What is MMTS-9 and how does the Internet turn out in Russia
I'll start with a joke about peering networks. A top manager of a telecommunications company was asked:
- Who are your competitors and who are your partners?
- What's the difference?
Joke accurately reflects the reality in the field of communication. Networking and providing access to them is like a cake that everyone wants to try. You will give a piece to one of your friends yourself, and from some of the enemies you will want to hit the arm ...
The history of the Russian Internet begins when there was still the phrase “computer connection” instead of the usual foreign term. Before the creation of Relcom , Internet-related development lay in the military industry and state defense. These were non-profit networks that existed thanks to the joint work of Soviet research institutes and Americans. Their popularization happened during the coup in the early 90s - as they managed to maintain their independence and the ability to speak the truth freely.
')
From those days to today, the history of the origin of the Internet in Russia is full of cunning moves, technical intricacies, secret and direct agreements. We selected the most significant events and added a surprise at the end of the article.
Andrei Sebrant, an employee of Glasneta and the current director (?) Of Yandex marketing, in an interview with Afisha magazine, said:
Interesting fact
According to Valery Bardin , one of the organizers of the cooperative Demos and the Relcom network itself, the USSR has been on the Internet since 1982. At that time, Nikolay Saukh and the staff of the All-Union Research Institute of Applied Automated Systems created a stable communication channel with colleagues from the Vienna Institute for System Analysis. This was the beginning of the Academy of Sciences network.

It was the first network of the all-Union scale. It was organized by Alexei Soldatov from the Institute of Atomic Energy. Kurchatov in 1990 year. He and his colleagues connected computers from scientific organizations in Moscow, Novosibirsk and St. Petersburg using analog telephone modems using the UUCP protocol - this is how email was transmitted. The work was carried out together with the cooperative programmers "Demos". In those days, messages were sent longer than five minutes (!).
The first commercial network - Relcom - appeared when business was allowed. She belonged to the cooperative " Demos ".
Thanks to the services of the first provider, individuals began to use the Internet. In 1989, Relcom was a group of 14 people. It consisted of employees of the Kurchatov Institute, the car industry ministries, and "affiliated citizens." Their task was to help create computer networks in the field and connect cities to each other. In 1990, the first computer connection took place in Helsinki, it was on August 28th, and on September 19, the first top-level domain
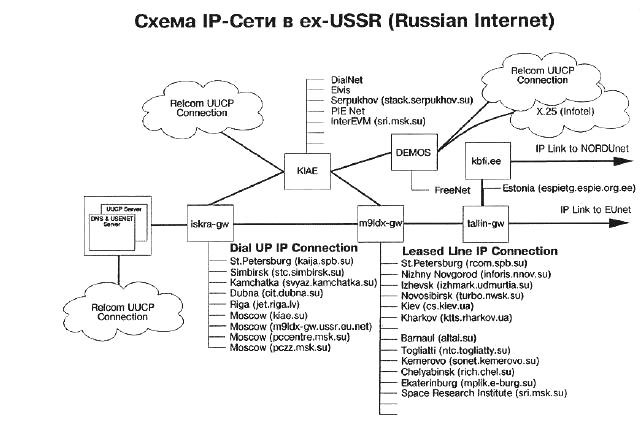
At first , Relcom had mail and newsgroups. During the coup in the 90s, Demos connected to Relcom a huge number of servers across the country. Literally in three days, the network got a more serious status. The network was based exclusively on e-mail technology, and with the possibility of correspondence in Russian ( UUCP / UUPC protocol). In 1991, Relcom began to use a dedicated channel Moscow-Tallinn-Helsinki, the C-News inter-site transfer technology and the first version of the newsgroup mail server appeared.
As joint-stock company Relcom was registered in 1992. The founders - RRC "Kurchatov Institute", RTSB, Rinako, Tehnobank and several others. Also in 1992, the Relcom network was officially registered at EUnet, Europe’s largest association of commercial networks providing access to Internet services. (according to data from ria.ru/history_spravki/20110919/439857350.html ) Later they began to use the new western channel passing through Amsterdam. Throughput increased fourfold. A SEQUENT machine appeared at the head node, increasing its power four times.
In December, the first remote access point of the Relcom-Moscow node “M9” was activated. The SUN (CREMLSUN) machine, which first appeared in the country, was used here. Relcom-Moscow has become a complex of machines connected to each other and separated across Moscow with the Network Control Center on the territory of the Kurchatov Institute.
Until 1993, Relcom was the actual monopolist in the network services market and provided its users with mostly e-mail. Actually, this was not yet the Internet, although it was a computer network — not the Internet protocols were used to send messages, but the older protocol called UUCP. Relcom's monopolistic position inevitably led to a fairly high level of prices for its services.
In 1994, an FTP mail server was launched, with e-mail access to FTP servers external to the Relcom-Moscow site. And in 1996, they created trunk lines with high carrying capacity.
ISDN appeared, the bandwidth of existing channels was expanded, new ones were organized. Only in 1996, the number of leased lines in the regions doubled, the number of telephone lines more than doubled, and the number of dedicated lines in Moscow at least one and a half times. The regions were contacted via digital dedicated channels with a maximum speed of 2 Mbit / s.
What happened in 1997 was important to Relcom. The total bandwidth from the Relcom network to the west was 6 Mbit / s - they became the leader in the Russian Internet market. And the bandwidth capacity of the high-speed channel to the foreign part of the Internet in 1998 was 34 Mbit / s. The channel runs along the ground and, passing from Moscow through St. Petersburg, falls into the Stockholm hub of the backbone of the UUNET company. At the same time, the serial 995-1050 expands to 60 lines, and a new 30-line 737-8107 is put into operation. The series is in a single digital network stream and is handled by the CISCO 5300 server, data transfer rate: 56 Kbps using the K56flex protocol. The Business Network company (Relcom project) provides Internet access via a radio modem in Moscow.
In 1999, the main modem user series received the actual equipment with support for the V.90 protocol. In order to expand the capacity of international channels, they organized a connection to the Moscow Rostelecom hub with a bandwidth of 34 Mbit / s. After that, we skipped a few years and in 2002 we see the so-called “Peering Split”, when major providers, including MTU-Intel, Golden Telecom and RTKomm, stopped traffic exchanges directly with everyone else. Traffic was redirected to foreign channels, and small companies left the field of competition.
Now the official website of Relcom says that the company operates as a telecom operator, providing services to commercial and state enterprises, as well as individuals.
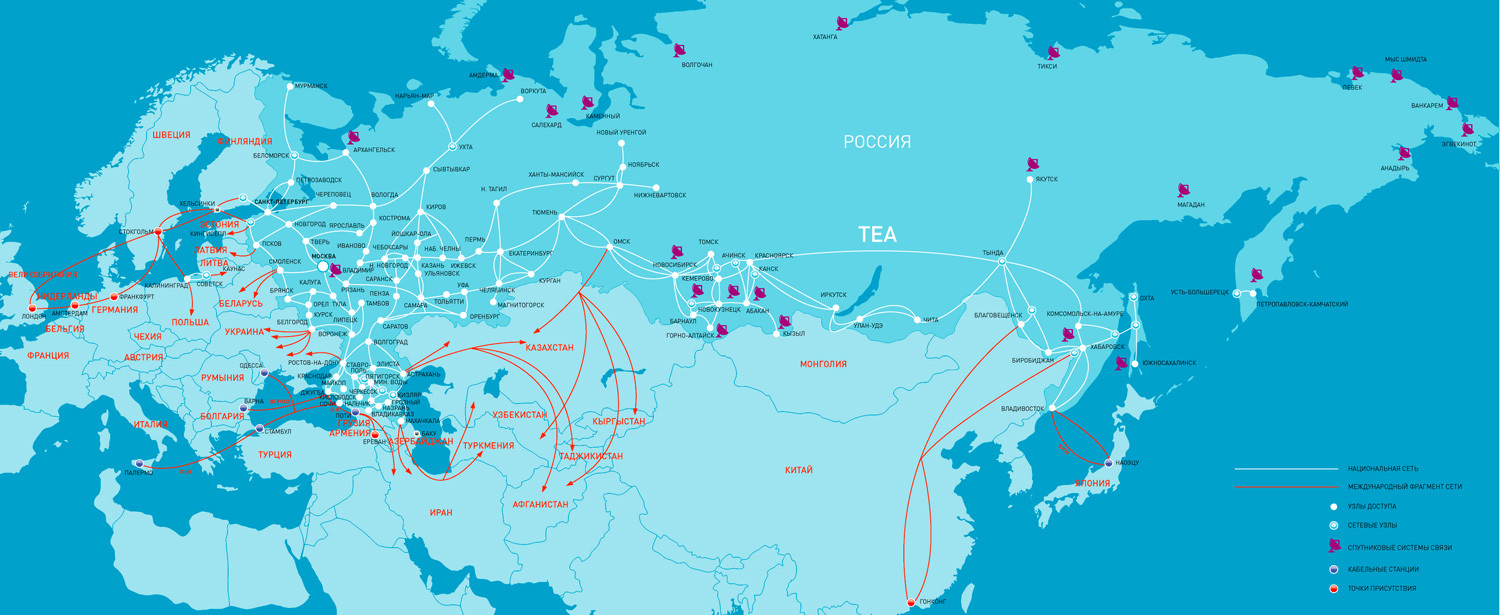
According to information from Wikipedia until 1990, communications were controlled by the Ministry of Communications, and on June 26 they founded the state joint-stock company Sovtelecom with the rights to operate the all-Union telecommunication network. A year later, it was already Intertelecom, and a year later - Rostelecom. In 1994, Rostelecom obtained a license to provide long-distance and international communication services. In the same year, Rostelecom was included in the holding company Svyazinvest.
We will continue to 1998, when the company was a Russian monopolist in the field of international and long-distance telephone communication. Together with Relcom, they created a new company called Relcom - DS (Business Network). It is considered the largest Internet service provider in the Russian Federation. Most of the territory of the state is covered by the Global One network, Sovam Teleport.
In 2006, Rostelecom received a certificate of quality for its IP-MPLS network and became the backbone Internet provider. Further, together with the Japanese telecommunications company KDDI, in the Transit Europe - Asia project, an agreement is concluded on the construction of the Nakhodka-Naoetsu line with a total capacity of 640 Gbit / s instead of the previous 560 Mbit / s. This is followed by a series of mergers and acquisitions with interregional communications companies.
All networks and providers tried to do their peering, but the so-called “ninth node” played a central role at all times.
In 1990, the state-owned enterprise "Moscow and Intercity and International Telephone" introduced two powerful digital international communications complex AX-10. In 1991, the Moscow site was already a system of three MicroVAX 3. In 1995, the main Moscow Internet providers: Demos, Relcom, Moscow State University, Research Institute of Nuclear Physics MSU (Radio-MSU), FREEnet, RELARN Association and Rosprint - create an interchange point of IP traffic . The Moscow Intercity Telephone Station No. 9 was chosen as the location for the traffic exchange point. International and intercity communication channels arrived at M9 and the equipment of the main Internet service providers was located. As a joint-stock company "Moscow Intercity Telephone Station №9" was founded in 1994. The main shareholder of the Company - Rostelecom - 74.86% of the authorized capital.
Today, MMTS-9 has been successfully operating in the telecommunications market for more than 20 years and is the largest technological platform in Moscow for interaction between Moscow, Russian and international telecom operators. Clients - more than 440 telecommunication companies.
MMTS-9 JSC is the largest peering point in Russia.
In the station building:
All technological rooms are connected by structured interfloor connecting cable lines. Thanks to high technology, nine works in fault tolerant mode.
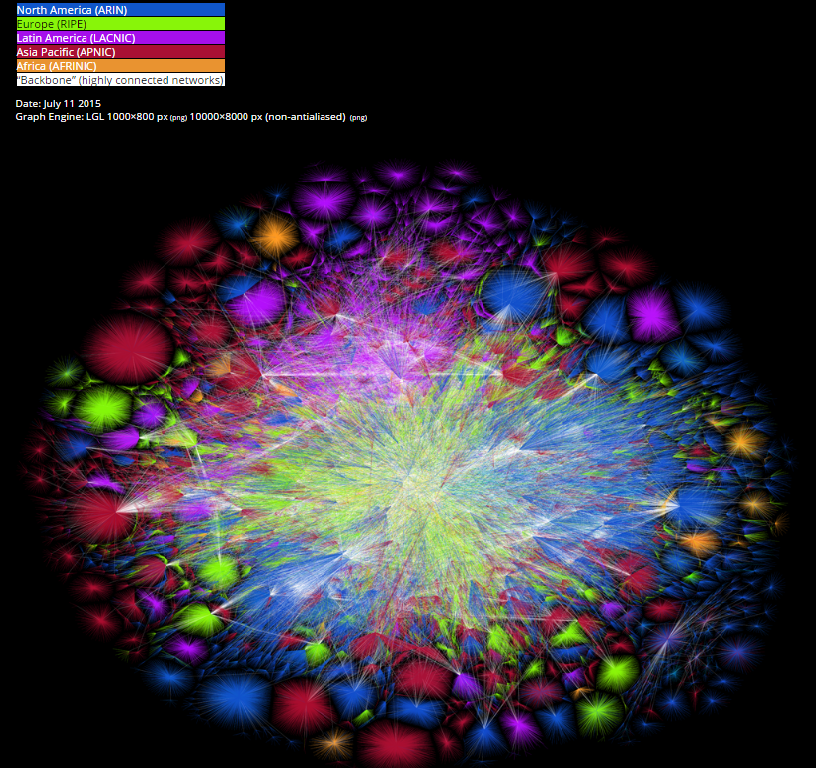
The author of this map made a ping to each network in the first version, and in the last (in the picture) he used Internet routing tables.
In 2013, a project was launched to upgrade the technological areas of the MMTS-9. The last involved machine room for energy consumption and the power supply and cooling systems installed in it is a full-fledged data center with a high level of reliability.
At the beginning of 2015:
Thus, the total power of the MMTS-9 will soon reach 15.3 MW.
Today MMTS-9 is a steadily developing technological platform in Russia, which occupies a leading position in the telecommunications market. Partners and customers of M9 are the largest Russian companies involved in information transfer: MSK-IX, MTS, Beeline, Megafon, TTC, Orange Business Services and many others. High-tech engineering infrastructure allows OJSC MMTS-9 to ensure the organization of a fault-tolerant point of presence by providing the necessary conditions for the functioning of the server and telecommunications equipment of telecom operators.
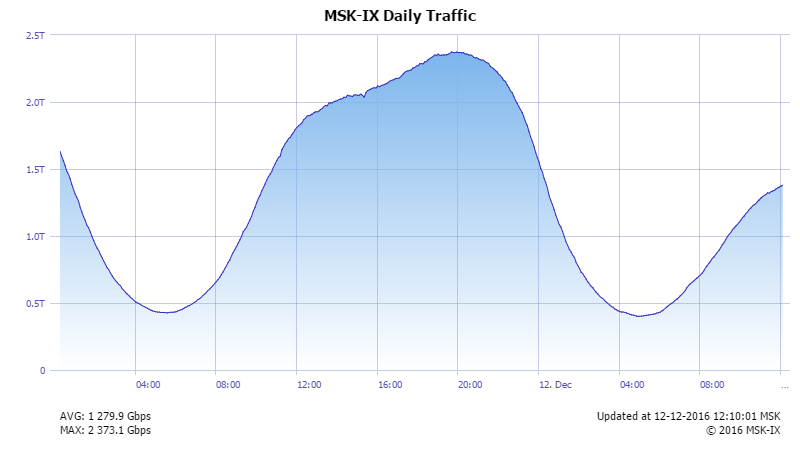
Accelerates communication between Internet companies by providing a neutral Internet eXchange platform for exchanging IP traffic between networks and a global distributed network of DNS servers to support root-domain zones.
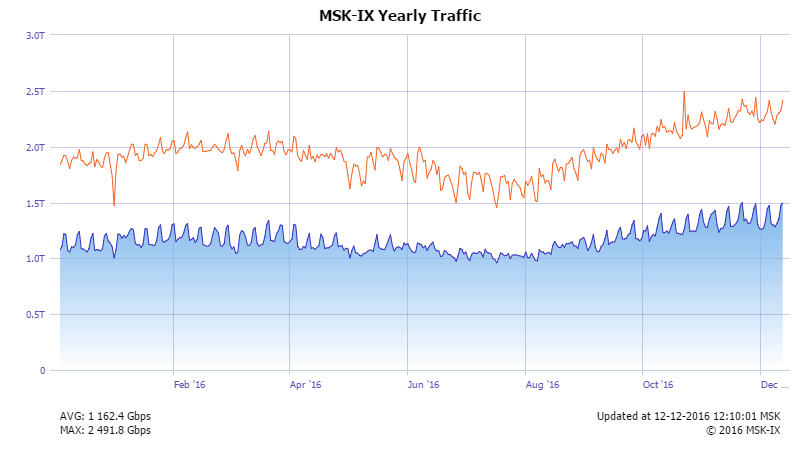
More than 500 organizations use MSK-IX services to develop a network presence in 9 Russian cities. Operators, social networks, search engines, video portals, cloud service providers, corporate and scientific educational networks are connected to MSK-IX.
The main node of the company is also “nine”.
Contel is based on a distance of less than a kilometer from the MMTS-9, to which 256 fibers stretch from the data center, laid completely independent from each other, so that the situation when the “bulldozer broke our cable” is completely excluded. The entire Internet is "coming" in Russia through the M9 node.
Contel’s position is as profitable as they use the M9 with its data center.
Unlike the M9, the data center of the Contel company will be able to accept (but also cool them) high-loaded racks up to 24 kW. In addition to two inputs from completely independent substations, the data center is also equipped with Emerson uninterruptible power supplies, which are enough to supply the data center with power for 40 minutes (at full load) or up to 4 hours with the existing one, this time is quite enough for in order to run diesel generators. Contel provides its customers with any amount of dark fibers to the optical cross-country on MMTS-9, or a ready-made channel from Rostelecom with a band of up to 10 GB. The data center also provides rental services for both budget dedicated servers and professional Blade equipment for HP G7-G8 servers. It is also possible to rent communication equipment from Cisco Systems, Arista with monitoring and system and network administration services from Contel (CCNP minimum).
Some of the benefits are:
Price examples
- Who are your competitors and who are your partners?
- What's the difference?
Joke accurately reflects the reality in the field of communication. Networking and providing access to them is like a cake that everyone wants to try. You will give a piece to one of your friends yourself, and from some of the enemies you will want to hit the arm ...
The history of the Russian Internet begins when there was still the phrase “computer connection” instead of the usual foreign term. Before the creation of Relcom , Internet-related development lay in the military industry and state defense. These were non-profit networks that existed thanks to the joint work of Soviet research institutes and Americans. Their popularization happened during the coup in the early 90s - as they managed to maintain their independence and the ability to speak the truth freely.
')
From those days to today, the history of the origin of the Internet in Russia is full of cunning moves, technical intricacies, secret and direct agreements. We selected the most significant events and added a surprise at the end of the article.
Relcom
Andrei Sebrant, an employee of Glasneta and the current director (?) Of Yandex marketing, in an interview with Afisha magazine, said:
“By 1991, several hundred people used the network in Moscow. The Internet worked smoothly, unlike all other communication channels. We could not listen to people from the First Division of the KGB "
Interesting fact
Schoolchildren from the USA came to the international camp of Baitik in Troitsk near Moscow in 1988. They left two modems that were used for international networks in the closed campus.
According to Valery Bardin , one of the organizers of the cooperative Demos and the Relcom network itself, the USSR has been on the Internet since 1982. At that time, Nikolay Saukh and the staff of the All-Union Research Institute of Applied Automated Systems created a stable communication channel with colleagues from the Vienna Institute for System Analysis. This was the beginning of the Academy of Sciences network.

It was the first network of the all-Union scale. It was organized by Alexei Soldatov from the Institute of Atomic Energy. Kurchatov in 1990 year. He and his colleagues connected computers from scientific organizations in Moscow, Novosibirsk and St. Petersburg using analog telephone modems using the UUCP protocol - this is how email was transmitted. The work was carried out together with the cooperative programmers "Demos". In those days, messages were sent longer than five minutes (!).
The first commercial network - Relcom - appeared when business was allowed. She belonged to the cooperative " Demos ".
Thanks to the services of the first provider, individuals began to use the Internet. In 1989, Relcom was a group of 14 people. It consisted of employees of the Kurchatov Institute, the car industry ministries, and "affiliated citizens." Their task was to help create computer networks in the field and connect cities to each other. In 1990, the first computer connection took place in Helsinki, it was on August 28th, and on September 19, the first top-level domain
.su was registered jointly by Relcom and Demos. Usenet conferences were used to share information. The rest of the Soviet cities came to the network.
At first , Relcom had mail and newsgroups. During the coup in the 90s, Demos connected to Relcom a huge number of servers across the country. Literally in three days, the network got a more serious status. The network was based exclusively on e-mail technology, and with the possibility of correspondence in Russian ( UUCP / UUPC protocol). In 1991, Relcom began to use a dedicated channel Moscow-Tallinn-Helsinki, the C-News inter-site transfer technology and the first version of the newsgroup mail server appeared.
As joint-stock company Relcom was registered in 1992. The founders - RRC "Kurchatov Institute", RTSB, Rinako, Tehnobank and several others. Also in 1992, the Relcom network was officially registered at EUnet, Europe’s largest association of commercial networks providing access to Internet services. (according to data from ria.ru/history_spravki/20110919/439857350.html ) Later they began to use the new western channel passing through Amsterdam. Throughput increased fourfold. A SEQUENT machine appeared at the head node, increasing its power four times.
In December, the first remote access point of the Relcom-Moscow node “M9” was activated. The SUN (CREMLSUN) machine, which first appeared in the country, was used here. Relcom-Moscow has become a complex of machines connected to each other and separated across Moscow with the Network Control Center on the territory of the Kurchatov Institute.
Until 1993, Relcom was the actual monopolist in the network services market and provided its users with mostly e-mail. Actually, this was not yet the Internet, although it was a computer network — not the Internet protocols were used to send messages, but the older protocol called UUCP. Relcom's monopolistic position inevitably led to a fairly high level of prices for its services.
In 1994, an FTP mail server was launched, with e-mail access to FTP servers external to the Relcom-Moscow site. And in 1996, they created trunk lines with high carrying capacity.
ISDN appeared, the bandwidth of existing channels was expanded, new ones were organized. Only in 1996, the number of leased lines in the regions doubled, the number of telephone lines more than doubled, and the number of dedicated lines in Moscow at least one and a half times. The regions were contacted via digital dedicated channels with a maximum speed of 2 Mbit / s.
What happened in 1997 was important to Relcom. The total bandwidth from the Relcom network to the west was 6 Mbit / s - they became the leader in the Russian Internet market. And the bandwidth capacity of the high-speed channel to the foreign part of the Internet in 1998 was 34 Mbit / s. The channel runs along the ground and, passing from Moscow through St. Petersburg, falls into the Stockholm hub of the backbone of the UUNET company. At the same time, the serial 995-1050 expands to 60 lines, and a new 30-line 737-8107 is put into operation. The series is in a single digital network stream and is handled by the CISCO 5300 server, data transfer rate: 56 Kbps using the K56flex protocol. The Business Network company (Relcom project) provides Internet access via a radio modem in Moscow.
In 1999, the main modem user series received the actual equipment with support for the V.90 protocol. In order to expand the capacity of international channels, they organized a connection to the Moscow Rostelecom hub with a bandwidth of 34 Mbit / s. After that, we skipped a few years and in 2002 we see the so-called “Peering Split”, when major providers, including MTU-Intel, Golden Telecom and RTKomm, stopped traffic exchanges directly with everyone else. Traffic was redirected to foreign channels, and small companies left the field of competition.
Now the official website of Relcom says that the company operates as a telecom operator, providing services to commercial and state enterprises, as well as individuals.
Meanwhile in Rostelecom

According to information from Wikipedia until 1990, communications were controlled by the Ministry of Communications, and on June 26 they founded the state joint-stock company Sovtelecom with the rights to operate the all-Union telecommunication network. A year later, it was already Intertelecom, and a year later - Rostelecom. In 1994, Rostelecom obtained a license to provide long-distance and international communication services. In the same year, Rostelecom was included in the holding company Svyazinvest.
We will continue to 1998, when the company was a Russian monopolist in the field of international and long-distance telephone communication. Together with Relcom, they created a new company called Relcom - DS (Business Network). It is considered the largest Internet service provider in the Russian Federation. Most of the territory of the state is covered by the Global One network, Sovam Teleport.
In 2006, Rostelecom received a certificate of quality for its IP-MPLS network and became the backbone Internet provider. Further, together with the Japanese telecommunications company KDDI, in the Transit Europe - Asia project, an agreement is concluded on the construction of the Nakhodka-Naoetsu line with a total capacity of 640 Gbit / s instead of the previous 560 Mbit / s. This is followed by a series of mergers and acquisitions with interregional communications companies.
MMTS-9
All networks and providers tried to do their peering, but the so-called “ninth node” played a central role at all times.
In 1990, the state-owned enterprise "Moscow and Intercity and International Telephone" introduced two powerful digital international communications complex AX-10. In 1991, the Moscow site was already a system of three MicroVAX 3. In 1995, the main Moscow Internet providers: Demos, Relcom, Moscow State University, Research Institute of Nuclear Physics MSU (Radio-MSU), FREEnet, RELARN Association and Rosprint - create an interchange point of IP traffic . The Moscow Intercity Telephone Station No. 9 was chosen as the location for the traffic exchange point. International and intercity communication channels arrived at M9 and the equipment of the main Internet service providers was located. As a joint-stock company "Moscow Intercity Telephone Station №9" was founded in 1994. The main shareholder of the Company - Rostelecom - 74.86% of the authorized capital.
Today, MMTS-9 has been successfully operating in the telecommunications market for more than 20 years and is the largest technological platform in Moscow for interaction between Moscow, Russian and international telecom operators. Clients - more than 440 telecommunication companies.
MMTS-9 JSC is the largest peering point in Russia.
Technical stuffing "nine"
In the station building:
- modern engineering infrastructure
- uninterruptible power systems,
- climate control,
- gas extinguishing,
- telemonitoring
- CCTV.
All technological rooms are connected by structured interfloor connecting cable lines. Thanks to high technology, nine works in fault tolerant mode.

The author of this map made a ping to each network in the first version, and in the last (in the picture) he used Internet routing tables.
Node functions
- accommodates telecommunications equipment with a power consumption of 5.5 kW per rack,
- highly loaded racks with power consumption up to 24 kW per unit;
- provides the possibility of providing an individual containment,
- allocates antenna places on the roof;
- performs installation and dismantling works, design works on equipment placement; carries out operational maintenance of equipment and communication lines;
- organizes access to network resources of telecom operators,
- provides terminal Internet access (provision of IP-transit service), provides round-the-clock technical support.
In 2013, a project was launched to upgrade the technological areas of the MMTS-9. The last involved machine room for energy consumption and the power supply and cooling systems installed in it is a full-fledged data center with a high level of reliability.
At the beginning of 2015:
- the total area of all server rooms, with 1497 racks, is 6900 square meters. m,
- supplied electric power - 6.5 MW,
- Additional work is underway to add 8.8 MW of additional electrical capacity.
Thus, the total power of the MMTS-9 will soon reach 15.3 MW.
Today MMTS-9 is a steadily developing technological platform in Russia, which occupies a leading position in the telecommunications market. Partners and customers of M9 are the largest Russian companies involved in information transfer: MSK-IX, MTS, Beeline, Megafon, TTC, Orange Business Services and many others. High-tech engineering infrastructure allows OJSC MMTS-9 to ensure the organization of a fault-tolerant point of presence by providing the necessary conditions for the functioning of the server and telecommunications equipment of telecom operators.
New company MSK-IX

Accelerates communication between Internet companies by providing a neutral Internet eXchange platform for exchanging IP traffic between networks and a global distributed network of DNS servers to support root-domain zones.
More than 500 organizations use MSK-IX services to develop a network presence in 9 Russian cities. Operators, social networks, search engines, video portals, cloud service providers, corporate and scientific educational networks are connected to MSK-IX.
The main node of the company is also “nine”.

Contel
Contel is based on a distance of less than a kilometer from the MMTS-9, to which 256 fibers stretch from the data center, laid completely independent from each other, so that the situation when the “bulldozer broke our cable” is completely excluded. The entire Internet is "coming" in Russia through the M9 node.
Contel’s position is as profitable as they use the M9 with its data center.
Unlike the M9, the data center of the Contel company will be able to accept (but also cool them) high-loaded racks up to 24 kW. In addition to two inputs from completely independent substations, the data center is also equipped with Emerson uninterruptible power supplies, which are enough to supply the data center with power for 40 minutes (at full load) or up to 4 hours with the existing one, this time is quite enough for in order to run diesel generators. Contel provides its customers with any amount of dark fibers to the optical cross-country on MMTS-9, or a ready-made channel from Rostelecom with a band of up to 10 GB. The data center also provides rental services for both budget dedicated servers and professional Blade equipment for HP G7-G8 servers. It is also possible to rent communication equipment from Cisco Systems, Arista with monitoring and system and network administration services from Contel (CCNP minimum).
Some of the benefits are:
- possibility of round-the-clock access to equipment
- installation of high-loaded racks, which is impossible on the M9 due to the lack of sufficient cooling and limiting the maximum power per rack to 7 kilowatts
- the possibility of placing equipment on the roof, which is especially useful for IPTV providers
Price examples
- Intel Core Processor i5-6400 8GB RAM HDD 500gb SATA or 280 SSD for only 2074.5 rubles (share price)
- Intel Xeon Processor E5-2609v4 8GB RAM HDD 500gb SATA or 280 SSD for only 3189 rubles
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/317382/
All Articles