Virtual supercomputer on demand
A virtual supercomputer (vSC) is a modern alternative to using our own supercomputer facilities for knowledge-intensive business and research groups in solving resource-intensive tasks. In the process of rapid development of cloud technologies, claudization began to penetrate into the most complex IT spheres - supercomputing and distributed computing. One of the possible approaches to the HPC claudization problem is implemented by HPC HUB.

High-performance computing clusters (IHC) are used both in pure science and in high-tech business in various fields:
IHC began to develop intensively in the late 90s as a commodity alternative to large supercomputers (mainframes) supplied by leading IT market firms such as IBM, SGI, DEC, Sun, HP, Cray, NEC, Hitachi, Siemens, Bull, etc. The most striking difference between IHC and traditional supercomputers in the late 90s is the lack of a single OS and, as a result, another structure of the organization of the computing system.
')

Despite the relative cheapness of IHC (on average ten times, all other things being equal) compared with traditional supercomputers, these systems are very expensive to use:
Thus, even relatively small IHCs with a dozen or so nodes, a low latency network and a data storage system are extremely expensive tools and are available to companies with solid IT budgets (for example, a typical cluster of 1000 cores can cost about US $ 500 thousand with annual maintenance in US $ 100-150 thousand). But even in the case of large IT budgets, buying and launching a cluster takes months, and on the public IHC there are problems in setting up software and organizing access to it.
Modern cloud providers are focused, as a rule, on the sale of single virtual servers, or on their small groups, but not on leasing time on IHC or similar systems. As a result of the current trends, dynamic small and medium-sized companies are practically deprived of the possibility of short-term rent of IHC for their needs (for example, approbation and pilot introduction of computing technologies, modeling systems in their business, peak loads in the case of small own capacities, etc.) .

At HPC HUB, we decided to focus our efforts on solving the problems of a niche consumer who needs a small IHC for 10–20 nodes with a low latency network and a terabyte class data storage system in a short-term lease (day, week, month) in monopoly mode. The main service of the company is the lease of a virtual IHC (the second name: a virtual supercomputer - vSC). From the user's point of view, a vSC is a regular cluster consisting of a head control node, several compute nodes equipped with a low latency network and storage from 50GB to 10TB implemented on GFS2. Nodes have access to the Internet through NAT, access to the control node from the outside is open on port 22, which is redirected to the port of the tunnel virtual machine.
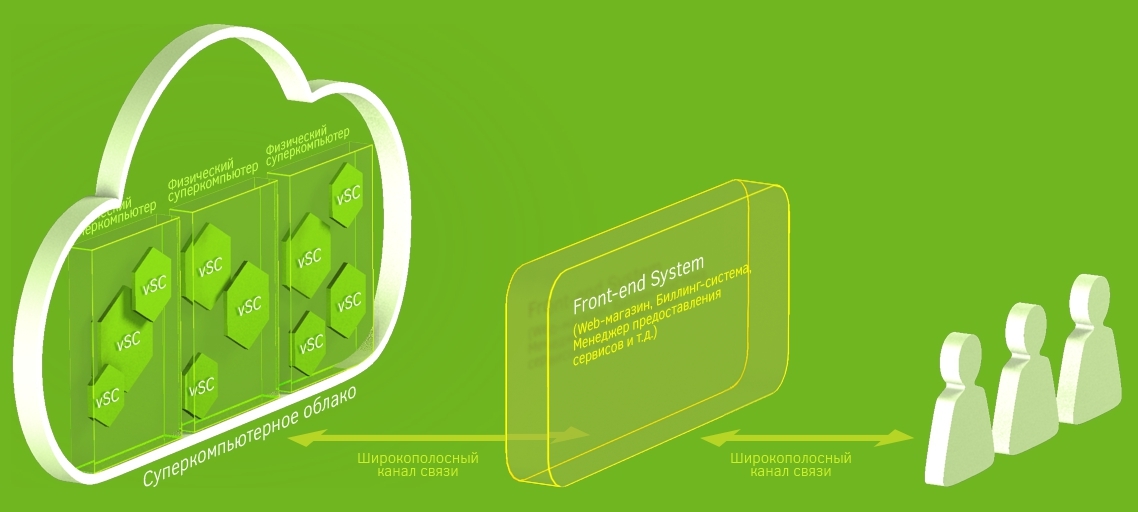
Different vSCs are isolated from each other, so the user has full control over the installed software in the vSC, i.e. can customize and modify it as you see fit. The basic vSC images are built on CentOS 7.1, using the IB OFED 3.3 drivers and the SGE 8.1.3 job management system. At the end of the work, the user can snapshot the state of the control node and one of the compute nodes. This snapshot can be used to launch the next vSC instance of a user. At the same time, vSC snapshot can scale to any number of compute nodes.
The vSC implementation is based on OpenStack cloud software and Ceph data storage. User node virtual machines are managed by the KVM hypervisor. SR-IOV technology is used for low latency network virtualization. One of the virtual functions of the Infiniband adapter is imported into counting node virtual machines.

This approach allows to achieve a minimum increase in the latency of virtualized Infiniband - 1.09 μs IB VF latency versus 0.85 μs from Infiniband without virtualization. The topology and characteristics of the processors of the virtual counting nodes are made as similar as possible to the physical nodes; NUMA extensions are supported. Typical aggregated for all nodes of a vSC instance, the exchange speeds with GFS2 are 1.5-2 Gb / s for reading, 350-450 Mb / s for writing, 10,000-12,000 IOPS.
Renting and deploying vSCs can be done in minutes from hpchub.net . The minimum rental time is now one day, but we plan to make the transition to smaller billing periods in the near future as our cloud grows. This removes the unpleasant restriction associated with the long organization of access to supercomputer capacities.
The HPC HUB Virtual Computing Cluster provides users with the ability to access the IHC teraflop class without significant time costs and the need for initial investment. At the same time, the user can customize the software of this IHC exclusively for his tasks, which is much simpler than similar procedures on public systems. In addition to its direct purpose - performing calculations, our virtualized IHC opens up a number of significant, previously absent in the market opportunities:
 A virtual supercomputer will be especially useful for distributing and selling cluster software by its manufacturers in a previously inaccessible segment of small and medium enterprises. Features like:
A virtual supercomputer will be especially useful for distributing and selling cluster software by its manufacturers in a previously inaccessible segment of small and medium enterprises. Features like:
It will help to reach cluster software producers not only users with large IT budgets at peak loads, but also various users with one-off projects, including start-ups, venture enterprises, and even users from the academic environment and government institutions.

Introduction
High-performance computing clusters (IHC) are used both in pure science and in high-tech business in various fields:
- bioinformatics (decoding and analysis of genomes, system biology, the development of new drugs, including individual ones);
- reservoir modeling and seismic data processing in Oil & Gas and mining;
- resource-intensive analytics and BigData;
- in industry for solving problems of hydro and aerodynamics, chemical industry, development of new composite materials, etc.
IHC began to develop intensively in the late 90s as a commodity alternative to large supercomputers (mainframes) supplied by leading IT market firms such as IBM, SGI, DEC, Sun, HP, Cray, NEC, Hitachi, Siemens, Bull, etc. The most striking difference between IHC and traditional supercomputers in the late 90s is the lack of a single OS and, as a result, another structure of the organization of the computing system.
')

Despite the relative cheapness of IHC (on average ten times, all other things being equal) compared with traditional supercomputers, these systems are very expensive to use:
- They require service by a team of highly qualified specialists, a special site with cooling, uninterrupted power, high-speed network connection.
- Integration of counting software and installation of accompanying software (environment switching, compilers, libraries, scheduler, etc.) for each specific IHC is a separate and not simple task, which often turns out to be much more complicated than it seemed at the beginning (which is typical for integration).
- The cost of licenses of commercial cluster software can be many times higher than the cost of the clusters themselves (for example, in geophysics the cost of a license for commercial software may start from US $ 40 thousand for 1 computing node per year).
Thus, even relatively small IHCs with a dozen or so nodes, a low latency network and a data storage system are extremely expensive tools and are available to companies with solid IT budgets (for example, a typical cluster of 1000 cores can cost about US $ 500 thousand with annual maintenance in US $ 100-150 thousand). But even in the case of large IT budgets, buying and launching a cluster takes months, and on the public IHC there are problems in setting up software and organizing access to it.
Modern cloud providers are focused, as a rule, on the sale of single virtual servers, or on their small groups, but not on leasing time on IHC or similar systems. As a result of the current trends, dynamic small and medium-sized companies are practically deprived of the possibility of short-term rent of IHC for their needs (for example, approbation and pilot introduction of computing technologies, modeling systems in their business, peak loads in the case of small own capacities, etc.) .

Virtual IHC from HPC HUB
At HPC HUB, we decided to focus our efforts on solving the problems of a niche consumer who needs a small IHC for 10–20 nodes with a low latency network and a terabyte class data storage system in a short-term lease (day, week, month) in monopoly mode. The main service of the company is the lease of a virtual IHC (the second name: a virtual supercomputer - vSC). From the user's point of view, a vSC is a regular cluster consisting of a head control node, several compute nodes equipped with a low latency network and storage from 50GB to 10TB implemented on GFS2. Nodes have access to the Internet through NAT, access to the control node from the outside is open on port 22, which is redirected to the port of the tunnel virtual machine.

Different vSCs are isolated from each other, so the user has full control over the installed software in the vSC, i.e. can customize and modify it as you see fit. The basic vSC images are built on CentOS 7.1, using the IB OFED 3.3 drivers and the SGE 8.1.3 job management system. At the end of the work, the user can snapshot the state of the control node and one of the compute nodes. This snapshot can be used to launch the next vSC instance of a user. At the same time, vSC snapshot can scale to any number of compute nodes.
The vSC implementation is based on OpenStack cloud software and Ceph data storage. User node virtual machines are managed by the KVM hypervisor. SR-IOV technology is used for low latency network virtualization. One of the virtual functions of the Infiniband adapter is imported into counting node virtual machines.

This approach allows to achieve a minimum increase in the latency of virtualized Infiniband - 1.09 μs IB VF latency versus 0.85 μs from Infiniband without virtualization. The topology and characteristics of the processors of the virtual counting nodes are made as similar as possible to the physical nodes; NUMA extensions are supported. Typical aggregated for all nodes of a vSC instance, the exchange speeds with GFS2 are 1.5-2 Gb / s for reading, 350-450 Mb / s for writing, 10,000-12,000 IOPS.
Renting and deploying vSCs can be done in minutes from hpchub.net . The minimum rental time is now one day, but we plan to make the transition to smaller billing periods in the near future as our cloud grows. This removes the unpleasant restriction associated with the long organization of access to supercomputer capacities.
findings
The HPC HUB Virtual Computing Cluster provides users with the ability to access the IHC teraflop class without significant time costs and the need for initial investment. At the same time, the user can customize the software of this IHC exclusively for his tasks, which is much simpler than similar procedures on public systems. In addition to its direct purpose - performing calculations, our virtualized IHC opens up a number of significant, previously absent in the market opportunities:
- use of virtualized IHC for developing and testing applications;
- use of IHC as a fast and easily scalable demo site;
- use of IHC for the sale of cluster software "at retail" (short-term rental software).
 A virtual supercomputer will be especially useful for distributing and selling cluster software by its manufacturers in a previously inaccessible segment of small and medium enterprises. Features like:
A virtual supercomputer will be especially useful for distributing and selling cluster software by its manufacturers in a previously inaccessible segment of small and medium enterprises. Features like:- flexibility,
- easy scaling
- pre-installed complex cluster software with the possibility of renting licenses for this software with a small time slice
It will help to reach cluster software producers not only users with large IT budgets at peak loads, but also various users with one-off projects, including start-ups, venture enterprises, and even users from the academic environment and government institutions.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/311394/
All Articles