Y. Schmidhuber: “It's great to be part of the future of artificial intelligence”

In the last days of September, the GTC EUROPE 2016 graphics technology conference was held in Amsterdam. Professor Jürgen Schmibdhuber presented his presentation as the scientific director of IDSIA, a Swiss laboratory, where he and his colleagues are engaged in research in the field of artificial intelligence.
The main thesis of the speech - a real artificial intelligence will change everything in a short time. For the most part, the article you are reading now is based on the presentation of Professor Schmidhuber.
The most influential discovery of the 20th century is the Haber-Bosch process : extracting nitrogen from the air to produce fertilizer. As a result, this led to an explosion of the population in less developed countries. For comparison:
')
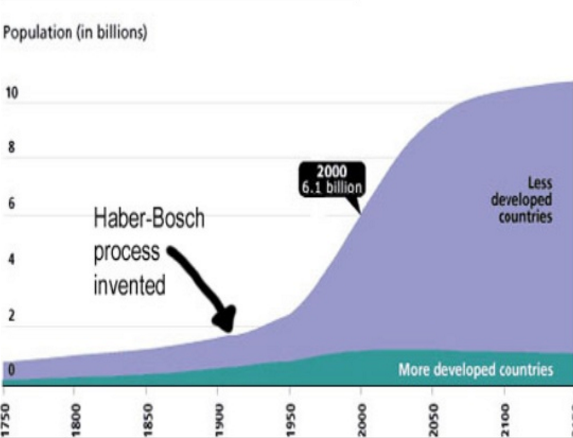
An impressive leap, and an artificial intelligence explosion in the 21st century will be even more impressive according to Jürgen Schmidhuber
It all started with the fact that in 1941 Konrad Zuse presented the first computer operating on common circuits. Computers are getting faster and cheaper every year. Over 75 years, they fell 1,000,000,000,000,000 times.
In 1987, the thesis of the thesis of Schmidhuber sounded like this: “the first concrete development of a recursive self-developing AI”.
The history of deep learning began in 1991. Schmidhuber deserves Alexey Grigorievich Ivakhnenko deservedly as the father of deep learning. Without his methodology and control systems, there would be no discoveries in the laboratory of a professor in Switzerland.
In 1965, he published the first learning algorithms for deep networks. Of course, what we used to call today “neural networks” didn’t even seem that way then. Ivakhnenko studied deep multilayer perceptrons with functions of polynomial activation and layer-progressive training with regression analysis. In 1971, a network of deep learning with eight layers was described. Today the finds of that time are still used.
Obtaining a training set of input vectors with the corresponding target of the output vectors, the layers with nodes of additional and multiplicative neurons grow incrementally and are trained using regression analysis. After that, the extra information is removed using the verification data, where regularization is used to screen out the extra nodes. The numbers of layers and nodes in one layer can be trained in a problem-dependent way.
Now about controlled feedback. Works of pioneers of the region:
- Continuous Feedback Euler-Lagrange Calculations + Dynamic Programming, Bryson 1960, Kelly 1961 ;
- Feedback through the chain rule, Dreyfus, 1962 ;
- Modern OS in rare discrete networks similar to neural networks (including Fortran-a code) networks, Linmainma, 1970;
- Changing the weights of the controllers, Dreyfus, 1973;
- Automatic differentiation could show the OS in any differentiable graph, Spilpenning, 1980;
- OS applied to neural networks, Verbos , 1982;
- RNN examples, Williams, Verbos, Robinson, 1980;
RNNs are recursive neural networks with deep learning. In 1991, Professor Schmidhuber created the first network with in-depth training. The process of uncontrolled training before training for hierarchical temporary memory looks like this: stack RNN & compressed history & accelerated supervised learning. LSTM - long short-term memory is a kind of neural network. LSTM RNN today is widely used in production and research to recognize data sequences in images or videos. Around 2010, the story repeated itself: uncontrolled FNNs were replaced by partially controlled FNNs everywhere.
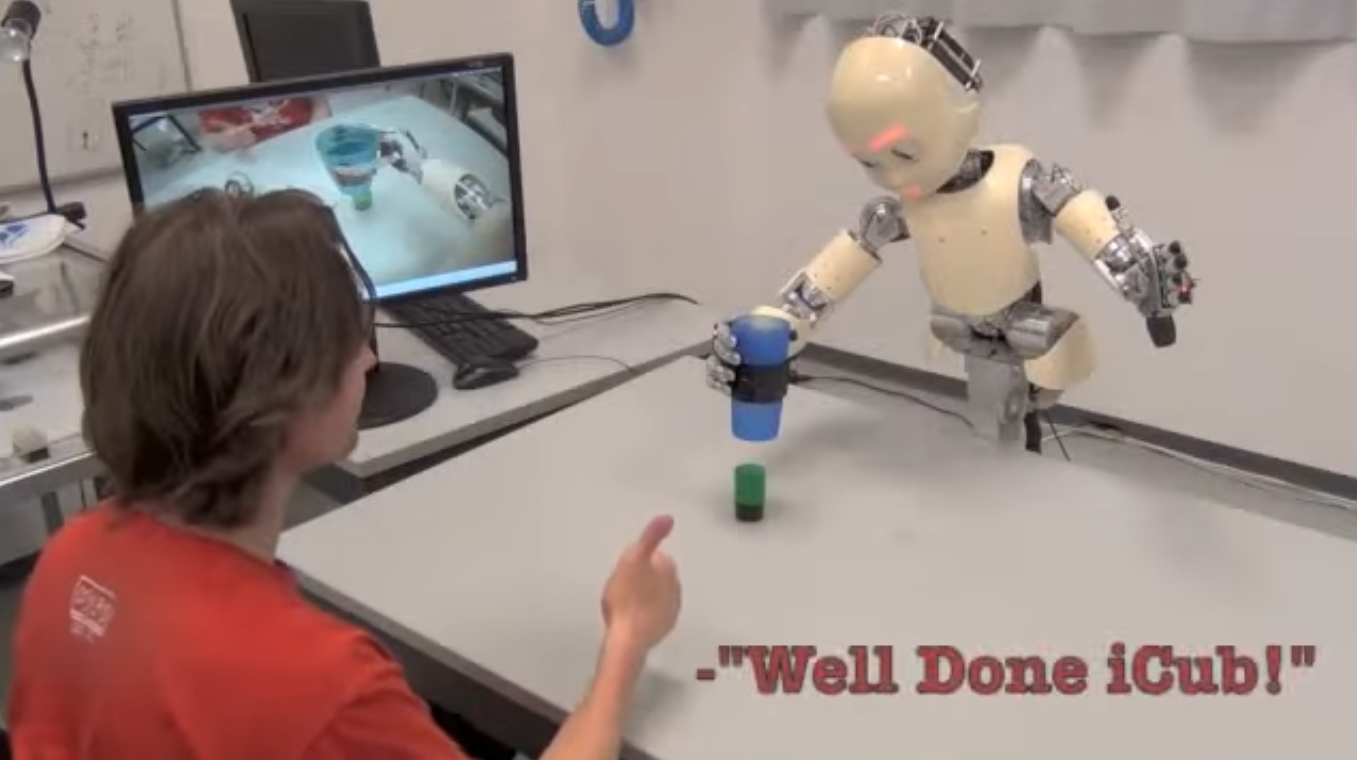
At the entrance to the AI network there are different types of signals: images, sounds, emotions, perhaps - and at the output of the system, muscle movement (in humans or robots) and other actions are obtained. The essence of the work is to improve the algorithm - it develops just as young children train motor skills.
The LSTM method was developed in Switzerland. These networks are more advanced and universal than the previous ones - they are ready for in-depth training and various tasks. The network was born because of the curiosity of the author, and is now widely used. For example, this is the voice input feature of Google Speech. Using LSTM has improved this service by 50 percent. The process of learning the network looked like this in this case: many people slandered phrases for example learning. At the beginning of the training, the neural network does not know anything, and then, after it listens to many passages, for example, English, it learns to understand it by memorizing the rules of the language. The network can later translate from one language to another. Examples of use - in the image below.

Most LSTM is used in Google, Microsoft, IBM, Samsung, Apple, Baidu. These companies need neural networks to recognize speech, images, machine translation tasks, create chat bots, and much more.
Let us go back again: twenty years ago, the car became the best chess player. Game champions of non-human origin appeared in 1994 - TD-Gammon in the game Backgammon. Learning winner created at IBM. For chess - also at IBM - they designed the non-learning Deep Blue. This refers to machine vision.
In 1995, the robokar traveled from Munich to Denmark and back along public highways at a speed of up to 180 km / h without GPS. In 2014, the year was also the 20th anniversary of the emergence of self-driving cars in the stream on the highway.
In 2011, a road sign competition was held in Silicon Valley. During him, the development of the Schmidhuber laboratory showed results twice as good as human, three times higher than the closest artificial competitor and six times better than the neuroneless FIRST (recognition of visual patterns). This is used in self-driving cars.
There were other victories.
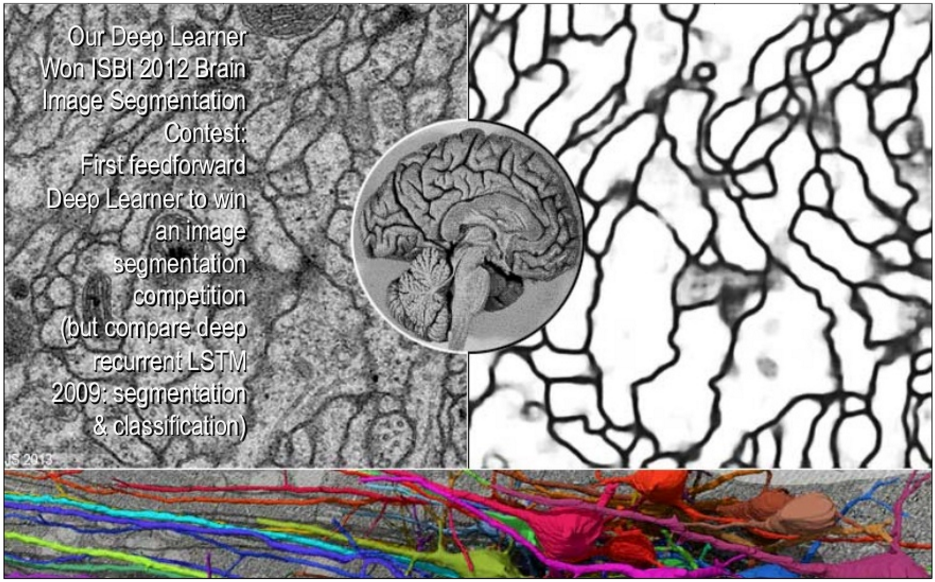
A similar technique is applicable in medical cases. For example, the recognition of dangerous pre-cancerous cells at an early stage of mitosis. This means that one doctor will be able to cure more patients per unit of time.
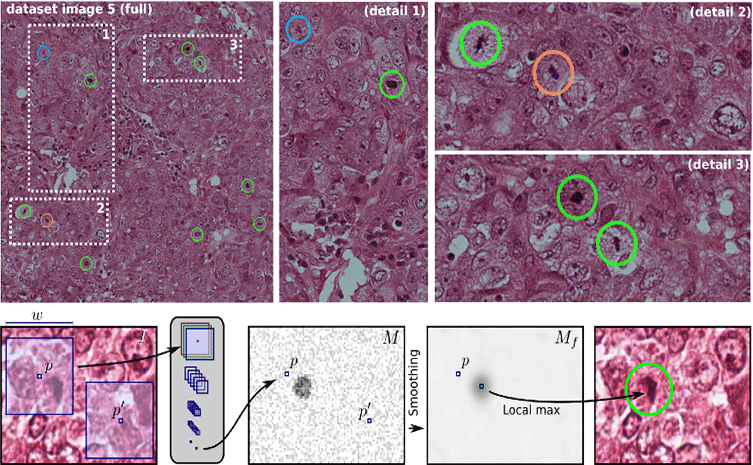
Pre- LSTM and backbone networks - in each layer, the function x + x, for training neural networks with hundreds of layers.
Best segmentation in LSTM networks:
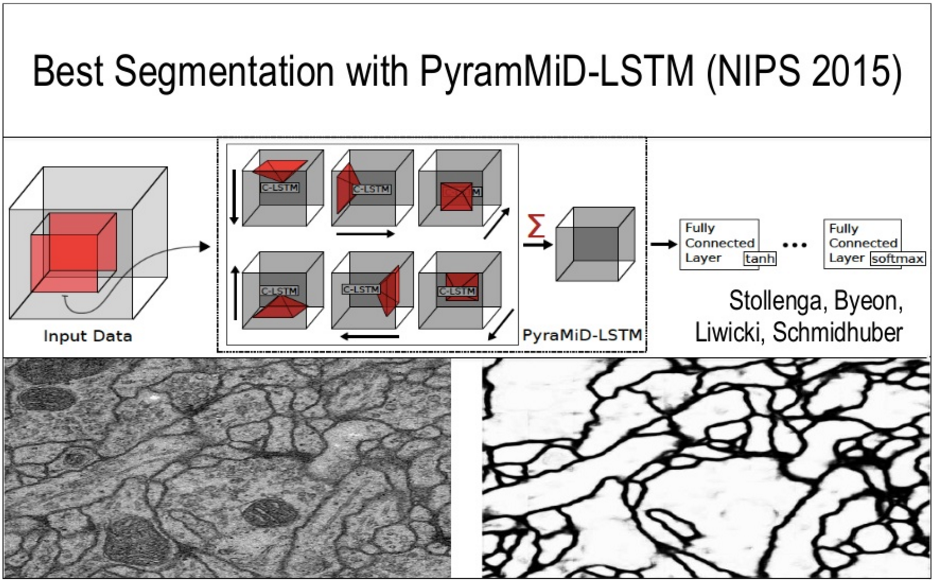
The students of the professor have created the Brainstorm open source library of neural networks .
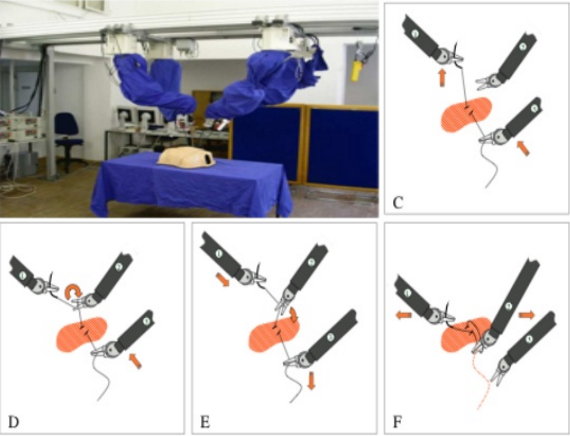
Meanwhile, the robots were busy developing fine motor skills. And LSTM networks learned how to tie knots.
For a little more than 20 years, in-depth training has gone from tasks with at least 1000 computational stages (1991-1993) to anticipatory recursive neural networks with more than 100 layers (2015).
Everyone remembers how Google bought DeepMind for $ 600 million. Now the company has a whole division dedicated to machine learning and AI. The first employees, the founders, DeepMind came from Professor Schmidhuber's laboratory. Later two more PhDs from IDSIA moved to DeepMind.
Another work of Professor Schmidhuber on finding complex neurocontrollers with millions of weights was presented in 2013 at GECCO . Refers to compressed network searches.
In the 1990-1991s, recursive learning of visual attention on slow computers was designed to get an additional fixed input. In 2015 - all the same. In 2004, he passed the robots' cup in the fastest league at a speed of 5 meters per second. The competition successfully used what Schmidhuber proposed back in 1990 - forecasting expectations and planning using neural networks.
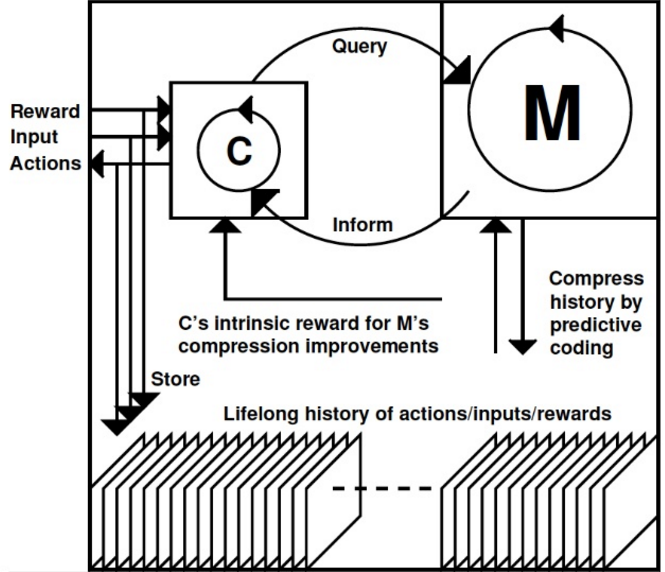
“Revival” 2014-2015 or as it is called in English RNNAIssance (Reccurent Neural Networks Based Artificial Intelligence), was already learning to think: the theory of algorithmic information for new combinations of enhanced learning of recurrent neuromodels of the world and RNN controllers.
An interesting scientific theory is given by the professor as an explanation of the phenomenon of "fun." Formally, fun is something new, amazing, eye-catching, creative, curious, it combines art, science, and humor. Curiosity, for example, is used in improving the skills of human-like robots. It takes a lot of time. During the experiment, the robot learns to put a glass on a small stand. The influence of intrinsic motivation and external praise on the learning process is being studied.
Know about PowerPlay ? He not only solves, but also constantly comes up with problems on the border of the known and the unknown. So, incrementally, the solution of common tasks is trained by constantly searching for the simplest, still unsolved problem.
What will happen next in Schmidhuber's opinion: the creation of a small, animal-like (for example, a monkey or a raven) AI that will learn to think and plan hierarchically. Evolutions took billions of years to create such animals and much less time to move from them to a human being. Technological evolution is much faster than natural.
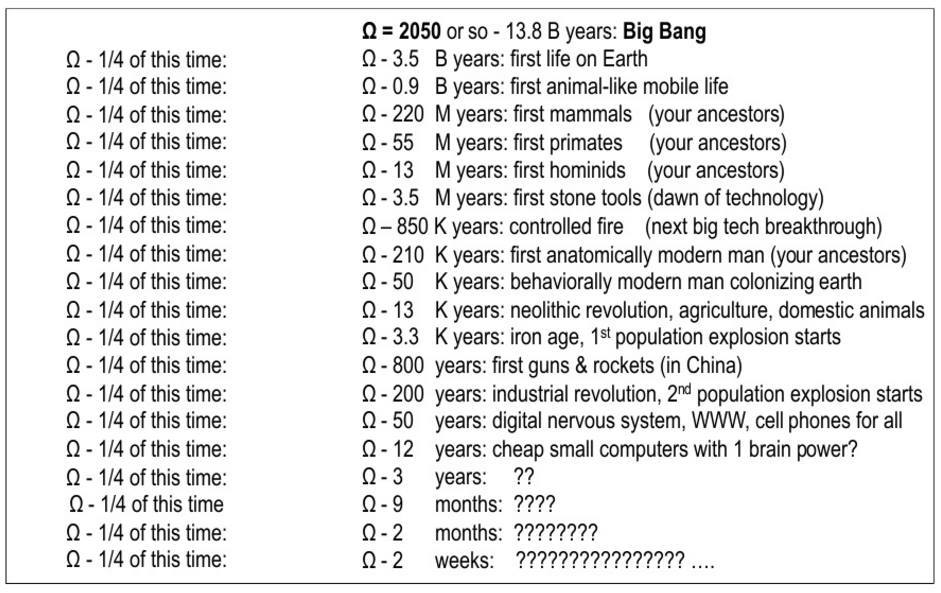
A few words about the beautiful simple pattern, opened in 2014. It deals with exponential growth in most historically important events in the universe from a human point of view.
Professor comment on science fiction:
I prefer to call the singularity Omega because this is exactly what Teilhard de Chardin said 100 years ago and because it sounds like “Oh my god”. In 2006, I described a historical pattern that confirms that 40,000 years of dominant Human positions will lead to the Omega point in the next few decades. So, I show incredibly accurate exponential growth, which describes the entire development path up to the Big Bang. In it - the whole story, probably the most important events from the point of view of man. The probability of error is less than 10%. I first spoke about this in 2014.
Cosmos is not human-friendly as opposed to properly designed robots.
After the presentation in Amsterdam, in terms of questions and answers, a moment was touched upon with the emergence of so-called robot journalists or any other models capable of performing the work of many people. The presenter was interested in whether people from the “text sphere” should worry about the presence of artificial intelligence and its development. The professor believes that robots can not replace people, they are created to help him. And they will not fight with a man, because they have different goals with him. Interestingly, popular science fiction films interpret the theme incorrectly. Wars in real life are fought between similar creatures — people fight other people, not bears, for example. But if AI will be used for “bad military things”, it depends on the ethics of people - so this question is not about the development of AI.
It is important to remember the origins.
Last year, Nature magazine published an article about how deep learning allows computational models, consisting of multiple layers of processing, to study data representations at many levels of abstraction. Such methods have greatly improved the state of things in speech recognition, visual objects and other areas, such as drug discovery and genome decoding. In-depth training uncovers intricate structuring in huge data sets. Feedback algorithms are used for this - they indicate how the machine should change its internal parameters, which are used to calculate the representation in each layer from the representation in the previous layer. Deep convolutional networks have been a breakthrough in image processing, video, speech and sound, and recurrent networks have shed light on consistent data such as text and speech.
This is the critical commentary given by Jürgen Schmidhuber.
Machine learning is the science of gaining trust. The machine learning society benefits from the right decisions to “give responsibility” to the right people. The inventor of an important method must receive approval for the invention of this method. Next, another person who popularizes the idea of the method should also gain confidence in it. It may be different people. A relatively young area of machine learning research should adopt a code of honor from more mature sciences — for example, mathematics. What does it mean. For example, if you prove a new theorem using methods that are already known, this should be clearly and clearly. Well, if you invent something that is already known and have learned about it in fact, then you should also clearly mention it, even later. Therefore, it is important to refer to everything that was invented earlier.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/315148/
All Articles