Why traditional anti-money theft protection in RBS systems is vulnerable
Electronic banking services directly or indirectly operate with money. And where there is money, there will always be those who want to steal it. Of particular interest among cybercriminals are the systems of remote banking services for legal entities, since significant amounts of money are accumulated in the accounts of the latter.
To protect against theft of cash in such systems, it is usually necessary to solve the following main tasks: to verify the authenticity of the user, as well as the authenticity and integrity of the electronic document expressing the user's intention. In practice, such a document is a payment order, among the details of which are given the amount of funds and the account of the recipient.
These tasks are traditionally solved with the use of strong two-factor authentication and electronic signature, made in the form of USB tokens or smart cards (hereinafter referred to as tokens).
Tokens in our market can be divided into 2 types.
- Store the private key in a container, access to which for the application software is provided upon presentation of a PIN code. The signature is formed by the software SKZI in the RAM of the PC. The private key leaves the token when forming the signature, i.e. is recoverable.
- Independently generate a key pair (private / public key). The signature is formed “on board” the token, the document hash is transferred to the token for this. The private key never leaves the token, i.e. is incurable.
When using a token of the first type, a key theft can be implemented in at least two ways.
- Malicious software intercepts the PIN for the token when it is entered on the PC keyboard, then using this PIN code decrypts the contents of the container on the token, thus gaining access to the private key itself.
- Malicious software is embedded in the program code and intercepts the private key in the RAM of the PC during the execution of an operation that requires its use (for example, when generating an ES).
After the key is “in the hands” of a cybercriminal, the latter gets the opportunity to sign any fake documents on this key. Theft of funds in this case can be realized by imposing on the banking service the fake payment orders signed on the key of the legal client of the bank, in which the account of the recipient of funds is indicated to the account of the cybercriminal or persons connected with it. A particular danger when a container is hacked is the possibility of unregulated replication of a private key. Signing transactions with it becomes possible from any computer .
When using a token of the second type, with a non-recoverable electronic signature key, this token reliably protects the key from theft. However, cybercriminals with the help of malware, taking into account the specifics of the attacked system, learned to sign fake documents without stealing keys.
- Attacks with the substitution of the signed document. The user sees one payment order on the PC screen, and at the moment of signing the malware, it invisibly replaces the recipient's details and amount in it. The hash of the replaced document is sent to the token to calculate the EA. As a result, the money from the bank’s client’s account “leaves” to the cybercriminal’s account. Moreover, the malware can then substitute the account balances displayed to the client of the bank. As a result, the user may long be unaware of the theft. Such attacks can be implemented in various ways.
- Interception of traffic via the USB-CCID protocol.
- The introduction of the code in a banking application or browser. The encrypted channel that can be established between the banking application and the token does not help in this case.
- Interception of traffic via the USB-CCID protocol.
- Attacks with the signature of extraneous forged documents. After receiving remote control, or by introducing malware onto the bank’s client’s computer, the cybercriminal can sign any unauthorized (including payment) documents on his keys during the period when the token is connected to the PC. Such attacks can be implemented in the following ways:
- use the “login” state when the token is connected to the PC and the user has entered the PIN code. At this point, the malware sends a hash of a stranger to the token and calculates the EA;
- By intercepting the PIN in advance with the help of malicious software, a cybercriminal can “log in” on the token and sign an extraneous document on it. Virtual keyboards do not guarantee protection against intercepting PIN-code.
Of particular concern is the possibility of using hardware support for virtualization to write malware, which is available in all modern processors. In the limit, this may allow malware to control the entire operating system entirely, randomly changing executable machine instructions on the fly, in particular, commands for working with all I / O devices, including USB, which makes it possible to manipulate sending commands to a connected token.
Read more about hardware virtualization here . - use the “login” state when the token is connected to the PC and the user has entered the PIN code. At this point, the malware sends a hash of a stranger to the token and calculates the EA;
You can reduce the risks of such attacks by strictly following security policies:
- use legal certified software;
- timely install updates;
- install and properly configure the firewall;
- use an antivirus capable of fighting against rootkits with a fresh updated base;
- install and configure the trusted boot and integrity integrity module.
Such an approach could be justified in a closed corporate environment controlled by security administrators. However, in the mass market, users are unlikely to follow all these rules. It is expensive and requires special knowledge and skills. Moreover, even the fulfillment of all these rules still cannot guarantee the protection against cybercrime attacks.
The need for additional protection against fraudsters is known to both banks and the regulator. This problem is quite relevant. In particular, according to Kommersant information dated July 14, 2016 . The Ministry of Finance and the Central Bank have prepared new amendments to protect bank customers from unauthorized operations. The amendments propose to give banks the right to suspend transactions if there is a suspicion that the transaction is performed without the consent of the client, despite the correct PIN-code and the use of a real electronic signature . Those. the scale of the disaster is such that the legislator explicitly permits fraud and prepares recommendations for countering it.
What is actually used today to protect against theft of cash
To protect against theft of cash in the RB systems, banks are introducing additional measures.
- Server anti-fraud systems that allow to detect suspicious transactions on one basis or another.
- Trust Screen devices on the client side, allowing you to confirm key details of payment documents in the trusted environment of such devices.
Server antifraud systems
Server anti-fraud systems that use certain mathematical models, including machine learning technologies, taking into account the accumulation of data, can eventually reduce the likelihood of errors of the first (false alarm) and second (skipping real attack) births, which positively affects their effectiveness . The advantage of such antifraud systems from the point of view of users of Internet banking is that such systems, as a rule, do not change the usual way for the user. The user has worked with the system and continues to work, he is not required to perform additional actions. In the event of the detection of suspicious transactions on his cash account, they contact him and request confirmation. Nevertheless, the risk of missing attacks is preserved, as cybercriminals invent more sophisticated attack methods. Moreover, in a targeted attack, even if the antifraud system detects a suspicious transaction, the cybercriminal can know in advance the client’s phone number to which the bank will call to confirm the transaction, and redirect the call to his phone. The fact that the redirection of calls is quite possible and is not something fantastic, it was written here . If we are talking about large sums of money, then such an attack becomes fully justified in terms of costs.
In fairness, it is worth noting that there are solutions on the market that can further identify people by voice. A more common version of the name of this technology contains the word “identification”, and not “authentication”, which even Google hints at:
Identification is usually used to present its identifier, and authentication is used to prove that the subject is who he claims to be.
Voice identification does not guarantee that the client of the bank is at that end. There are technologies and even ready-made solutions for voice cloning . And it is quite possible that cybercriminals already know how or in the near future they will learn to fake the voice of a “victim” in such a way as to successfully deceive recognition systems. However, voice recognition is another echelon that reduces the risk of theft of funds.
Trust Screen Devices

Trust Screen-device, as a rule, has a small size, equipped with a screen and (optional) buttons. It is used on the client side, its main task is to enable the user to confirm (or reject) the transaction in a trusted environment, different from the computer environment in which the payment documents are created. The classic script for using Trust Screen devices looks like this:
- The user on the computer prepares a payment order indicating the details of the beneficiary and gives the bank application a command to sign the payment document and send it for execution.
- The banking application displays the payment document on the PC screen and additionally asks to confirm its key details on the Trust Screen device.
- The user looks at the screen of the Trust Screen device and confirms the operation with a special button on the keyboard or on the touch screen.
- In case of confirmation, the payment document is signed using the ES tool used, and the signature is sent to the server.
The advantage of using such devices is that if they are correctly implemented and correctly integrated into the application software, the risk of theft of funds is significantly reduced.
The weak link in the correct implementation remains the user. The possibility of theft of funds in this case is determined by how responsibly the user compares the details on the Trust Screen device. If, during intensive work, to force him to confirm hundreds of documents every day, the user can begin to do it automatically, without paying enough attention to what is displayed on the device screen. In this regard, the scenario of integrating such devices into banking systems should pay particular attention to the convenience of their use.
Fortunately, there is a good way to significantly reduce the number of documents that need to be confirmed on a Trust Screen device without compromising security. The solution is to use white lists of trusted counterparties. Such a list includes those contractors with whom the user works regularly and whom they trust. The greater the proportion of such counterparties, the fewer transactions are required to further confirm. If out of 100 transactions about 90 will be sent to the address of the trusted counterparties, then the user will need to confirm only 10 out of 100.
Many banks have been practicing the use of such lists for a long time and without using Trust Screen devices to increase trust in transactions. In some cases, such lists are created by banks for each client on the basis of the history of his interaction with counterparties. In other cases, banks provide users with the opportunity to create such lists themselves.
What is important when working with white lists is how this list is created and changed. If a cybercriminal can unauthorized add himself to the “white list”, the whole idea of such lists becomes void. For example, if a “white list” is prepared by a user in an untrusted environment, then such a list cannot be trusted.
Antifrod-terminal
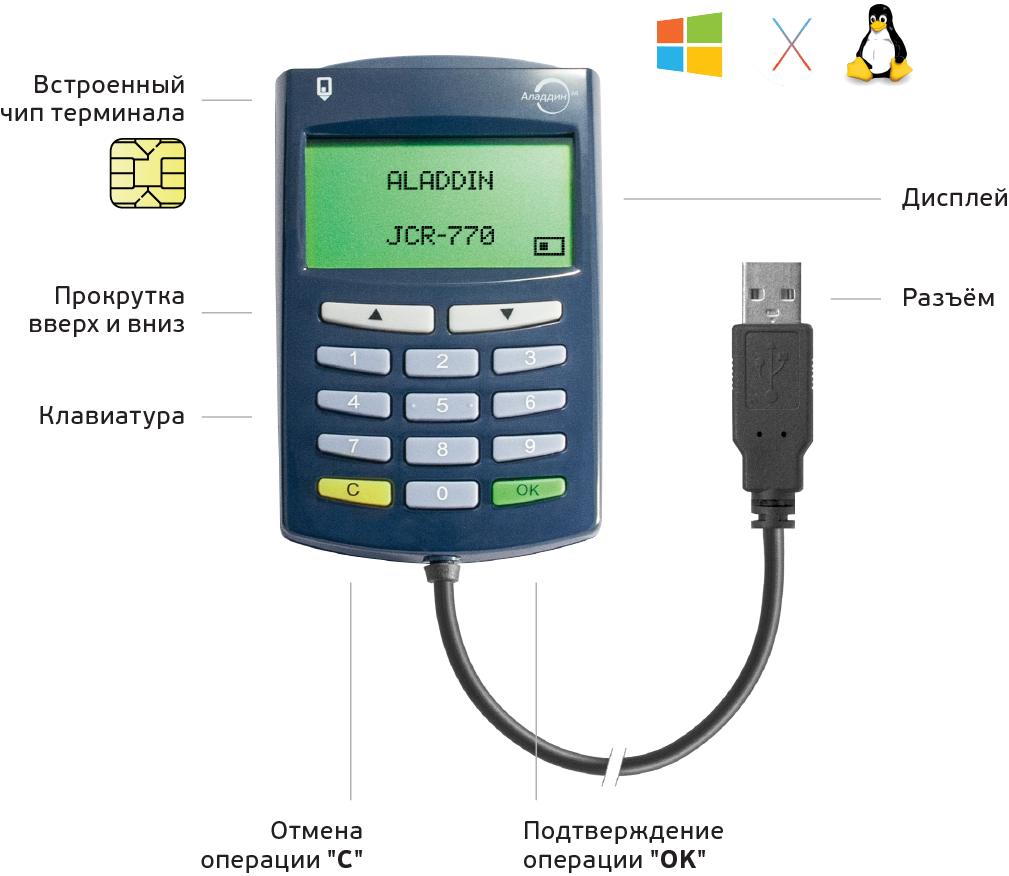
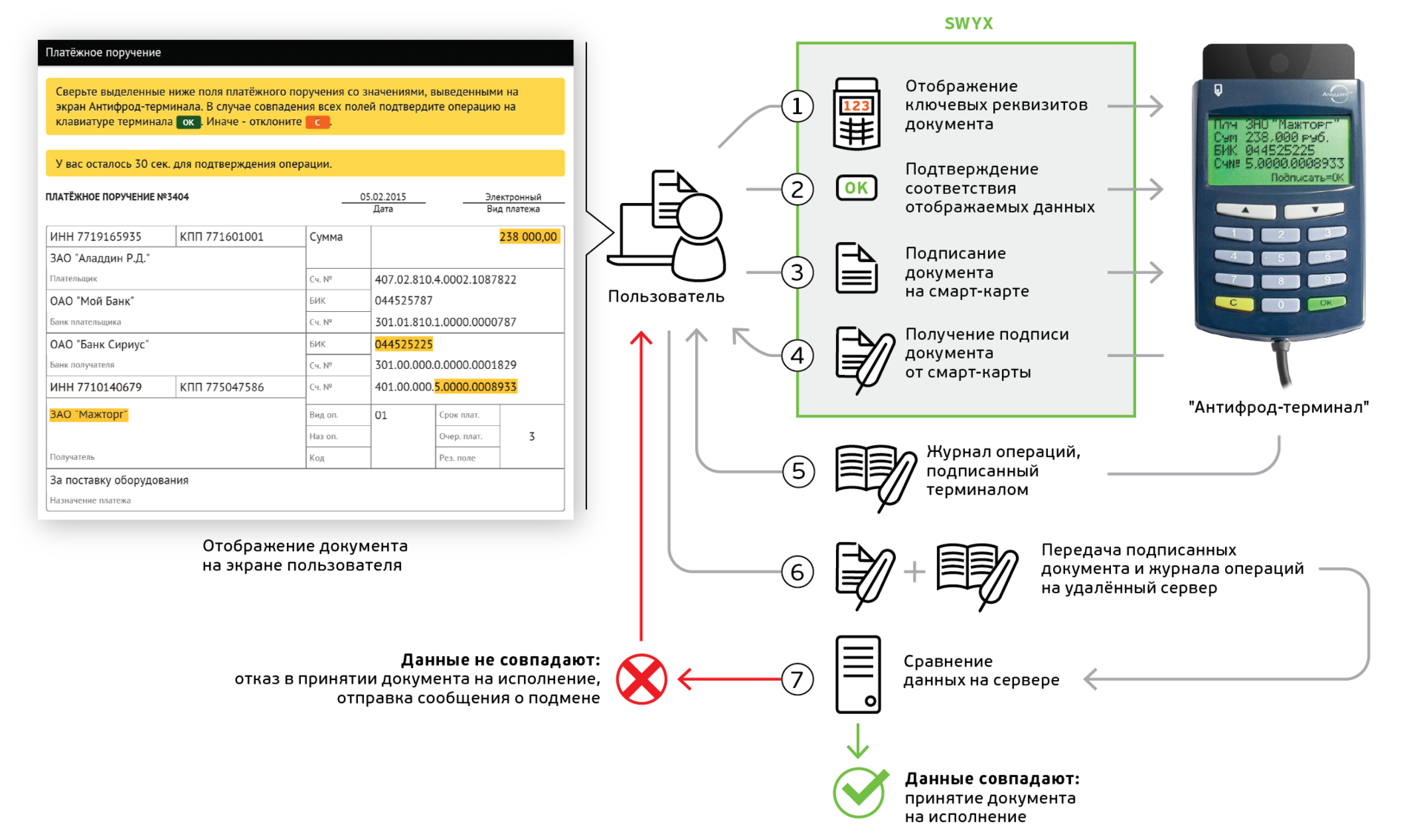
Some time ago we brought to the market the Trust Screen Device Antifraud Terminal . This product was developed by us in conjunction with the company VASCO, was based on the well-proven device DIGIPASS 920 , which was sold worldwide in quantities of more than a million pieces. That is why the Antifrod Terminal looks so much like it.
The peculiarity of Antifrod terminal is that the device:
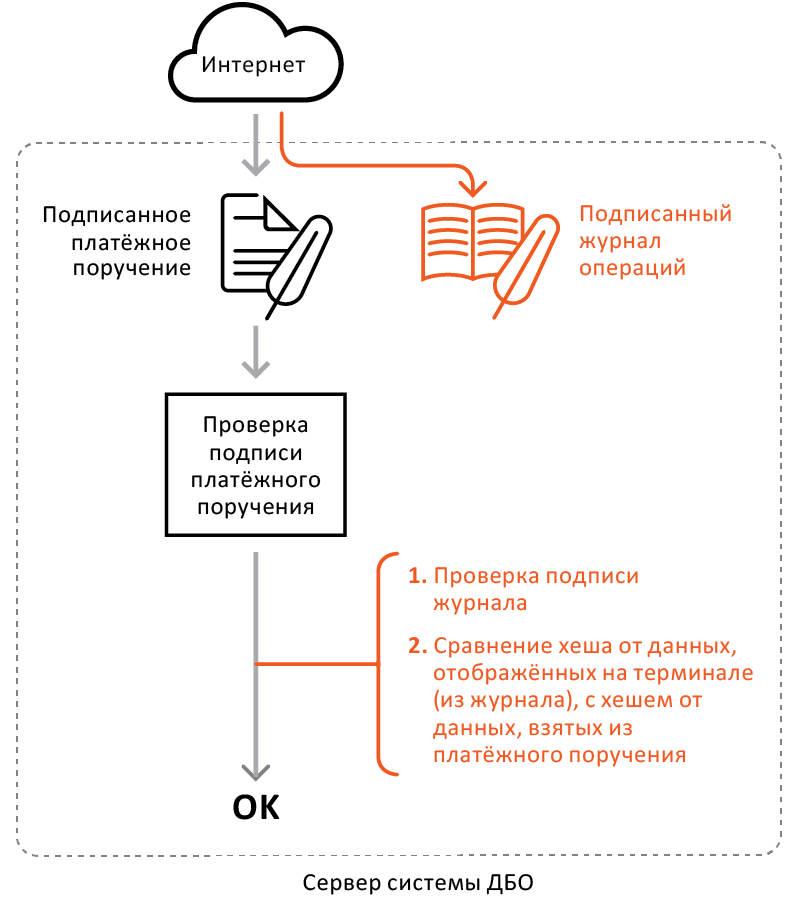
- Keeps an internal transaction log. This log records information that was displayed on the device screen and confirmed by the user by pressing the “OK” button on the device keyboard.
- It contains its own cryptographic chip, which implements Russian cryptography.
- Signs the log of operations of its own ES on this chip.
The transaction log is not permanently stored in the device. The antifraud terminal begins to keep a journal every time when the so-called "start" begins. SWYX-device operation mode. SWYX means Sign What You eXecuted - I sign what is being done. At the end of the SWYX mode, the terminal signs the log of its own ES and returns it along with the signature to the application software. To control the SWYX mode, there are special commands that the application software sends to the terminal.
Before being issued to the client, Antifrod Terminal is registered in the accounting system of the bank with reference to its public key. The corresponding private key of the terminal is non-recoverable and is stored on the cryptographic chip embedded in the terminal.
After signing the document and confirming its key details on the Antifraud terminal, the client application software sends to the server not only the signed document, but also the signed transaction log. The server verifies the document signature and journal signature. Verification of the signature of the journal allows you to make sure that the user is working with a trusted, registered terminal and protects the client from counterfeit devices. After the terminal is authenticated, the server verifies the details from the signed document with the details confirmed by the user on the Antifraud terminal (from the terminal-signed journal), and if they match, it accepts the document for execution.
The transaction log is stored on the bank’s server for the ability to handle conflict situations and investigate incidents.
The presence of such a journal is also an additional motivation for customers to be more attentive to the confirmation procedure, since the journal can later be used by the bank as an evidence base.
To protect against “laziness of customers”, Antifrod Terminal has additional control that the user has read all the data that was displayed on the terminal screen. If the data does not fit on one screen, the terminal will not allow confirming the operation until the user scrolls to the end. This is also important from the point of view of the evidence base, since such an implementation allows, if necessary, to prove that the user personally scrolled all the data to the end, checking all the details, and confirmed the operation, having familiarized himself with all the details.
Protection against re-sending the transaction log to the bank
The transaction log of Antifraud Terminal contains a special Reference field for storing the identifier of a payment document. When you create and save a payment document, the server assigns it an identifier. When confirming the details of this document, on the Antifraud Terminal, the application software on the client side calls the command, which contains this identifier as part of the parameters. The terminal, together with the data that the client has confirmed on the device, records this identifier in the Reference field. When checking the log, the server additionally checks that the identifier of the payment document on the server matches the identifier from the Reference log field.
This implementation allows you to protect yourself from intercepting the journal and attempting to reimpose it, along with copies of documents that have already been approved once. Such an imposition could lead to an empty account. But the identifier reliably binds the journal to a specific copy of the payment document.
The new version of Antifrod Terminal supports any type of ES tool.
The first version of Antifraod Terminal as a means of electronic signature was only able to work with smart cards that were connected directly to the device. However, in the Russian market for many years, a sufficiently large installation base of ES facilities, made in the form of software SKZI and / or USB tokens, has accumulated. And the transition to new types of ES funds takes time and additional costs for both banks and end customers.
In this regard, we have developed a new version of Antifrod-terminal, which does not impose any restrictions on the type of ES used. This may be a software SKZI, storing the key in the registry or on a conventional USB flash drive, software SKZI, storing the key EP on an alienable USB-token, and USB-token with non-recoverable key EP, and an ISO 7816 smart card.
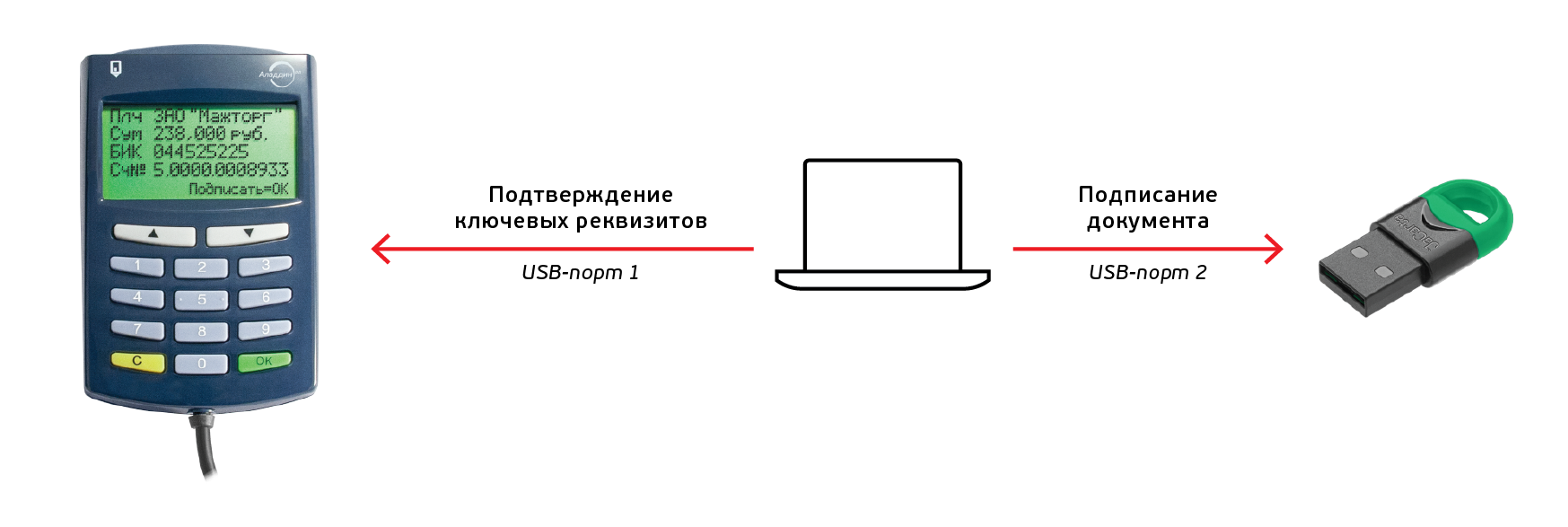
How did we manage to achieve this? The architecture of Antifraud-terminal allowed to completely separate the function of signing a document from the confirmation function at Antifrod-terminal. The work with the ES tool is carried out independently of the Antifraud Terminal. The ES tool does not know anything about the presence of Antifraud terminal, and the Antifrod terminal does not know anything about the type of ES tool used, it does not need it.
If a USB token is used as a means of electronic signature, then it is connected to one USB port of the PC, and Antifrod terminal is connected to another. The application software works with USB-token as with the means of electronic signature, and with Antifrod-terminal - as with the means of trusted confirmation of the key details of the document.
Perform group operations
To shorten the documents that need to be confirmed at the terminal, you should use the “white lists” of trusted counterparties.
It is important that Antifraod terminal allows you to safely create and modify such lists. It is enough to confirm all operations related to the change of the “white list”, including its creation, at the Antifraud Terminal. This protects against unauthorized changes to the “white list” by cybercriminals.
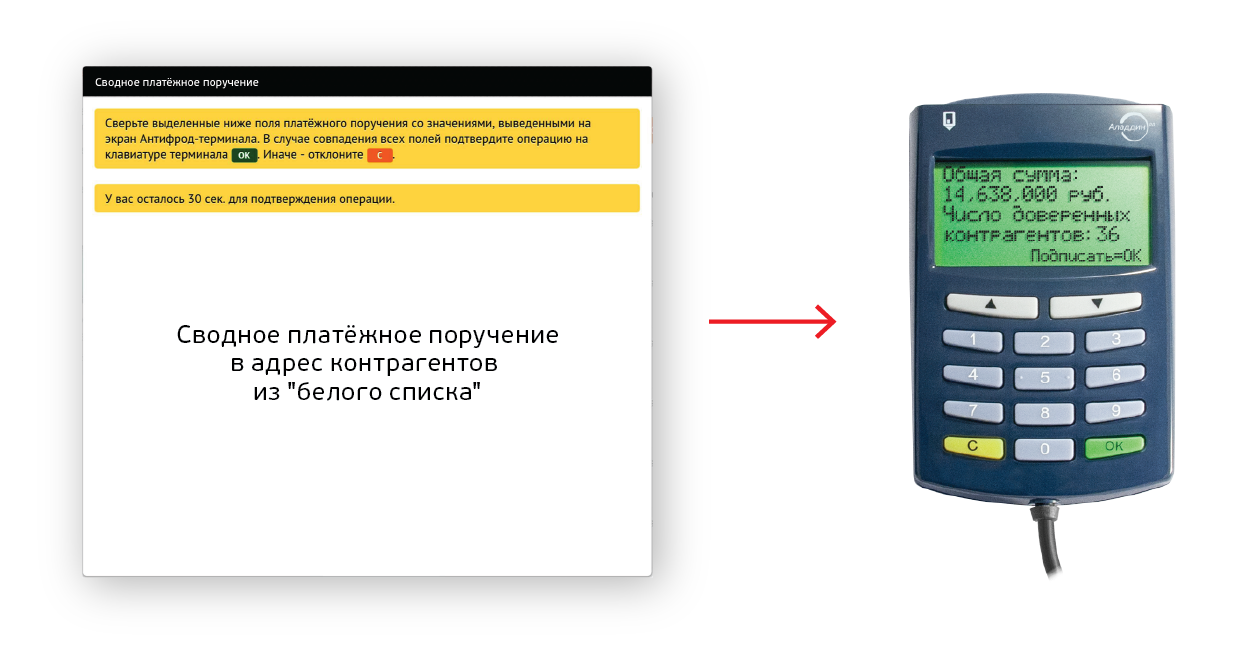
When performing a group operation, it suffices to confirm the consolidated payment order to all counterparties that are on the white list, and each order to counterparties that are not on the white list.
A consolidated payment order may contain:
- the total amount of payment to the recipients of the “white list”;
- The number of such recipients or their list.
Confirmation of such a consolidated payment order allows you to protect against attacks aimed at emptying the company's account in favor of trusted contractors (for example, in tax).
The client signs and confirms at the terminal each of the remaining payment orders.
Signing arbitrary documents
Antifraud terminal allows you to display on your screen any text data up to 400 characters.
This allows you to confirm not only payment documents, but also the signing of arbitrary unstructured documents. For such documents, the key data of such documents should be displayed on the Anti-fraud terminal, which may be, for example, the essential terms of contracts and agreements. For example:
Due to the fact that the signing operation is logically separated from the confirmation operation, it is still possible to sign a real document, and not some kind of structure that includes this document or hash from this document. This allows users, after signing the document in their account, to see the real signed document and a separate signature from this real document.
Benefits of sharing server antifraud systems and Antifrod terminal
When reviewing server antifraud systems, it was noted that in case of detection of suspicious transactions made using, for example, a simple electronic signature, it becomes necessary to contact the client to confirm or reject the operation. As we have already said, calling the client by phone does not guarantee that the client himself will confirm the operation, since the cybercriminal can redirect the call to his phone and even try to tilt the client’s voice.
The described problem of trusted confirmation of suspicious transactions can be successfully solved by Antifrod-terminal. It is enough to notify the client about the need to confirm the operation and request this confirmation via the Antifrod-terminal.
The integration of Antifraud Terminal into application software
When the terminal is integrated into the application software, the modifications are performed on the client and on the server side.
The integration feature is that the modifications do not change the current implementation of the signing of payment documents, but complement it.
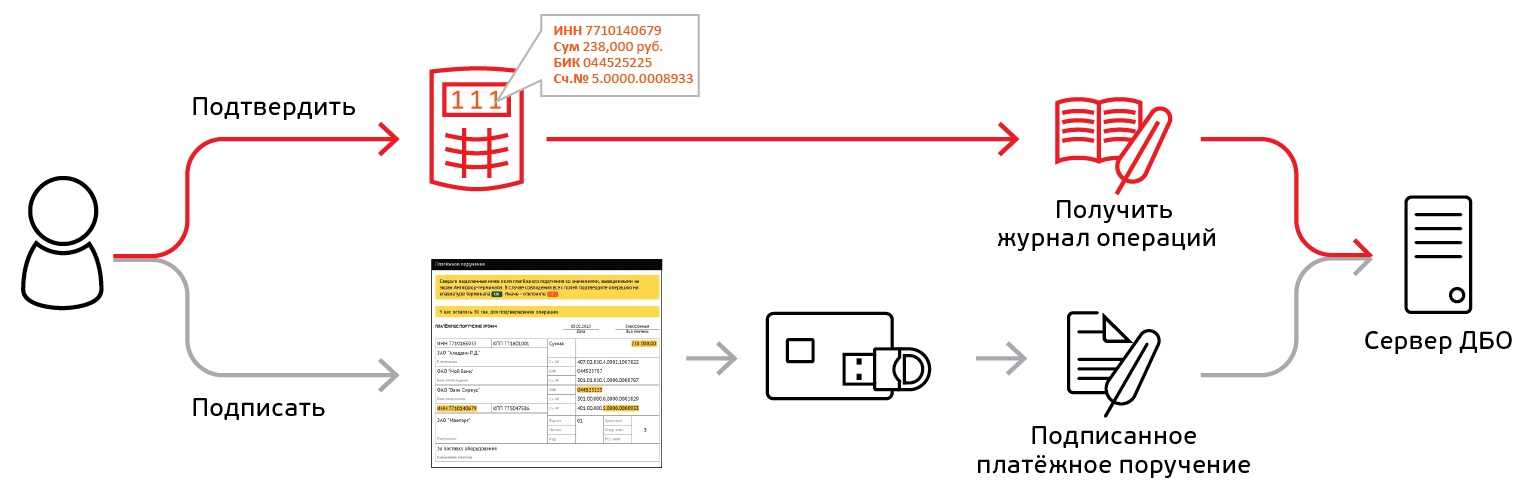
Before the usual signing of the document, the application program additionally:
- forms a text string (up to 400 characters) containing the key details of the document;
- sends this text string to the Anti-fraud terminal and receives confirmation / rejection of the user.
After the usual signing of the document, the application program additionally:
- asks the Antifraud terminal an operation log;
- sends the transaction log along with the signed document to the RBS server.
The server receives from the client not only a payment document, but also a signed transaction log.
After the usual verification of the document signature, the application program additionally:
- verifies the log signature, thereby enforcing strong terminal authentication;
- calculates the hash from the payment document data that the client had to confirm on the terminal screen;
- compares the calculated hash with the hash from the transaction log;
- if there is a mismatch, the processing of the document is blocked.
In the client profile, the transaction log is saved (needed when parsing conflict situations).
Thus, a legally significant evidence base (with a strengthened electronic signature) is additionally formed on the server that the client received this document, saw it and confirmed signing on its (received in the bank in its name) terminal.
To integrate Antifraud Terminal into application software, two types of development kits are prepared:
- JaCarta SDK - for integration into desktop applications (available on request) .
- JC-WebClient SDK - for integration into web applications with support for all popular browsers.
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/311596/
All Articles