Google fixed Android vulnerabilities
 Google has released a monthly update for Android Android Security Bulletin — October 2016 . Like last time, the Android update was a two-step, the first 2016-10-01 contains fixes for vulnerabilities of Android itself, and the second 2016-10-05 applies only to Nexus devices. As part of the second stage, as many as seven critical vulnerabilities were closed, two of them with the identifiers CVE-2016-0758 and CVE-2016-7117 allow for remote routing of the device, which may entail a flashing of the device to return to its original state. Zerodium estimates exploit costs for such vulnerabilities as $ 200k.
Google has released a monthly update for Android Android Security Bulletin — October 2016 . Like last time, the Android update was a two-step, the first 2016-10-01 contains fixes for vulnerabilities of Android itself, and the second 2016-10-05 applies only to Nexus devices. As part of the second stage, as many as seven critical vulnerabilities were closed, two of them with the identifiers CVE-2016-0758 and CVE-2016-7117 allow for remote routing of the device, which may entail a flashing of the device to return to its original state. Zerodium estimates exploit costs for such vulnerabilities as $ 200k.Below is a table of critical vulnerabilities that were released during 2016-10-05. The first two vulnerabilities are universal and allow you to remotely execute code with kernel privileges in the system (RCE + LPE). The first is relevant only for Nexus 5X and Nexus 6P devices, and the second is more universal and covers all Nexus models. In case of successful operation, an attacker can remotely obtain maximum root privileges on the device. This situation, in turn, may lead to the fact that in order to remove the malicious code from the device it may be necessary to reflash it.

')
A similar flashing operation to regain control of the device applies to all other critical vulnerabilities from the table above. However, their remote operation is impossible and the attacker first needs to lure the user to download an application with an exploit. The following Nexus device components are subject to upgrade during 2016-10-05.
- ASN.1 decoder core component.
- Kernel network subsystem.
- MediaTek video driver.
- Component of shared kernel memory driver.
- Qualcomm components and drivers.
- NVIDIA MMC driver.
- Mediaserver service.
- Synaptics touchscreen driver.
- Subsystem system_server .
- NVIDIA GPU driver.
- Motorola USBNet driver.
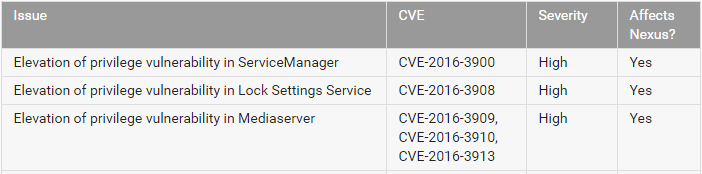
A total of 20 vulnerabilities were closed in the first stage of the update and 58 in the second. The first stage was not addressed to any critical vulnerabilities in Android. LPE-type vulnerabilities in ServiceManager, Lock Settings, Mediaserver services allow attackers to raise the rights of their malicious applications in the system, but not to the level of the system root (root). In addition, the attacker must also force the user to download this malicious application to the smartphone and launch it. The following table lists these vulnerabilities for the components mentioned.
Exploits for remote Android routing are the most expensive of all possible exploits for this mobile platform, Zerodium estimates the cost of such an instance at $ 200K. As in the case of the Trident for iOS exploit, the attacker will have to use three types of vulnerabilities for this, one for remote code execution, one for circumventing kernel defenses (which appeared in Android 7) and one for final privilege escalation. In addition, with the distributed architecture of the most vulnerable for remote operation of the MediaServer service in Android 7, this will not be easy.
We encourage users to install the appropriate updates to their Android devices.

be secure.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/311842/
All Articles