UI and UX dichotomy: UI designer дизайнер UX designer
Who is told to tweet - do not purr!
Who is told to purr - do not chirp!
(c) Confusion, Korney Chukovsky
On job search sites, 99% of vacancies with the title “UI / UX Designer” contain texts about interfaces, usage scenarios and design. Who was the primary source of this is difficult to say, but the UI and UX have very little in common.
')

I would like to give a goodbaton of argument to my colleagues for expanding their capabilities, well, in general, to finally understand the differences between UI and UX ...
It must be said bluntly that confusion with the UI and UX is happening all over the world, and this concerns many people already. For example, you meet a person who seems to be a specialist in UI / UX. Since there is no clear understanding of who is who, then an awkward moment comes ...

It got to the point that in the Valley UI specialists began to call Digital Product Designer, and UX specialists (sometimes) - Product Manager.
In the original, the term UX was coined by Don Norman and its definition was: UX includes all aspects of user interaction with the company, its services and products.

Most likely, the UX wording turned out to be unnecessarily complicated, and specialists in various fields reduced everything to user interaction via the interface, which was closer to the UI - from which the usage scenarios, interactive interactions, etc. came.
According to Norman’s definition, UX is responsible for all aspects of user interaction with the company , which, of course, includes the user interface (UI). But it turned out that UI professionals specialize in this aspect and it turned out to be some kind of hodgepodge.
It is important that in addition to the interaction through the UI, the client interacts with the company in many more ways and now the UX is already responsible for all these (remaining) methods.
Below, in the examples, I will try to show it more clearly - the UI is responsible for the external side of the question - what the client interacts directly with, and the UX is responsible for the hidden mechanics, but which affects the interaction between the client and the company.
When you enter a restaurant, you pay attention to the interior, table setting, menu design, lights, music, etc. This is all - UI - i.e. everything the client interacts with directly.
UX is responsible for the hidden part: how many places should be in the parking lot, the cost of meals, the number of waiters, order ready time, etc.

Agree, the cost and waiting time of the order greatly affect your impressions (your interaction experience). But for the selection of prices, it is necessary to conduct a segmentation of users - how much the target audience is ready to pay. To estimate acceptable waiting times, one must perform a competitive analysis and compare waiting times at nearby restaurants. Ideally, parking spaces should always be available, but for this you need to predict the capacity of the restaurant and the average time of stay of guests. This is all UX.
You are creating a project to sell online figures from the Marvel universe. You have a UX specialist who is responsible for the client's interaction with your company (remember, besides the UI). To do this, the UX expert should penetrate as deeply as possible into the understanding of who the key user is and, based on this understanding, build the entire interaction strategy.

When the audience became clear, its emotional background is clear, what it wants, what it does not want ... then you can proceed:
After that, all this is shipped to the UI expert, who begins to create and create something tangible. This can begin with branding and end with the packaging in which the product is sent, not to mention the website and all its elements.
Another small example of what the UX is responsible for is the delivery of goods. How often should notifications be sent to the user, where and how he can find out the location of the parcel, what happens if he cancels the order, etc. The UX Specialist doesn’t do the actual logistics or issue of notifications. He forms the view from the user and shares it with logistics experts, contact center, UI specialists. All these people are pros and they will do everything right. The task of UX is to get into the client’s head and understand how it will be most comfortable for him to interact with the service throughout the life cycle.
Suppose you are a home designer. First of all, you discuss with the client UX-questions:

After that, you proceed to the UI-questions:
UX is responsible for common sense - so that people “with eyes closed” still feel comfortable in the house. The UI is responsible for the effect you get from what you see, from tactile sensations to smells.
UX is associated with understanding the user in the broadest sense of the term. UX calculates all possible routes of customer interaction with the company / product / service.
He shares this knowledge (in the form of Storytelling, Wireframing, Prototyping) with his colleagues, including a UI expert. The UI is responsible for the places in the project where direct contact of the company / project / service with the user takes place.
All of you probably know the scheme of the business model from Osterwald:
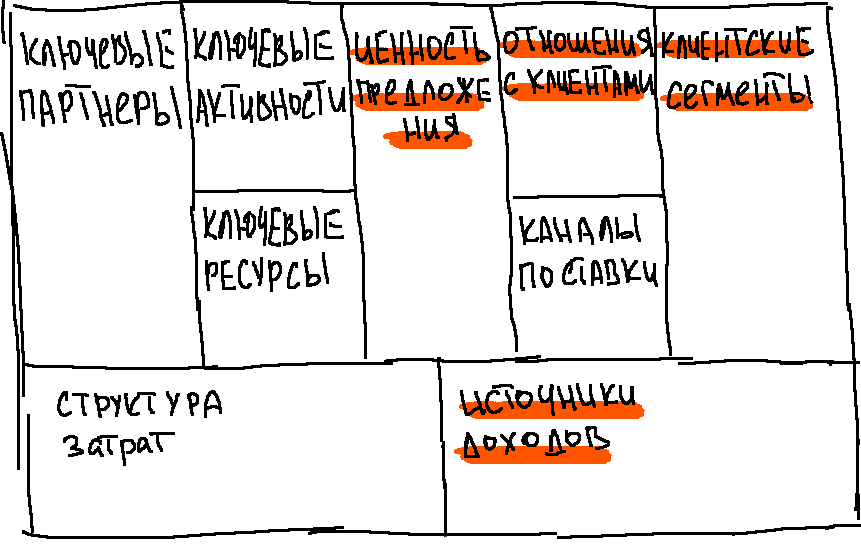
The points on which the UX depends are important for us:
The remaining items are outside our area of expertise.
This distinction is conditional and is not a reason for holivar. Of course, that indirectly all items can affect the quality of customer-company relations. But we all work in a team and it is better to be in close contact with colleagues who are responsible for related issues.
I do not want to repeat myself, so I will try very concisely. The words “strategy and analysis” refer to the UX more. While the UI is more related words - perception and design. The article is written to bring some clarity to the question of the UI / UX relationship and to define the expertise of each of the parties a little more precisely.
PS
I forgot. In my opinion, UI and UX are united by empathy. To understand the user of one analysis is far from enough. Well, in the UI world, this is probably one of the key elements.
Who is told to purr - do not chirp!
(c) Confusion, Korney Chukovsky
On job search sites, 99% of vacancies with the title “UI / UX Designer” contain texts about interfaces, usage scenarios and design. Who was the primary source of this is difficult to say, but the UI and UX have very little in common.
')

I would like to give a good
It's everywhere
It must be said bluntly that confusion with the UI and UX is happening all over the world, and this concerns many people already. For example, you meet a person who seems to be a specialist in UI / UX. Since there is no clear understanding of who is who, then an awkward moment comes ...

It got to the point that in the Valley UI specialists began to call Digital Product Designer, and UX specialists (sometimes) - Product Manager.
Story
In the original, the term UX was coined by Don Norman and its definition was: UX includes all aspects of user interaction with the company, its services and products.

Most likely, the UX wording turned out to be unnecessarily complicated, and specialists in various fields reduced everything to user interaction via the interface, which was closer to the UI - from which the usage scenarios, interactive interactions, etc. came.
Where is UI, where is UX
According to Norman’s definition, UX is responsible for all aspects of user interaction with the company , which, of course, includes the user interface (UI). But it turned out that UI professionals specialize in this aspect and it turned out to be some kind of hodgepodge.
It is important that in addition to the interaction through the UI, the client interacts with the company in many more ways and now the UX is already responsible for all these (remaining) methods.
Below, in the examples, I will try to show it more clearly - the UI is responsible for the external side of the question - what the client interacts directly with, and the UX is responsible for the hidden mechanics, but which affects the interaction between the client and the company.
Examples
A restaurant
When you enter a restaurant, you pay attention to the interior, table setting, menu design, lights, music, etc. This is all - UI - i.e. everything the client interacts with directly.
UX is responsible for the hidden part: how many places should be in the parking lot, the cost of meals, the number of waiters, order ready time, etc.

Agree, the cost and waiting time of the order greatly affect your impressions (your interaction experience). But for the selection of prices, it is necessary to conduct a segmentation of users - how much the target audience is ready to pay. To estimate acceptable waiting times, one must perform a competitive analysis and compare waiting times at nearby restaurants. Ideally, parking spaces should always be available, but for this you need to predict the capacity of the restaurant and the average time of stay of guests. This is all UX.
- UI is responsible for aesthetics and comfort
- UX is responsible for the internal kitchen, which (indirectly) affects the impression of the client
E-commerce project
You are creating a project to sell online figures from the Marvel universe. You have a UX specialist who is responsible for the client's interaction with your company (remember, besides the UI). To do this, the UX expert should penetrate as deeply as possible into the understanding of who the key user is and, based on this understanding, build the entire interaction strategy.

- Who is the target audience
- What is the tone of communication with her choose
- What value can a company provide to a client compared to competitors?
- How to choose a price range
- How and where to attract customers
- What to keep customers
When the audience became clear, its emotional background is clear, what it wants, what it does not want ... then you can proceed:
- Wireframing
- Prototyping
After that, all this is shipped to the UI expert, who begins to create and create something tangible. This can begin with branding and end with the packaging in which the product is sent, not to mention the website and all its elements.
Another small example of what the UX is responsible for is the delivery of goods. How often should notifications be sent to the user, where and how he can find out the location of the parcel, what happens if he cancels the order, etc. The UX Specialist doesn’t do the actual logistics or issue of notifications. He forms the view from the user and shares it with logistics experts, contact center, UI specialists. All these people are pros and they will do everything right. The task of UX is to get into the client’s head and understand how it will be most comfortable for him to interact with the service throughout the life cycle.
- The UI does everything the user interacts with directly.
- The UX is responsible for understanding the user and for building all the processes that lead to user interaction.
New house
Suppose you are a home designer. First of all, you discuss with the client UX-questions:

- What material will the house be built from (in terms of sound / noise insulation)
- The number of windows in each room
- How many children design
- How often guests will be - the size of the living room and the number of bedrooms
- Should there be bathrooms in the corridor or in each bedroom
- Wi-Fi hotspot location
- Etc.
After that, you proceed to the UI-questions:
- What should be facing the house
- What color should be painted walls
- The overall style of the interior decor
- What material should be the furniture
- Lighting Design
UX is responsible for common sense - so that people “with eyes closed” still feel comfortable in the house. The UI is responsible for the effect you get from what you see, from tactile sensations to smells.
Total examples
UX is associated with understanding the user in the broadest sense of the term. UX calculates all possible routes of customer interaction with the company / product / service.
He shares this knowledge (in the form of Storytelling, Wireframing, Prototyping) with his colleagues, including a UI expert. The UI is responsible for the places in the project where direct contact of the company / project / service with the user takes place.
What does not affect the UX
All of you probably know the scheme of the business model from Osterwald:

The points on which the UX depends are important for us:
- Value proposition
- Customer relationship
- Customer segments
- Sources of income
The remaining items are outside our area of expertise.
This distinction is conditional and is not a reason for holivar. Of course, that indirectly all items can affect the quality of customer-company relations. But we all work in a team and it is better to be in close contact with colleagues who are responsible for related issues.
Conclusion
I do not want to repeat myself, so I will try very concisely. The words “strategy and analysis” refer to the UX more. While the UI is more related words - perception and design. The article is written to bring some clarity to the question of the UI / UX relationship and to define the expertise of each of the parties a little more precisely.
PS
I forgot. In my opinion, UI and UX are united by empathy. To understand the user of one analysis is far from enough. Well, in the UI world, this is probably one of the key elements.

Literature
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/315936/
All Articles