Wi-Fi on Linux will be faster
- let it be better small, but Feuerbach ...
Victor Pelevin "Generation Pi"
The recent release of the Linux kernel 4.9 is an excellent opportunity to talk about the upcoming WiFi overclocking. Immediately make a reservation - the post is not about how to increase the coverage area or change regulatory domains . You do not need to do anything of this; it is enough to update the kernel after the patches of the Dave Täht buffer-supporter are in a stable branch.
Significant increase in speed achieved by reducing the delay [1] and excessive buffering [2] in the network. Developers had to shovel mac80211 for this, remove something from above, add below, and after that network latency was reduced by an order of magnitude. Price issue? Patch in 200 lines. Details under the cut.
That Bufferbloat
Bufferbloat is excessive buffering in the network equipment of the provider, which leads to undesired data transfer delays. With a sufficiently loaded channel, each connection eats away milliseconds, which then turn into seconds and sometimes minutes of waiting. If the network delay is 1 second, then slashdot.org will load as long as 4 minutes!
# flent -l 300 -H server –streams=12 tcp_ndown & # wget -E -H -k -K -p https://www.slashdot.org ... FINISHED --2016-10-22 13:43:35-- Total wall clock time: 232.8s Downloaded: 62 files, 1.8M in 0.9s (77KB/s) The first team uses a python wrapper for netperf , it is a powerful tool for making control measurements. [3] network connections.
-l 300 # 5 -H server # server -streams=12 tcp_ndown #12 tcp download Flent loads the channel so that the connection is established with a second delay. The connection setup took 99.6% of the execution time , as a result the real speed dropped to a measly 77 KB / s. With zero delay, the same page loads in 8 seconds. Thus, the time of a circular path [4] and latency are more important than throughput .
On the side of the IS provider, it has the character of an epidemic , but it also suffices on the user equipment. For quite a while, each network driver was designed with the expectation of unrealistically high data buffering needs, as the developers optimized the packet scheduler for the highest speeds. However, their IRLs are rarely used during a WiFi connection. That's why the seals load slowly, and the video calls turn into torture. Check your IB without SMS and registration.
The trouble is that the main bufferbloat on the side of the provider, correcting the situation there, you get an increase in connection speed for free. Speedtest ISP Xfinity and Google Fiber .
Not to say that the case was limited to only whining. Since Linux 3.3, a whole series of fixes and optimizations aimed at eliminating information security has been released.
- Linux 3.3: Byte Queue Limits
- Linux 3.4 RED bug fixes & IW10 added & SFQRED
- Linux 3.5 Fair / Flow Queuing packet scheduling (fq_codel, codel)
- Linux 3.7 TCP small queues (TSQ)
- Linux 3.12 TSO / GSO improvements
- Linux 3.13 Host FQ + Pacing (sch_fq)
- Linux 3.15 Change to microseconds from milliseconds throughout networking kernel
- Linux 3.17 Network Batching API
- Linux 4.9 BBR (Bottleneck Bandwidth and RTT)
The latest BBR algorithm in this series of fixes. News from opennet.ru .
The kernel includes the implementation of the congestion control (BBR (Bottleneck Bandwidth and RTT)) algorithm proposed by Google and successfully used to increase throughput and reduce data transmission delays for traffic from google.com and YouTube. BBR requires changes only on the side of the sender, the software of the network infrastructure and the receiving side remain unchanged. Instead of using packet loss as an overload indicator, BBR uses a simulation of a communication channel that predicts the available throughput through sequential checks and an estimate of the time-of-arrival (RTT), but not leading to packet loss or transmission delays. At the initial stage of connection, BBR evaluates the channel bandwidth ceiling, then reduces the send rate for unloading the queue and goes into adjustment mode, then increasing, then reducing the send rate, balancing between the maximum bandwidth and the incomplete packet queue;
These changes affected almost all network protocols, but bypassed WiFi and LTE. It could not go on for a long time and took WiFi seriously. The Make WiFi Fast project brought together hundreds of participants led by a team of nuclear networkers.
Terminology
QDiscor Queuing Discipline is a regular FIFO scheduler, it is located between the IP stack and the driver.
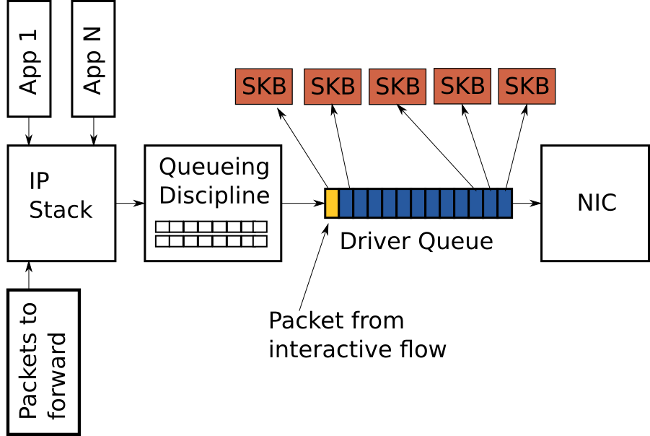
- The
fq_codelnot that simple. About him already wrote on Habré , therefore I will not repeat.
fq_codel is one of the most efficient and advanced algorithms using AQM .- TXOP - transmit opportunity, attempt to send.
How patched up WiFi
Dave Täht, who has already saved the Internet for the past six years, attacked the problem with the help of new and better benchmarks, which he himself had to develop. Iperf3 , quite popular in the scientific community and beyond, turned out to be Iperf3 in general, since by default it assumes unrealistic 100 ms information security.
while( testing) sleep 100ms while( total_bytes_sent / total_elapsed_time < target_rate) transmit buffer of data So it was before the patch. Notice the huge latency at> 10 on the top and bottom levels of the WiFi stack.

- QDisc removed completely. The queue is now formed by stations and advancing in a circular cycle, aka Round Robin Fair Queuing.
- Buffering has moved to the MAC80211 intermediate scheduler level, which is controlled by
fq_codel. it has a minimum size of no more than 2 TXOPs. - Driver buffering minimum, at most 2 TXOP pools (1.2-10ms): 1 ready aggregated frame for retry and another 1 in response.

The MAC80211 no longer stores the packets at the lower level of the driver, but sends them to the intermediate scheduler , reports this to the driver, and he takes them as they arrive. Because of this, the MAC80211 has more information about when data transfer occurs. Due to this delay from buffering amounted to only 2-12 ms.
What has been achieved
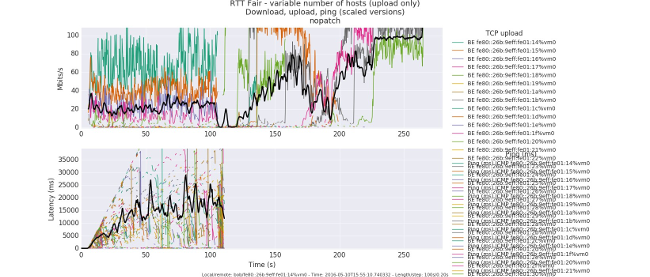
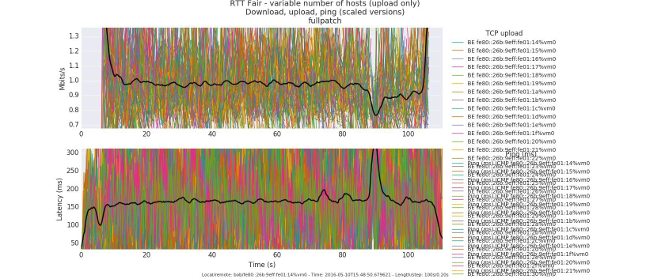
IB managed to exceed so much that delays decreased from peak values of 1-2 seconds to 40 msec. The most graphic illustration will be a picture that shows WiFi sessions on 100 workstations before and after the patch.
Before the patch, only 5 stations started successfully. Monstrous> 15 seconds brakes. Clickable
After the patch, all stations started successfully. Delays are acceptable 150-300 msec. Clickable
Now a fly in the ointment. So far only ath9k drivers fully support all these innovations, ath10k is almost ready. The rest will have to wait for now, but I'm sure the rest of the drivers will also be actively updated after the patches fall into a stable branch.
Used materials and useful links
- Making WiFI Fast
- Linux wifi latencies
- Petition to the FCC
- Project Make WiFi Fast.
- Queuing in the linux network stack
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/317548/
All Articles