Cloud on Microsoft Hyper-V, Part 3: Storage Spaces Storage
Part 1: Introduction to the Control Panel
Part 2: Deploying Exchange Server
Part 3: Storage Spaces
We continue a series of articles on virtual infrastructure on Microsoft Hyper-V.
Today we will tell you how the storage is based on Storage Spaces and what difficulties we encountered when building it.
Content

The most difficult task when creating a Cloud-V cloud turned out to be the creation of fast software-defined storage based on Microsoft Storage Spaces.
')
At the core of storage is a cluster based on two Dell PowerEdge 730 servers with a Dell PowerVault 3060e disk array connected to them.
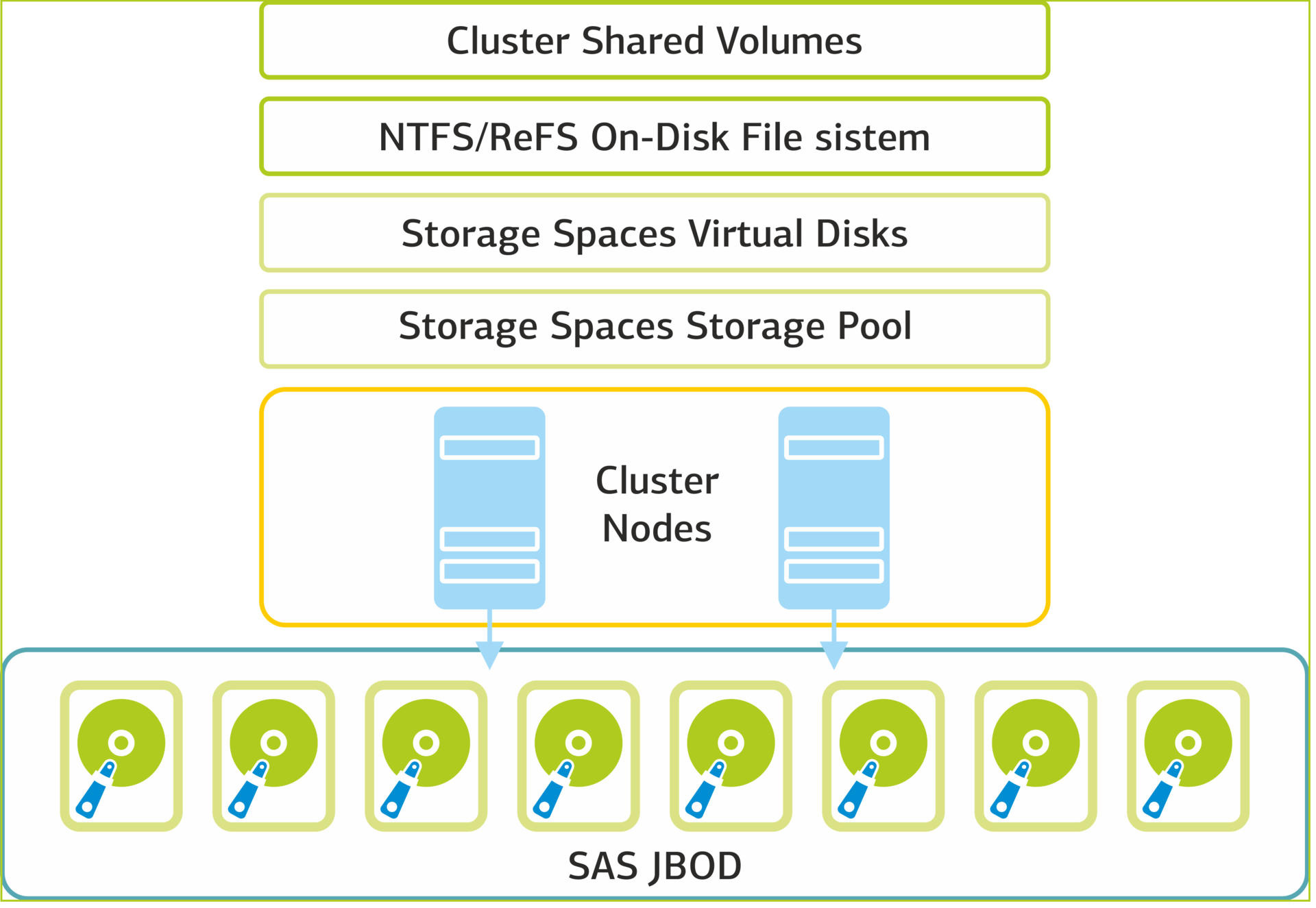
Storage Spaces Architecture
Instead of the traditional SAN storage network, we built a converged local area network with a capacity of 40 Gbps. In the cluster, the Scale-out-file server role was deployed with support for SMB Direct and SMB Multichannel components.
SMB Multichannel allows you to balance the connections of the computing cluster nodes to the storage resources when there are several network adapters on the server. We used Mellanox ConnectX-3 Pro 40GbE network adapters that support the ROCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet) function.
The SMB Direct component uses ROCE to directly access the memory of a remote server, which reduces network latency. Applications from one node access directly the memory of applications on another node, bypassing the network stack of the operating system. As a result, data transfer between nodes is significantly accelerated.
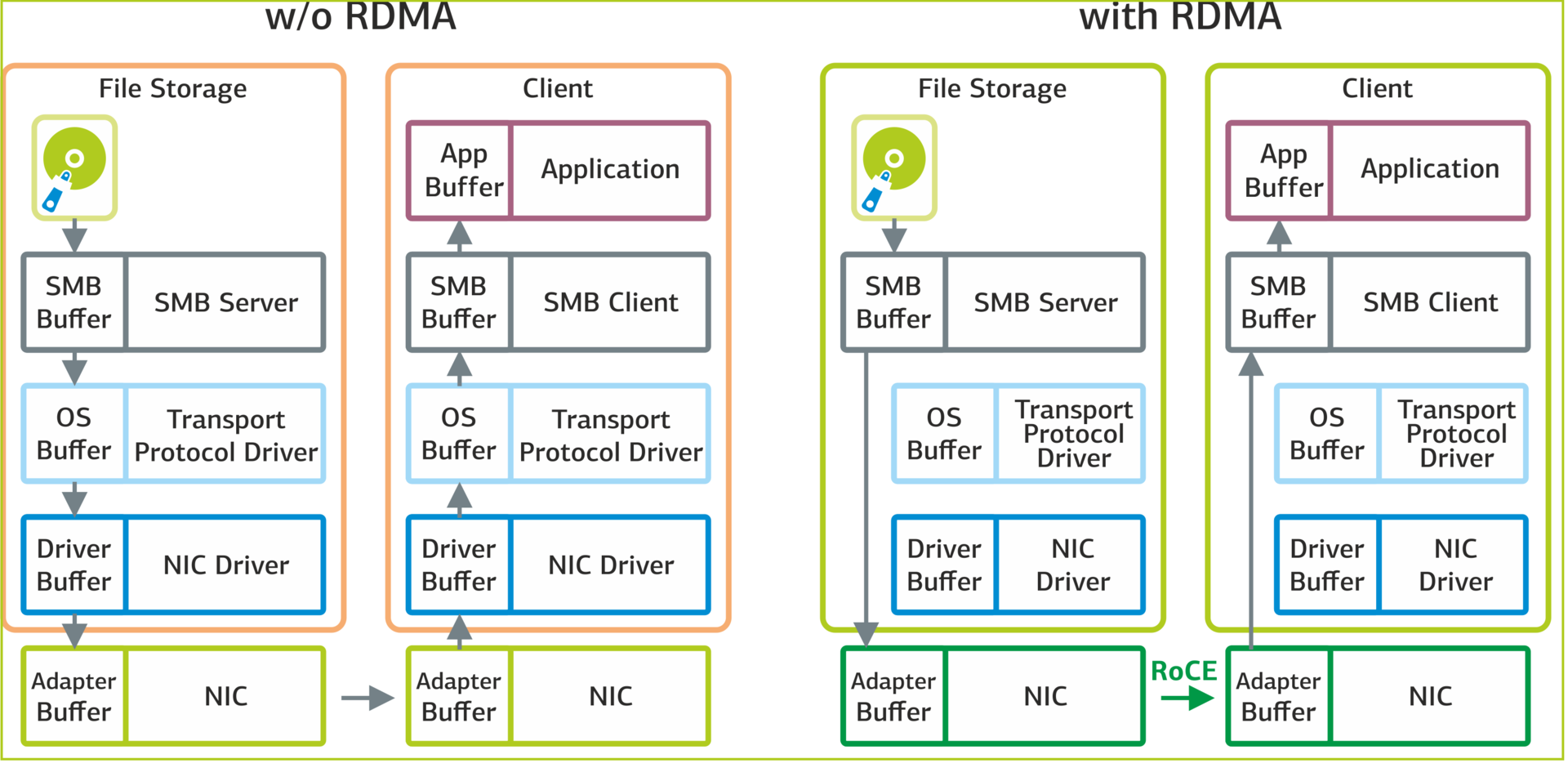
Interaction between the application and disk storage: without RDMA (left) and with RDMA (right).
High performance software-defined storage Storage Spaces is achieved through the use of different types of disks (SATA, SAS, SSD). In fact, we have a multi-level storage, the data in which are distributed across different types of disks, depending on the intensity of use. Storage Spaces filters data and sends rarely used to the lower level (HDD), and “hot” data - to fast SSD drives at the upper level. This type of storage allows more efficient use of resources.
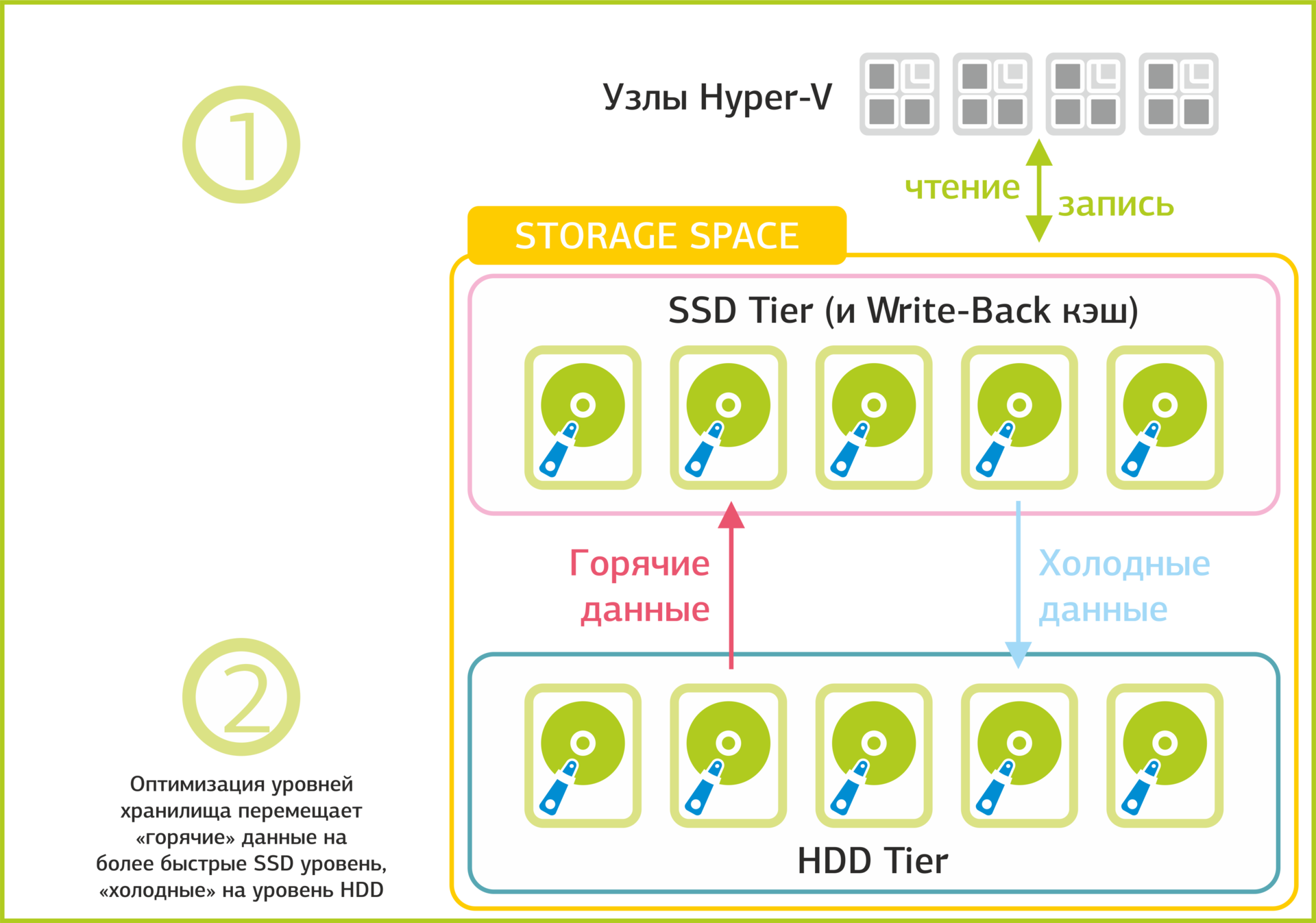
Record and filter data in multi-level storage.
To get such a smart store and make it work, we had to make war. The problem we are facing is low processing speed. Record SSD-drives did not exceed 100 Mbit / s, which is 10 times lower than required for normal performance. The problem appeared immediately when a VM was deployed from a template: one VM of 10 GB in size was deployed for 30–40 minutes, the deployment of two VMs took about two hours.
Suspicion fell on the firmware of the disks: the default did not support simultaneous access from different nodes of the cluster. After upgrading the firmware, the deployment of several VMs ceased to lead to such a dramatic drop in performance. However, everything was still long.
We continued to look for a problem at the lowest level of the architecture and began to analyze the process of exchanging OS driver data with the disk, namely reading and writing sectors to disk. There are two definitions of the sector: logical and physical. The logical sector is operated by the operating system driver, the physical one is directly controlled by the hard disk controller. At this time, hard drives are divided into three types according to the size ratio of the logical / physical sector:
When there are disks of the same type in the pool, there are no problems with the CSV volume created and the virtual hard disk files located on it. Problems begin when different types of disks are combined in the pool. In our case, the pool contained 512 Native (SATA) and 512e (SSD) drives. It is logical to think that a CSV volume will be created with a logical sector of 512 bytes. In reality, it turned out that for newly created VMs, the developers set the default creation of a CSV volume with a logical sector of 4096.
The result was the following picture:
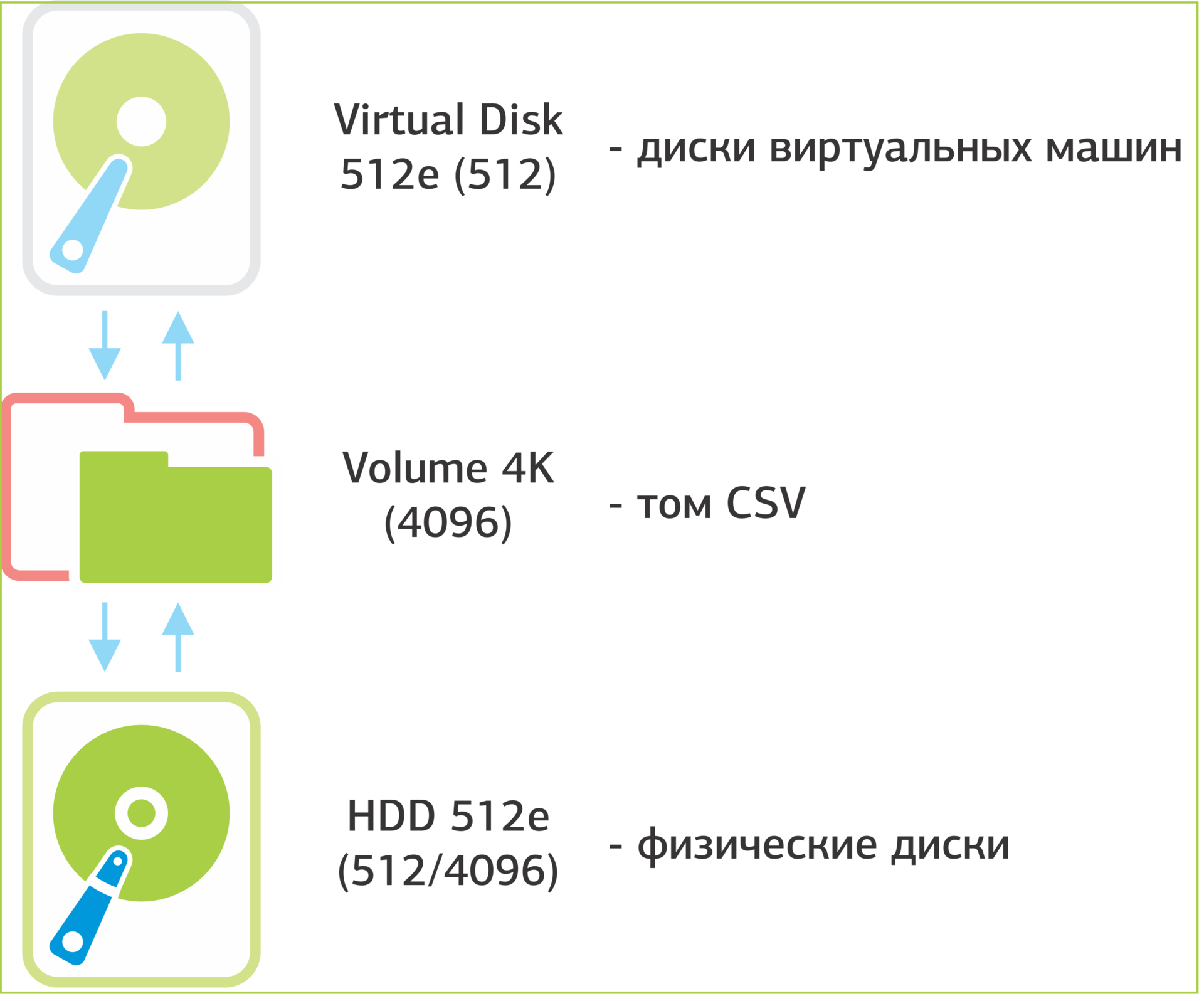
Interaction scheme The physical sector is considered only at the level of the hard disk controller.
A situation has developed in which the logical sector of an overlying disk is smaller than that of the underlying one. This led to the execution of the Read-Modify-Write policy: reading the 4K sector into the cache, editing the required 512 bytes, writing 4K back to the disk. As a result, to a catastrophic decline in the performance of the disk subsystem during recording is 8 times.
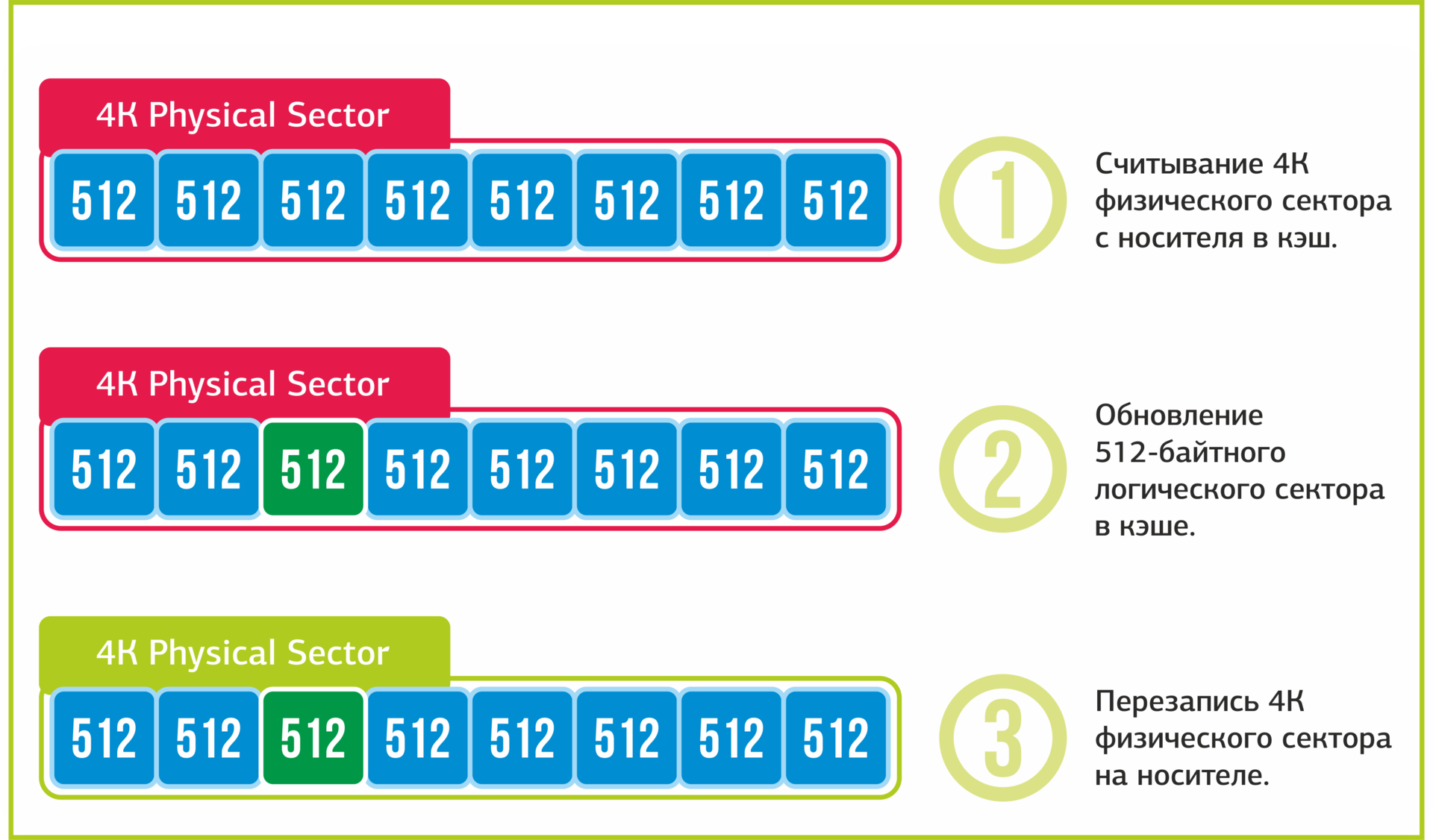
The process of writing a 512-byte sector to a 4096-byte sector media.

As part of Windows Server 2016, an updated version of Storage Spaces - Storage Spaces Direct has been released. As the vendor promises, the new solution eliminates the problems of the current implementation of software-defined storage and there are new features:
We have already started experimenting with Storage Spaces Direct and will talk about first impressions in the near future. Ask questions in the comments.
Author: Sergey Gruzdov
Part 2: Deploying Exchange Server
Part 3: Storage Spaces
We continue a series of articles on virtual infrastructure on Microsoft Hyper-V.
Today we will tell you how the storage is based on Storage Spaces and what difficulties we encountered when building it.
Content
Storage architecture
Storage Performance Issue on Storage Spaces
What is ahead: Storage Spaces Direct

Storage architecture
The most difficult task when creating a Cloud-V cloud turned out to be the creation of fast software-defined storage based on Microsoft Storage Spaces.
')
At the core of storage is a cluster based on two Dell PowerEdge 730 servers with a Dell PowerVault 3060e disk array connected to them.

Storage Spaces Architecture
Instead of the traditional SAN storage network, we built a converged local area network with a capacity of 40 Gbps. In the cluster, the Scale-out-file server role was deployed with support for SMB Direct and SMB Multichannel components.
SMB Multichannel allows you to balance the connections of the computing cluster nodes to the storage resources when there are several network adapters on the server. We used Mellanox ConnectX-3 Pro 40GbE network adapters that support the ROCE (RDMA over Converged Ethernet) function.
The SMB Direct component uses ROCE to directly access the memory of a remote server, which reduces network latency. Applications from one node access directly the memory of applications on another node, bypassing the network stack of the operating system. As a result, data transfer between nodes is significantly accelerated.

Interaction between the application and disk storage: without RDMA (left) and with RDMA (right).
High performance software-defined storage Storage Spaces is achieved through the use of different types of disks (SATA, SAS, SSD). In fact, we have a multi-level storage, the data in which are distributed across different types of disks, depending on the intensity of use. Storage Spaces filters data and sends rarely used to the lower level (HDD), and “hot” data - to fast SSD drives at the upper level. This type of storage allows more efficient use of resources.

Record and filter data in multi-level storage.
Storage Performance Issue on Storage Spaces
To get such a smart store and make it work, we had to make war. The problem we are facing is low processing speed. Record SSD-drives did not exceed 100 Mbit / s, which is 10 times lower than required for normal performance. The problem appeared immediately when a VM was deployed from a template: one VM of 10 GB in size was deployed for 30–40 minutes, the deployment of two VMs took about two hours.
Suspicion fell on the firmware of the disks: the default did not support simultaneous access from different nodes of the cluster. After upgrading the firmware, the deployment of several VMs ceased to lead to such a dramatic drop in performance. However, everything was still long.
We continued to look for a problem at the lowest level of the architecture and began to analyze the process of exchanging OS driver data with the disk, namely reading and writing sectors to disk. There are two definitions of the sector: logical and physical. The logical sector is operated by the operating system driver, the physical one is directly controlled by the hard disk controller. At this time, hard drives are divided into three types according to the size ratio of the logical / physical sector:
- 512 Native - logical 512, physical 512;
- 512e - logical 512, physical 4096;
- 4096 Native - logical 4096, physical 4096.
When there are disks of the same type in the pool, there are no problems with the CSV volume created and the virtual hard disk files located on it. Problems begin when different types of disks are combined in the pool. In our case, the pool contained 512 Native (SATA) and 512e (SSD) drives. It is logical to think that a CSV volume will be created with a logical sector of 512 bytes. In reality, it turned out that for newly created VMs, the developers set the default creation of a CSV volume with a logical sector of 4096.
The result was the following picture:

Interaction scheme The physical sector is considered only at the level of the hard disk controller.
A situation has developed in which the logical sector of an overlying disk is smaller than that of the underlying one. This led to the execution of the Read-Modify-Write policy: reading the 4K sector into the cache, editing the required 512 bytes, writing 4K back to the disk. As a result, to a catastrophic decline in the performance of the disk subsystem during recording is 8 times.

The process of writing a 512-byte sector to a 4096-byte sector media.
We found two ways to solve the problem:
- Re-create existing virtual hard disks with a 4K logical sector size. As a result, this option did not suit us, since not all components of the architecture support virtual disks located on volumes with sector 4096.
- Migrate existing virtual hard disks to a temporary location and re-create a CSV volume with a logical sector size of 512. This is the option we chose.
The table below shows the speed values before and after the implementation of this solution. In the case of “after”, the check was performed by simultaneously running DiskSpd testing on 15 virtual machines.

What is ahead: Storage Spaces Direct
As part of Windows Server 2016, an updated version of Storage Spaces - Storage Spaces Direct has been released. As the vendor promises, the new solution eliminates the problems of the current implementation of software-defined storage and there are new features:
- Multi-threaded deduplication, which allows you to allocate certain processor cores to the deduplication process. In Storage Space, only single-threaded deduplication is currently available based on a single processor core. Real-time deduplication is not possible, and the process itself takes a long time.
- Rebalancing All data can be redistributed by volume. This allows for greater performance of the disk subsystem. In Storage Space, when adding new hard drives to the pool, data will start to fall on the added hard drives only after the initially allocated disks are filled.
- Various scaling options. In Storage Spaces, scaling occurs only by adding new disk shelves, which is expensive and inconvenient.
We have already started experimenting with Storage Spaces Direct and will talk about first impressions in the near future. Ask questions in the comments.
Author: Sergey Gruzdov
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/315472/
All Articles