Windows Server 2016: clouds - to the masses
Microsoft has released the server operating system Windows Server 2016, adding to its support for containers and the new edition of the Nano Server. Windows Server 2016 was developed for several years and in parallel with the improvement of the OS, its preliminary versions were released. From October 1, 2016, the Windows Server 2016 product line is available, consisting of six editions: WS 2016 Datacenter, Standard, Essentials, MultiPoint Premium Server, CAL, Windows Remote Desktop Services CAL 2016.
One of the main directions in the development of Microsoft Server 2016 was the support of public and private clouds. Many innovations of Windows Server 2016 are borrowed from Azure and brought to the level of the mainstream. In Windows Server 2016, the Hyper-V hypervisor has also been significantly improved, support for containers and Nano Server, a new “trimmed” version of Windows Server, has been added. The goal is the same - native support for cloud applications.

10 reasons to love Windows Server 2016: security (privilege / identity management, security), platform for applications (Nano Server, containers), platform for software-defined data centers (computing, data storage, network functions, RDS), management (server management tools, new version of PowerShell).
In fact, this OS resembles Windows 10 in server version. Server 2016 uses the same kernel as Windows 10 Anniversary, and by typing ver on the command line, you will get the same answer: Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.14393]. In Windows Server 2016, the same Start menu as in Windows 10 Anniversary (when installed from the Desktop Experience).
')
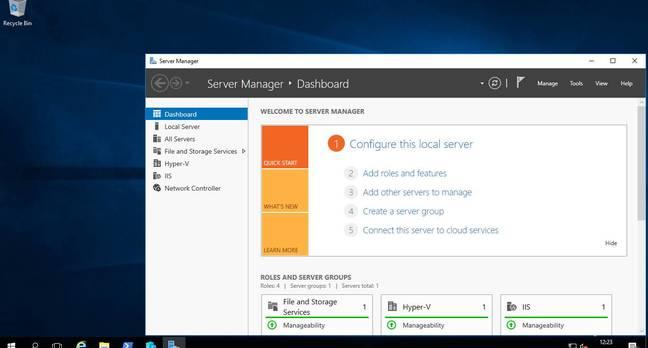
Windows Server 2016, now with the Windows 10 desktop.
What interesting things can be noted? Microsoft has more than 40 new features on the list, including embedded virtualization for Hyper-V containers and deployment of Hyper-V hosts in Azure or other public clouds. Many new Hyper-V tools are related to the creation and maintenance of guest VMs.
You can "on the fly" to change the capacity of virtual disks, memory, add and delete virtual network cards. Virtual machines can provide discrete access to devices on a PCIe bus, such as disk controllers. A cluster of Windows Server 2012 R2 with Hyper-V can be upgraded to Server 2016 without interrupting services.
Of course, some solutions are not cheap, and therefore do not belong to the mass category. For example, a crash-proof configuration with two Azure Stack systems spread over different sites. Of course, you can run Azure Stack and on the same server, but, rather, for the purpose of testing. However, most of the changes relate to a wide range of users.
Hyper-V hypervisor underwent numerous improvements. The following changes can be distinguished:

New features in Hyper-V are the most popular and expected Windows Server 2016 innovations ( according to SpiceWorks survey data ). They are celebrated by more than 30% of respondents.
It also includes support for nested virtualization (Nested virtualization), which allows running virtual machines on a hypervisor, which is itself installed in a virtual environment.

Nested virtualization means that you can run Hyper-V on the VM, which is guest on the Hyper-V server, guest on the Hyper-V server, etc.
This feature may be relevant for developers and modeling of virtual infrastructures, as well as for more efficient use of container applications. Many previous restrictions have been eliminated.

Hyper-V in Server 2016 has become more scalable.
Now Microsoft Hyper-V allows you to allocate a virtual machine with up to 12 TB of RAM (instead of one) and up to 240 virtual processors (instead of 64). Hyper-V host supports up to 24 TB of RAM. To reduce unproductive losses and enhance security on a Hyper-V host, you can run a Nano Server. For administration in this case, you can use PowerShell and remote access.
In Windows Server 2016, security mechanisms have been further developed. In particular, the most valuable system data, the Windows Server 2016 cryptographic modules, the components responsible for the integrity of the OS kernel, passwords, etc. are placed in a separate Hyper-V container called the Virtual Security Module (VSM). Access to this data is impossible even when the system is compromised .
Another important tool is a virtual TPM (Trusted Platform Module), which allows Bitlocker to use encryption tools in virtual machines, and Credential Guard for secure storage of identification data. The use of Virtual TPM is especially important, for example, when placing a VM in the cloud.
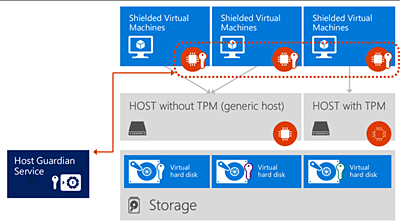
Host Guardian Service is an important component of security. It works in conjunction with other components of Windows Server 2016 and provides a high level of protection for Shielded VM.
In terms of security, protected virtual machines became the Shielded VM, but creating them requires Windows Server Datacenter and a separate server with the Host Guardian Service for storing keys and checking VM rights to run on a specific platform.
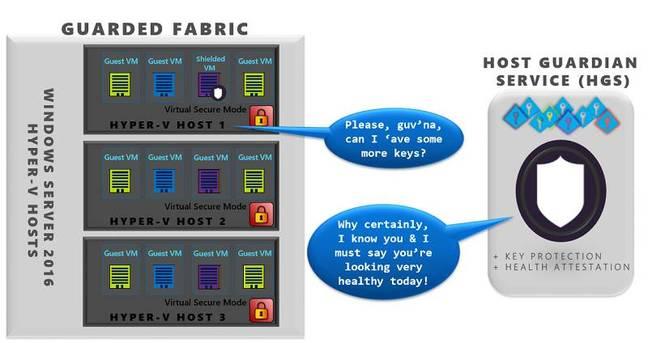
Host Guardian Service is used to verify the launch of the Shielded VM. And using the Guarded Fabric toolkit, you can flexibly configure your network infrastructure and break it into separate isolated network segments.
Shielded VM technology allows you to create secure virtual machines in the cloud infrastructure that only their owner can access. The administrator is only allowed to enable and disable such virtual machines. He has no right to interfere in their work, read data, intercept traffic, change their configuration. Shielded VM may be required by hosting providers providing virtual server rental services.
The ability to connect a virtual display to a VM using the Hyper-V administration tool in Shielded VM is also blocked. How to fix the VM, if something went wrong, and it does not start? On this occasion, Microsoft offers a tricky solution - running such a VM inside another Shielded VM. When creating a Shielded VM, you must also take into account that they have increased requirements for system resources.
Improved PowerShell provides easier and more comprehensive control over environments, which greatly increases the level of system security. Also one of the key security functions is the separation of access rights during administration.
In Windows Server 2016, a tool called Just Enough Administration (JEA) also appeared. This means that administrators can log in under temporary accounts limited to certain roles. That is, the administrator, logging in from a PC infected with a virus, will not do much harm. Windows Credential Guard also limits the potential damage from malware in such a scenario. And you can grant temporary administration rights (Just in Time Administration) using Microsoft Identity Manager Privileged Access Manager.
As you know, in Window Server 2012 using Storage Spaces, you can create fault-tolerant memory pools on SAS disks connected to the server without the help of a traditional SAN (Storage Area Network). Storage Spaces Direct gives you the ability to directly connect SAS, SATA or SSD drives to a Server 2016 cluster. This can be used to create software-defined storage systems (Software-Defined Storage, SDS).

Storage Spaces Direct can be used to connect drives directly.
Added the ability to dynamically manage the bandwidth of Storage Quality of Service (QoS) virtual disks. Storage QoS policies can be applied both to the disk subsystem of a separate virtual machine and to a VM group.
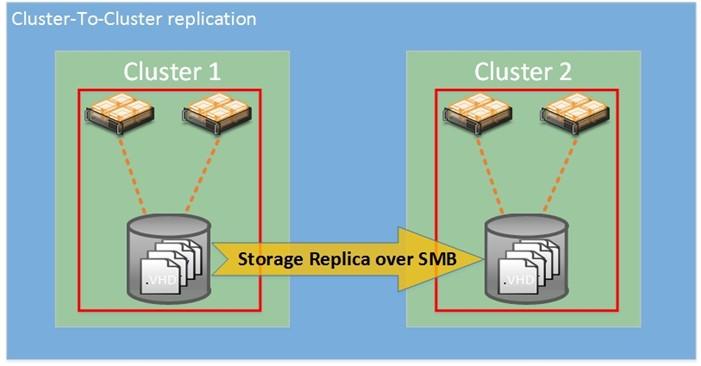 Storage Replica implements block synchronous replication between configured servers using the SMB 3.1.1 protocol.
Storage Replica implements block synchronous replication between configured servers using the SMB 3.1.1 protocol.
Using the Storage Replica toolkit, administrators can replicate data between remote servers, cluster systems, and data centers, thereby increasing disaster recovery and preventing losses at the file system level.
To support SDN (Software Defined Networking), the Server Controller role has been added to Server 2016. The network controller is designed to manage virtual switches, load balancers, firewall rules and virtual gateways in Hyper-V. VXLAN (Virtual Extensible Local Area Network) is also supported.
Nano Server is an even more compact version of Server Core. It is convenient to use it as a host system for deploying virtual machines, use it as a DNS or IIS server, and run applications in containers.

Improvements in service level: fewer vulnerabilities, fewer reboots.
According to Microsoft, the Nano Server has 93% smaller VHD size, it requires 80% fewer reboots. Such a system can be used for various special functions and tasks. Moreover, the Nano Server runs both on a physical server and in a VM. It has no GUI - only Sysinternals tools.
Nano Server is also convenient to use in the infrastructure of the Microsoft Cloud Platform to support cloud services and maintenance of applications running in virtual environments, containers, or on physical servers. It can be used to deploy compute clusters and build horizontally scalable file storage.

Due to its compactness and efficient use of resources, Nano Server provides a higher density of VMs, that is, more OS instances can be placed on a single physical host, which reduces the cost of IT infrastructure.
An important difference between Windows Server 2016 and previous versions of Microsoft server operating systems is support for container technologies. Windows Server Containers are part of the open Docker project. They allow you to run applications in isolated environments on different platforms, quickly deploy and move them between servers.
Windows supports two types of containers - Windows Server containers and Hyper-V containers. Lightweight server containers do not require a Windows license. Windows Server containers function like Docker containers for the Linux platform. They use the common core of the operating system, which makes them more compact and flexible than regular virtual machines.
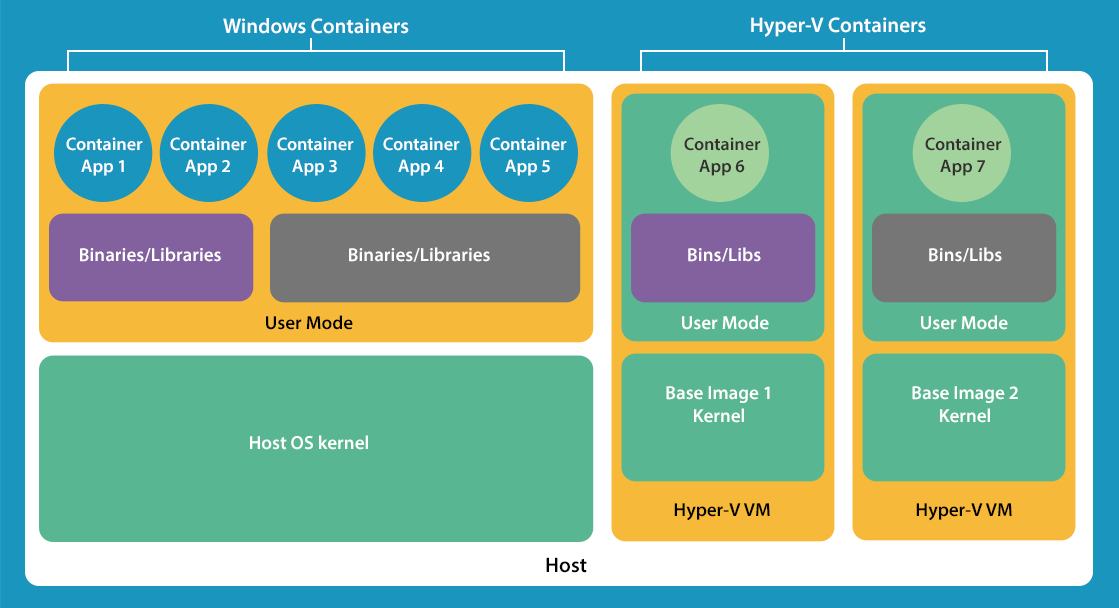
Each Hyper-V container has its own copy of the Windows Server kernel, and the isolation is implemented not by the operating system, but by the hypervisor.
Windows Server containers share OS resources, but behave as independent instances of the operating system. However, in a Windows Server OS environment, you cannot start a Linux container and vice versa. To launch a container, its image is taken from the repository (public or private) and, if necessary, modified.

Docker Container running in Windows Server 2016.
Hyper-V containers are isolated by means of virtualization, have their own copy of the Windows kernel, and in the Standard version they do not need a license for them. Such containers have a higher isolation level comparable to virtual machines. This approach is more demanding of server resources, but it improves the stability of the server operating system and the reliability of the containers.
Both types of containers are managed in the same way. Windows Server and Hyper-V containers can be managed using PowerShell and WMI, as well as using Docker tools. The latter provide a unified administration environment and allow you to manage container applications in a Windows Server or Linux environment.

Configuring containers in Windows Server 2016. Hyper-V containers can be used to launch applications with increased information security requirements.
A good option for deploying containers is the Nano Server. However, you need to remember that the Nano Server is a truncated Windows. If IIS, for example, works in it, then the .NET Framework no longer exists (only cross-platform .NET Core). Not all applications are currently compatible with the Nano Server.

Docker images in the Nano Server can be very compact.
Docker containers in Windows - so far in the initial stage. It will take time for administrators to master them, and developers - to bring to mind. Microsoft will also need to replenish the options with existing tools like Visual Studio.
There are many other innovations in Windows Server 2016. The system received a new mechanism for downloading and distributing updates, which operates on the principle of the P2P protocol BitTorrent, support for the SSH protocol. Windows Server 2016 comes with the Windows Management Framework 5.1 and a new version of PowerShell using the .NET Framework 4.6.
The updated Windows PowerShell allows you to operate with even more cmdlets (cmdlets) that perform various management tasks. In particular, PowerShell 5 offers cmdlets to manage local users and groups, and the Get-ComputerInfo cmdlet to get detailed information about the system.
Innovations have touched and Active Directory. Now you can use smart cards for certification keys. Active Directory Domain Services provides an even higher level of security when identifying corporate and personal devices.
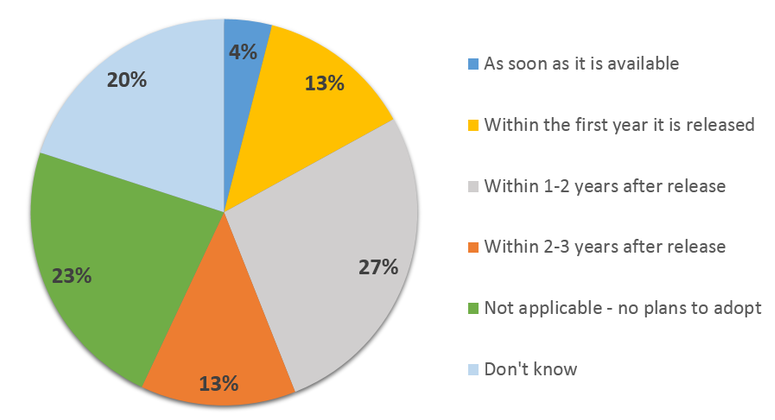
Plans for the transition of organizations to Windows Server 2016 ( according to a SpiceWorks survey conducted in November 2015).
A new virtual machine configuration file format (.VMCX and .VMRS) appeared with a higher degree of protection against failures at the storage level. The ability to safely load Linux guest operating systems and OpenGL and OpenCL Remote Desktop Service (RDS) was added.
The OS update mechanism of the cluster hosts without stopping it (Cluster Operating System Rolling Upgrade) makes it possible, with zero downtime, to update the cluster with a sequential update of its individual nodes.
Windows Server 2016 also includes the IP Address Management Toolkit (IPAM), which allows you to simplify the management of IP addresses. Of course, it is impossible to tell about all the innovations of the new OS in one article. This is only a very superficial "first look."
How many editions does Windows Server 2016 have? Good question. Above mentioned six. There are editions Standard and Datacenter, differing licensing schemes. Standard includes licenses for only two VMs or Hyper-V containers under Windows Server, while in Datacenter the number of VMs is not limited. The Datacenter version will be required to work with some new tools, including Storage Spaces Direct, Storage Replica, Shielded Virtual Machine and a number of network functions. There is a Standard version from $ 882 for 16 cores. Datacenter will cost at least $ 6155.

Functional differences between Datacenter and Standard editions in Windows Server 2016.
Below are the features that are only in the edition of Windows Server 2016 Datacenter:
Nano Server is licensed as a Windows Server tool, but requires Software Assurance license instead of base license and is not sold separately. There is also a free Windows Hyper-V Server, used only as a Hyper-V host, and a small business version of Windows Server Essentials for up to 25 users and 50 devices that do not need Client Access Licenses (CAL). Essentials costs $ 501, but there are cheaper OEM versions. OEM versions of Windows Server Foundation are no longer shipped.

The purpose of editions of Windows Server 2016 and the licensing model.
There are a couple of special editions: Windows Storage Server for storage systems and Multipoint Premium Server, mainly for remote desktops in education. Standard and Datacenter versions are installed by default without a GUI (Server Core option).
By default, the installation of Windows Server 2016 is done without a GUI.
Summarizing, it can be noted that Windows Server 2016 provides many opportunities for the full deployment and operation of IT infrastructure in the cloud. The new OS facilitates the ability to access and identify the services and applications of the organization if they are located both in the cloud and on physical servers. The Microsoft server platform is actively developing in accordance with industry trends and business preferences. The work done a lot, the system is developing in the right direction. You can test Windows Server 2016 by taking a virtual VPS server for a free trial period of 3 days.
One of the main directions in the development of Microsoft Server 2016 was the support of public and private clouds. Many innovations of Windows Server 2016 are borrowed from Azure and brought to the level of the mainstream. In Windows Server 2016, the Hyper-V hypervisor has also been significantly improved, support for containers and Nano Server, a new “trimmed” version of Windows Server, has been added. The goal is the same - native support for cloud applications.

10 reasons to love Windows Server 2016: security (privilege / identity management, security), platform for applications (Nano Server, containers), platform for software-defined data centers (computing, data storage, network functions, RDS), management (server management tools, new version of PowerShell).
In fact, this OS resembles Windows 10 in server version. Server 2016 uses the same kernel as Windows 10 Anniversary, and by typing ver on the command line, you will get the same answer: Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.14393]. In Windows Server 2016, the same Start menu as in Windows 10 Anniversary (when installed from the Desktop Experience).
')

Windows Server 2016, now with the Windows 10 desktop.
What interesting things can be noted? Microsoft has more than 40 new features on the list, including embedded virtualization for Hyper-V containers and deployment of Hyper-V hosts in Azure or other public clouds. Many new Hyper-V tools are related to the creation and maintenance of guest VMs.
You can "on the fly" to change the capacity of virtual disks, memory, add and delete virtual network cards. Virtual machines can provide discrete access to devices on a PCIe bus, such as disk controllers. A cluster of Windows Server 2012 R2 with Hyper-V can be upgraded to Server 2016 without interrupting services.
Of course, some solutions are not cheap, and therefore do not belong to the mass category. For example, a crash-proof configuration with two Azure Stack systems spread over different sites. Of course, you can run Azure Stack and on the same server, but, rather, for the purpose of testing. However, most of the changes relate to a wide range of users.
Updated hypervisor
Hyper-V hypervisor underwent numerous improvements. The following changes can be distinguished:
- Hyper-V client supports Windows 10.
- Compatible with Connected Standby.
- Purpose of a discrete device.
- Monitor virtual machine activity to optimize the use of system resources (RCT).
- Use alternate accounts when connecting to another Windows Server 2016 system.
- Updated management protocol and other improvements.

New features in Hyper-V are the most popular and expected Windows Server 2016 innovations ( according to SpiceWorks survey data ). They are celebrated by more than 30% of respondents.
It also includes support for nested virtualization (Nested virtualization), which allows running virtual machines on a hypervisor, which is itself installed in a virtual environment.

Nested virtualization means that you can run Hyper-V on the VM, which is guest on the Hyper-V server, guest on the Hyper-V server, etc.
This feature may be relevant for developers and modeling of virtual infrastructures, as well as for more efficient use of container applications. Many previous restrictions have been eliminated.

Hyper-V in Server 2016 has become more scalable.
Now Microsoft Hyper-V allows you to allocate a virtual machine with up to 12 TB of RAM (instead of one) and up to 240 virtual processors (instead of 64). Hyper-V host supports up to 24 TB of RAM. To reduce unproductive losses and enhance security on a Hyper-V host, you can run a Nano Server. For administration in this case, you can use PowerShell and remote access.
Security
In Windows Server 2016, security mechanisms have been further developed. In particular, the most valuable system data, the Windows Server 2016 cryptographic modules, the components responsible for the integrity of the OS kernel, passwords, etc. are placed in a separate Hyper-V container called the Virtual Security Module (VSM). Access to this data is impossible even when the system is compromised .
Another important tool is a virtual TPM (Trusted Platform Module), which allows Bitlocker to use encryption tools in virtual machines, and Credential Guard for secure storage of identification data. The use of Virtual TPM is especially important, for example, when placing a VM in the cloud.

Host Guardian Service is an important component of security. It works in conjunction with other components of Windows Server 2016 and provides a high level of protection for Shielded VM.
In terms of security, protected virtual machines became the Shielded VM, but creating them requires Windows Server Datacenter and a separate server with the Host Guardian Service for storing keys and checking VM rights to run on a specific platform.

Host Guardian Service is used to verify the launch of the Shielded VM. And using the Guarded Fabric toolkit, you can flexibly configure your network infrastructure and break it into separate isolated network segments.
Shielded VM technology allows you to create secure virtual machines in the cloud infrastructure that only their owner can access. The administrator is only allowed to enable and disable such virtual machines. He has no right to interfere in their work, read data, intercept traffic, change their configuration. Shielded VM may be required by hosting providers providing virtual server rental services.
The ability to connect a virtual display to a VM using the Hyper-V administration tool in Shielded VM is also blocked. How to fix the VM, if something went wrong, and it does not start? On this occasion, Microsoft offers a tricky solution - running such a VM inside another Shielded VM. When creating a Shielded VM, you must also take into account that they have increased requirements for system resources.
Improved PowerShell provides easier and more comprehensive control over environments, which greatly increases the level of system security. Also one of the key security functions is the separation of access rights during administration.
In Windows Server 2016, a tool called Just Enough Administration (JEA) also appeared. This means that administrators can log in under temporary accounts limited to certain roles. That is, the administrator, logging in from a PC infected with a virus, will not do much harm. Windows Credential Guard also limits the potential damage from malware in such a scenario. And you can grant temporary administration rights (Just in Time Administration) using Microsoft Identity Manager Privileged Access Manager.
Data and Network Storage - Software Defined
As you know, in Window Server 2012 using Storage Spaces, you can create fault-tolerant memory pools on SAS disks connected to the server without the help of a traditional SAN (Storage Area Network). Storage Spaces Direct gives you the ability to directly connect SAS, SATA or SSD drives to a Server 2016 cluster. This can be used to create software-defined storage systems (Software-Defined Storage, SDS).

Storage Spaces Direct can be used to connect drives directly.
Added the ability to dynamically manage the bandwidth of Storage Quality of Service (QoS) virtual disks. Storage QoS policies can be applied both to the disk subsystem of a separate virtual machine and to a VM group.

Using the Storage Replica toolkit, administrators can replicate data between remote servers, cluster systems, and data centers, thereby increasing disaster recovery and preventing losses at the file system level.
To support SDN (Software Defined Networking), the Server Controller role has been added to Server 2016. The network controller is designed to manage virtual switches, load balancers, firewall rules and virtual gateways in Hyper-V. VXLAN (Virtual Extensible Local Area Network) is also supported.
Nano server
Nano Server is an even more compact version of Server Core. It is convenient to use it as a host system for deploying virtual machines, use it as a DNS or IIS server, and run applications in containers.

Improvements in service level: fewer vulnerabilities, fewer reboots.
According to Microsoft, the Nano Server has 93% smaller VHD size, it requires 80% fewer reboots. Such a system can be used for various special functions and tasks. Moreover, the Nano Server runs both on a physical server and in a VM. It has no GUI - only Sysinternals tools.
Nano Server is also convenient to use in the infrastructure of the Microsoft Cloud Platform to support cloud services and maintenance of applications running in virtual environments, containers, or on physical servers. It can be used to deploy compute clusters and build horizontally scalable file storage.

Due to its compactness and efficient use of resources, Nano Server provides a higher density of VMs, that is, more OS instances can be placed on a single physical host, which reduces the cost of IT infrastructure.
Containers
An important difference between Windows Server 2016 and previous versions of Microsoft server operating systems is support for container technologies. Windows Server Containers are part of the open Docker project. They allow you to run applications in isolated environments on different platforms, quickly deploy and move them between servers.
Windows supports two types of containers - Windows Server containers and Hyper-V containers. Lightweight server containers do not require a Windows license. Windows Server containers function like Docker containers for the Linux platform. They use the common core of the operating system, which makes them more compact and flexible than regular virtual machines.

Each Hyper-V container has its own copy of the Windows Server kernel, and the isolation is implemented not by the operating system, but by the hypervisor.
Windows Server containers share OS resources, but behave as independent instances of the operating system. However, in a Windows Server OS environment, you cannot start a Linux container and vice versa. To launch a container, its image is taken from the repository (public or private) and, if necessary, modified.

Docker Container running in Windows Server 2016.
Hyper-V containers are isolated by means of virtualization, have their own copy of the Windows kernel, and in the Standard version they do not need a license for them. Such containers have a higher isolation level comparable to virtual machines. This approach is more demanding of server resources, but it improves the stability of the server operating system and the reliability of the containers.
Both types of containers are managed in the same way. Windows Server and Hyper-V containers can be managed using PowerShell and WMI, as well as using Docker tools. The latter provide a unified administration environment and allow you to manage container applications in a Windows Server or Linux environment.

Configuring containers in Windows Server 2016. Hyper-V containers can be used to launch applications with increased information security requirements.
A good option for deploying containers is the Nano Server. However, you need to remember that the Nano Server is a truncated Windows. If IIS, for example, works in it, then the .NET Framework no longer exists (only cross-platform .NET Core). Not all applications are currently compatible with the Nano Server.

Docker images in the Nano Server can be very compact.
Docker containers in Windows - so far in the initial stage. It will take time for administrators to master them, and developers - to bring to mind. Microsoft will also need to replenish the options with existing tools like Visual Studio.
Other features
There are many other innovations in Windows Server 2016. The system received a new mechanism for downloading and distributing updates, which operates on the principle of the P2P protocol BitTorrent, support for the SSH protocol. Windows Server 2016 comes with the Windows Management Framework 5.1 and a new version of PowerShell using the .NET Framework 4.6.
The updated Windows PowerShell allows you to operate with even more cmdlets (cmdlets) that perform various management tasks. In particular, PowerShell 5 offers cmdlets to manage local users and groups, and the Get-ComputerInfo cmdlet to get detailed information about the system.
Innovations have touched and Active Directory. Now you can use smart cards for certification keys. Active Directory Domain Services provides an even higher level of security when identifying corporate and personal devices.

Plans for the transition of organizations to Windows Server 2016 ( according to a SpiceWorks survey conducted in November 2015).
A new virtual machine configuration file format (.VMCX and .VMRS) appeared with a higher degree of protection against failures at the storage level. The ability to safely load Linux guest operating systems and OpenGL and OpenCL Remote Desktop Service (RDS) was added.
The OS update mechanism of the cluster hosts without stopping it (Cluster Operating System Rolling Upgrade) makes it possible, with zero downtime, to update the cluster with a sequential update of its individual nodes.
Windows Server 2016 also includes the IP Address Management Toolkit (IPAM), which allows you to simplify the management of IP addresses. Of course, it is impossible to tell about all the innovations of the new OS in one article. This is only a very superficial "first look."
Windows Server 2016 Editions
How many editions does Windows Server 2016 have? Good question. Above mentioned six. There are editions Standard and Datacenter, differing licensing schemes. Standard includes licenses for only two VMs or Hyper-V containers under Windows Server, while in Datacenter the number of VMs is not limited. The Datacenter version will be required to work with some new tools, including Storage Spaces Direct, Storage Replica, Shielded Virtual Machine and a number of network functions. There is a Standard version from $ 882 for 16 cores. Datacenter will cost at least $ 6155.

Functional differences between Datacenter and Standard editions in Windows Server 2016.
Below are the features that are only in the edition of Windows Server 2016 Datacenter:
- Storage Spaces Direct is an extension of Storage Spaces technology for creating high-availability cluster storage;
- Storage Replica - block data replication technology between storages;
- Shielded Virtual Machines - technology to protect the contents of virtual machines Hyper-V;
- Host Guardian Service - server role designed to support secure virtual machines (Shielded VM) and prevent unauthorized access to them;
- Network Fabric - centralized monitoring and management of network infrastructure;
- Microsoft Azure Stack - SDN-stack support for building hybrid solutions.
Nano Server is licensed as a Windows Server tool, but requires Software Assurance license instead of base license and is not sold separately. There is also a free Windows Hyper-V Server, used only as a Hyper-V host, and a small business version of Windows Server Essentials for up to 25 users and 50 devices that do not need Client Access Licenses (CAL). Essentials costs $ 501, but there are cheaper OEM versions. OEM versions of Windows Server Foundation are no longer shipped.

The purpose of editions of Windows Server 2016 and the licensing model.
There are a couple of special editions: Windows Storage Server for storage systems and Multipoint Premium Server, mainly for remote desktops in education. Standard and Datacenter versions are installed by default without a GUI (Server Core option).

By default, the installation of Windows Server 2016 is done without a GUI.
Summarizing, it can be noted that Windows Server 2016 provides many opportunities for the full deployment and operation of IT infrastructure in the cloud. The new OS facilitates the ability to access and identify the services and applications of the organization if they are located both in the cloud and on physical servers. The Microsoft server platform is actively developing in accordance with industry trends and business preferences. The work done a lot, the system is developing in the right direction. You can test Windows Server 2016 by taking a virtual VPS server for a free trial period of 3 days.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/313292/
All Articles