The most popular network for supercomputers or Why did we choose InfiniBand?

Foreword
Bandwidth inside the cloud - this item is very important from a technological point of view. This is a scrupulous moment, many suppliers are reluctant to talk about this topic. They do not want to reveal the structure of their network. But if you look at the essence of the issue, then it depends on how much quality service you buy from your provider. It depends a lot on the speed inside the cloud. How are the nodes connected? At what speeds? What protocols? Services of many enterprises may well work on 1 gigabit, but you need to consider that most providers use 10G, and only the most advanced build their clouds on 40G or InfiniBand 56G.
')
Under the cut a couple of thoughts about why we chose InfiniBand for our cloud.
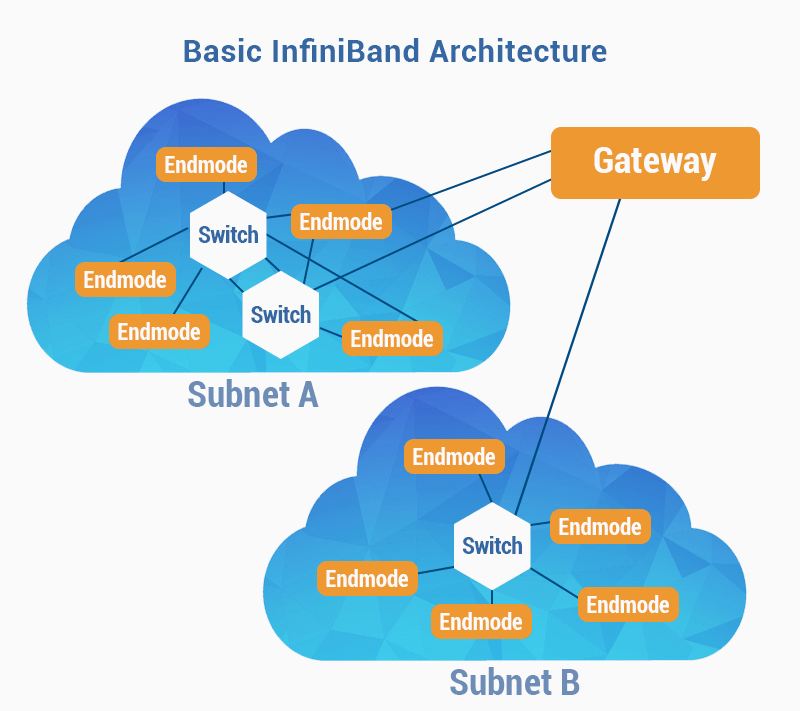
The InfiniBand technology itself has existed for a long time, it was developed and started to be used among supercomputers. In a high-performance system environment, it was necessary to combine large clusters with a linking bus for fast data exchange.
InfiniBand infrastructure tasks
Infiniband itself is as old as ethernet. This protocol was developed in the depths of the supersystems, respectively, its tasks for which it was designed, the requirements for performance, latency and architecture were dictated by cluster systems. With the further development of the Internet, InfiniBand has not developed so rapidly, most likely for the reason that this standard is quite niche.
Now, with the growth of cloud technologies that have already come out so to speak to the people, when clouds are already used not only in high-computing systems, but are used at the consumer level - here InfiniBand has gained a second wind.
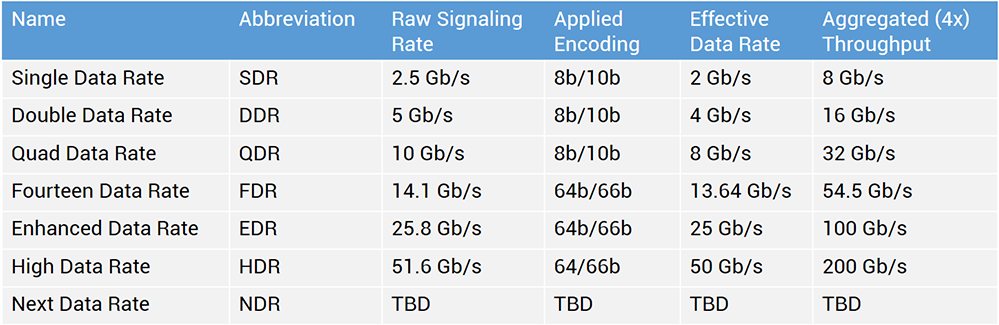
This protocol has not only increased in performance, but has already become quite widespread; earlier, even in high-performance environments, the data exchange rate was significantly lower - 4, 8 gigabits. Today, 56 gigabits is the current standard, which has already become widespread. Now manufacturers of InfiniBand equipment, such as Mellanox, sell equipment with a bandwidth of 100 gigabits.
At this rate, InfiniBand vendors next year can release even faster equipment. The main advantages of the InfiniBand protocol are high throughput speeds and, most importantly, low latency rates. The standard itself and the equipment allow transmitting a packet 10 times faster than ethernet. For high-performance computers and modern data transmission systems, this played a big role.
The next important point is that this technology has already been improved in the environments where it was developed. This standard already has, so to speak, the “right” plug-in-play architecture — everything is quite automated: building a tree, infrastructure, etc. Therefore, from the engineer does not require a large number of gestures to configure. In addition, in the protocol itself, the margin of fault tolerance has already been laid.
Of course, on Ethernet, all these capabilities are also present - but implemented by a whole pool of technologies - that all need to be configured separately, and which need to be tested and tested for compatibility. The engineer, when working with Ethernet, needs to take into account a larger number of infrastructure parts.
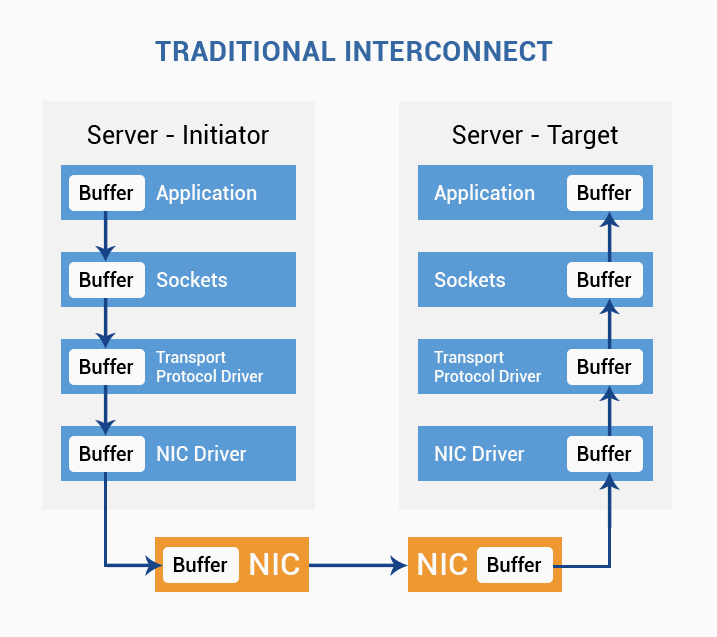
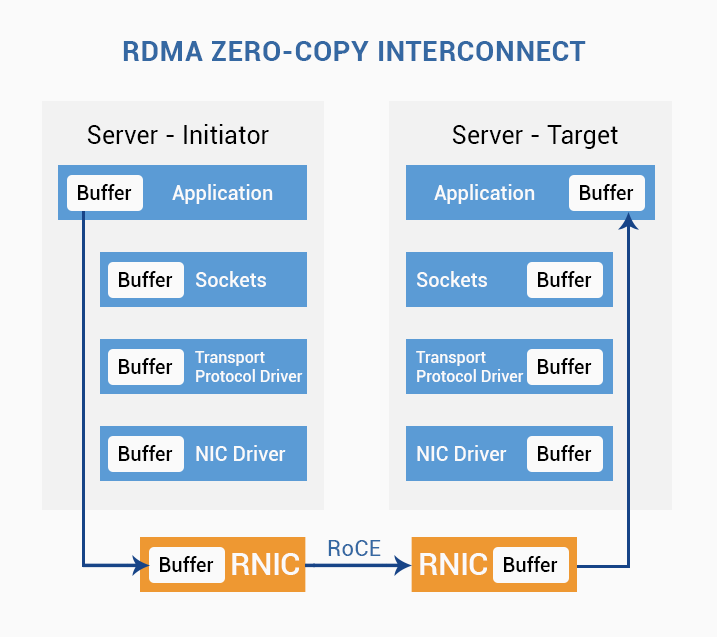
Melanox also positioning InfiniBand equipment as hyperconvergent - all their equipment can be used for both InfiniBand networks and ethernet networks - Ethernet is implemented on top of the InfiniBand network. This means that there will be no need to install different switches for different networks - we install one device and select a port group as san, the second port group will be Ethernet 40 gigabits. This trend comes from the environment of the birth of the protocol - hyperconvergent infrastructures. Thus, the maximum number of roles is combined in one device - the equipment is unified. At the same time, it must be said that, all other things being equal, InfiniBand as a technology is simple, it does not have many other functions that the ethernet standard has.
Now InfiniBand protocol is actively used at the san network level in cloud environments.
At the moment, we are designing and planning to implement the second architecture of our cloud, where we will fully switch to the hyper-convergent infrastructure - InfiniBand will be at the level of the san network and at the level of the wan network. If we compare this equipment with conventional switches, the speed is higher with lower delays (which is very important for high-loaded applications). If we talk in numbers, then when using the ethernet-protocol, delays are on the order of 20-30-40 milliseconds, then in InfiniBand - a delay of 1-2 milliseconds.
In our cloud infrastructure, in our data centers, we use equipment Mellanox 56 gigabits. So far, we are not considering switching to 100 gigabits, since for our tasks 56 gigabits is enough with a margin, and there is a reserve for the future. We chose this protocol for several reasons:
- universality;
- hyperconvergence;
- cost;
- growth opportunity.
Mellanox, how to produce InfiniBand equipment makes, in our opinion, the biggest contribution to the development of this protocol: introduces many new functions, and improves the protocol itself. By the way, many manufacturers either brand the Mellanox platform, or take melanox chips and solder them into their equipment.
At the moment there are all-flash systems built on fast flash disks on the market. But for this kind of systems a fast data transfer environment is required. With an insufficient exchange rate between the storages, consumers of the service will not receive data at a good speed, then the whole point is lost in fast flash memory (just as a very fast machine requires a very good road). There are often opinions that 50% of IT tasks still do not require such crazy speeds. Flash drives show themselves well where there are large databases, and you need high performance for fast data retrieval, where administrators complain most often - “more powerful processors are needed ... faster disks ...”. Also, high-speed, high-performance storage requires a solution like DaaS, VDI, for example, when all virtual machines access the storage, which leads to so-called bootstorm and freeze storage. For other tasks, such as: terminal servers, mail servers - there is enough speed of SSD and SATA drives. Therefore, we believe that there is no need to pay for unnecessary speed.
Why did we decide to use InfiniBand?
Our task was to build a fairly scalable storage facility - and there was a variant of the classic storage facility - FiberChannal + regular storage. Or it was possible to look towards the new-fashioned SDS (Sofware Define Storage) - by studying this technology in more detail, it became obvious that with this option of building the infrastructure, not so much bandwidth (on average 15 Gigabits per channel is enough), but very low packet transfer delays. Yes, there are ethernet switches that can do delays, like InfiniBand - but these are such big “combines” - that we didn’t fit for either the price or the necessary tasks (in our opinion, this equipment is not quite suitable for network storage) , and more convenient for use in a van network. It was decided to take InfiniBand Mellanox equipment on the test. After successful tests, the equipment was installed in our IT infrastructure.
Nota Bene: During the tests, they noted that in the presentations of Mellanox there was no “pure” marketing - all the characteristics of the equipment fully corresponded to the declared functionality.
Useful UPD from the comment (thanks to Igor_O ):
You have forgotten another very important feature of Infiniband that grew out of its supercomputer past: the possibility of building a non-blocking network (with a thick tree topology). Those. such a network, where if 50% of the network nodes simultaneously start transmitting data to another 50% of the network, the delays and data transfer rate will remain at the same level as when communicating one node with one node.
Useful links:
» InfiniBand in questions and answers (eng)
» How did we transfer the cloud from Ethernet 10G to Infiniband 56G
» Infiniband: matrix for data
» About InfiniBand: how we reduced ping from 7 μs to 2.4 μs (and test results)

SIM-CLOUD - Fail-safe cloud in Germany
Dedicated servers in reliable data centers in Germany!
Any configuration, quick build and free installation
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/313750/
All Articles