VMware Replication and Disaster Recovery Solutions: vSphere Replication and Site Recovery Manager (SRM)
Site Recovery Manager (SRM)
VMware Site Recovery Manager (SRM) is a business continuity and disaster recovery solution designed to plan, test and restore VMs (virtual machines) from a protected (primary) site to a (backup) recovery site.
SRM offers 3 approaches to VM protection (replication):
• Storage groups (datastore groups). Protecting VMs in storage groups via third-party replication mechanisms (3rd party). Array-based replication is used at the array level.
• Separate VMs . Protection of individual VMs at the host level. SRM is used in combination with VMware vSphere Replication technology.
• Storage policies. VM protection based on special retention policies. Array-based replication is used at the array level.
SRM provides 2 options for restoring a site (data center):
')
• Planned migration. It assumes the availability and full functionality of the main and backup sites. Eliminates data loss, this is a scheduled operation, runs in working order, without emergency situations.
• Disaster recovery. Calculated on the sudden fall of the main site, switching to a backup site, an unplanned operation.
SRM orchestrates data center recovery processes and replication mechanisms, which minimizes data loss and recovery time:
• SRM provides VM extinguishing at the primary site and data synchronization between sites in the event that the primary site is operational.
• SRM runs replicated VMs on the backup site in the order determined by the recovery plan.
SRM allows you to test recovery plans. For tests, temporary copies of the replicated data are used, which allows eliminating the impact on the basic processes of both sites.
SRM provides 2 deployment options in the context of relationships between sites:
• Basic (unidirectional) option - suggests the possibility of migrating the services of the main data center (protected site) to the backup site (recovery site).
• Bidirectional option - provides VM protection in both directions. Each site in the formed pair is the main one, performing the backup function for its neighbor.
Site configuration requirements for SRM operation:
• Identity and compatibility of SRM, vCenter Server, vSphere Replication versions on both sites.
• In the case of replication at the array level (Array-based replication), the selected replication technology must be maintained at both sites, and the arrays must be paired.
• The infrastructure of the backup site (hosts, networks, storage) must correspond to the VM and support the load of the main site. The backup site can be loaded (above the norm) with unproductive or non-critical VMs that can be stopped if the main site is restored.
• Sites must be connected through a reliable IP network that provides the necessary bandwidth.
• The backup site must have a connection to public and private networks accessible to the main site.
The technology requires the installation of SRM servers (Site Recovery Manager Server) on the primary and backup sites. For small data centers, it is permissible to install an SRM server on the same system as the vCenter server, in particular, installing them on one VM. For large infrastructures for reasons of load and availability, it is advisable to install the SRM server on a separate system (on a separate VM).
Multi-site SRM configurations
The standard configuration, which was discussed above, included 2 sites: primary and backup. Both sites have a vCenter server that is connected via SRM servers installed on both sites. Thus, VMs belonging to the primary site vCenter can be restored to the backup site vCenter.
In case the data center has more than 2 sites, SRM supports various multi-site configurations:
• Shared recovery site - shared recovery site (many-to-one, N: 1) - many protected sites can replicate and restore their VMs to one shared backup site;
• Shared primary site - shared protected site (one-to-many, 1: N) —the primary site has several backup sites;
• Many to many - many-to-many (N: N).
SRM entities (SRM servers) on the primary and backup sites must be paired, they are assigned the same identifier (extension ID). Therefore, on a common site, the number of SRM entities equal to the number of its partner sites should be raised. For example, if the general recovery site serves 5 protected sites, then 5 SRM servers must be deployed on it, which are paired with the protected sites. Shared site SRM servers must be installed on different VMs (host machines) and have unique identifiers. At the same time, multiple SRM entities of a common site interact with one vCenter server that manages this site.
You cannot install multiple SRM servers on a single host machine (VM). Each SRM server must have its own database. One recovery site can have no more than 10 protected sites.

SRM with array-level replication (Array-based replication)
This approach involves the replication of data between sites at the level of arrays (SHD), through their replication mechanisms. SRM integration with arrays is done through storage replication adapters (SRAs), these are software components that must be developed by array manufacturers. To support Array-based replication on the SRM-server, each site must have SRA installed for each array connected to it.
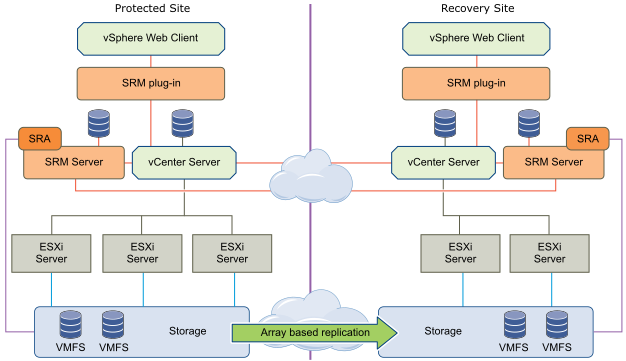
SRM using vSphere Replication
SRM can use vSphere Replication (a built-in and free VMware vSphere technology package) to replicate data at the VM level between sites. The operation of vSphere Replication does not depend on the type and model of the storage, does not require integration with the array (developed by SRA), and supports any storage compatible with vSphere.
vSphere Replication allows you to create a chain of snapshots for replicated VMs on a backup site — many replicas of protected machines at different points in time. Thus, it is possible to select the optimal state of the VM to restore among the many snapshots of the replica.

Mixed replication mode
SRM supports a mixed mode of operation in which both replication mechanisms are shared: Array-based replication and vSphere Replication. This mode requires the deployment and configuration of these technologies on both sites. Configuring different replication mechanisms for the same VMs is not supported. However, SRM allows you to include in the same plan restoration tasks with different replication mechanisms, but for different VMs.

vSphere Replication
vSphere Replication is an extension for vCenter that provides replication and recovery of VMs at the hypervisor level, as well as provides monitoring and management of these processes. This technology is an alternative to replication at the array level. The solution supports the following options for replicating a VM site:
• between the source site and the target site (site-to-site);
• between clusters within one site;
• between multiple sources sites and a common target site (many-to-one).
vSphere Replication is independent of the type of array and supports any vSphere compatible storage. The solution is included in all editions of vSphere (with the exception of the most simple and useless) and does not require the purchase of licenses.
Replication is accomplished by transferring modified blocks between sites or clusters of source and target. This implies an initial full synchronization of the source and replica VMs. Configuring the replication task allows you to set the RPO, as well as activate the ability to save multiple intermediate time states of the replica (MPIT - multiple points in time) - an analog of VM snapshots.
It is possible to monitor and manage the status of replication, obtaining information about incoming and outgoing replications, the status of sites, replication results and errors.
The process of recovering a VM from a replica is not automated and requires manual intervention. In particular, it requires manually selecting the state of the VM to synchronize with the source site or restore the last state from the replica. The restored VM does not have network connections in order not to cause potential conflicts, which requires manual connection of the VM to the necessary virtual data center networks. MPIT provides recovery of a replicated VM with a given snapshot chain, which makes it possible to select the desired state of the restored VM.
The vSphere Replication appliance is the main essence of the solution, which is registered and connected as an extension to the vCenter server. vCenter allows the installation and connection of only one vSphere Replication appliance (VR appliance). The VR appliance includes an embedded vSphere Replication server that manages all replication processes. For load balancing, deployment of additional vSphere Replication servers is supported, which are connected to the main VR appliance of this site (vCenter) and, in fact, are themselves virtual elasens.
Sample site-to-site replication configuration:

An example of replication configuration between clusters within a single site, using 2 VR servers for load balancing (this is not necessary, you could do with one VR appliance):

An example of many-to-one replication configuration:
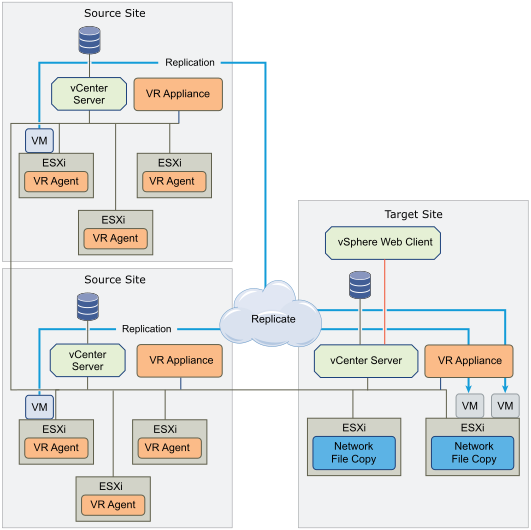
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/315020/
All Articles