Infrastructure communications center from the kettle, or the next construction of server - part 1
Hello! Having read publications on the topic of building a data center for a small hosting provider, as well as “how to make a server room with my own hands”, from people who apparently did not know how to say why they should order their services, I decided to present my experience of building a small communication center in during this year, for placement, with the subsequent registration in Roskomnadzor, such objects as OTMUS, TZUS, SPD.
This year, we had so much information to search and apply, that I felt my limit in remembering useful information. Therefore, it is difficult for me to immediately remember where I got the information from (I am talking about orders from the Ministry of Communications, the Ministry of Information Technologies, Roskomnadzor, SNIP, VSN ...).
Under the cut, I will try to superficially go through all the aspects that need to be decided and implemented in your hardware.
If you start with the choice of premises, then you must take into account that the infrastructure of this premises should have at least such a set of elements and structures:
')
Depending on what plans you have at your bus station, you can choose a certain level of protection from power outages.
You can open any of the parts of the “Rules for the use of equipment of transit, terminal-transit and terminal communication centers” (there are 14 parts for different types of communication centers) and in all there will be a reference to
And also on:
... which, in turn, is no longer valid due to a bunch of changes ... and in general, we must now be guided
But at the same time, there is a link to 32 orders, and in 97 it is not written which communications center belongs to which category of electrical receivers. In this regard, it is not clear which category is required to provide. If suddenly someone in the subject - please share the information.
But let's say you have decided on what category of power receiver you have and you are going to provide it. For the safety of your business, in any case, you should have input from a city substation, a UPS and a 2-5 kW generator (approximately as much as you need for a small hardware room with two racks clogged with various equipment). It means that it is necessary to organize automatic transfer switch (automatic transfer of reserves) with the functions of starting the generator (manually if there is a duty shift at the facility) in the input distribution device (ASU).
Perhaps someone will be asked how to implement all this, in what form, how to place it?
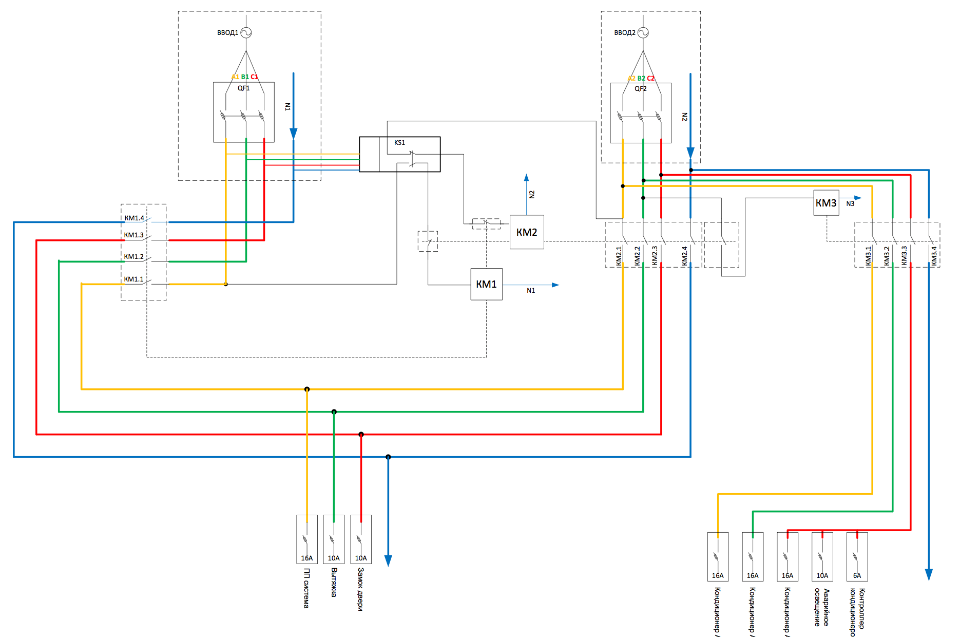
Simple AVR to work with two inputs:
So, you have the electrical installation inside your future Avtosa. Then you will need to take the line from there to the load. Due to the fact that equipment racks, cabinets for batteries and other metal structures (including the door) are usually located around the perimeter, it would be good to make a grounding tape around the perimeter to which you can attach everything you want to put along the walls and be grounded .
Due to the fact that your equipment must be connected via a UPS, the first obvious line from your ASU will go exactly to the UPS. In my case, this is a 3-phase APC Symmetra, which I would not advise buying because of its current value. You can find UPS more modest manufacturers. I would highlight the following criteria for myself:
And already from the UPS, take the lines to the socket blocks in the rack (s), depending on the installation location of your UPS (common or individually in each cabinet).
There is a bottleneck in the power scheme - UPS. Therefore, the design of the UPS should be either such that there is nothing to break (APC Symmetra, for example, without power and battery modules is just a copper bus (almost)).
If you use the UPS individually to the cabinet, then make sure that the cabinets have lines from different UPSs, and the power supply units of the equipment are connected to different UPSs.
Or there is a third option: you have a UPS that allows you to take a power line from it, drag it back to your emergency transfer station, and then assemble a circuit in which you can supply power to the line either through the UPS or directly from the city input or generator. This scheme will allow you to remove the UPS from the line for routine maintenance and repair.
With the current inverter, the circuits are similar to the UPS circuits, if you are serious enough to load the lines with more or less serious terminals. And if you have small inverters, then, as a rule, they are not sharpened by the fact that it would take a large section of the power to the load. These are placed inside the rack where they will be used. And if there is a need to connect a lot of equipment (rather than one or two pieces of iron), then the line in the control panel in the cabinet itself is retracted from the terminal block of the inverter and there through the bus or AB 2P (or via AB for minus and bus for positive) the lines for load.
I have for the purposes of the placement of the UPS and inverters installed separate frame rack with a large figure in the value of the carrier mass, which come power lines from ASU with AVR. And then from which the power lines go to the cabinets with equipment.
Here I would like to note a couple of points related to the choice of materials and components:
In order to understand how many batteries you need to buy (namely, this is the question, because it requires a lot of money), then there is nothing difficult if you know what load on your power grid you expect in CNN (peak hour) . For embedded battery packs, information on autonomy can be found in the materials for the UPS, and to calculate the required capacity of the external assembly, multiply the assembly voltage by the capacity and divide it by the load (t = V * Ah / Wt). But since the discharge of the battery is not a linear process, it is necessary to look at the discharge charts in the manuals for the batteries and, depending on the time you have, apply the coefficient found in the passport. Then you will get more or less real time autonomy from your battery system. Based on this, you will understand what capacity of your battery assembly should be provided.
The article about the construction of its own small data center for a small hosting provider used car batteries, because of their low cost relatively unattended batteries designed for use on communication networks (special modes of operation - constant charge, rare charge, long-term return). If you want to change them after 1-2 years (depending on the discharge and the depth of this discharge), then of course you can use this option. Only it is necessary to take into account that these batteries are serviced, so if something happens (overheating for example), they can leak or evaporate through the caps - which means they need to be installed in a separate ventilated room and all that ... In the case of using sealed unattended batteries, you you can place them even in racks with equipment (at the bottom of the cabinet or on cantilever shelves), operate from 3 to 8 years (depending on the manufacturer’s warranty on the life cycle) and test your power system according to the regulations.
I wrote above about the socket blocks ... but in fact I think that it is more correct to connect the equipment from the AV to the RC in the rack. So the connection is reliable and secure. But there is some inconvenience. They are mainly due to the fact that the equipment has a very specific C14 outlet, the plug for which (C13) is not always possible to find the proper quality. As a result, she can wander there and the weak spot will already be there. In addition, it should be borne in mind that not all engineers at least know what the PES is, and they need to be able to safely turn on the equipment (omitting the moment that, according to safety, any engineer must be at least with the 3rd group in the electrical safety crust + escort responsible with the 4th group - we all understand the reality of being).
In order to lay the cable from different parts of your room (from the inputs to the hardware itself or from the cabinet with batteries) you will need cable trays. This could be a cable trays system under the raised floor, or trays under the ceiling, running around the perimeter of the room and above the racks ... In my case, the optimal decision was made: cable elbows go under the ceiling, and a trench going under the telecommunication cabinets was cut out of the cabinet, a battery cabinet and a branch to ASU on the wall. The trough is iron-trimmed (and grounded), and the top is covered with 4mm steel sheets, which, like the rest of the floor, are covered with antistatic non-combustible linoleum. We need to put new racks - remove the hatches from the right places, put up the racks, dragging AC and DC power lines along the channel, that's all. In this case, the chute in the floor is used only for power wiring, and mesh elbows under the ceiling are used for copper SL and optical cable.
In spite of the fact that the equipment has not yet been installed in this motor hall, cable elbows are already engaged in copper cable harnesses and optical cables. Namely cross over crosses between racks were piecemeal. I have two cross designs: one-frame stand and constructive with tubular mounting profiles for 10 paired skirtings. From the telecommunications racks, UTP harnesses from each rack come to the single-frame rack, which are embroidered on the patch panels on both sides. An optical crossover is similarly organized. In this way, any cross-connection between equipment in different racks is performed with short patch cords inside its rack. And the incoming single copper lines to the AvtoZal (ACS from the 8-line office and the copper connections with partners also come to the frame with crosses, after which they are transferred to the necessary equipment.
I need a hefty frame for skirtings because of the need to organize a large amount of PRI port connections between the station and transport side. The SDH or media gateway transport card is immediately sewn onto the desired side of the construct, and then cross-linked if necessary with a conventional cross-over cord.
Due to the fact that the power cables I go along the groove in the floor, and the low current goes into the cabinets on top, they practically do not intersect with each other (I have equipment, the power of which is turned on from the front), even taking into account that the crosses are located on the rear mounting profiles.
In my opinion, if you build a communications center or server, where your main location, or one of the main locations, will be, then the minimum cabinet size should be 800x1000 (W × D), standard height 42U, with a plinth or 10 cm elevated above the floor, cable entry ports, both through the base and through the ceiling. Although I prefer 47U, because when everyone is stuffed in the closet, units become scarce and nothing can be done about it.
And I did not just write "cabinet dimensions". I believe that the racks (just a double frame frame) can only be used for testing stands and crosses. After some time of operation of a number of racks, you will find that the patch cords were prokinut vines between racks on all sides, even if you yourself like the order, then someone else will necessarily throw such a snoop to speed up the process, and then forget to redo it before how customer service will be launched there. That is why there must be cabinets and they must have closed side panels and lockable doors.
In order for the doors to always close, you need to install the mounting profiles at least 10 cm deep, both in front and behind. If you put them close to the door - there may be inconvenience with the equipment that comes forward with its front panel behind the mounting profiles, + SFP module sticks out + optical patch cord in it. As a result, the door will bend patch cords, if it can close at all. Just recently, because of such a lack of forethought, I had to travel several times to the site where we had the cwdm installed in the rental stand (by the way, he did not even stick out of the plane of the mounting profiles). The door could be closed in different ways and she pressed patch cords in different ways, dropping links. It is good that they understood what was going on at the testing stage and got a quick decision. And in order to be able to drown the mounting profiles, and you need a cabinet depth of 1000mm - in case of purchasing a content server (for example 800), you will not be able to fix the slide on profiles closer than 800mm and the server itself will not be able to drop by in rack. (at least for Intel platforms, this design of the slide).
The doors themselves are glass or perforated (someone buys the whole steel without perforation). Here is the choice for the tasks and ways of providing climate. If the cold air is fed into the corridor, then there’s no point in taking a glass door (or a door without perforation). Take the perforated doors and all your equipment will be cooled taking the air from the front (especially server), expelling heated back. If you let the sleeves with cold under the rack, then you need to take the rack with deaf doors.
In the cabinet there must be vertical organizers on the front mounting profile and, if necessary, on the rear. I have vertical organizers on both sides, because the front organizes the rise and descent of copper and optics, and behind the power supply to the equipment and UTP from the servers (again, the copper with data goes on one side, and the power cords on the other). And with the supply of power cables in the rack, think about which side you will have the power supply - with that and lead the line. Then you will have another one for laying copper from servers and katalists (for example) with boards in the rear slots ...
It is considered seemingly not difficult. If you don’t know what needs you will have afterwards, then you can quickly estimate and go to 2 options:
In any case, there should be a reserve system to maintain the temperature from 18 to 24 ° C and humidity in the region of 50-60% in your car hall. We have, for example, a large air conditioner powered by another power supply network than a car hall. And if someone can redeem it, then a split system will automatically start, which will also cope with this task without any problems, but they will take power from the mains with a diesel engine, but without the precious stand-alone UPS resource.
You can also deal with automation and monitoring, depending on what the air conditioners are capable of ... We for example have a split system control unit that monitors temperatures at several points in the avalanche and sets the operation mode of several air conditioners.
But in general, for me this topic is quite far away and everything that we needed to do on this issue was done by the contracting organization. The plans are only to fasten an alarm from systems like netping or something similar to this system, so that additional air conditioners can be launched not only when the big one turns off.
Due to the fact that small telecom operators have the right to register nodes using a simplified scheme, recently there has been no need to prepare projects for all engineering systems of the node (power supply, air conditioning, lighting, fire suppression, and it seems there was a cable cable project before). This means that when submitting documents to Roskomnadzor for registration of a communication center, you have the right not to provide this package of documents. But you should have done everything, because nobody has canceled the inspection commissions of the technical supervision and they can come to themselves and inspect your dangerous (or especially dangerous) facility. Therefore, you should not deviate from the implementation of all this just because your management has found out that this is not necessary for node registration. Sooner or later, these systems will work out and save them from loss or death.
After you have decided that you have finished arranging your hardware and now it’s all just about installing and turning on the equipment, make sure that you have a certain set of documentation and procedures that is stored in close proximity to the serviced equipment:
It makes no sense to fight with noise unprecedented racks with soundproofing panels ... Tishunu can only be done in three ways:
Of course, this material can hardly be called useful by 146%. I am not a designer, and therefore I cannot give you exhaustive references to the materials on which you have to prepare yourself for the tasks described in the article. I suspect that even the designers do not keep in mind all the SNIP, VSN, NTP on the building and premises, PUE, and regulatory documents from Mincom / InformSvyaz, Roskomnadzor, Ros / Technical Supervision. I know practically nothing about labor protection - this is a separate topic. But I tried to talk about what to dwell on and begin to read carefully, so as not to be mistaken.
You can start with this document and try to understand what you need to follow. NTP 112-2000 RD 45.120-2000 - documents with a bunch of references to everything that you need to rely on when building a communication center. From it the truth is useful to all, probably, only a few points:
And the promise that I just did not find where to stick:
Probably many will say that they do not need it all in the server, especially in small business. You are right, but to strive for something right? Choose the limits you are willing to reach and reach. In any case, the norm in the field of communications seems to me the most adequate and reasonable.
In the next part, I will try to set out the principles for the selection and placement of equipment, as well as how to connect to low-voltage networks and power supply.
All comments on spelling, spelling and typing errors please in private messages.
Also I will be glad if you share what solutions you used in the arrangement of infrastructure.
PS: please forgive me for the lack of tabulation - it is in the editor, but is not transferred to the post by the parser. I could not solve this issue.


2.
This year, we had so much information to search and apply, that I felt my limit in remembering useful information. Therefore, it is difficult for me to immediately remember where I got the information from (I am talking about orders from the Ministry of Communications, the Ministry of Information Technologies, Roskomnadzor, SNIP, VSN ...).
Under the cut, I will try to superficially go through all the aspects that need to be decided and implemented in your hardware.
Room infrastructure
If you start with the choice of premises, then you must take into account that the infrastructure of this premises should have at least such a set of elements and structures:
')
- Calculated load on the floor - you need to watch the project of the building. Remember that per 1m 2 can be placed and 700kg in the form of a cabinet with battery. If the area allows - better of course the rack
- Cable routes: trays on the ceiling and / or in the floor (as a carved chute in the concrete floor, and under the raised floor.
- Power supply and distribution system
- Cabinet / rack for placement of assemblies circuits battery.
- Gas extinguishing system.
- ACS.
- CCTV.
- A stand-alone construction with tubular profiles for fastening 10 twin skirtings, if you have a need to organize a multitude of copper SLs (PRI, for example) between equipment or from closely located partners / customers.
- Inter-rack copper and optical crosses.
- Of course cabinets / racks.
- A / C (climate) with reserve
- Fire resistance of the building (II or III degree).
- Over the premises of the hall (we will call our server room this way) there should not be sanitary facilities and other communications related to the use of water.
- Floors in the hall should be fireproof, on which clean floors are laid in the form of antistatic non-combustible linoleum or raised floor tiles.
- If there are windows in the room, then at least they need to be tinted with film or covered with plywood, as the sun rays are not allowed on transformers and batteries. In other matters, the sun's rays will not do anything good for other equipment. Ideally, there should be no windows at all, but this is unlikely to be the deciding factor if all other conditions can be met.
- The walls of the halls should not be made of combustible materials. This is not only the cause of fire, but also the need to build an isolated chamber in case of fire extinguishing systems.
- Gas smoke exhaust system, in case of fire extinguishing system operation.
- Lighting should be good. In some sort of VSN on lighting, I saw a figure of 200 lx. But in principle, I think there is no such problem, so just take care of good lighting, preferably with dust protection.
- Fire door with perimeter seal (for tightness).
- All metal structures (cabinets, trays, racks, door) must be grounded.
- All space in the walls of the hall around the cable and ventilation inlets should be sealed with asbestos or special fire-fighting foam (orange or red).
- Batteries and other metal structures that can serve as a grounding device must be fenced off with non-conductive materials in order to exclude the possibility of short-circuiting equipment racks or housings on these structures through the human body (while touching).
- And a bit of labor protection and electrical safety: signs of the category of premises and the degree of danger, with the name of the person in charge; markings on sockets and grounding devices, posters on electrical safety, fire fighting and first aid (usually, poster themes are chosen to bring the described situations closer to their industry); carbon dioxide fire extinguishers and first aid kit; rubber dielectric mats in front of and behind cabinets and racks
Power supply
Depending on what plans you have at your bus station, you can choose a certain level of protection from power outages.
You can open any of the parts of the “Rules for the use of equipment of transit, terminal-transit and terminal communication centers” (there are 14 parts for different types of communication centers) and in all there will be a reference to
Order No. 59 of May 16, 2006:
P.9.3. Transitions from the main sources to the backup, including the battery and back, are carried out without interrupting the power supply.
P.9.4. The minimum reserve capacity of the battery ensures the normal functioning of the communication center for 2 hours.
P.9.4. The minimum reserve capacity of the battery ensures the normal functioning of the communication center for 2 hours.
And also on:
Order No. 32 of 03/13/2007
7. In order to ensure uninterrupted power supply to electrical receivers of I reliability category, including electrical receivers of a special group of I reliability category, when there is a power failure during switching from one power source to another, rechargeable batteries are used with a capacity that provides electrical power supply to electrical receivers with an estimated discharge time 2 hours for electric receivers of a special group of I category of reliability and at least 8 hours for electric consumers of I category n reliability.
8. The power supply of electrical consumers of the second category of reliability in the normal mode is provided from two independent mutually redundant power sources.
9. As one of the independent power sources of power consumers of the second category of reliability, the use of a diesel power station is allowed.
8. The power supply of electrical consumers of the second category of reliability in the normal mode is provided from two independent mutually redundant power sources.
9. As one of the independent power sources of power consumers of the second category of reliability, the use of a diesel power station is allowed.
... which, in turn, is no longer valid due to a bunch of changes ... and in general, we must now be guided
Order No. 97 of August 8, 2005
6. In order to ensure uninterrupted functioning of communication facilities that are part of communication nodes, communication network connection points, fixed subscriber access base stations, as well as mobile radio telephone communication network base stations and mobile radio communication networks, backup autonomous power sources are used to ensure in case of external disturbance power supply operation of the specified communication facilities as part of a communication network for at least 4 hours at a load corresponding to the busy hour.
But at the same time, there is a link to 32 orders, and in 97 it is not written which communications center belongs to which category of electrical receivers. In this regard, it is not clear which category is required to provide. If suddenly someone in the subject - please share the information.
But let's say you have decided on what category of power receiver you have and you are going to provide it. For the safety of your business, in any case, you should have input from a city substation, a UPS and a 2-5 kW generator (approximately as much as you need for a small hardware room with two racks clogged with various equipment). It means that it is necessary to organize automatic transfer switch (automatic transfer of reserves) with the functions of starting the generator (manually if there is a duty shift at the facility) in the input distribution device (ASU).
Perhaps someone will be asked how to implement all this, in what form, how to place it?
- First, it is a question for electricians. If you don’t have one in your staff, contact the organization that will install the ASU with ATS. A passport must be attached to the product.
- Secondly, - you can try to assemble yourself, using a pair of power contactors with mechanical and electrical mutually interlocking, voltage control relays with NC / NO contacts. I had to collect this for the purpose of providing a certain infrastructure of the object as a whole (video surveillance, fire extinguishing system, ACS, ventilation, emergency light). And Avtozal is powered from the input, where the AVR system is organized separately from two feeders from different substations and the launch of a diesel generator.
Simple AVR to work with two inputs:

So, you have the electrical installation inside your future Avtosa. Then you will need to take the line from there to the load. Due to the fact that equipment racks, cabinets for batteries and other metal structures (including the door) are usually located around the perimeter, it would be good to make a grounding tape around the perimeter to which you can attach everything you want to put along the walls and be grounded .
Due to the fact that your equipment must be connected via a UPS, the first obvious line from your ASU will go exactly to the UPS. In my case, this is a 3-phase APC Symmetra, which I would not advise buying because of its current value. You can find UPS more modest manufacturers. I would highlight the following criteria for myself:
- 3-phase, if all the power through one UPS or 1-phase, if you put the UPS in each rack to provide individual (on the scale of the gates) reserve.
- output quality
- availability of bypass
- hot-swappable battery module (possibly a power module)
- monitoring
- Power supply to the load through the sockets C19 or terminal contacts
- connecting external battery assembly
And already from the UPS, take the lines to the socket blocks in the rack (s), depending on the installation location of your UPS (common or individually in each cabinet).
There is a bottleneck in the power scheme - UPS. Therefore, the design of the UPS should be either such that there is nothing to break (APC Symmetra, for example, without power and battery modules is just a copper bus (almost)).
If you use the UPS individually to the cabinet, then make sure that the cabinets have lines from different UPSs, and the power supply units of the equipment are connected to different UPSs.
Or there is a third option: you have a UPS that allows you to take a power line from it, drag it back to your emergency transfer station, and then assemble a circuit in which you can supply power to the line either through the UPS or directly from the city input or generator. This scheme will allow you to remove the UPS from the line for routine maintenance and repair.
With the current inverter, the circuits are similar to the UPS circuits, if you are serious enough to load the lines with more or less serious terminals. And if you have small inverters, then, as a rule, they are not sharpened by the fact that it would take a large section of the power to the load. These are placed inside the rack where they will be used. And if there is a need to connect a lot of equipment (rather than one or two pieces of iron), then the line in the control panel in the cabinet itself is retracted from the terminal block of the inverter and there through the bus or AB 2P (or via AB for minus and bus for positive) the lines for load.
I have for the purposes of the placement of the UPS and inverters installed separate frame rack with a large figure in the value of the carrier mass, which come power lines from ASU with AVR. And then from which the power lines go to the cabinets with equipment.
Here I would like to note a couple of points related to the choice of materials and components:
- Circuit breakers in VRU should be selected taking into account selectivity, not only at the nominal value, but also according to the response time (to do this, choose a product line from manufacturers, and, preferably, use products of the same brand).
- Try to use the most fire-safe materials inside your garage, so I chose the cable VVGng-RFLS + corrugated PND pipe (black and orange).
- For the same reasons, we chose the socket blocks - non-flammable plastic, fire safety tests, without a switch and always with a terminal block, for connecting the cable from the UPS to it. Maybe I have one such problems, but I spent a few days looking for the right blocks of sockets for me. All that is offered in the search is frankly not high-quality "China" with a built-in cable, usually of a small section, or with a C13 connector from which the cord will sooner or later fall out, not to mention the fact that the finished cable with 2.5 mm 2 conductors is not to find, besides, I wanted to use wwgng-rfls, and it would not be good to plug it into a C14 plug. As a result, I found fireproof plastic socket outlets with a terminal block inside. By the way, they are produced in Yekaterinburg and the product as a whole is excellent, but I had to refine it - drill out the opening for input, look for the fixing cable clips ... bought 8 pieces - used until 4 and not a single product came across :). Now I would recommend either the same method, or blocks of sockets with built-in cable with an industrial connector. And if you have a large AvtoZal, and you will install racks as needed, then the variant with power outlets with industrial connectors looks more convenient, since you simply connect a new cabinet to the supplied line. And it will be a reliable connection.
- Supply lines for direct current SCHRZ in each cabinet I made of PUGG cable (blue and red) in the corrugation. If you google SCHRZ, you will see what it is and that even the functionality of monitoring the status of the line from AV to equipment can be there.
Calculation of the autonomy of your electrical installation and the choice of battery
In order to understand how many batteries you need to buy (namely, this is the question, because it requires a lot of money), then there is nothing difficult if you know what load on your power grid you expect in CNN (peak hour) . For embedded battery packs, information on autonomy can be found in the materials for the UPS, and to calculate the required capacity of the external assembly, multiply the assembly voltage by the capacity and divide it by the load (t = V * Ah / Wt). But since the discharge of the battery is not a linear process, it is necessary to look at the discharge charts in the manuals for the batteries and, depending on the time you have, apply the coefficient found in the passport. Then you will get more or less real time autonomy from your battery system. Based on this, you will understand what capacity of your battery assembly should be provided.
The article about the construction of its own small data center for a small hosting provider used car batteries, because of their low cost relatively unattended batteries designed for use on communication networks (special modes of operation - constant charge, rare charge, long-term return). If you want to change them after 1-2 years (depending on the discharge and the depth of this discharge), then of course you can use this option. Only it is necessary to take into account that these batteries are serviced, so if something happens (overheating for example), they can leak or evaporate through the caps - which means they need to be installed in a separate ventilated room and all that ... In the case of using sealed unattended batteries, you you can place them even in racks with equipment (at the bottom of the cabinet or on cantilever shelves), operate from 3 to 8 years (depending on the manufacturer’s warranty on the life cycle) and test your power system according to the regulations.
Alternative opinion
I wrote above about the socket blocks ... but in fact I think that it is more correct to connect the equipment from the AV to the RC in the rack. So the connection is reliable and secure. But there is some inconvenience. They are mainly due to the fact that the equipment has a very specific C14 outlet, the plug for which (C13) is not always possible to find the proper quality. As a result, she can wander there and the weak spot will already be there. In addition, it should be borne in mind that not all engineers at least know what the PES is, and they need to be able to safely turn on the equipment (omitting the moment that, according to safety, any engineer must be at least with the 3rd group in the electrical safety crust + escort responsible with the 4th group - we all understand the reality of being).
Cable infrastructure
In order to lay the cable from different parts of your room (from the inputs to the hardware itself or from the cabinet with batteries) you will need cable trays. This could be a cable trays system under the raised floor, or trays under the ceiling, running around the perimeter of the room and above the racks ... In my case, the optimal decision was made: cable elbows go under the ceiling, and a trench going under the telecommunication cabinets was cut out of the cabinet, a battery cabinet and a branch to ASU on the wall. The trough is iron-trimmed (and grounded), and the top is covered with 4mm steel sheets, which, like the rest of the floor, are covered with antistatic non-combustible linoleum. We need to put new racks - remove the hatches from the right places, put up the racks, dragging AC and DC power lines along the channel, that's all. In this case, the chute in the floor is used only for power wiring, and mesh elbows under the ceiling are used for copper SL and optical cable.
In spite of the fact that the equipment has not yet been installed in this motor hall, cable elbows are already engaged in copper cable harnesses and optical cables. Namely cross over crosses between racks were piecemeal. I have two cross designs: one-frame stand and constructive with tubular mounting profiles for 10 paired skirtings. From the telecommunications racks, UTP harnesses from each rack come to the single-frame rack, which are embroidered on the patch panels on both sides. An optical crossover is similarly organized. In this way, any cross-connection between equipment in different racks is performed with short patch cords inside its rack. And the incoming single copper lines to the AvtoZal (ACS from the 8-line office and the copper connections with partners also come to the frame with crosses, after which they are transferred to the necessary equipment.
I need a hefty frame for skirtings because of the need to organize a large amount of PRI port connections between the station and transport side. The SDH or media gateway transport card is immediately sewn onto the desired side of the construct, and then cross-linked if necessary with a conventional cross-over cord.
Due to the fact that the power cables I go along the groove in the floor, and the low current goes into the cabinets on top, they practically do not intersect with each other (I have equipment, the power of which is turned on from the front), even taking into account that the crosses are located on the rear mounting profiles.
Telecommunication cabinets and racks
In my opinion, if you build a communications center or server, where your main location, or one of the main locations, will be, then the minimum cabinet size should be 800x1000 (W × D), standard height 42U, with a plinth or 10 cm elevated above the floor, cable entry ports, both through the base and through the ceiling. Although I prefer 47U, because when everyone is stuffed in the closet, units become scarce and nothing can be done about it.
And I did not just write "cabinet dimensions". I believe that the racks (just a double frame frame) can only be used for testing stands and crosses. After some time of operation of a number of racks, you will find that the patch cords were prokinut vines between racks on all sides, even if you yourself like the order, then someone else will necessarily throw such a snoop to speed up the process, and then forget to redo it before how customer service will be launched there. That is why there must be cabinets and they must have closed side panels and lockable doors.
In order for the doors to always close, you need to install the mounting profiles at least 10 cm deep, both in front and behind. If you put them close to the door - there may be inconvenience with the equipment that comes forward with its front panel behind the mounting profiles, + SFP module sticks out + optical patch cord in it. As a result, the door will bend patch cords, if it can close at all. Just recently, because of such a lack of forethought, I had to travel several times to the site where we had the cwdm installed in the rental stand (by the way, he did not even stick out of the plane of the mounting profiles). The door could be closed in different ways and she pressed patch cords in different ways, dropping links. It is good that they understood what was going on at the testing stage and got a quick decision. And in order to be able to drown the mounting profiles, and you need a cabinet depth of 1000mm - in case of purchasing a content server (for example 800), you will not be able to fix the slide on profiles closer than 800mm and the server itself will not be able to drop by in rack. (at least for Intel platforms, this design of the slide).
The doors themselves are glass or perforated (someone buys the whole steel without perforation). Here is the choice for the tasks and ways of providing climate. If the cold air is fed into the corridor, then there’s no point in taking a glass door (or a door without perforation). Take the perforated doors and all your equipment will be cooled taking the air from the front (especially server), expelling heated back. If you let the sleeves with cold under the rack, then you need to take the rack with deaf doors.
In the cabinet there must be vertical organizers on the front mounting profile and, if necessary, on the rear. I have vertical organizers on both sides, because the front organizes the rise and descent of copper and optics, and behind the power supply to the equipment and UTP from the servers (again, the copper with data goes on one side, and the power cords on the other). And with the supply of power cables in the rack, think about which side you will have the power supply - with that and lead the line. Then you will have another one for laying copper from servers and katalists (for example) with boards in the rear slots ...
Climate
It is considered seemingly not difficult. If you don’t know what needs you will have afterwards, then you can quickly estimate and go to 2 options:
- immediately industrial or semi-industrial air conditioners with a capacity sufficient to cover the maximum heat generation (calculated on the basis of the maximum possible electricity consumption per rack, with a factor of 0.9 for confidence; and for accuracy - you should look at the equipment passport).
- put a household split ... then another ... then another ... Just make sure that in the future you could connect some control module with sensors to this split, so that it would all be a little clever.
In any case, there should be a reserve system to maintain the temperature from 18 to 24 ° C and humidity in the region of 50-60% in your car hall. We have, for example, a large air conditioner powered by another power supply network than a car hall. And if someone can redeem it, then a split system will automatically start, which will also cope with this task without any problems, but they will take power from the mains with a diesel engine, but without the precious stand-alone UPS resource.
You can also deal with automation and monitoring, depending on what the air conditioners are capable of ... We for example have a split system control unit that monitors temperatures at several points in the avalanche and sets the operation mode of several air conditioners.
But in general, for me this topic is quite far away and everything that we needed to do on this issue was done by the contracting organization. The plans are only to fasten an alarm from systems like netping or something similar to this system, so that additional air conditioners can be launched not only when the big one turns off.
Security systems
- Fire extinguishing system. To extinguish a fire must use gas. It is dangerous for people, but safe for your infrastructure. Of course, when triggered, the system will shout a predetermined number of seconds and only after that will it open the gas cylinder. Therefore, the staff should be instructed, not deaf and not blind, to see the light-signal information about the state of the fire system. As a rule, fire extinguishing systems have indication and control panels - the staff must be trained in advance to understand and use these devices.
- Security alarm. It is better to use the regulations of the operation of the system, which will issue a security organization. There is nothing to say here. If you have someone permanently present at the facility, and the room is located on the territory protected by the security service of the building owners, then you may not need it.
- ACS. According to the regulatory and legal documentation from the Ministry of Information Technologies and Communications (Order No. 1 of January 9, 2008), only persons who install, operate and maintain equipment should have access to communication facilities. Here, the issue is not only the security of access to equipment (after all, electronic tags or passwords can be stolen from less well-trained individuals, such as an accountant or manager), but also on safety measures. It is unlikely that the same manager has a certificate for electrical safety and he was instructed. And from the moment you pulled the power supply through the cabinets - all your room is one electrical installation.
- CCTV. Like any other security system, its power should be reserved and access to its controls should be limited. Cameras should be selected with PoE powered, so that there would be no dependency on any wall outlet. Cameras should be located in the avtozale not only for fixing security incidents, but also for debriefing with technical staff. The fact is that an engineer can do something by chance, and then not confess, fearing reprisals. For example, if you still use socket outlets with a plug-in cable in connector C14, then sooner or later the plug C13 will fall out, especially if someone chooses to climb and loosen the cable. Similarly, from the side of the equipment - if the cord does not sit well in the power supply connector of the equipment - find a way to improve its fit. Sometimes it is just a bad cheap wire - I throw it away right away. And sometimes the connector in the equipment has already been deformed (plastic has dried over time, for example). Or the engineer may accidentally remove the patch cord. I myself had a case in the first year of work in telecom, when the SFP module was stuck in the board, and it was very urgent to replace it. As I just did not try to remove it from there. Juniper MX5-T… , — 201Gb … , .
Due to the fact that small telecom operators have the right to register nodes using a simplified scheme, recently there has been no need to prepare projects for all engineering systems of the node (power supply, air conditioning, lighting, fire suppression, and it seems there was a cable cable project before). This means that when submitting documents to Roskomnadzor for registration of a communication center, you have the right not to provide this package of documents. But you should have done everything, because nobody has canceled the inspection commissions of the technical supervision and they can come to themselves and inspect your dangerous (or especially dangerous) facility. Therefore, you should not deviate from the implementation of all this just because your management has found out that this is not necessary for node registration. Sooner or later, these systems will work out and save them from loss or death.
After you have decided that you have finished arranging your hardware and now it’s all just about installing and turning on the equipment, make sure that you have a certain set of documentation and procedures that is stored in close proximity to the serviced equipment:
- power distribution schemes
- lighting schemes
- air conditioning routes
- regulations and dates of commissioning of the battery, air conditioners, generator, automatic transfer switch, grounding devices.
- crossover circuits
- : .. , , — - SFP , , — (kercher )
- literally everything must be signed and marked - any element of power distribution, cabinets and doors with signs for the purpose and danger class, responsible evacuation schemes on the basis of a glow in the dark; if you have a grounding tire along the perimeter, then it should not be painted over and marked as a grounding device. At one enterprise, a technical supervisor demanded to paint the edge of the tire in red and green stripes.
Why I did not write anti-noise?
It makes no sense to fight with noise unprecedented racks with soundproofing panels ... Tishunu can only be done in three ways:
- unplug everything that makes noise
- adhere to the rules for choosing a premise for an auto-room described in this article and the noise problem will disappear, provided that jobs are found outside this premises
- to some extent, it will help to enable silent mode in server BIOS.
Of course, this material can hardly be called useful by 146%. I am not a designer, and therefore I cannot give you exhaustive references to the materials on which you have to prepare yourself for the tasks described in the article. I suspect that even the designers do not keep in mind all the SNIP, VSN, NTP on the building and premises, PUE, and regulatory documents from Mincom / InformSvyaz, Roskomnadzor, Ros / Technical Supervision. I know practically nothing about labor protection - this is a separate topic. But I tried to talk about what to dwell on and begin to read carefully, so as not to be mistaken.
You can start with this document and try to understand what you need to follow. NTP 112-2000 RD 45.120-2000 - documents with a bunch of references to everything that you need to rely on when building a communication center. From it the truth is useful to all, probably, only a few points:
- VSN 45.122-77 - design of artificial lighting of a telecommunications company
- VSN 116-93 - may be useful, but rather old instructions for designing linear cable communication structures
- VSN 332-93 - Instructions for the design of electrical installations of enterprises and structures of telecommunications
And the promise that I just did not find where to stick:
- , , , – — , . / , . , , , … — .
- . . krone «», , krone , «» , , . , . , noname krone.
Probably many will say that they do not need it all in the server, especially in small business. You are right, but to strive for something right? Choose the limits you are willing to reach and reach. In any case, the norm in the field of communications seems to me the most adequate and reasonable.
In the next part, I will try to set out the principles for the selection and placement of equipment, as well as how to connect to low-voltage networks and power supply.
All comments on spelling, spelling and typing errors please in private messages.
Also I will be glad if you share what solutions you used in the arrangement of infrastructure.
PS: please forgive me for the lack of tabulation - it is in the editor, but is not transferred to the post by the parser. I could not solve this issue.


2.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/313588/
All Articles