Security Week 42: winter is coming, exploding pigs, half the Internet is encrypted
 As you probably already understood, this issue of the weekly newsletter in the field of information security is dedicated to combating yellow headlines. Researcher John Sawyer found a vulnerability in a number of Android-based smartphones made by Foxconn ( news , research ). The vulnerability occurred due to the manufacturer’s error, which also provided its own version of the OS for some customers: there was a debugging module that allows you to easily get the privileges of the root and full access to the smartphone.
As you probably already understood, this issue of the weekly newsletter in the field of information security is dedicated to combating yellow headlines. Researcher John Sawyer found a vulnerability in a number of Android-based smartphones made by Foxconn ( news , research ). The vulnerability occurred due to the manufacturer’s error, which also provided its own version of the OS for some customers: there was a debugging module that allows you to easily get the privileges of the root and full access to the smartphone.Despite the fact that the error turned out to be rather serious, Sawyer, in his study, spoke out against using vulnerabilities “for public relations” - not in the sense that they should not be reported to the public, but that there is no need to inflate the danger of detectable holes for the sages and likes. Hence the name of the vulnerability, parodying other attempts to brand vulnerabilities up to the creation of a logo
Operated by
 easy peasy. It is enough to connect the phone to the computer, enter a couple of commands via the debugger and is ready. However, not quite. The researcher discovered that it would not be possible to enter a command desk via the standard adb console and slightly modified the software to send the necessary sequence of characters to the phone. Result: download the phone in debug mode, with full access to the system. This does not allow you to directly read the encrypted information, but gives a lot of opportunities for brute force or other specialized events.
easy peasy. It is enough to connect the phone to the computer, enter a couple of commands via the debugger and is ready. However, not quite. The researcher discovered that it would not be possible to enter a command desk via the standard adb console and slightly modified the software to send the necessary sequence of characters to the phone. Result: download the phone in debug mode, with full access to the system. This does not allow you to directly read the encrypted information, but gives a lot of opportunities for brute force or other specialized events.
As a result, several second-tier manufacturers, purchasing ready-made devices, and not the most well-known in our market, such as InFocus and NextBit, suffered. The latter has already released a firmware update, closing the vulnerability. The problem, with a high probability, arose from the fact that they forgot to remove the factory debug mode from the firmware with the rights level iddqd.
')
More than 50% of network traffic is encrypted.
News Mozilla Foundation Tracker .
The topic of the ratio of encrypted traffic and the amount of data transmitted in clear text, I first picked up in one of the digests for August. Then it was a figure from the researchers who raised the Tor node: it turned out that in encrypted form only 25% of the traffic is transmitted through it. But Tor is not quite the right tool, and much more precisely, in theory, there should be statistics from browser developers. Firefox even has a tracker for this purpose, providing real-time information.
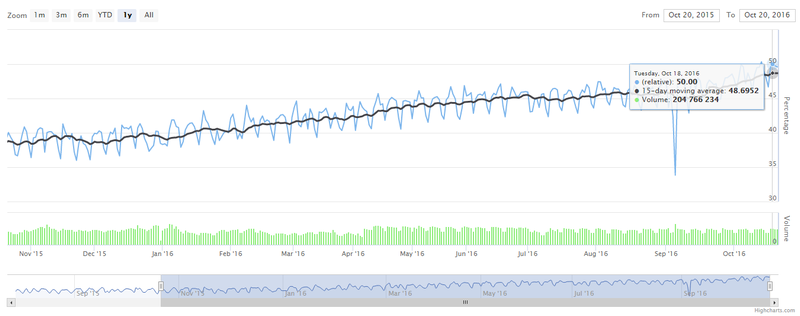
According to the Mozilla Foundation, over the year, the share of encrypted traffic (measured as the percentage of pages loaded over HTTPS, to be exact) increased by 10% and came close to 50%. At the moment 50% was obtained for the first time
Vulnerability in the Exchange client for Android allows you to steal user passwords
News Post on the Rapid7 blog.
Researchers at Rapid7 have discovered a serious vulnerability in the Nine for Android email client, which supports connection to Microsoft Exchange mail servers and can be used for mobile access to work mail. As it turned out, the email client did not check the validity of SSL / TLS certificates.

This makes it quite easy to organize a Man-In-The-Middle attack against a client. For example, you can force the user to connect to a prepared WiFi network, intercept and decrypt traffic, thus obtaining a password to access the mail, as shown in the screenshot above. The vulnerability is fixed in the client update of October 13, and those who have left an unpleasant aftertaste from this story are invited to monitor connections from this client in the server logs, using the characteristic identification string. A great example of a story, when data protection seems to be there, but in fact it does not exist.
What else happened
The leakage of the Mirai source code, a malware attack on IoT devices, has predictably led to an increase in the number of compromised devices. According to the estimate of the telecom provider Level 3, the number of infected devices has grown from 200 thousand to almost half a million.
Serious vulnerabilities patched in VeraCrypt, fork TrueCrypt.
21 The vulnerability is closed by another update of Google Chrome.

Antiquities
"Typo-Boot"
A dangerous virus, using the “Brain” method, infects the boot sector of a hard drive and floppy disks when reading from them (int 13h, ah = 2). On the disc is a standard way. It works only on IBM PC / XT computers, as it contains the command MOV CS, AX (inter-segment JMP), which is executed only by the 8086 processor. It hooks int 13h, 17h. Replaces characters that are printed to the printer.
Quote from the book "Computer viruses in MS-DOS" Eugene Kaspersky. 1992 Page 103.
Disclaimer: This column reflects only the personal opinion of its author. It may coincide with the position of Kaspersky Lab, or it may not coincide. Then how lucky.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/313312/
All Articles