How cybersecurity trends affect the theft of money
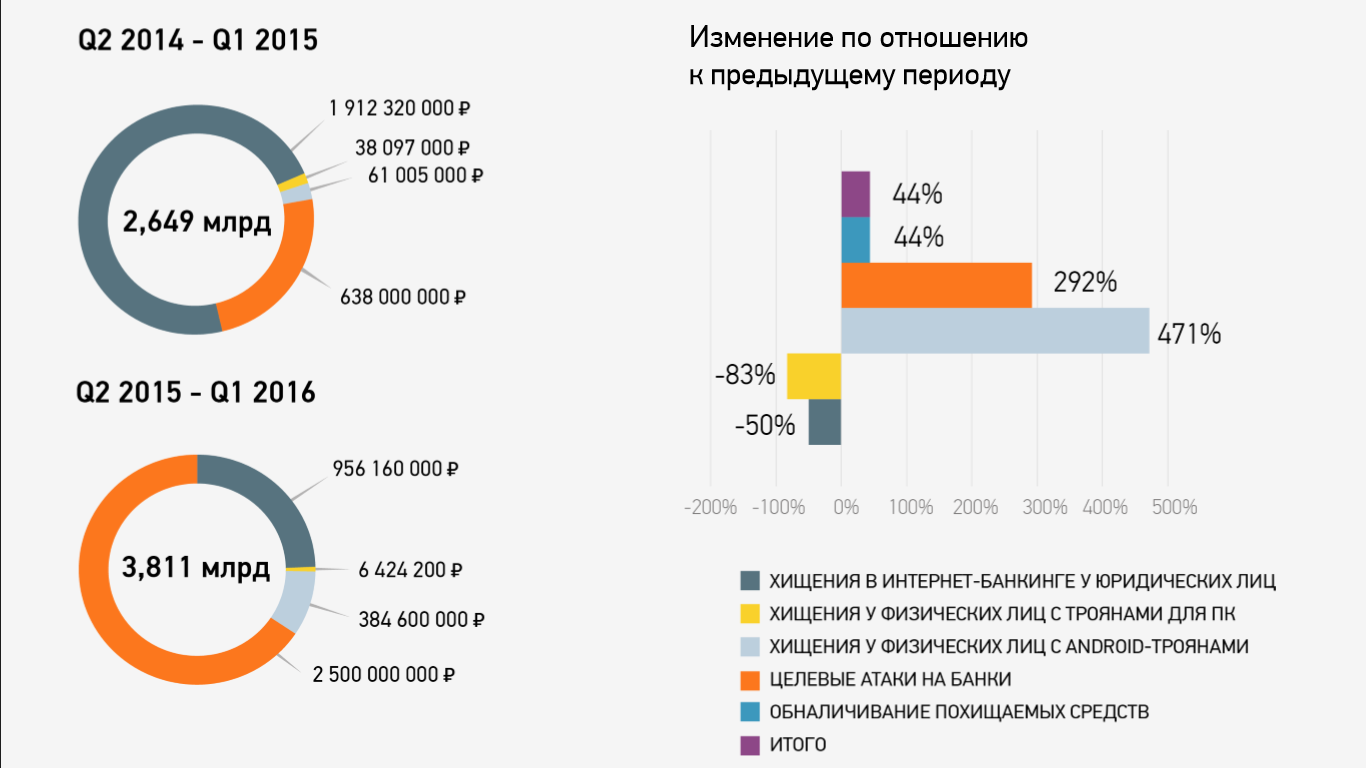
For the 2015-2016 fiscal year in Russia, hackers stole more than 5.5 billion rubles. This is 44% more than last year. The largest share in the total damage was provided by the hacking of Russian banks. So, they lost 2.5 billion rubles, which is four times higher than last year.
The total amount of theft, which was prevented, amounted to five billion rubles, said on Thursday the deputy head of the Central Security and Data Protection Directorate of the Central Bank Artem Sychev. This includes individuals, legal entities and banks as such.
')
The number of cyber attacks on computers of individuals decreased by 83%. For the 2015-2016 fiscal year, they lost 6.4 million. The number of attacks on the Internet banking systems of legal entities has halved: hackers stole 956 million rubles from them in a year.
Significantly affected users of mobile devices based on Android. With the help of special Trojans, cybercriminals for the year were able to steal 348.6 million rubles from their accounts in Russian banks.

Experts recorded in this area the largest increase in crime - 471 percent. And the number of users of Android-devices infected with viruses, has grown to 350 new people a day.
In May, Reuters reported that Russian hackers stole data from 272 million users.
Computer security expert Alex Holden, who first discovered the attacks on Adobe and JPMorgan, said that hackers had carried out the largest cyber attack, as a result of which attackers from the “Russian underworld” got passwords and logins from 272 million accounts.
According to Holden, the Mail.ru mail service suffered more than others from the attack. Also, the victims of hackers have become the e-mail service of US companies Google, Yahoo and Microsoft.
On Thursday, October 13, the largest cyber security conference in Eastern Europe, CyberCrimeCon, was held in Moscow. Representatives of Interpol and Europol, as well as leading European companies and banks, spoke about the main hacker threats to businesses and ordinary users of the network.

Fernando Ruiz, head of the special operations department at the European Center for Combating Cybercrime, implicitly hinted at the need for closer cooperation between Russia and the West.
The representative of Interpol Nur Azhar Aiob noted that the very real threat of large-scale network wars should push the leading world powers to the signing of pacts banning the use of cyber weapons.
Interpol representative was supported by Group-IB CEO Ilya Sachkov, who called international cooperation a key condition for the success of the fight against hackers: “If we wake up tomorrow and all states unite, exchange their big data and information available to the special services, then the problem may well be solved by itself.”
In the meantime, fighters against cyber threats have called on journalists to write less about network criminals: this only attracts attention and makes them popular. “Today being a hacker is glamorous. If a person has hacked someone, everyone will immediately admire. But he broke the law, - said Sachkov.
He also noted that 99% of computer crimes are connected with an attempt to make money. However, the goal of the remaining 1% of computer crimes is espionage and cyber-terrorism.
In November 2015, the company Zerodium, which deals with the search and elimination of vulnerabilities, published prices for hacking a number of products of IT companies. For hacking Safari and Internet Explorer, experts are ready to pay hackers 50 thousand dollars, for Google Chrome - 80 thousand dollars, and for unauthorized access to systems on Android and Windows Phone - 100 thousand dollars. The most expensive is the gap in the protection of iOS - for it, the hacker will receive 500 thousand dollars.
Meanwhile, in China they use a more cunning scheme.

The Chinese company ShenZhen Computer Users Association (SZCUA) intends to acquire vulnerabilities on Russian information security engineers on iPhone, Android smartphones and computer browsers.
As representatives of several Russian companies told the Kommersant publication, a representative of SZCUA named Robert Nevsky addressed them. According to him, SZCUA wants to buy exploits (tools for carrying out attacks on computer systems) that use so-called “zero-day vulnerabilities” (software errors that its manufacturer does not know about). For similar programs for mobile platforms iOS and Android, as well as a number of web applications and browsers, the Chinese are ready to pay from 100 thousand dollars.
At the same time, experts note that the Chinese company is likely to be engaged in buying up vulnerabilities for government hacker groups, which then use them to create cyber weapons.
In conclusion, let us present the facts and forecasts voiced at the conference on information security:
Every day, hackers successfully attack 8 Russian companies, each of which loses an average of 480,000 rubles.
Russian-language virus writers are more focused on foreign markets: to 16 out of 19 Trojans for PCs that are most widely used for embezzlement around the world, are associated with Russian-speaking criminals.
The Internet of Things industry (Internet of things, IoT) is gaining popularity and attracts hackers: IoT devices that are not protected by antivirus programs have become the main driver of botnet growth for DDoS attacks.
The range of threats to brands is expanding. Trust in brands allows you to successfully attack not only individuals, but also legal entities.
Successful targeted attacks on banks will continue, the average damage to one successful attack will increase.
There will be more incidents with encryption programs, including encryption of mobile devices.
The number of attacks on industrial facilities will increase, the likelihood of an attack on a critical infrastructure facility is high with significant damage.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/312720/
All Articles