Security Week 49: Google fuzz open source, Android Trojan steals user accounts, Microsoft fixes old bug
 On December 1, a team of security experts Google announced a new program, OSS-Fuzz, in which it plans to allocate resources for continuous fuzzing open source software ( news , post on the Google Security blog). Fuzzing is an automated program testing method, the idea of which was formulated back in the late 80s ( PDF ). With the increase in computer performance, a fairly straightforward process of feeding arbitrary data to software in the search for vulnerabilities is becoming more and more important. And indeed, in a world where computers are increasingly being run by other computers, this is a good topic, already included, for example, in Microsoft's Secure Development Lifecycle methodology.
On December 1, a team of security experts Google announced a new program, OSS-Fuzz, in which it plans to allocate resources for continuous fuzzing open source software ( news , post on the Google Security blog). Fuzzing is an automated program testing method, the idea of which was formulated back in the late 80s ( PDF ). With the increase in computer performance, a fairly straightforward process of feeding arbitrary data to software in the search for vulnerabilities is becoming more and more important. And indeed, in a world where computers are increasingly being run by other computers, this is a good topic, already included, for example, in Microsoft's Secure Development Lifecycle methodology.Explaining the success of the approach with respect to free software, Google gives an example of a vulnerability in the Freetype library, discovered by OSS-Fuzz fuzzer. Freetype is installed on billions of devices, and therefore it is important to explore such software. Serious open source vulnerabilities such as Heartbleed have shown that the very possibility of independent auditing does not equal increased security. People just do not have enough hands to analyze everything, so robots come on the scene. It's strange that Google doesn't say anything about Android fuzzing, although researchers from other companies do it .
In fact, the main benefit of the project is that Google invites third-party researchers and open source software maintainers, in essence, providing them with computing resources within the project. In his impressions, researcher and developer Alex Gaynor writes that in less than a day his test code added to OSS-Fuzz processed 17 trillion test cases, which would have taken him a month at home.
Visual demonstration of fuzzing technology
')
Android Trojan attacked more than a million users, possibly with a burglary Google account
News Research Check Point Software. Google response .
The very news in which the estimates of the consequences of the work of a malicious program differ between the researcher and the vendor. Everyone agrees that the Gooligan campaign has been around for a couple of years, its traces were found even in malicious attacks on Windows systems. The spread of the Android Trojan occurs through unofficial app stores. In Check Point, found more than 80 applications for smartphones with built-in malicious code, with their help allegedly managed to infect more than a million devices. After the Trojan is activated, additional software is downloaded from the command server to obtain root privileges: Android 4 and 5 smartphones are subject to privilege escalation, by the way, almost three-quarters of active devices still work on these versions.
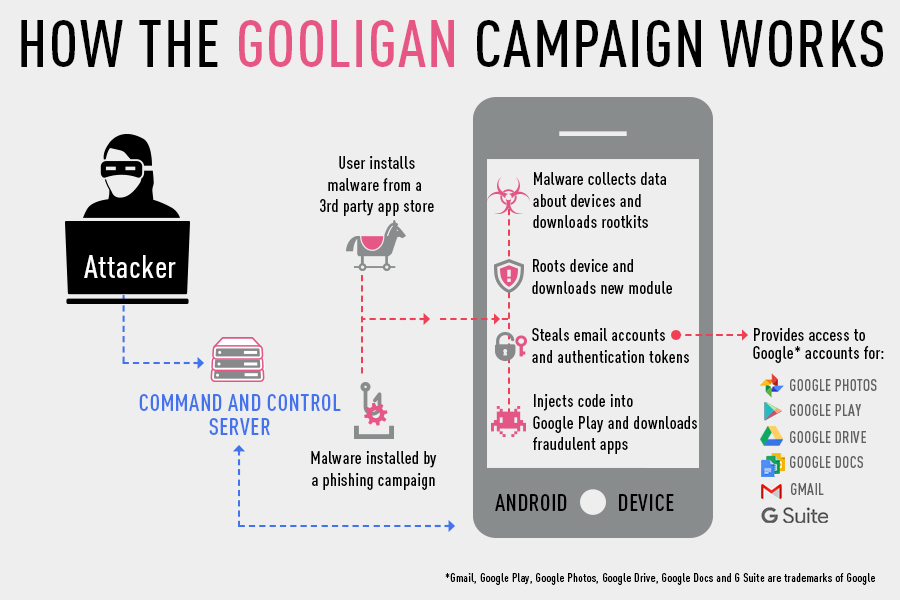
All gestures are made to “hijack” a Google account, but then the readings start to differ. Check Point claims that the theft of an authorization token allows attackers to gain access to all user resources — mail, disk, and so on. Adrian Ludwig, chief Google security officer for Android, says that in fact personal data is not stolen. Profit is achieved by creative interception of access to the official Google Play store. Infected phones without demand begin to download applications, which affects their rating. Apparently, the shop will soon be covered. And not because Google will convince everyone not to install applications from unverified sources anymore. And because it bans applications that are actively using a malicious campaign for promotion, in the official Google Play.
Microsoft without fanfare closed a two-year-old bug in the Windows kernel
News Description of the vulnerability in the Google Project Zero bug tracker.
And this is news about third-tier vulnerabilities - which do not carry an immediate threat, or are exploited under some rare combination of circumstances. However, here, too, it all depends on the evaluation of the parties involved. Two years ago, an expert with the Google Project Zero reported to Microsoft the details of the Windows kernel vulnerability related to the operation of the SeFastTraverseCheck method, which is responsible for checking whether an object has permission to access a particular type of access to files or directories. In some cases, the vulnerability allowed to get (fairly limited) access to the hardware, and in situations where this should not happen at all, for example, when executing code in the sandbox of Google Chrome.
In general, the situation is like in a joke: “Doctor, when I press this way here, it hurts here. - And you do not press. The researcher honestly said that this feature can be considered not a bug, but features, and simply taken into account when developing. Microsoft two years ago rather quickly replied that it did not consider this a serious enough problem to qualify as a vulnerability. At that time, the problem was confirmed by a researcher for Windows 7 and 8. And at the end of November, the same researcher suddenly discovered that the problem was solved, though already in Windows 10.
That's how we live.

Antiquities
"Ufa-1201"
Nonresident very dangerous virus. Sent from Ufa. Typically it infects .COM files that it finds when passing through a directory tree. Writes NOP commands to the top of the file CALL Vir_Loc. Depending on the system time, it erases the FAT of the current disk.
Quote from the book "Computer viruses in MS-DOS" Eugene Kaspersky. 1992 Page 86.
Disclaimer: This column reflects only the personal opinion of its author. It may coincide with the position of Kaspersky Lab, or it may not coincide. Then how lucky.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/317272/
All Articles