On quantum cryptography. Protocols E91 & Lo05
Good time of the day, Habrazhiteli! As promised in the first article , I will talk about the E91 and Lo05 protocols.
This protocol was developed by Arthur Eckert in 1991. It also has the name EPR (Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen) as it is based on the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen paradox .
The protocol proposes to use, for example, pairs of photons produced in antisymmetric polarization states. Interception of one of the photons of the pair does not bring any information to Eve, but is a signal to Alice and Bob that their conversation is being listened to.
The EPR effect occurs when a spherically symmetric atom radiates two photons in opposite directions towards two observers. Photons are emitted with indefinite polarization, but due to the symmetry of their polarization are always opposite. An important feature of this effect is that the polarization of photons becomes known only after measurement. Based on EPR and Eckert proposed a protocol that guarantees secure transfer and key storage. The sender generates a number of EPR photon pairs. He leaves one photon from each pair for himself, sends the second one to his partner. At the same time, if the registration efficiency is close to unity, when the sender receives a polarization value of 1, his partner will register the value 0 and vice versa. It is clear that in this way partners, whenever required, can get identical pseudo-random code sequences.
')
Let N of maximally entangled EPR pairs of photons be created first, then one photon from each pair is sent to Alice, and the other to Bob. Three possible quantum states for these EPR pairs are

This can be written generally as
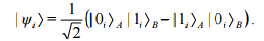
The last formula clearly shows that each of these three states encodes bits "0" and "1" in a unique basis. Then Alice and Bob take measurements on their parts of the separated EPR pairs using the appropriate projectors.
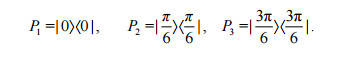
For each bit, Alice and Bob randomly choose a basis for measuring a particle, as in the case of BB84, they discuss which methods they used to measure particles in an open channel:
Due to the principles of quantum entanglement, using the same basis, Alice and Bob should expect opposite results, if roughly, it means that in order to get the key one of them must invert his result. For the rest of the results, Alice and Bob check Bell's fulfillment of the inequality as a test for Eve’s presence.
Lo05 is a quantum cryptographic key distribution protocol created by scientists Luo H.-K. Ma K. and Chen K.
Quantum key distribution (QKD) allows two users, Alice and Bob, to communicate in absolute security in the presence of an interceptor, Eve.
Unfortunately, all these exciting recent experiments are, in principle, unsafe due to the imperfections of real life. More specifically, highly attenuated lasers are often used as sources. But sources sometimes produce signals that contain more than one photon. These multi-photon signals open the door to a world of powerful new attacks, including attacks aimed at splitting multi-photons. For example, Eva can, in principle, measure the number of photons of each signal emitted by Alice and selectively suppress single-photon signals. She breaks down the multi-photon signals, keeping one copy for herself and sending one copy to Bob. Now, since Eve has an identical copy of what Bob possesses. And as a result, the unconditional security of QKD (in, for example, the BB84 protocol) is completely violated.
Therefore, in 2005, Lo's group proposed a protocol that allows to circumvent such shortcomings of the existing protocols. The idea of this protocol is based on “trap states”. That is, quantum states, which are used only to determine the presence of the spy in the communication channel.
As stated by the creators themselves, the method has an advantage over the others as it can be safely implemented on the basis of current hardware. The basic idea is that Alice is preparing a set of additional “states - baits”, in addition to the standard states used in BB84. Baits are used only for the purpose of detecting eavesdropping, while standard BB84 states are used to generate keys. The main difference between the two is intensity.
Let's imagine that the state of a signal and the state of a signal have the same characteristics (wavelength, timing information, etc.). Thus, Eve cannot distinguish between a lure state and a signal state, and only a portion of the information available to Eve is the number of photons in the signal.
Assuming that the two detectors have equal chances, the error rate is 50%. If the signal has N ≥ 1 photons, it also has a certain frequency error rate. That is, if we speak correctly, the error consists of two parts:
1. Detection error
2. Background contribution
But for the Lo05 protocol, this is not the case. Alice and Bob have the ability to isolate single-photon signals, plus using signals - bait, you can transfer data over a distance of more than 140 km. The protocol is also resistant to small speed disturbances, which ideally eliminates background errors. In addition, the key generation speed was increased by several times, more precisely, the creators talk about an increase of 5 times. Thus, as they say, “using the best of two worlds,” the authors were able to achieve not only an increase in distance, but also an increase in security, not only at small but also at relatively large distances.
PS And by the way about “BUT”, about which I promised to say despite my seemingly ideal nature, the algorithm is very difficult to implement and costly due to the fact that its basic principles are connected with direct current.
PSS When describing the Lo05 algorithm, I deliberately did not load the description with equations, otherwise I would simply have to rewrite the whole article. By the way, if you wish, you can take the link here.
E91
Some teroria ...
This protocol was developed by Arthur Eckert in 1991. It also has the name EPR (Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen) as it is based on the Einstein-Podolsky-Rosen paradox .
The protocol proposes to use, for example, pairs of photons produced in antisymmetric polarization states. Interception of one of the photons of the pair does not bring any information to Eve, but is a signal to Alice and Bob that their conversation is being listened to.
The EPR effect occurs when a spherically symmetric atom radiates two photons in opposite directions towards two observers. Photons are emitted with indefinite polarization, but due to the symmetry of their polarization are always opposite. An important feature of this effect is that the polarization of photons becomes known only after measurement. Based on EPR and Eckert proposed a protocol that guarantees secure transfer and key storage. The sender generates a number of EPR photon pairs. He leaves one photon from each pair for himself, sends the second one to his partner. At the same time, if the registration efficiency is close to unity, when the sender receives a polarization value of 1, his partner will register the value 0 and vice versa. It is clear that in this way partners, whenever required, can get identical pseudo-random code sequences.
')
Let N of maximally entangled EPR pairs of photons be created first, then one photon from each pair is sent to Alice, and the other to Bob. Three possible quantum states for these EPR pairs are

This can be written generally as
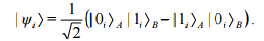
The last formula clearly shows that each of these three states encodes bits "0" and "1" in a unique basis. Then Alice and Bob take measurements on their parts of the separated EPR pairs using the appropriate projectors.
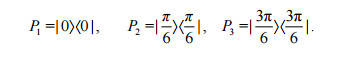
And now, in a simple way ...
For each bit, Alice and Bob randomly choose a basis for measuring a particle, as in the case of BB84, they discuss which methods they used to measure particles in an open channel:

Due to the principles of quantum entanglement, using the same basis, Alice and Bob should expect opposite results, if roughly, it means that in order to get the key one of them must invert his result. For the rest of the results, Alice and Bob check Bell's fulfillment of the inequality as a test for Eve’s presence.
Lo05
Lo05 is a quantum cryptographic key distribution protocol created by scientists Luo H.-K. Ma K. and Chen K.
Quantum key distribution (QKD) allows two users, Alice and Bob, to communicate in absolute security in the presence of an interceptor, Eve.
Unfortunately, all these exciting recent experiments are, in principle, unsafe due to the imperfections of real life. More specifically, highly attenuated lasers are often used as sources. But sources sometimes produce signals that contain more than one photon. These multi-photon signals open the door to a world of powerful new attacks, including attacks aimed at splitting multi-photons. For example, Eva can, in principle, measure the number of photons of each signal emitted by Alice and selectively suppress single-photon signals. She breaks down the multi-photon signals, keeping one copy for herself and sending one copy to Bob. Now, since Eve has an identical copy of what Bob possesses. And as a result, the unconditional security of QKD (in, for example, the BB84 protocol) is completely violated.
Therefore, in 2005, Lo's group proposed a protocol that allows to circumvent such shortcomings of the existing protocols. The idea of this protocol is based on “trap states”. That is, quantum states, which are used only to determine the presence of the spy in the communication channel.
As stated by the creators themselves, the method has an advantage over the others as it can be safely implemented on the basis of current hardware. The basic idea is that Alice is preparing a set of additional “states - baits”, in addition to the standard states used in BB84. Baits are used only for the purpose of detecting eavesdropping, while standard BB84 states are used to generate keys. The main difference between the two is intensity.
Let's imagine that the state of a signal and the state of a signal have the same characteristics (wavelength, timing information, etc.). Thus, Eve cannot distinguish between a lure state and a signal state, and only a portion of the information available to Eve is the number of photons in the signal.
Assuming that the two detectors have equal chances, the error rate is 50%. If the signal has N ≥ 1 photons, it also has a certain frequency error rate. That is, if we speak correctly, the error consists of two parts:
1. Detection error
2. Background contribution
But for the Lo05 protocol, this is not the case. Alice and Bob have the ability to isolate single-photon signals, plus using signals - bait, you can transfer data over a distance of more than 140 km. The protocol is also resistant to small speed disturbances, which ideally eliminates background errors. In addition, the key generation speed was increased by several times, more precisely, the creators talk about an increase of 5 times. Thus, as they say, “using the best of two worlds,” the authors were able to achieve not only an increase in distance, but also an increase in security, not only at small but also at relatively large distances.
PS And by the way about “BUT”, about which I promised to say despite my seemingly ideal nature, the algorithm is very difficult to implement and costly due to the fact that its basic principles are connected with direct current.
PSS When describing the Lo05 algorithm, I deliberately did not load the description with equations, otherwise I would simply have to rewrite the whole article. By the way, if you wish, you can take the link here.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/316252/
All Articles