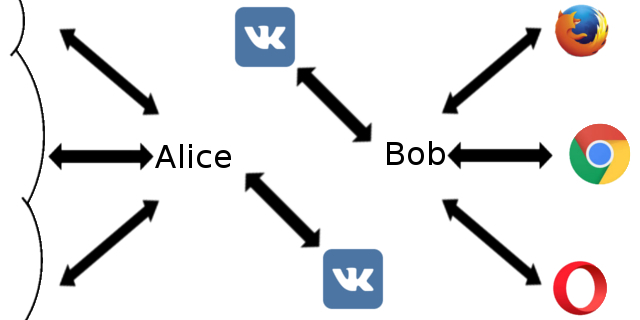
This scheme relies on third-party service, which means it is completely dependent on it. On the other hand, the exchange of pictures between users does not cause any suspicion, even with a high frequency (bots, for the most part, are legal). From the minuses we get reduced throughput and the ability to be without a communication line at the right moment - if usually a spare channel is optional, then this is a prerequisite for work.
Bob is implemented as a normal proxy relay type [Socket-Stegochanel], listening to a specific port. He hides all the data arriving at him in stegocontainers using a pre-negotiated algorithm and sends it to Alice's stego channel. All recording and extraction operations are carried out with a secret established beforehand (in steganography, in principle, it is possible without it, there are no restrictions on the implementation).
Alice of the [Stegochanel-Socket] type receives all traffic from Bob through the stegokanal, extracts it from the stegocontainers and redirects to the real proxy the server you want to use, allocating a separate connection to the proxy for each instance of the stegokanal (to avoid confusion). After all, who knows in advance what kind of traffic and why you need to send, right?
For testing, I rented a cheap ARM server in France as a proxy server, deployed Ubuntu 16.10 and Squid along with a repeater on it. All measurements were taken from home with the Internet at 5 Mbps through ADSL of the national Russian provider. If someone wants to check at normal speed, I’ll leave links to GitHub at the end.
As a proof of concept, I implemented a stegokanal over sockets. If there is interest, I will conduct similar testing for implementation with VK as a medium of exchange. The algorithm is its own version of the LSB method with a maximum capacity of about a quarter of bytes of the total number of pixels, working with images without compression, which I may write about later. At first, a single image of Che Guevara was used as a container in png with a resolution of 518x587.
Test results as a proxy in firefox without any plug-ins and add. settings:
It should be noted that such speeds (very modest, especially if you look at the calendar) are explained not only by the fact that steganography transmits an excessive amount of information, but also by the overhead of the steganographic algorithm itself. And it would be strange to expect from an ARM server for 3 green presidents something unusual in terms of performance. Renting a faster server gives a strong acceleration (2 times on the old weak x86 server).
By turning off images and media elements, turning on the adblock, the speed can be increased. Moving the same method about 10 years (15?) Ago, we obtain the corresponding page loading speed corresponding to the same time. But in general, the conclusion remains the same - such a steganographic proxy is only suitable for emergency cases.
Impressions of such an Internet are far from positive. Perhaps with other methods of steganography, or simply by optimizing mine, you can achieve great results. However, so far, the resulting Proof of Concept only says that such a proxy is only suitable for emergency cases. That, in fact, is not particularly surprising. Or unexpectedly. Most of the problems with delays are timings when shaking hands in ssl. Here you have the universal plant https.
Having thought it over, it was decided to replace poor static Che Guevara with random images with minimal redundancy. After all, if you transmit not 16 times more information, but 4, then theoretically, we will get a nice bonus to speed. Fortunately, the generators of random images of a given size on the Internet is full.
Results from retesting:
It is already possible to live with such an Internet, especially if there are few alternatives. Steganographic stability falls with an increase in the ratio of noise / useful information, to donate or not - it's not up to me to decide.
On this I consider the experiment completed. The sources, binaries, instructions for use and help are on the github below. If there are additional questions - I will wait in the comments.
→ GitHub

World of censorship
The fact is that recently the active distribution of Roskomnadzor, SORM, gold shields, root certificates, black FBI vans and other methods of interception / restriction / substitution of traffic on everyone’s favorite Internet began.
Against this background, many began to have a disease, beautifully described by the phrase "the walls have ears." And it would have been without a reason - but all your data goes through routes that are unknown to you, through black boxes that do not belong to you, servers that you do not control, and soon all this will also be saved. Well, how can you not get nervous?
')
They say encryption will save everyone. But is it? By omitting the problems of classical and modern cryptography, one way or another, encrypted traffic can always be relatively easy to detect and tritely cover the transmission channel. And here steganography comes to the rescue.
To penetrate and understand why we need it, let's look at the classical scheme of transferring traffic from Alice to Bob on the Internet:

We take into account that the Internet and communication channels in it are beyond our control and vulnerable by design. Moreover, between Alice and Bob, there is someone who controls the transmission medium and restricts ( listening to / inserting her word) their message exchange.
In fact, transmission via data via the Internet increasingly resembles the problem of prisoners.
And the scheme looks like this:

Where Willy is not a gardener, as it seems at first glance, but a security guard, restricting the transfer of any messages to Bob. Alice is a free man (or a prisoner in another cell), with whom Bob wants to communicate bypassing the guard.
Accordingly, the task of steganography is that the security guard simply does not notice the exchange of messages. And who exactly is the guard - pkn or FBI van - special cases.
And what have the proxy?
- Bob is software on a controlled device, through which you really want free exchange of information, regardless of its position in the world.
- Willy is evil providers, regulators, corporate proxy servers, and others who want to stop this exchange.
- Alice is the gateway through which we receive information from the external (or other internal) world.
Depending on the situation, between Alice and Bob can be both a controlled communication channel by Willy, his (channel) may not be in principle. For the sake of truth, it is worth noting that few people completely cut off communication channels, and even behind a great firewall you can, if you wish, sit on Facebook. So this case will be the first and easiest option.
The steganographic channel will then be created simply on top of the previously known channel controlled by Willy. Consider as an example the implementation using ordinary sockets.
A stegokanal is created by connecting Bob to Alice via a socket on a pre-set port.

The resulting scheme is simple and reliable. But, this is not exactly steganography. For Willy, it is quite obvious that the exchange of pictures on non-standard ports is no accident. Partially, you can reduce the level of suspicion using standard ports and protocols. For example, file sharing via FTP. In general, one of the fastest and most convenient options. You can use it as long as the degree of inadequacy and suspicion on the part of Willy is not very high.
Now imagine that Willie forbade Bob to exchange messages with Alice. At all.
Then, to create a steganographic tunnel (a channel without a direct link), a shared resource is needed. A classic example is social networks - accessible from most points of the world, public. Ideal for the exchange of steganograms, not quite suitable for proxies due to the need for a large flow of information. However, sekyurnost requires sacrifice. In this case, the victim will fall speed, but more on that later. Consider the implementation using the VC as a public medium of exchange:

This scheme relies on third-party service, which means it is completely dependent on it. On the other hand, the exchange of pictures between users does not cause any suspicion, even with a high frequency (bots, for the most part, are legal). From the minuses we get reduced throughput and the ability to be without a communication line at the right moment - if usually a spare channel is optional, then this is a prerequisite for work.
And now about the implementation itself and what happened
Bob is implemented as a normal proxy relay type [Socket-Stegochanel], listening to a specific port. He hides all the data arriving at him in stegocontainers using a pre-negotiated algorithm and sends it to Alice's stego channel. All recording and extraction operations are carried out with a secret established beforehand (in steganography, in principle, it is possible without it, there are no restrictions on the implementation).
Alice of the [Stegochanel-Socket] type receives all traffic from Bob through the stegokanal, extracts it from the stegocontainers and redirects to the real proxy the server you want to use, allocating a separate connection to the proxy for each instance of the stegokanal (to avoid confusion). After all, who knows in advance what kind of traffic and why you need to send, right?
And how does it work?
For testing, I rented a cheap ARM server in France as a proxy server, deployed Ubuntu 16.10 and Squid along with a repeater on it. All measurements were taken from home with the Internet at 5 Mbps through ADSL of the national Russian provider. If someone wants to check at normal speed, I’ll leave links to GitHub at the end.
As a proof of concept, I implemented a stegokanal over sockets. If there is interest, I will conduct similar testing for implementation with VK as a medium of exchange. The algorithm is its own version of the LSB method with a maximum capacity of about a quarter of bytes of the total number of pixels, working with images without compression, which I may write about later. At first, a single image of Che Guevara was used as a container in png with a resolution of 518x587.
Test results as a proxy in firefox without any plug-ins and add. settings:
- wikipedia.org - 1:13;
- en.wikipedia.org - 2:01, after that, communication with the server continues, but the entire content is already loaded;
- google.com (.fr) - ~ 2m, hints do not work, search results are loaded by the minute;
- duckduckgo.com - did not load in 10 minutes;
- txti.es - ~ 3s per page. True, fast web pages;
- garfield.vexer.ru - 1:35. Advertising did not load (and the adblock is not needed);
- reddit.com - it loads for a very long time (more than 10 minutes), it loads something, but you hardly have enough patience;
- bing.com - 1:45 full download. ~ 50 seconds per search results page;
- jcgonzalez.com - not loaded;
- minergate.com - 4m;
- vk.com - ~ 1m, images load longer, dialogs run fast;
- linkedin.com - ~ 50c, but the huge image background will load for a long time;
- weather.com - not loaded;
It should be noted that such speeds (very modest, especially if you look at the calendar) are explained not only by the fact that steganography transmits an excessive amount of information, but also by the overhead of the steganographic algorithm itself. And it would be strange to expect from an ARM server for 3 green presidents something unusual in terms of performance. Renting a faster server gives a strong acceleration (2 times on the old weak x86 server).
By turning off images and media elements, turning on the adblock, the speed can be increased. Moving the same method about 10 years (15?) Ago, we obtain the corresponding page loading speed corresponding to the same time. But in general, the conclusion remains the same - such a steganographic proxy is only suitable for emergency cases.
Impressions of such an Internet are far from positive. Perhaps with other methods of steganography, or simply by optimizing mine, you can achieve great results. However, so far, the resulting Proof of Concept only says that such a proxy is only suitable for emergency cases. That, in fact, is not particularly surprising. Or unexpectedly. Most of the problems with delays are timings when shaking hands in ssl. Here you have the universal plant https.
Having thought it over, it was decided to replace poor static Che Guevara with random images with minimal redundancy. After all, if you transmit not 16 times more information, but 4, then theoretically, we will get a nice bonus to speed. Fortunately, the generators of random images of a given size on the Internet is full.
Results from retesting:
- wikipedia.org - 21s;
- en.wikipedia.org - 21s;
- google.com (.fr) - 23s to work, 45s to full load, 3s to issue;
- duckduckgo.com - 45s to work, 55s to full load;
- txti.es - instantly;
- garfield.vexer.ru - 1:10 with advertising, the next strips are loaded for 10 seconds each, since all the hardest is already in the cache;
- reddit.com - 44c without content, 1:20 with its preview;
- bing.com - 13c full download, 5c for issue with pictures;
- jcgonzalez.com - fell, but 404 issues quickly;
- minergate.com - 1m;
- vk.com - 23c, pages with messages of 10 seconds or more, depending on the content;
- linkedin.com - 40c;
- weather.com - not loaded;
It is already possible to live with such an Internet, especially if there are few alternatives. Steganographic stability falls with an increase in the ratio of noise / useful information, to donate or not - it's not up to me to decide.
On this I consider the experiment completed. The sources, binaries, instructions for use and help are on the github below. If there are additional questions - I will wait in the comments.
→ GitHub
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/319148/
All Articles