Bypassing the detection of virtual machine programs in VMWare
Virus software developers and developers who simply do not want to reverse their program, during the launch or installation phase, carry out checks on the virtual machine, and in case of its detection they refuse to work, or even self-destruct. Under the cat described a way to try to solve this problem.
I used VMWare Fusion for Mac, but it works just as well in Workstation for Win.
1) To work, you need a newly installed system, how to make changes to an existing one - did not find it.
Prepare a virtual disk, specify the system, as you usually do, and in the settings for the installed machine, I have this item called Isolation, turn off any data exchange with the host OS.
')
2) Next, you need to find the VMX configuration file created during the creation of the machine in VMWare, and add lines to the end:
These options prevent programs from detecting the virtual environment through such complex checks as tracking the address space of the memory counters.
Important! If during installation setup there is an option like “Express install”, “Quick install” - turn them off. Also, do not install VMWare Tools in the installed system, because Some software also includes the presence of this package.
3) Save the file, specify the ISO for the boot with the installer of the system, install the OS as usual.
4) Despite the fact that the overwhelming majority of programs that do not like the virtual environment, do not go beyond the checks that we cut off in step 2, some particularly persistent ones go further and try to look for, for example, everything that looks like the name of virtual controllers drives.
To defeat them in Windows, go to the registry editor in the branch HKLM \ SYSTEM \ CurrentControlSet \ Services \ Disk \ Enum. As you can see, there is a very obvious reference to the fact that the disk is virtual.

We need to change it by removing VMware, Virtual, Ven, etc. from the parameter, and save it.
It also makes sense to replace the search in the registry for VMware / Virtual on any Intel or IBM all that changes, not just disk variables.
Then try to run your stubborn experiment object - in 70 percent of cases, the described steps will help pass the tests for a virtual environment.
Important! The value in HKLM \ SYSTEM \ CurrentControlSet \ Services \ Disk \ Enum is overwritten after each reboot, so it needs to be changed after each new system startup.
You can check how much you have protected yourself against detection, as well as familiarize yourself with other means of sandboxing and virtual women detection that are popular with developers, using the Pafish tool.
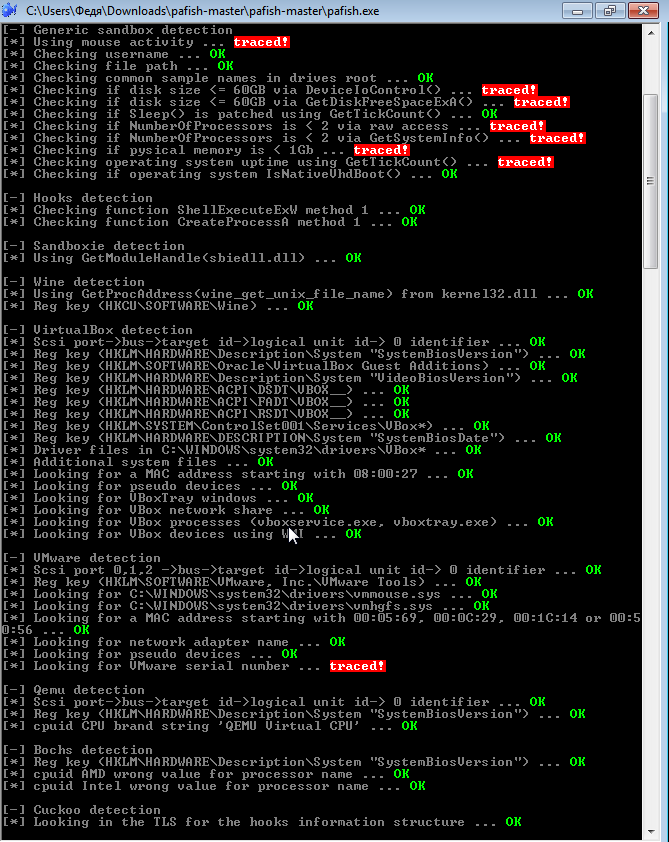
Despite the fact that there are places where you can betray yourself, the proposed method leads to outwit most software that does not want to work in a virtual environment, in this case, in VMWare.
As you can see, stealth can also be improved by allocating more system resources to the virtual machine. As for the memory, choose values that are multiples of 1024.
Thanks to everyone who mastered the article and helped in complementing it with sensible comments!
I used VMWare Fusion for Mac, but it works just as well in Workstation for Win.
1) To work, you need a newly installed system, how to make changes to an existing one - did not find it.
Prepare a virtual disk, specify the system, as you usually do, and in the settings for the installed machine, I have this item called Isolation, turn off any data exchange with the host OS.
')
2) Next, you need to find the VMX configuration file created during the creation of the machine in VMWare, and add lines to the end:
isolation.tools.getPtrLocation.disable = "TRUE"
isolation.tools.setPtrLocation.disable = "TRUE"
isolation.tools.setVersion.disable = "TRUE"
isolation.tools.getVersion.disable = "TRUE"
monitor_control.disable_directexec = "TRUE"
monitor_control.disable_chksimd = "TRUE"
monitor_control.disable_ntreloc = "TRUE"
monitor_control.disable_selfmod = "TRUE"
monitor_control.disable_reloc = "TRUE"
monitor_control.disable_btinout = "TRUE"
monitor_control.disable_btmemspace = "TRUE"
monitor_control.disable_btpriv = "TRUE"
monitor_control.disable_btseg = "TRUE"
These options prevent programs from detecting the virtual environment through such complex checks as tracking the address space of the memory counters.
Important! If during installation setup there is an option like “Express install”, “Quick install” - turn them off. Also, do not install VMWare Tools in the installed system, because Some software also includes the presence of this package.
3) Save the file, specify the ISO for the boot with the installer of the system, install the OS as usual.
4) Despite the fact that the overwhelming majority of programs that do not like the virtual environment, do not go beyond the checks that we cut off in step 2, some particularly persistent ones go further and try to look for, for example, everything that looks like the name of virtual controllers drives.
To defeat them in Windows, go to the registry editor in the branch HKLM \ SYSTEM \ CurrentControlSet \ Services \ Disk \ Enum. As you can see, there is a very obvious reference to the fact that the disk is virtual.

We need to change it by removing VMware, Virtual, Ven, etc. from the parameter, and save it.
It also makes sense to replace the search in the registry for VMware / Virtual on any Intel or IBM all that changes, not just disk variables.
Then try to run your stubborn experiment object - in 70 percent of cases, the described steps will help pass the tests for a virtual environment.
Important! The value in HKLM \ SYSTEM \ CurrentControlSet \ Services \ Disk \ Enum is overwritten after each reboot, so it needs to be changed after each new system startup.
UPD from @Denisoid :
Naturally, this is not an exhaustive guide; some software may also attempt to determine the virtual system by the following methods:
1) Check the range of MAC addresses (just replaced in the settings of the virtual network adapter before starting the virtual machine)
2) Via WinAPI by polling the OS configuration and other system information (FirmwareTable)
3) Low-level tricks.
You can check how much you have protected yourself against detection, as well as familiarize yourself with other means of sandboxing and virtual women detection that are popular with developers, using the Pafish tool.

Despite the fact that there are places where you can betray yourself, the proposed method leads to outwit most software that does not want to work in a virtual environment, in this case, in VMWare.
As you can see, stealth can also be improved by allocating more system resources to the virtual machine. As for the memory, choose values that are multiples of 1024.
Thanks to everyone who mastered the article and helped in complementing it with sensible comments!
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/311492/
All Articles