Live Container Migration: An Inside Look
Today we will look at a topic that is not fully disclosed in the modern IT world: live container migration, how it works behind the scenes and what problems it solves. The demand for this technology continues to grow rapidly as it opens up new opportunities, providing more freedom in managing the application lifecycle.
Live container migration involves the process of moving an application between different physical machines or clouds without interrupting the application and breaking the connection with the user. Memory, file system and network connection of containers running on top of bare hardware are transferred from the source host computer to the destination, maintaining a working state without interrupting work.
There are several problems that live migration can solve:
')
All the above mentioned problems can be solved, and now we will tell you several options for solving these problems without the help of live migration.
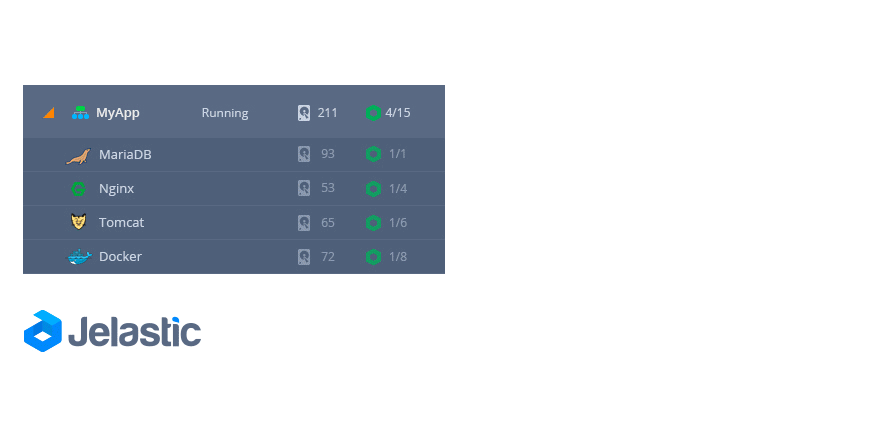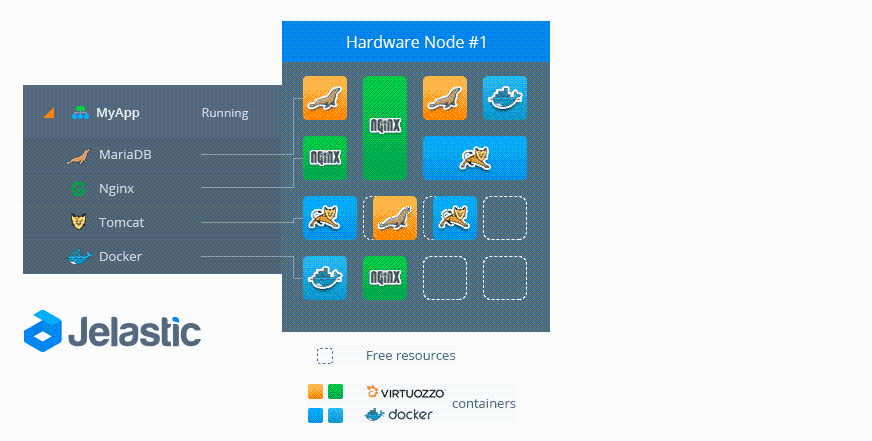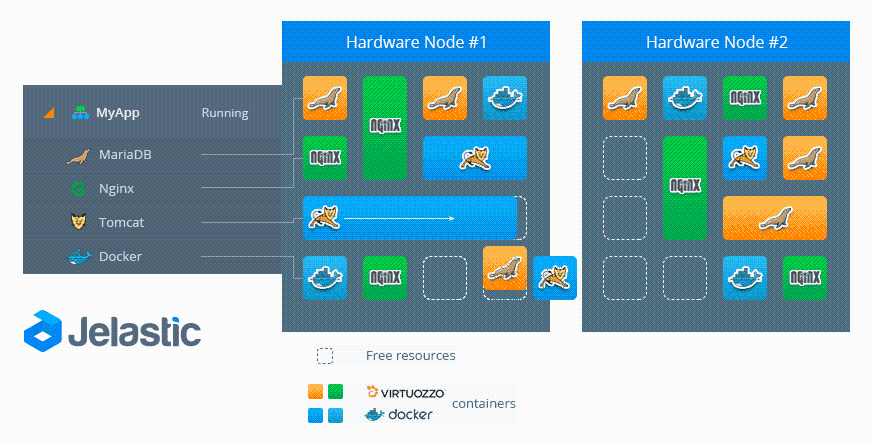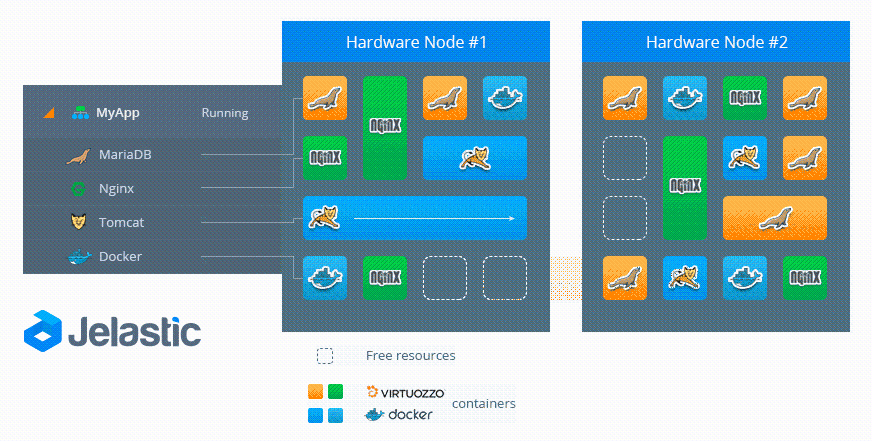
Let's look at the live migration process from the technical side using the following scheme:
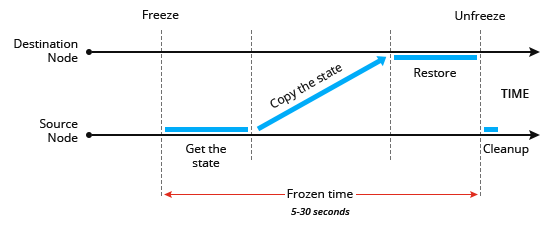
To complete the migration, the platform freezes the container in the source node, locking the memory, processes, file system, and network connections, and saves the state of that container. After that, it is copied to the destination node. The platform restores the state and thaws the container in this node. Then, in the source node, the process of quickly clearing the data of the migrating container is carried out.
It's pretty simple: you get, copy and restore the state of the container. However, in this case, it is necessary to take into account the freezing period, which must be taken into account when developing (architecture) applications, since this point may be critical for some of them.
There are two ways to do live migration. One of these is memory pre-copying. If you want to transfer the container, the platform will direct the monitored memory to the source node, and will copy this memory at the same time as the destination node until the difference is minimal. After that, the platform freezes the container, gets the remaining state, transfers it to the destination node, restores and defrosts it.
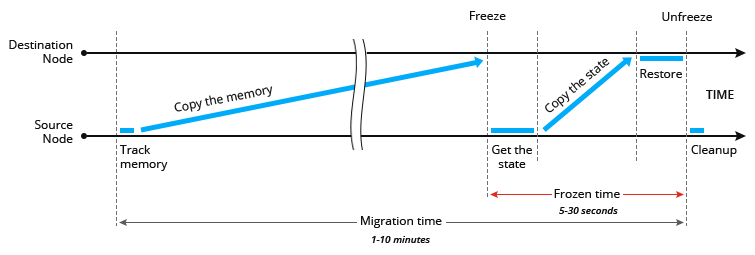
Another way is to post-copy memory , or in other words, lazy migration . The system first freezes the container in the source node, obtains the state of the most rapidly changing memory pages, transfers the state to the destination node, restores it and unfreezes the container. The rest of the state in the background is copied from the source node to the destination node.

Usually, depending on the application, the freezing time for each container takes from 5 to 30 seconds. This is indeed a short period of time compared to the possible idle hours during cluster maintenance.
With all the benefits of live migration, there are also a few drawbacks that need to be taken into account before starting the migration:
What companies offer live container migration today?
To see the Minecraft process from AWS to Azure in real-time without downtime, watch the following video:
Live container migration is still a relatively new technology on the market. Nevertheless, the advantages of this technology for modern business are obvious - no downtime during maintenance, no need to spend a lot of effort on preparing and testing the working environment in another cloud. That is why live migration is a great solution for better availability and flexibility. Share your experience in real-time container migration between clouds or data centers.
Live migration - what is it?
Live container migration involves the process of moving an application between different physical machines or clouds without interrupting the application and breaking the connection with the user. Memory, file system and network connection of containers running on top of bare hardware are transferred from the source host computer to the destination, maintaining a working state without interrupting work.

Problems that live migration solves
There are several problems that live migration can solve:
')
- Idle period during equipment maintenance
- Unbalanced cluster load
- Cloud issues
Alternative Solutions
All the above mentioned problems can be solved, and now we will tell you several options for solving these problems without the help of live migration.
- Scheduled idle periods . To perform technical maintenance of the cluster, you need to go through three steps:
1. Notify users (application owners) in advance of the maintenance window and possible idle time.
2. Disconnect hardware
3. Connect back only after all necessary changes are made. In this case, the problem is a relatively large period of inactivity.
- Redirect traffic . To perform cluster maintenance, you must restore a copy of each application in a different hardware node, then redirect traffic to this new copy and close the previous one. In this case, the problem is the complexity of this process - you need to have specially designed applications to obtain high availability and data synchronization. In addition, more hardware resources may be required to complete this task.
- Microservices. Detailed division of application services into separate containers and their distribution across different physical servers helps to avoid idle periods in the event of a hardware failure. Broken containers will be automatically restored to the active hardware node. However, in this case, the problem is again the complexity of the process, since the applications in the cluster must be designed so that you can manage the high availability and recovery process after a crash.
How Live Migration Works
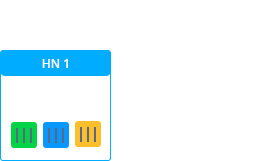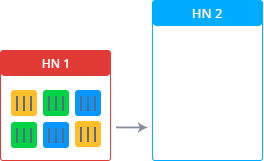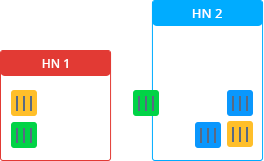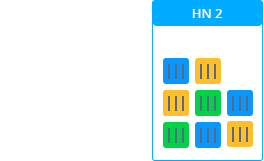
Let's look at the live migration process from the technical side using the following scheme:

- Source Node — The location of the container before live migration.
- Destination Node - container location after live migration
To complete the migration, the platform freezes the container in the source node, locking the memory, processes, file system, and network connections, and saves the state of that container. After that, it is copied to the destination node. The platform restores the state and thaws the container in this node. Then, in the source node, the process of quickly clearing the data of the migrating container is carried out.
It's pretty simple: you get, copy and restore the state of the container. However, in this case, it is necessary to take into account the freezing period, which must be taken into account when developing (architecture) applications, since this point may be critical for some of them.
There are two ways to do live migration. One of these is memory pre-copying. If you want to transfer the container, the platform will direct the monitored memory to the source node, and will copy this memory at the same time as the destination node until the difference is minimal. After that, the platform freezes the container, gets the remaining state, transfers it to the destination node, restores and defrosts it.

Another way is to post-copy memory , or in other words, lazy migration . The system first freezes the container in the source node, obtains the state of the most rapidly changing memory pages, transfers the state to the destination node, restores it and unfreezes the container. The rest of the state in the background is copied from the source node to the destination node.

Usually, depending on the application, the freezing time for each container takes from 5 to 30 seconds. This is indeed a short period of time compared to the possible idle hours during cluster maintenance.
Live Migration Examples
- Maintain hardware without downtime
- Load redistribution

- High availability between availability areas in data centers
- Switch to another cloud provider

Pitfalls and Possible Disadvantages
With all the benefits of live migration, there are also a few drawbacks that need to be taken into account before starting the migration:
- During live migration, you may notice some performance degradation while the container is in a frozen state. For some applications, this is a critical drawback, since they do not accept any performance degradation (for example, monolithic high-load online applications). However, short-term freezing is not a serious drawback for most applications on the Internet, especially if we talk about web applications.
- Another difficulty is the large amount of fast-changing data that is not easily transferred from one cloud provider to another. The waiting period and a large amount of data can impede the success of live migration.
- Public IP addresses in multi-cloud. It is not possible to transfer containers with a public IP address from one cloud provider to another, because the IP address is tied to a specific provider.
- If an application inside a container uses a proprietary API or proprietary cloud services of a particular cloud provider, it can be very difficult or even impossible to perform live migration from one cloud to another.
Live Migration in the Modern IT Market
What companies offer live container migration today?
- Virtuozzo - this company, in fact, created the technology of live migration of containers; they were pioneers in this area and currently offer a live migration engine that allows atomic migration of a container from one physical host to another.
- The runC from the Open Containers Initiative is another promising container solution that supports live migration based on CRIU .
- Jelastic offers a container-orchestrated platform that provides live migration of both atomic containers and applications with a complex deployment topology between hardware hosts, availability zones, data centers, and cloud providers.
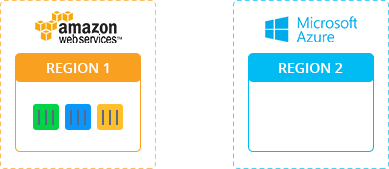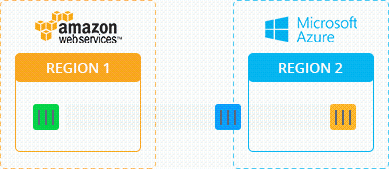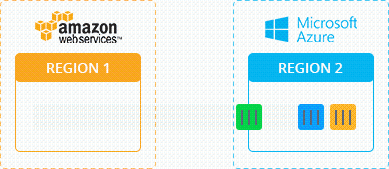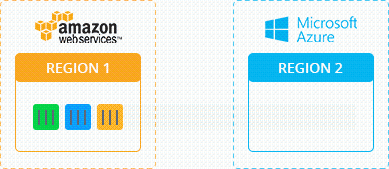
Demo: Minecraft Migration in Real Time
To see the Minecraft process from AWS to Azure in real-time without downtime, watch the following video:
Live container migration is still a relatively new technology on the market. Nevertheless, the advantages of this technology for modern business are obvious - no downtime during maintenance, no need to spend a lot of effort on preparing and testing the working environment in another cloud. That is why live migration is a great solution for better availability and flexibility. Share your experience in real-time container migration between clouds or data centers.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/313512/
All Articles