What VPS hosting really is and how to choose a reliable VPS provider
Everyone who creates a website faces a number of problems, and one of the most difficult tasks is choosing between numerous offers. The budget of the majority of beginners is very limited, so that they have not very many options.

One of the most suitable is virtual hosting (shared hosting). This is an ideal choice for sites that have not yet become popular, that is, with low attendance. But if the load on the site may increase significantly in the near future, or a high-load project is hosted on the same physical server, for example, an e-commerce platform, then this option is not the best. In such situations, preferred VPS-hosting - a virtual private server. For a slightly higher price, you will get better functionality, security, and several other benefits.
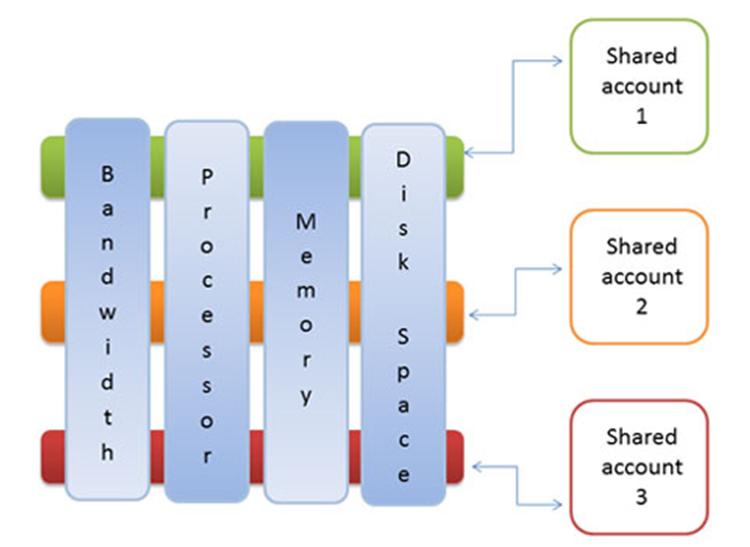
Anatomy of a virtual VPS hosting.
')
 In the case of VPS hosting, each website is hosted on a virtual private server, which is located on a fairly powerful physical server. The physical system is divided into several virtual ones: the software isolates the virtual servers and controls their collaboration. Virtual servers function independently of each other, so that when hosting multiple sites on a physical server, they do not affect the performance of each other. Each virtual server receives allocated resources.
In the case of VPS hosting, each website is hosted on a virtual private server, which is located on a fairly powerful physical server. The physical system is divided into several virtual ones: the software isolates the virtual servers and controls their collaboration. Virtual servers function independently of each other, so that when hosting multiple sites on a physical server, they do not affect the performance of each other. Each virtual server receives allocated resources.
The owner of the VPS gets full access (root) to its virtual server and can work with it in the same way as with a dedicated physical server. In the case of a VPS, virtual servers share the resources of their physical server — its processors, RAM, storage capacity, and network bandwidth. Thus, VPS hosting gives you full control over your server and almost the same benefits as a dedicated physical server. In this case, the virtual server is much cheaper than the dedicated one, and its performance is higher than with virtual hosting.
VPS hosting is the golden mean between virtual and dedicated hosting. It combines an acceptable cost of virtual hosting and the independence of a dedicated one. Unlike virtual hosting, where resources are shared, and "neighbors" may influence your site, the picture is different. Each virtual partition is an isolated environment, and all the capabilities of a physical server are available to you, but for a much lower price.

Shared hosting
+ easy start, low cost
- insufficient level of control and performance
VPS hosting
+ root access, secure environment
- a bit more expensive than shared hosting ( VPS for 65 rubles )
Dedicated hosting
+ maximum control, good server performance
- high cost, need qualified personnel
While the traffic at the site is small, the budget does not need to be increased - it will feel quite well on a virtual hosting. However, as traffic grows, most virtual hosting servers will not be able to provide the desired performance. One of the signs may be increased page load time. Overloading can also lead to frequent inaccessibility of the site from the outside (it regularly “falls”). If such symptoms appear, it means that virtual hosting for your website is not enough.
Sometimes hosters notify customers that their site has exhausted resources for the current month. In this case, it's time to switch to VPS hosting. If your site has a lot of multimedia content, then it will also require more powerful VPS hosting.
You can manage all VPS services using a user-friendly interface - a control panel : Plesk, cPanel, or another web console. Sometimes hosters offer their tools.

A good option is the ISPmanager 5 Lite panel. This is a unique set of services that allow you to simultaneously configure and administer the web server, domains, mail, databases, user access control.

If you have decided to switch to VPS hosting, then when choosing a provider you need to take into account a number of factors. And, unlike virtual hosting, when choosing a VPS hosting service that is truly useful for your project, you have to take into account many more factors. We list the main ones.

With virtual hosting you do not have access to the server as root, so the question of managing the server is not worth it. But in the case of a VPS, the entire virtual server is yours. Therefore, it is necessary that someone looked after him, monitored performance. If these functions are taken over by the VPS provider, then this is managed hosting (managed VPS), and in the case of unmanaged VPS you are responsible for your virtual server.
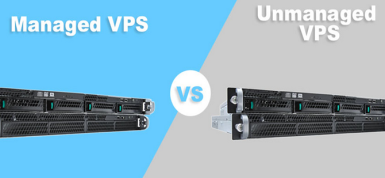
Unmanaged VPS are prepared only for root access, and users will need to independently install and configure the software, the control panel, and ensure the protection of the server and its maintenance / maintenance. Unmanaged hosting will require you to monitor the performance of the virtual server and maintain its performance.
If the server is "down", or there are some security problems, then you can solve them - you are the only administrator of your VPS. This option is more suitable for professionals with professional server management skills. So if you are a seasoned geek and are familiar with such things as correct system shutdown, its restoration, restart, server reboot, then unmanaged hosting can be a good option.
As for “normal” users and business owners, they should pay a little more and use managed VPS: a professional system administrator will follow the server in 24x7 mode. And users can do a more familiar thing for themselves.

Again, the degree of this control may be different and depends on the hosting provider and hosting plans. This must be borne in mind when comparing different plans VPS or hosters.
Another important point is the server operating system. Most hosters offer popular Windows and Linux. Linux OS as Open Source is cheaper than Windows. Linux-based hosting is completely user friendly and supports a wide range of applications. In many cases, this is a good (maybe even better) choice. However, there are applications that are either not supported in Linux at all or are better supported in Windows. If you need to use such software, for example, as ASP or ASP.NET, then your choice is Windows-based VPS. A Windows server is often required for developing on .NET or for deploying Microsoft applications and other applications for this platform.
Server configuration plays an important role in site speed and performance. How much processor power, RAM, and disk space you get is all that matters. In addition, it makes sense to ask which physical server will host your VPS. It is better if it is powerful enough equipment of a famous brand. And if the foundation is weak, it is difficult to expect the stability of the whole structure.

 Many hosters VPS guarantee the reliability of 99.9%. However, the stated figure may differ from the real one, and it is always useful to get acquainted with reviews on the Internet. For reliable and relatively uninterrupted operation of the site, this indicator should not be below 99.95%.
Many hosters VPS guarantee the reliability of 99.9%. However, the stated figure may differ from the real one, and it is always useful to get acquainted with reviews on the Internet. For reliable and relatively uninterrupted operation of the site, this indicator should not be below 99.95%.
Redundancy usually involves the reservation of resources, especially in the data center. For example, when the main power fails, UPS and diesel generators begin to work. If the problem is with the Internet provider, then there should be alternative communication channels. If one physical server is overloaded, then a backup should be provided, etc. Scalability, in turn, means the ability to cope with a sharp increase in server load, usually at the expense of reserve resources. All of this means increased uptime and consistently high performance.

Most VPS providers limit the bandwidth for a virtual server and may charge extra for an additional fee. When choosing a VPS host, you should make sure that you do not have to pay too much for sufficient network bandwidth.
Regardless of the performance of your hosting provider and the proposed functionality, there are always some problems. Convenient and effective support is needed in this case. If the hoster is not able to provide support in 24/7 mode, it is simply not worth your money. When your site will be idle for a long time, it can lead to an outflow of visitors, and maybe to serious financial losses. It is useful to first test the support service of the hosting provider, and then decide whether it makes sense to contact him.
Of course, to select a host, you need to find out the cost of its services. The price depends on the type of service (managed or not) and the resources allocated. Which hosting plan best meets your requirements is up to you.
A very important point, not all hosters have a money back guarantee, if the customer does not like hosting.
The closer the server is to your audience, the more efficient it will be for users to access it and the higher the chances of rising in search engine rankings. Web analytics tools will help you understand where the target audience is concentrated and find the VPS closer. You can also create a copy of the VPS, but you should take into account the distance during data transfer and the responsibility for ensuring communication between remote servers.
They may be required in several situations:
As your site grows and develops, VPS hosting at some point becomes a necessity, and you should very carefully select a service that meets your preferences. To do this, you need to at least know these requirements, so use a calculator and try to quantify them.
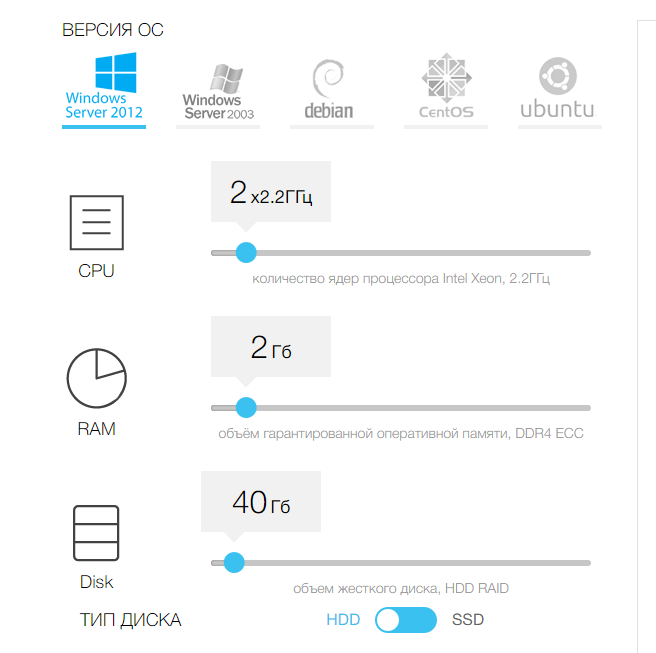
Virtual private servers can be easily scaled: if necessary, you can add memory, disk capacity or computing resources in a few clicks.
However, you need to know the initial requirements, including the necessary network bandwidth, the number of IP addresses, what additional services are needed (for example, protection against DDoS attacks ). An important parameter is the capacity of RAM. A minimum of 512 MB is recommended. This will provide the required speed and groundwork for the development of the site. This option will be a good starting point for those who switch to a VPS from a virtual hosting.

If you need high performance, then your choice is SSD VPS. Due to the high I / O speed of solid-state drives, VPS performance will be an order of magnitude higher than in the case of HDD. Enterprise-class SSDs with eMLC memory type, disks combined into RAID arrays reach data transfer rates of up to 100,000 IOPS, and Windows VPS starts within 7 seconds.

One of the most suitable is virtual hosting (shared hosting). This is an ideal choice for sites that have not yet become popular, that is, with low attendance. But if the load on the site may increase significantly in the near future, or a high-load project is hosted on the same physical server, for example, an e-commerce platform, then this option is not the best. In such situations, preferred VPS-hosting - a virtual private server. For a slightly higher price, you will get better functionality, security, and several other benefits.

Anatomy of a virtual VPS hosting.
')
What is a VPS?
 In the case of VPS hosting, each website is hosted on a virtual private server, which is located on a fairly powerful physical server. The physical system is divided into several virtual ones: the software isolates the virtual servers and controls their collaboration. Virtual servers function independently of each other, so that when hosting multiple sites on a physical server, they do not affect the performance of each other. Each virtual server receives allocated resources.
In the case of VPS hosting, each website is hosted on a virtual private server, which is located on a fairly powerful physical server. The physical system is divided into several virtual ones: the software isolates the virtual servers and controls their collaboration. Virtual servers function independently of each other, so that when hosting multiple sites on a physical server, they do not affect the performance of each other. Each virtual server receives allocated resources.The owner of the VPS gets full access (root) to its virtual server and can work with it in the same way as with a dedicated physical server. In the case of a VPS, virtual servers share the resources of their physical server — its processors, RAM, storage capacity, and network bandwidth. Thus, VPS hosting gives you full control over your server and almost the same benefits as a dedicated physical server. In this case, the virtual server is much cheaper than the dedicated one, and its performance is higher than with virtual hosting.
VPS hosting
VPS hosting is the golden mean between virtual and dedicated hosting. It combines an acceptable cost of virtual hosting and the independence of a dedicated one. Unlike virtual hosting, where resources are shared, and "neighbors" may influence your site, the picture is different. Each virtual partition is an isolated environment, and all the capabilities of a physical server are available to you, but for a much lower price.

Shared hosting
+ easy start, low cost
- insufficient level of control and performance
VPS hosting
+ root access, secure environment
- a bit more expensive than shared hosting ( VPS for 65 rubles )
Dedicated hosting
+ maximum control, good server performance
- high cost, need qualified personnel
Why might you need to upgrade to a VPS?
While the traffic at the site is small, the budget does not need to be increased - it will feel quite well on a virtual hosting. However, as traffic grows, most virtual hosting servers will not be able to provide the desired performance. One of the signs may be increased page load time. Overloading can also lead to frequent inaccessibility of the site from the outside (it regularly “falls”). If such symptoms appear, it means that virtual hosting for your website is not enough.
Sometimes hosters notify customers that their site has exhausted resources for the current month. In this case, it's time to switch to VPS hosting. If your site has a lot of multimedia content, then it will also require more powerful VPS hosting.

VPS site management
You can manage all VPS services using a user-friendly interface - a control panel : Plesk, cPanel, or another web console. Sometimes hosters offer their tools.

A good option is the ISPmanager 5 Lite panel. This is a unique set of services that allow you to simultaneously configure and administer the web server, domains, mail, databases, user access control.

How to choose a VPS: important factors
If you have decided to switch to VPS hosting, then when choosing a provider you need to take into account a number of factors. And, unlike virtual hosting, when choosing a VPS hosting service that is truly useful for your project, you have to take into account many more factors. We list the main ones.

Factor 1: Managed or Unmanaged
With virtual hosting you do not have access to the server as root, so the question of managing the server is not worth it. But in the case of a VPS, the entire virtual server is yours. Therefore, it is necessary that someone looked after him, monitored performance. If these functions are taken over by the VPS provider, then this is managed hosting (managed VPS), and in the case of unmanaged VPS you are responsible for your virtual server.

Unmanaged VPS are prepared only for root access, and users will need to independently install and configure the software, the control panel, and ensure the protection of the server and its maintenance / maintenance. Unmanaged hosting will require you to monitor the performance of the virtual server and maintain its performance.
If the server is "down", or there are some security problems, then you can solve them - you are the only administrator of your VPS. This option is more suitable for professionals with professional server management skills. So if you are a seasoned geek and are familiar with such things as correct system shutdown, its restoration, restart, server reboot, then unmanaged hosting can be a good option.
As for “normal” users and business owners, they should pay a little more and use managed VPS: a professional system administrator will follow the server in 24x7 mode. And users can do a more familiar thing for themselves.

Again, the degree of this control may be different and depends on the hosting provider and hosting plans. This must be borne in mind when comparing different plans VPS or hosters.
Factor 2: Windows or Linux
Another important point is the server operating system. Most hosters offer popular Windows and Linux. Linux OS as Open Source is cheaper than Windows. Linux-based hosting is completely user friendly and supports a wide range of applications. In many cases, this is a good (maybe even better) choice. However, there are applications that are either not supported in Linux at all or are better supported in Windows. If you need to use such software, for example, as ASP or ASP.NET, then your choice is Windows-based VPS. A Windows server is often required for developing on .NET or for deploying Microsoft applications and other applications for this platform.

Factor 3: server configuration
Server configuration plays an important role in site speed and performance. How much processor power, RAM, and disk space you get is all that matters. In addition, it makes sense to ask which physical server will host your VPS. It is better if it is powerful enough equipment of a famous brand. And if the foundation is weak, it is difficult to expect the stability of the whole structure.

Factor 4: Reliability
 Many hosters VPS guarantee the reliability of 99.9%. However, the stated figure may differ from the real one, and it is always useful to get acquainted with reviews on the Internet. For reliable and relatively uninterrupted operation of the site, this indicator should not be below 99.95%.
Many hosters VPS guarantee the reliability of 99.9%. However, the stated figure may differ from the real one, and it is always useful to get acquainted with reviews on the Internet. For reliable and relatively uninterrupted operation of the site, this indicator should not be below 99.95%.Factor 5: Redundancy and Scalability
Redundancy usually involves the reservation of resources, especially in the data center. For example, when the main power fails, UPS and diesel generators begin to work. If the problem is with the Internet provider, then there should be alternative communication channels. If one physical server is overloaded, then a backup should be provided, etc. Scalability, in turn, means the ability to cope with a sharp increase in server load, usually at the expense of reserve resources. All of this means increased uptime and consistently high performance.

Factor 6: Bandwidth Quota
Most VPS providers limit the bandwidth for a virtual server and may charge extra for an additional fee. When choosing a VPS host, you should make sure that you do not have to pay too much for sufficient network bandwidth.
Factor 7: Customer Support
Regardless of the performance of your hosting provider and the proposed functionality, there are always some problems. Convenient and effective support is needed in this case. If the hoster is not able to provide support in 24/7 mode, it is simply not worth your money. When your site will be idle for a long time, it can lead to an outflow of visitors, and maybe to serious financial losses. It is useful to first test the support service of the hosting provider, and then decide whether it makes sense to contact him.
Factor 8: Price
Of course, to select a host, you need to find out the cost of its services. The price depends on the type of service (managed or not) and the resources allocated. Which hosting plan best meets your requirements is up to you.
A very important point, not all hosters have a money back guarantee, if the customer does not like hosting.
Factor 9: VPS Location
The closer the server is to your audience, the more efficient it will be for users to access it and the higher the chances of rising in search engine rankings. Web analytics tools will help you understand where the target audience is concentrated and find the VPS closer. You can also create a copy of the VPS, but you should take into account the distance during data transfer and the responsibility for ensuring communication between remote servers.
Factor 10: Additional IP Addresses
They may be required in several situations:
- installation of an SSL certificate;
- Assigning a dedicated IP to each site on your virtual server (otherwise they will automatically get the IP address of the VPS server);
- different IP for different channels (website, mobile applications, etc.);
- different IP for different services (CMS, database, etc.);
- assigning multiple IPs to a single site, for example, having domains in different languages (mysite.co.uk, mysite.ru, mysite.it, mysite.ca, etc.).
Summary
As your site grows and develops, VPS hosting at some point becomes a necessity, and you should very carefully select a service that meets your preferences. To do this, you need to at least know these requirements, so use a calculator and try to quantify them.

Virtual private servers can be easily scaled: if necessary, you can add memory, disk capacity or computing resources in a few clicks.
However, you need to know the initial requirements, including the necessary network bandwidth, the number of IP addresses, what additional services are needed (for example, protection against DDoS attacks ). An important parameter is the capacity of RAM. A minimum of 512 MB is recommended. This will provide the required speed and groundwork for the development of the site. This option will be a good starting point for those who switch to a VPS from a virtual hosting.

If you need high performance, then your choice is SSD VPS. Due to the high I / O speed of solid-state drives, VPS performance will be an order of magnitude higher than in the case of HDD. Enterprise-class SSDs with eMLC memory type, disks combined into RAID arrays reach data transfer rates of up to 100,000 IOPS, and Windows VPS starts within 7 seconds.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/311608/
All Articles