How the server works with a screwdriver in the power supply

PSU firmware is outdated .
When I first saw this inscription when polling versions of HP DL380 firmware, I was somewhat discouraged. Um, okay, if you really need to - download and install. But what kind of software can be in the banal power supply? It turned out that to diagnose the local life-support system and the treatment of power failures. There is a natural cluster of power supplies, with its own arbiter and logic. Under the cut a story about the device of such a "cluster" and why 2 x 1400 = 2300W.
Two power supplies - twice as reliable? Not always, because it depends on the power supply system settings. Here's more about it and talk. As a subject of the story, I chose a medium server class equipment, like this:
That is, not blades and mainframes - everything is different for them. Please note that the server form factor does not matter for the presence or absence of additional power supplies.
Reliability or Convenience
Let's start with the answer to the question "why how many BPs, if you can just store a small spare parts stock." Systems with redundancy in the server are always useful, even if you do not consider fault tolerance. For example, they increase the convenience of service and allow us not to sleep in the server room when replacing disks or the same power supplies.
For example, a second power supply will help if:
The UPS will fail;
Road workers will find a mine of electricity;
It will be necessary to transfer the server to another rack;
- The gland needs more power than the most efficient power supply available in the catalog provides.
Two power supplies offer more flexibility when designing a server room. For example, a working connection scheme for one client: in the server two phases, connected to different power supply units of the servers. One phase is connected to the UPS, and the second works only through stabilizers. But this line comes from the generator with auto start. When a power outage occurs, the diesel engine starts and the servers continue to operate, even if the UPSs are low. This is just one of the options, tailored to the wishes of the client and the possibilities of the budget.
In total, several power supplies are needed for administrator convenience , improving system reliability and providing more power .
Theory "on the knee"
The simplest version of a system with two power supplies looks like the powering of individual computer components from different units, with one of them controlling and powering the motherboard. Such solutions are practiced by gamers and miners , because there will not be enough power to install three or more video cards of one power source. To connect using these adapters:

When you click on Power, the green signal wire with the ground is closed, giving the command to start both power supplies.
I remember once I had a Pentium III-level PC with a set of SCSI disks. The standard power supply was no longer sufficient, and I connected the old AT-unit separately for hard drives. The launch of the miracle machine was like this: we press the button for additional power and wait for the buzzing of the disks, then we turn on the main power supply and the download begins.
Even in the era of the all-pervading China, there are many ways to connect two power supplies with your own hands for DIY, to get a similar configuration:

But back to the industrial server solutions.
The power supply device is quite simple in its logic. The units are connected to the special Power Distribution Backplane , where the Power Distribution Unit microcontroller is also present (not to be confused with the power distributor for the server rack ). The controller is responsible for the scheme of use of available power supplies: simultaneously or in the primary-backup mode.
Setup and Logic
Such an advanced power subsystem can be customized for specific needs. When using a server with two power supplies, several modes of operation are available:
Redundancy in which one power supply is constantly loaded, and the second is ready to pick up the load in case of failure;
- The load distribution in which the server uses both power supplies at the same time.
Very similar to RAID - its fault tolerant level 1 and productive 0.
Most manufacturers allow the administrator to select the desired mode. For example, in this HP server, setting via BIOS is as follows:

The image is a bit outdated, as in new systems, setting via iLO is used, but to understand the essence of it is enough.
Let's look at the output power of a pair of HP DL360 power supplies with different configuration modes and light load. For this we use the console utility hpasmcli .
- Balanced mode
hpasmcli> SHOW POWERSUPPLY
| Power supply # 1 | Power supply # 2 | |
| Present: | Yes | Yes |
| Redundant: | Yes | Yes |
| Condition: | Ok | Ok |
| Hotplug: | Supported | Supported |
| Power: | 110 watts | 95 watts |
Not deceived by the manufacturer, power supplies give about the same power.
- High Efficiency Mode
hpasmcli> SHOW POWERSUPPLY
| Power supply # 1 | Power supply # 2 | |
| Present: | Yes | Yes |
| Redundant: | Yes | Yes |
| Condition: | Ok | Ok |
| Hotplug: | Supported | Supported |
| Power: | 90 watts | 20 watts |
Indeed, when using the load sharing mode, the blocks are loaded approximately equally. But when you turn on fault tolerance, only one power supply is used, and the second is transferred to Standby and consumes a minimum of energy.
A kind of "sleep mode" is needed in order to avoid a cold start when connecting a backup power supply unit, save time and minimize the risks of power supply failure during the process of its activation. As in the case of household light bulbs, during any cold start-up, peak loads are formed on the element base of the electrical circuit, which can lead to its damage.
Setup of operating modes for each manufacturer is performed in its own way. For example, in Lenovo (IBM) in systems with two power supply units, the setting via the GUI is as follows:

A choice of three modes of operation are offered:
Fault tolerance without reducing energy consumption - back to it later;
Fault tolerance with decreasing power;
- Without fault tolerance, but with maximum power.
Generic servers, like Intel and Supermicro, are not always well documented and there was no open information about the settings of the BP operating modes. I had to contact our engineers and forums . It turned out that such systems usually work in load balancing mode.
If you have worked closely with similar platforms and have other information - please share in the comments.
More interesting is the situation with systems of three or more BP.
Three, four - who is more?
As in the analogy with RAID, a greater number of nodes opens up more sophisticated usage patterns. For example, the Supermicro server with three blocks uses the 2 + 1 mode of operation, that is, two are working at the same time and the third in reserve.
In the case of four power supplies in Lenovo, you can customize the use of power supplies more flexibly . The interface even counts the power indicators independently:

In terms of the balance of performance and reliability, such configurations of 4 PSU are justified only when using "voracious" components. In other cases, the power reserve will be redundant, and convenience and safety margin provide 2 power supply units with different supply of electricity.
In my opinion, in such platforms it is more interesting to put backup batteries instead of the third and fourth PSU (examples for Supermicro and HP ). They insure against problems with UPS and 5 minutes will increase the time without electricity in the network. In addition, with similar modules it is more convenient to handle iron: I pulled out the cable - and quietly moved the server to another cabinet. Server running time from the built-in battery is about five minutes.
One for 800 or two 400 each
Experience Engineers Server Mall shows that power supplies in second place after failure, after hard drives. At least during the restoration of servers, these components often change due to the use of electrolytic capacitors in their design.
If we are accustomed to failures of the disk subsystem and keep a spare disk at the ready, then the replacement for the power supply system is found on the shelves of spare parts. The situation is to some extent saved by the guarantee and the opportunity to get a replacement of the failed BP in a couple of days with a courier, but you should not discard Murphy's Law. In my practice there was a case when, while waiting for the replacement of the failed BP, the remaining one failed. It's good that nothing vital was on the server.
If we leave aside reliability, then the question remains with power. As a rule, it is better to take two power supplies at once, each with an adequate margin of output power. But if the budget of such liberties does not allow, then we will have to weigh the needs in more detail and take into account the power sinking of power sources. Referring to the manual from HP , which presents a graph of the efficiency of the power system in different configurations:
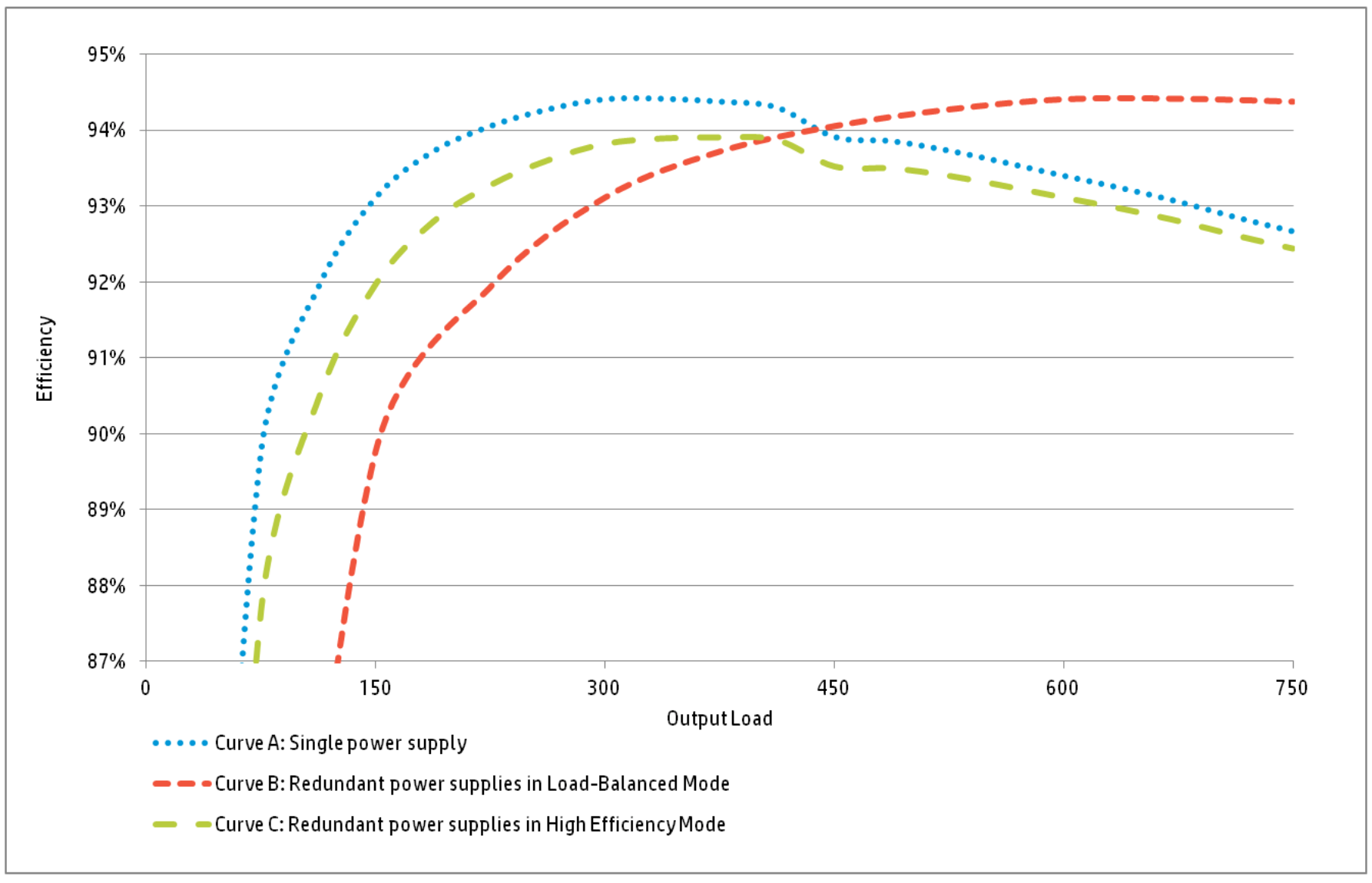
In case of low load of the machine, the efficiency of one power supply unit is higher, but the picture changes if we have a high-loaded server.
What will happen if one of the power supply fails, and the remaining power is not enough?
Many vendors have a power reduction mechanism in case of a failure - Fujitsu's PowerSafe G uard , Lenovo's Throttling . The use of such mechanisms does not always save the situation, and a significant drop in performance is sometimes worse than idle time.
There is another nuance: the load on the second power supply increases, which increases the likelihood of its failure. It is better to assume that a single power supply from a pair must provide the server as a whole, at least at regular loads. The difference in the cost of power supplies of different power is not so great, so you should choose a more productive model. For example, here are the prices for options from Supermicro:
The 400-watt PWS-406P-1R power supply costs an average of $ 12,000;
- The 700-watt PWS-706P-1R power supply unit costs an average of $ 14,000.
Prices are taken from Yandex Market, so in reality they may even be lower. Saving $ 4,000 to the detriment of fault tolerance looks so-so even for a small server.
So what's up with the firmware
A modern power supply contains a set of diagnostic mechanisms for monitoring the internal cooling system, voltage, current strength and the mass of internal states.
In addition to the automatic shutdown in case of overheating, it is useful to be able to connect the power subsystem performance indicators to the centralized monitoring. For example, they can be used to predict the failure of a particular power supply or to identify an unstable supply of electricity. All this is provided by microcontrollers, the internal logic of which the manufacturer periodically improves in new updates.
And now about the minuses
With all the advantages described, solutions with several power supplies have negative sides:
The need to buy more expensive proprietary power supplies . As a rule, they should be the same, which can cause replacement problems for very old servers;
The power supply controller and the board to which they are connected (Power Distribution Backplane) becomes a bottleneck;
At low load, greater power consumption , as a result of a specific algorithm of use;
- The probability of failure of a single power supply from a group is still higher than the failure of the only one - the banal theory of probability. Therefore, you should pay attention to the choice of energy-intensive solutions that fully use both power supplies.
If you have your own negative experience with configurations from several power units - it would be interesting to read in the comments.
In conclusion, I will provide several useful links to the power calculators of popular vendors:
If you are too lazy to estimate the power when choosing the next new server, then these tools will help in calculating both the power of the power supply units and the power consumption of the entire data center.
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/310698/
All Articles