Overview of the domestic digital gateway Eltex SMG-1016M (VoIP)

Good day!
This article will highlight the capabilities of VoIP equipment of the Russian company Eltex, in particular the trunk gateway SMG-1016M. Under the cut I will share the experience of setting up this gateway from personal practice.
First, a little about the gateway. Below is a description from the manufacturer's website:
The SMG-1016M platform can be used as a trunk gateway for interfacing TDM and VoIP networks and media streams, IP PBXs with support for DVO and SORM functions, as well as being a universal solution for building infocommunication communication networks of the new generation. The wide functionality, strict compliance with standards and high reliability of the carrier class make it possible to solve on the basis of the SMG-1016M most of the problems arising from operators and service providers.
The manufacturer claims the versatility of this gateway to solve most problems with telecom operators.
I note that the capabilities of the gateway depend on the number of licenses and plug-ins.
To demonstrate the application possibilities, I demonstrate the gateway in conjunction with Asterisk, Huawei SBC, Audio Codes MP-124 and NEC mini-PBX with the E1 card. The equipment is specially selected from different manufacturers. In the demo scheme, the gateway will act as a routing center and extreme point to the sip trunk provider, Asterisk as the new sip phone enablers, and the PBX and Audio Codes as the old FXS ports scheme that suits everyone.
')
Alarm scheme:

Consider setting the gateway for this scheme. After you have gained access to the gateway, we will perform further configuration via the web interface, as the most convenient way (there is also a configuration via Telnet, SSH or RS-232). You can also fill in the finished configuration file, and then edit it for a new inclusion (by the way, a good way for single-type inclusions and recovery in case of an accident).
But we are interested in setting up a clean gateway from the warehouse. When installing new network settings on the gateway, they need confirmation to save to non-volatile memory, so if you make a mistake, just reboot the device and accessibility will be restored. Very useful feature.
We start by updating the software to the current one on the network. There were no problems with upgrade and downgrade, but do not forget to clean the cookies.
To change any settings you need to save the configuration in Flash, the platform will remind you about it.
After we dealt with the network part, we configure sip connectivity. In the Interfaces sip tab - we set the parameters for sip and for individual interfaces. In our case, there will be 3 directions: Asterisk, Audio Codes and SBC. In the interface parameters, we specify the ip address: port, how to register, which codecs we use, the DTMF transmission method, fax detection and other VoIP settings. It is also possible to remove and convert optional fields in sip messages (user agent ...). To monitor transactions help traces from interfaces. In the example, we will use sip trunk without registration with the control of the opposite side with OPTIONS packets. Control is required to switch to another trunk group, in case of an accident.
Next, go to the settings of E1. We turn on Stream 0 and set the parameters agreed upon with the PBX: synchronization source, the presence of CRC4, how many connecting lines we use, etc. I recommend to put synchronization from PBX, as there may be situations when several streams of different providers are connected to PBX, which leads to the formation of slips. If flows from different PBXs are brought to the gateway, then correctly select the synchronization sources. The gateway supports priority selection of synchronization sources over E1 streams and external synchronization sources. The E1 Flow Monitoring tab gives a complete picture of the status of flows, and there is the possibility of removing signaling traffic using PCMdump.
Create and add trunk groups to the created interfaces (4 pieces). Trunk groups are a set of connecting lines (trunks) and have modifiers for inbound and outbound communication with respect to the gateway. Groups can be created both on the whole E1 flow and on individual connecting lines in it, which helps to distinguish concrete sl. under certain numbers at incoming communication.
Modifiers are rules of change. They contain the masks of the number A and the number B, according to them the modifier determines the call in which it can convert CdPN, CgPN / Redir PN, and the type of the number in the case of Q.931. I also note that the modifier can be applied both before the passage of the call through the routing (modifiers of incoming numbers) and after it (the modifiers of outgoing numbers).
Routing parameters interconnection scheme:
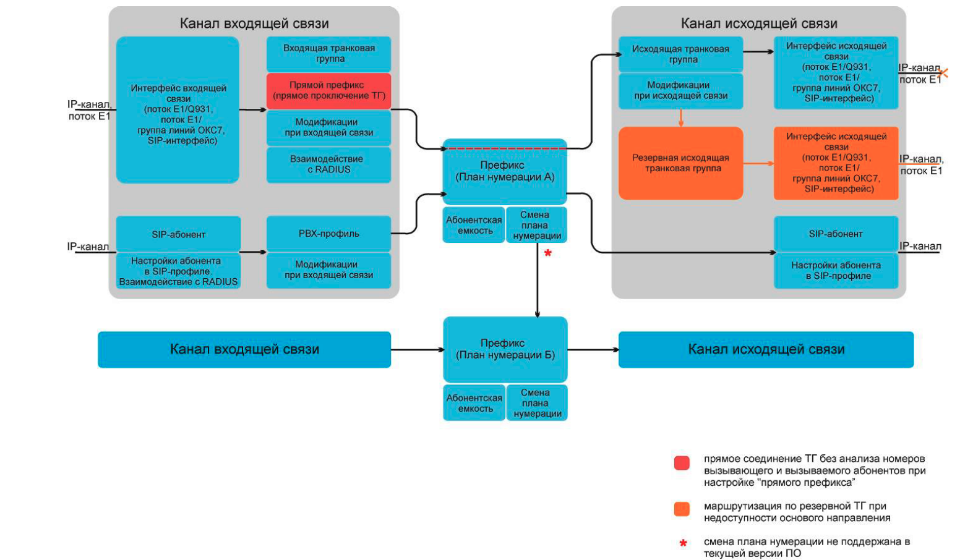
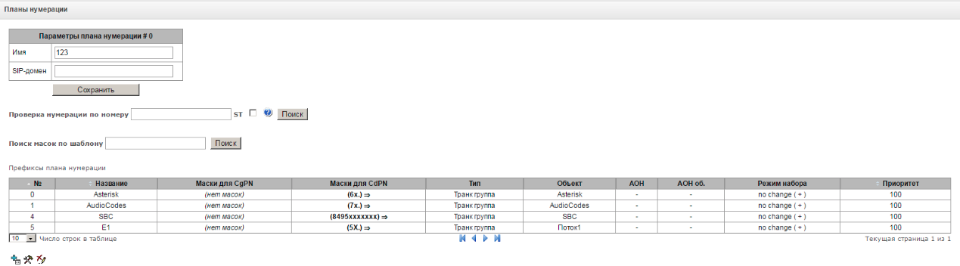
Next, we attach a numbering plan to the created interfaces; it will route calls from this port. The gateway supports several numbering plans (up to 16). They have three criteria by which the route can be searched: by number A, number B, or the base of subscribers configured on the device. In some cases, you can do without the numbering plan, indicating the direct prefix in the trunk group. The search in terms of numbering goes to the first most accurate mask.
A number mask is a pattern or set of patterns with which a subscriber number is compared; it has a simple syntax.
If there is any doubt where the call will go, then we use a hint in the form of checking the numbering by number. Each numbering plan has its own prefix, we bind a trunk group to it, where the call will be routed.
Sample numbering test plan:
At this stage, calls are already possible between all subscribers. But let's imagine that we have a very old mini-PBX and E1 flow drops are possible. The backup trunk group assigned to the trunk group Stream0 will help solve this problem. The transition to the reserve in the case of E1 is carried out according to the error codes that can be assigned (for example, the occurrence of the 27th error (Destination out of order)). It is also possible transitions from sip interfaces to 4XX - 6XX responses or unavailability of the opposite side (Control of accessibility of the opposite side).
The state of the gateway can be monitored by graphics in the CPU usage graph. Zabbix can also be used with snmp queries.
An example of a SYS graph is the percentage of CPU time used by kernel processes:

The article did not consider interaction with the RADIUS server, configuring CORM, FTP storage under CDR (a very flexible function), its own fail2bane, firewall, schedule routing.
Of particular note is the readability of the logs and the ability to write cap files with different filters, as well as detailed and understandable equipment documentation.
From myself I would like to wish the further development and success of the company Eltex. With comments and questions with pleasure I will read in the comments.
List of resources used:
- Documentation from the manufacturer’s website
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/315544/
All Articles