Checking an open source partner

In our country, no one is insured by the contract partner: “customers do not pay freelancers, co-founders leave the project, and suppliers refuse to execute contracts. Good buyers are valued for having good bases and connections in tax and can informally check any counterparty. Fortunately, the opaque Russian market in recent years is becoming clear: several free public services appeared at once to check the counterparty for honesty. About them will be discussed in the article.
No one is insured against the refusal of the counterparty to pay under the contract. To get your money, you have to go to court, and, at a minimum, spend your time; in a particularly neglected case, the counterparty may not have a penny. As a result, he will shirk responsibility completely unpunished (liquidation of the company does not count) In practice, only one hundred percent prepayment will protect one hundred percent; if the counterparty does not agree, you should at least go through the first points of the checklist.
')
Basic checklist
1. Check reviews of the counterparty on the Internet (Yandex.market, groups dissatisfied in social networks). It is advisable to check not only by brand, but also by the name of the company (which is specified in the contract and on the accounts), and by the name of the director / founder (there may be several firms).
A case from practice: an office manager ordered a coffee machine for our company, by clicking on the cheapest offer in Yandex Market. The car was brought the next day. After it was unpacked and refilled, it turned out that one of the internal hoses had been torn in the car and it was leaking. It turned out that we bought the car from Labion, a company known for its dishonesty: it sold (and still sells) deliberately broken and illiquid goods to legal entities. The Law “On Protection of Consumer Rights” does not apply to relations between entrepreneurs, and no one wants to go to court. In the end, the coffee machine repulsed, but the sediment, of course, remained.
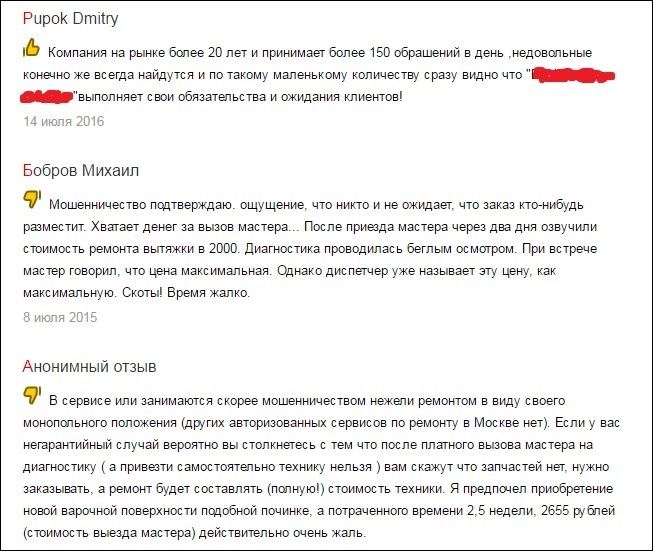
Low rating and paid reviews are a bad sign.
2. Check the company for the register - legal entities . Main questions:
- How long is it registered?
- How often did the director change?
- In which region (mismatch of regions will affect the cost of the court)?
- Where is the office (in the business center, apartment, on the "mass address")?
- Does the address coincide with the addresses of other companies (the address is plugged into a search engine)?

They do not write directly about the cases of a director change in the Unified State Register of Legal Entities, but the form 14001 is with a probability of 95% either a director change or an address change. The address change can be indirectly checked by the TIN and the change history of the statement.
3. The base of decisions of arbitration courts was previously partially available through systems like Consultant Plus, but now the service “Card file of arbitration cases” is working with decisions of all instances and searching by the name of the organization. There you can check with whom the company is suing or suing, whether the old debtor was suddenly declared bankrupt, and so on.
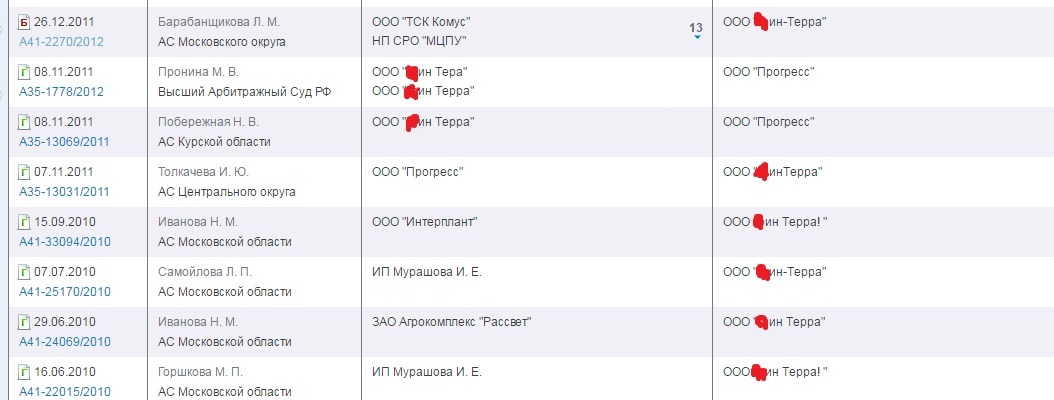
The most unpleasant option: to find that your partner has at least two parallel companies with similar names, one of which was recently declared bankrupt with heavy debts.
4. Rosstat’s accounting records base: gks.ru/accounting_report Contains basic accounting information about the counterparty - net profit, assets, balances for the last years. Of course, not everyone transmits information to Rosstat, so the fact of being there already speaks in favor of your counterpart. In addition, responsibility for evasion has recently been tightened, and many new faces should now appear in the Rosstat base.
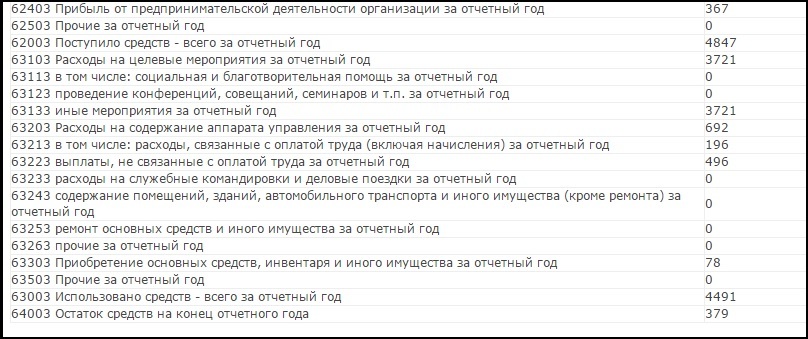
Secret becomes clear: you can find out even the director's salary
Additional checklist
In addition to the basic checks, if you have time, you can also run according to the additional list:
5. The register of unscrupulous suppliers of the FAS, which fall into the "purchasing trolls" and suppliers who have not fulfilled the conditions of the state contract: rnp.fas.gov.ru.
6. Register of bankruptcy information. The counterparty is unlikely to be there (if only he is under external management), but other companies of the same owner can be found. Compared to the “filing cabinet”, there are more documents here - say, you can see whether the creditors' claims are satisfied and whether managers are not held accountable. bankrot.fedresurs.ru .
7. The data bank of enforcement proceedings - here are all defaulters who evade enforcement of court decisions: fssprus.ru/iss/ip/ .
8. The base of tax evaders and "abandoned" companies (while working in test mode and only for legal entities): service.nalog.ru/zd.do .
9. Counterparty representatives can also be checked in the register of disqualified ones - whether the court has prohibited them from running companies for administrative or tax offenses: service.nalog.ru/disqualified.do .
And finally, be sure to check the credentials of the person who signs the transaction on behalf of the other party. Remember: the contract becomes valid on the basis of a signature, not a seal, therefore, the presence of a seal with a representative does not guarantee the completion of the transaction. When it comes to invoice or invoice, it is not so important; but if you sign a large contract, it is important to check that the other party has the right to sign all the papers.
If you know other counterpart checking services - let's complement the checklist together :-)
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/314076/
All Articles