Writing an extension using the php-cpp library for php7
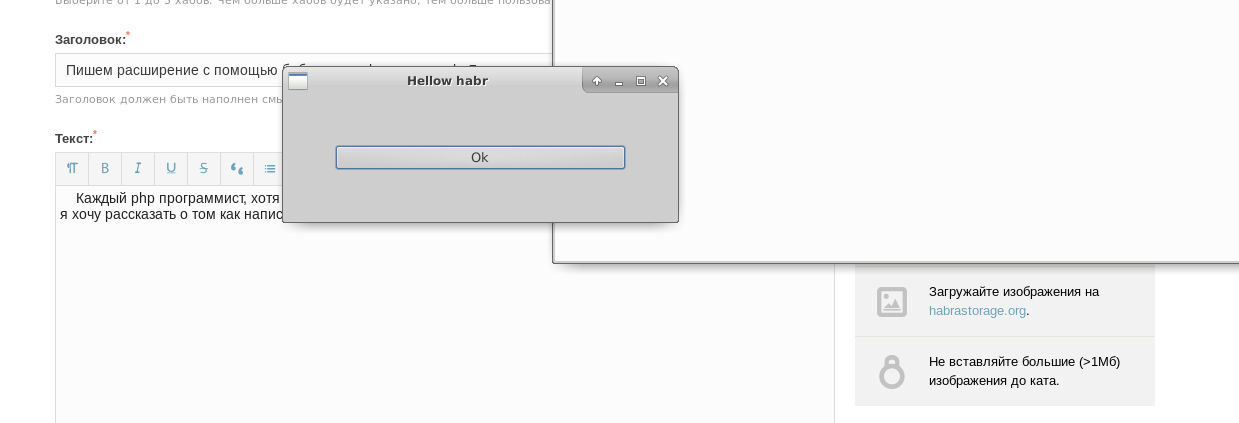
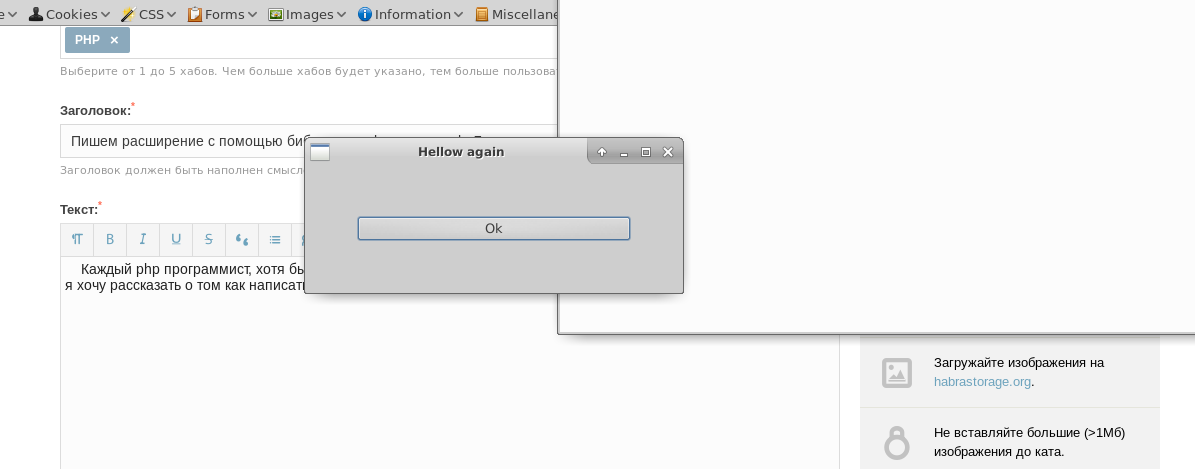
Those who are interested in the process please under the cat.
Dependencies:
1. libgtk2.0-dev
2. php7.0-dev
3. php-cpp - a library that will help us all to develop
')
The first two dependencies are made from the repositories of your linux distribution.
$ apt-get install libgtk2.0-dev php7.0-dev To install php-cpp we clone the repository with github.com php-cpp , I will collect everything in the tmp directories:
$ cd /tmp/ $ git clone https://github.com/CopernicaMarketingSoftware/PHP-CPP.git $ cd PHP-CPP/ # $ make # $ sudo make install # And so everything is ready, now we can proceed to the development, create a directory with the project I have called gtkPHP7. Before we begin, download the skeleton of the future expansion via the link empty-extension.zip , and unpack the archive into the project folder. After that, we will have the following files:
1. extensions.ini
2. Makefile
3. main.cpp
four.
Rename extensions.ini and open it for editing. Replace the line 'extensions = extensions.ini' with 'extensions = gtkphp7.ini'. Next, we need to make changes to the Makefile file by editing the following lines:
NAME = gtkphp7 INI_DIR = /etc/php/7.0/mods-available/ COMPILER_LIBS = `pkg-config --cflags --libs gtk+-2.0` all: ${OBJECTS} ${EXTENSION} ${EXTENSION}: ${OBJECTS} ${LINKER} ${LINKER_FLAGS} -o $@ ${OBJECTS} ${LINKER_DEPENDENCIES} ${COMPILER_LIBS} NAME - the name of our extensions
INI_DIR - directories for php module configurations, I have turned /etc/php/7.0/mods-available/ yours may differ.
COMPILER_LIBS - loads the libraries we need in this case gtk
And the last one I added was COMPILER_LIBS to the all target.
We proceed directly to the development of the extension. For this, I installed a clion from jetbrains and imported the project into ide. We will carry out all other work in the main.cpp file. I decided to develop a class that will be instantiated in php, and with consistent methods create an alert window.
#include <phpcpp.h> #include <iostream> #include <gtk/gtk.h> class Gtk : public Php::Base { private: GtkWidget *_window; char *_titleWindow; char *_buttonTitle; GtkWidget *_button; Php::Value callB; public: Php::Value setTitle(Php::Parameters ¶ms); Php::Value setButtonTitle(Php::Parameters ¶ms); Php::Value createWindow(); Php::Value setButton(); static void callback(GtkButton *button, gpointer data); Php::Value render(); }; This is a prototype extension class:
1. setTitle - sets window title
2. setButtonTitle - button header
3. createWindow - creates a window
4. setButton - creates a button and sets it in a window.
5. callback - the callback function that is called when the button is clicked
6. render - displays a window with a button on the screen.
We omit the first two methods, since they simply set the corresponding variables for use as headings.
/** * create window gtk * @return Gtk */ Php::Value Gtk::createWindow() { int argc = 0; char **argv = NULL; gtk_init(&argc, &argv); _window = gtk_window_new(GTK_WINDOW_TOPLEVEL); gtk_window_set_title(GTK_WINDOW(_window), _titleWindow); gtk_container_set_border_width(GTK_CONTAINER(_window), 50); return this; } In order to initialize gtk, we created the variables argc and argv, respectively, passing them 0 and NULL, as if the application was launched without parameters. We create the window with the 'gtk_window_new' method and assign it to the _window variable - this is a private class parameter.
/** * set button gtk * @return Gtk */ Php::Value Gtk::setButton() { _button = gtk_button_new_with_label(_buttonTitle); gtk_container_add(GTK_CONTAINER(_window), _button); g_signal_connect(G_OBJECT(_button), "clicked", G_CALLBACK(&Gtk::callback), G_OBJECT(_window)); return this; } This method creates a button widget and assigns it to the _window window. The g_signal_connect function tracks button presses; we pass the following parameters to the function:
1. button object
2. type of action
3. callback function (it should not be a member of the class, in other words, it must be either a static or a separate function)
4. here we pass the window object for use in the callback function.
Let's sort callback-function:
/** * callback click * @param button * @param window */ void Gtk::callback(GtkButton *button, gpointer window) { gtk_widget_destroy(GTK_WIDGET(window)); gtk_main_quit(); } The second parameter is as races, what was passed to the 4 parameter in the function above, the first is actually our button. The function is simple; it just comes out of gtk. Well and the last we will consider the render function:
/** * render alert * @return */ Php::Value Gtk::render() { gtk_widget_show_all(_window); gtk_main(); return true; } In general, the method shows all window widgets, and runs gtk. After stopping, via the callback function, it returns true.
As a final step, we need to register our class and its methods:
/** * tell the compiler that the get_module is a pure C function */ extern "C" { /** * Function that is called by PHP right after the PHP process * has started, and that returns an address of an internal PHP * strucure with all the details and features of your extension * * @return void* a pointer to an address that is understood by PHP */ PHPCPP_EXPORT void *get_module() { static Php::Extension extension("gtkphp7", "1.0"); Php::Class<Gtk> gtk("Gtk"); // gtk.method<&Gtk::setTitle>("setTitle"); // gtk.method<&Gtk::setButtonTitle>("setButtonTittle"); gtk.method<&Gtk::setButton>("setButton"); gtk.method<&Gtk::createWindow>("createWindow"); gtk.method<&Gtk::render>("render"); extension.add(std::move(gtk)); // // return the extension return extension; } } The full main.cpp code under the spoiler:
#include <phpcpp.h> #include <iostream> #include <gtk/gtk.h> class Gtk : public Php::Base { private: GtkWidget *_window; char *_titleWindow; char *_buttonTitle; GtkWidget *_button; Php::Value callB; public: Php::Value setTitle(Php::Parameters ¶ms); Php::Value setButtonTitle(Php::Parameters ¶ms); Php::Value createWindow(); Php::Value setButton(); static void callback(GtkButton *button, gpointer data); Php::Value render(); }; /** * set title to window * @param params * @return Gtk */ Php::Value Gtk::setTitle(Php::Parameters ¶ms) { std::string title = params[0]; _titleWindow = new char[title.size() + 1]; std::copy(title.begin(), title.end(), _titleWindow); _titleWindow[title.size()] = '\0'; return this; } /** * set button title * @param params * @return Gtk */ Php::Value Gtk::setButtonTitle(Php::Parameters ¶ms) { std::string title = params[0]; _buttonTitle = new char[title.size() + 1]; std::copy(title.begin(), title.end(), _buttonTitle); _buttonTitle[title.size()] = '\0'; return this; } /** * create window gtk * @return Gtk */ Php::Value Gtk::createWindow() { int argc = 0; char **argv = NULL; gtk_init(&argc, &argv); _window = gtk_window_new(GTK_WINDOW_TOPLEVEL); gtk_window_set_title(GTK_WINDOW(_window), _titleWindow); gtk_container_set_border_width(GTK_CONTAINER(_window), 50); return this; } /** * set button gtk * @return Gtk */ Php::Value Gtk::setButton() { _button = gtk_button_new_with_label(_buttonTitle); gtk_container_add(GTK_CONTAINER(_window), _button); std::cout << callB << std::endl; g_signal_connect(G_OBJECT(_button), "clicked", G_CALLBACK(&Gtk::callback), G_OBJECT(_window)); return this; } /** * callback click * @param button * @param window */ void Gtk::callback(GtkButton *button, gpointer window) { gtk_widget_destroy(GTK_WIDGET(window)); gtk_main_quit(); } /** * render alert * @return */ Php::Value Gtk::render() { gtk_widget_show_all(_window); gtk_main(); return true; } /** * tell the compiler that the get_module is a pure C function */ extern "C" { /** * Function that is called by PHP right after the PHP process * has started, and that returns an address of an internal PHP * strucure with all the details and features of your extension * * @return void* a pointer to an address that is understood by PHP */ PHPCPP_EXPORT void *get_module() { static Php::Extension extension("gtkphp7", "1.0"); Php::Class<Gtk> gtk("Gtk"); gtk.method<&Gtk::setTitle>("setTitle"); gtk.method<&Gtk::setButtonTitle>("setButtonTittle"); gtk.method<&Gtk::setButton>("setButton"); gtk.method<&Gtk::createWindow>("createWindow"); gtk.method<&Gtk::render>("render"); extension.add(std::move(gtk)); // return the extension return extension; } } Moving on to the next step, compiling and installing the extension:
$ make $ sudo make install After installation we make symlinks for connection or phpenmod:
$ sudo ln -s /etc/php/7.0/mods-available/gtkphp7.ini /etc/php/7.0/cli/conf.d/20-gtkphp7.ini $ sudo service php7.0-fpm restart # php $ php -m | grep gtkphp7 # To rebuild and reinstall the extension, just run:
$ make clean $ make $ sudo make install For the test, a simple php script was written:
<?php function alert($title) { $gtk = new Gtk; return $gtk ->setTitle($title) ->setButtonTittle("Ok") ->createWindow() ->setButton() ->render(); } if(alert("Hellow habr")) { alert("Hellow again"); } The result of the script, the screenshots in the title of the article ... For the convenience of working on the extension function was written:
void dump(Php::Value dumping) { Php::call("var_dump",dumping); } It calls the var_dump php function, it is quite convenient to make dumps of php variable arrays, etc.
As conclusions, here are some links:
1. php-cpp documentation
2. Repository with an example from the article
ps On c ++ it is one of the first experiences, on this, if something is wrong with the code, write in the comments, and have a good weekend.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/311506/
All Articles