Alcatel Lucent Service Router as an Access Domain Gateway
For many, the first acquaintance with the Alcatel Lucent service routers (now Nokia) is not very pleasant due to the particular vendor look at the service delivery model. Unlike Cisco equipment, it is not always obvious how to make such a device work in a simple scenario: a router for several access switches (usually such switches are connected in a ring). Those who are disappointed, not finding the command spanning-tree in configuration mode, is dedicated.
Imagine a simple topology:
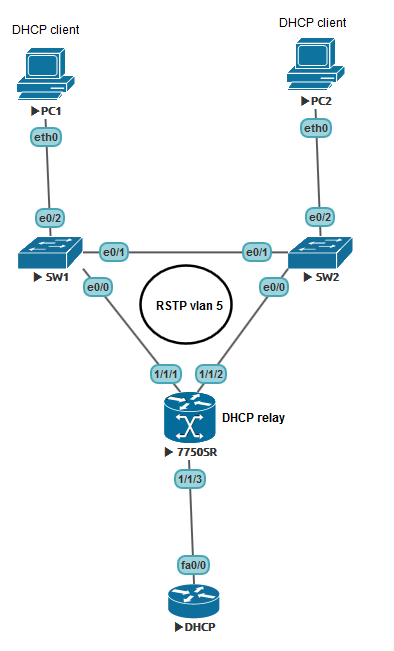
Two access switches connected in a ring with a router, a device with TimOS on board (in this case the SR7750 emulator) and an external DHCP server serving several IP networks. In this situation, the 7750 has several alter egos:
1) Default gateway. PC1 and PC2 quite naturally want to communicate with external networks, so you need to provide them with an IP address where you can send all unwanted packets.
')
2) DHCP realy. As a message, discover is sent by Broadcast; it must be sent to the external server by a unicast message.
3) RSTP root bridge. It is hardly rational to allow the access switch to become root.
Immediately make a reservation that the SR7750 is a router. It is not intended for switching traffic between two interfaces; it does not support SVI in the classical form with all that it implies. To use the device in such a topology, it is necessary to create an improvised and very simple VPLS (although, of course, in the case of two interfaces, a pseudowire would also be suitable). In order to configure VPLS in our case, it is not necessary to understand the principles of MPLS operation.
So let's get started.
0. Our preliminary step will be user configuration. VPLS from the point of view of SR is a service, and any service must belong to the user.
1. Configure interfaces 1/1/1 and 1/1/2.
After that, using the
2. Configure the VPLS service.
SAP (Service access point) is an attachment circuit in slightly better known terminology. The point to which the subscriber device is connected. In our case, the access switch. The number after the colon is the vlan number.
This is where we enable STP. The default mode is RSTP, and our SAP will be point-to-point interfaces from an STP perspective. Priority 4096 set with the intent to turn our pseudo-switch into a root bridge.
Basic verification can be done using
3. So, the interface.
As you can see, here we killed two birds with one stone: the default gateway was configured, and DHCP clients were provided with DHCP Relay. Note that IES and VPLS are different services, with different id.
Verify that the UP interface is available using
4. Configure the interface in the direction of the kernel where the DHCP server is located. For simplicity, we will achieve connectivity with the server by a static route. Do not forget about the value of MTU from the core.
Enable the interface:
Configuring the IP part:
The routing table can be viewed using
This is a simple, but slightly unusual setting Alcatel completed. At first glance, VRRP is not enough here, but in an amicable way, to enable VRRP, you need to add an MPLS interface between two routers. In addition to SAP, SDP will be added to our VPLS. But that's another story.
Software Version: TiMOS-B-12.0.R6.
Picture and console: UNL
Thanks for attention.
Imagine a simple topology:

Two access switches connected in a ring with a router, a device with TimOS on board (in this case the SR7750 emulator) and an external DHCP server serving several IP networks. In this situation, the 7750 has several alter egos:
1) Default gateway. PC1 and PC2 quite naturally want to communicate with external networks, so you need to provide them with an IP address where you can send all unwanted packets.
')
2) DHCP realy. As a message, discover is sent by Broadcast; it must be sent to the external server by a unicast message.
3) RSTP root bridge. It is hardly rational to allow the access switch to become root.
Immediately make a reservation that the SR7750 is a router. It is not intended for switching traffic between two interfaces; it does not support SVI in the classical form with all that it implies. To use the device in such a topology, it is necessary to create an improvised and very simple VPLS (although, of course, in the case of two interfaces, a pseudowire would also be suitable). In order to configure VPLS in our case, it is not necessary to understand the principles of MPLS operation.
So let's get started.
Do not forget to configure the card in the emulator.
If you do not use an emulator, the types of cards and modules can be determined by simple commands:
card 1 card-type iom3-xp-b mda 1 mda-type m5-1gb-sfp-b no shutdown exit no shutdown If you do not use an emulator, the types of cards and modules can be determined by simple commands:
show card show mda 0. Our preliminary step will be user configuration. VPLS from the point of view of SR is a service, and any service must belong to the user.
customer 5 create description "Access ring 1" exit 1. Configure interfaces 1/1/1 and 1/1/2.
port 1/1/1 ethernet mode access encap-type dot1q exit no shutdown exit port 1/1/2 ethernet mode access encap-type dot1q exit no shutdown exit After that, using the
show port command you can verify that the settings are correct. Note that the MTU has become 1518 = 1500 for IP + 14 Ethernet + 4 dot1q vlan. It is quite natural that in the QinQ configuration, the device itself will determine the frame size in 1522.Spoiler
===============================================================================
Ports on Slot 1
===============================================================================
Port Admin Link Port Cfg Oper LAG/ Port Port Port C/QS/S/XFP/
Id State State MTU MTU Bndl Mode Encp Type MDIMDX
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1/1/1 Up Yes Up 1518 1518 - accs dotq xcme GIGE-LX 10KM
1/1/2 Up Yes Up 1518 1518 - accs dotq xcme GIGE-LX 10KM
2. Configure the VPLS service.
service vpls 5 customer 5 create allow-ip-int-binding stp priority 4096 no shutdown exit service-name "Access-ring-1" sap 1/1/1:5 create exit sap 1/1/2:5 create exit no shutdown exit exit SAP (Service access point) is an attachment circuit in slightly better known terminology. The point to which the subscriber device is connected. In our case, the access switch. The number after the colon is the vlan number.
This is where we enable STP. The default mode is RSTP, and our SAP will be point-to-point interfaces from an STP perspective. Priority 4096 set with the intent to turn our pseudo-switch into a root bridge.
allow-ip-int-binding required in order to allow IP interface binding (read SVI) to our VPLS. This interface will be bound using our service name.Basic verification can be done using
show service id 5 baseSpoiler
===============================================================================
Service Basic Information
===============================================================================
Service Id : 5 Vpn Id : 0
Service Type : VPLS
Name : Access-ring-1
Description : (Not Specified)
Customer Id : 5 Creation Origin : manual
Last Status Change: 12/06/2016 21:37:01
Last Mgmt Change : 12/06/2016 21:37:01
Etree Mode : Disabled
Admin State : Up Oper State : Up
MTU : 1514 Def. Mesh VC Id : 5
SAP Count : 2 SDP Bind Count : 0
Snd Flush on Fail : Disabled Host Conn Verify : Disabled
Propagate MacFlush: Disabled Per Svc Hashing : Disabled
Allow IP Intf Bind: Enabled
Def. Gateway IP : None
Def. Gateway MAC : None
Temp Flood Time : Disabled Temp Flood : Inactive
Temp Flood Chg Cnt: 0
VSD Domain : none
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Service Access & Destination Points
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Identifier Type AdmMTU OprMTU Adm Opr
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sap:1/1/1:5 q-tag 1518 1518 Up Up
sap:1/1/2:5 q-tag 1518 1518 Up Up
===============================================================================
3. So, the interface.
service ies 15 customer 5 create interface "DGW-1" create address 10.0.0.6/29 dhcp server 10.10.10.10 relay-unicast-msg no shutdown exit vpls "Access-ring-1" exit exit no shutdown exit As you can see, here we killed two birds with one stone: the default gateway was configured, and DHCP clients were provided with DHCP Relay. Note that IES and VPLS are different services, with different id.
Verify that the UP interface is available using
show service id 15 interfaceSpoiler
===============================================================================
Interface Table
===============================================================================
Interface-Name Adm Opr(v4/v6) Type Port/SapId
IP-Address PfxState
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
DGW-1 Up Up/-- IES rvpls
10.0.0.6/29 n/a
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Interfaces : 1
===============================================================================
4. Configure the interface in the direction of the kernel where the DHCP server is located. For simplicity, we will achieve connectivity with the server by a static route. Do not forget about the value of MTU from the core.
Enable the interface:
port 1/1/3 ethernet exit no shutdown exit Configuring the IP part:
router interface "To-CORE" address 172.16.0.0/31 port 1/1/3 no shutdown exit interface "system" no shutdown exit static-route 10.10.10.10/32 next-hop 172.16.0.1 The routing table can be viewed using
show router route-tableSpoiler
===============================================================================
Route Table (Router: Base)
===============================================================================
Dest Prefix[Flags] Type Proto Age Pref
Next Hop[Interface Name] Metric
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
10.0.0.0/29 Local Local 00h17m25s 0
DGW-1 0
10.10.10.10/32 Remote Static 00h05m05s 5
172.16.0.1 1
172.16.0.0/31 Local Local 00h05m05s 0
To-CORE 0
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
No. of Routes: 3
Flags: n = Number of times nexthop is repeated
B = BGP backup route available
L = LFA nexthop available
S = Sticky ECMP requested
===============================================================================
This is a simple, but slightly unusual setting Alcatel completed. At first glance, VRRP is not enough here, but in an amicable way, to enable VRRP, you need to add an MPLS interface between two routers. In addition to SAP, SDP will be added to our VPLS. But that's another story.
Software Version: TiMOS-B-12.0.R6.
Picture and console: UNL
Thanks for attention.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/317138/
All Articles