Why does the network of mobile operators sometimes “fall”?
Good day to all lovers of telecom. We continue to tell you about the most interesting moments of the MTS network operation together with Andrey Seregin, Director of the Department of Operation of Convergent Networks and Services of MTS.
Recall that in our first post, Andrey Vyacheslavovich told how our Center for the operational management of a mobile network in Krasnodar works. In the second post I answered your questions about the work of the center. Today, Andrei Vyacheslavovich will answer the question of concern to everyone, why the network of mobile operators sometimes falls.
Each subscriber, sooner or later, may encounter a situation when, with a good network signal level, it is impossible to make a call or download / send information. I propose to talk about the causes of this phenomenon in cellular networks and the ability of operators to minimize inconvenience for subscribers.
')
In the language of technical experts, this situation is called “local overload”. In our life, we also often encounter “local overloads” - whether on the road in the Friday traffic jam on the outskirts of the city or even in a shopping center in the queue for a new iPhone on the night of the start of sales. Bottlenecks may also appear on the network at some time or in some place.
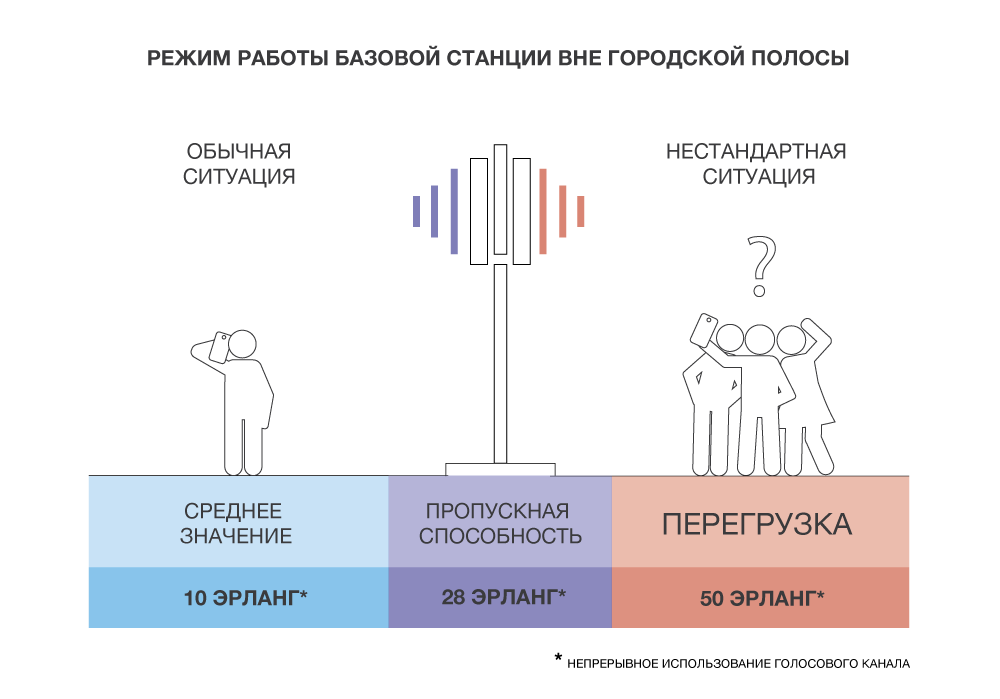
Our network never falls at the level of switching or “on transport”, because there is always high bandwidth supported there. Problems arise, as a rule, on the radio subsystem. Here, for example, there is a tower with a base station far beyond the city, in an open field. Under normal circumstances, she has a load of 10 erlang (continuous use of the voice channel) - that is, 10 people always speak at the same time. This may be, for example, grandmothers from a neighboring village, summer residents, vacationers from a nearby boarding house, drivers of cars passing nearby, etc. In general, the base station can be designed for 28 calls simultaneously. And suddenly 50 people come to corporate events in this field or pension. And everyone starts to call at the same time. Naturally, they "overwhelm" this station. This will be comparable to the way in the subway 50 people at the same time try to squeeze through one door of the car.
By the way, since we are talking about the subway. Communication in the metro has an interesting feature. If you are traveling in a tunnel, and there is no network signal between the stations, then upon the arrival of the train at the station, your telephone, as well as the phones of hundreds more subscribers, will simultaneously begin to establish a connection with the appeared network. At this moment service signaling channels become a bottleneck. Due to the sudden overload, this does not allow for a short time to transmit / receive data or make calls.
After a while, the alarm avalanche subsides, and the Internet pages will start loading again, and the calls will reach subscribers. But as soon as the train leaves the station, the connection can be interrupted again.
What can an operator who cares about subscribers do in such situations?
In the subway, of course, it’s best to lay the radiating cable in the tunnel so that the radio coverage is continuous. This will eliminate the root cause of the problem. You can also deal with the consequences of the problem by increasing the number of signaling channels or selecting special parameters for base stations in the metro that reduce the signal load. All this is done depending on the technical capabilities and engineering difficulties.
But back to our topic. Naturally, in order to solve the problem of network overload, with the mass accumulation of subscribers, additional base stations are installed: directly in boarding houses, business and shopping centers, at sports stadiums, in entertainment complexes. These are the so-called indore base stations.
It is important to follow the development of the city or region proactively and to build all channels of communication and establish indor base stations even at the stage of building new facilities. It is also necessary to follow the planned major events: concerts, sports games, forums, congresses, etc., in order to assess in advance the possibilities of the network and have time to pull them up to the necessary level.
In general, this is already the usual, one might say, everyday work of each operator. Interestingly, in recent times, operators have begun to join forces to jointly build a high-capacity network in local areas. This is most clearly manifested in the provision of communications for new stadiums being built for the 2018 World Cup.
A rather new and interesting technology implemented here in Moscow is SON (self-organizing network - self-organizing networks). Among the many useful functions of SON, there are functions that help to avoid the network “falling”. How it works? Suppose some base station has failed - what will the SON system do? She looks at the statistics - if the traffic is distributed between stations and the quality of coverage has suffered slightly, then, of course, she does nothing. If SON sees that the traffic has "sank" and a "hole" appeared in the coverage and that the subscribers from the station that turned off have not redistributed anywhere, then it increases the power, changes the antenna tilt angles of the neighboring stations to cover this area with a signal. "Wound" on the network is delayed. So SON can be called a “doctor” for the network.
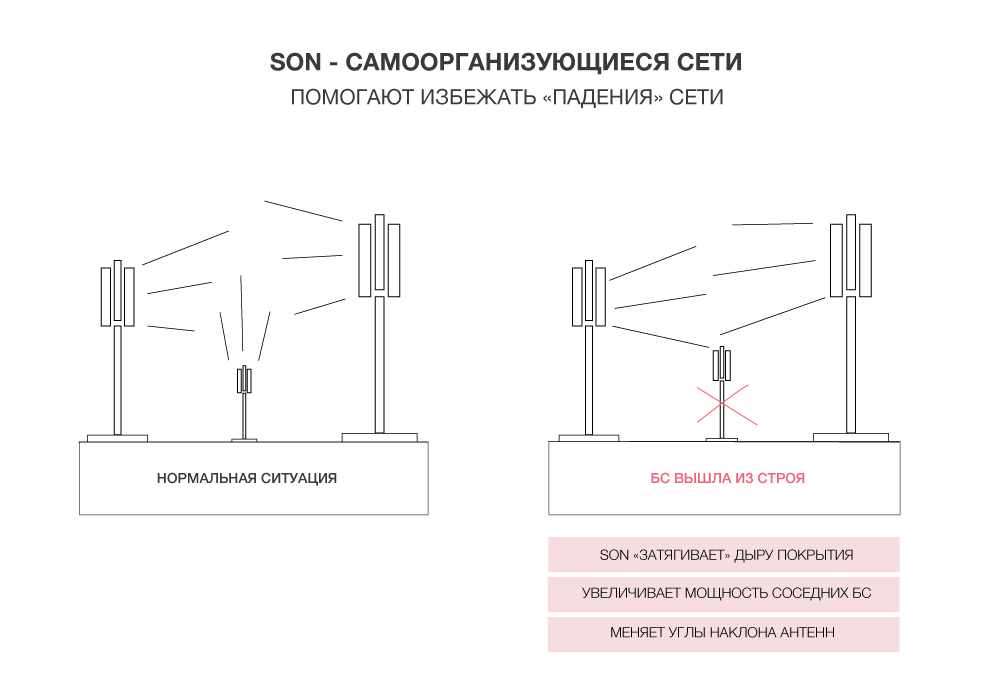
Similarly, the function of the "doctor" SON can almost instantly change the parameters of base stations in order to reduce the load on one base station due to the resource of neighboring ones. The algorithm is similar to that described above, only it is used not when the BS fails, but when it is under excessive load.
New Year's Eve is a special example of network overload, which is hardly local. In the first hours of the New Year, the load on the network increases wherever there are subscribers meeting the New Year. It is worth noting that no one in the world expands base stations under such a surge of load.
At the same time on the New Year we introduce special network parameters that allow you to pass the increased load to the detriment of some minor functions. For example, we disable re-paging. What does it mean. If someone tries to reach you, the first thing the network does is search for you by sending paging messages. Whether you are in network coverage or not. If your phone does not respond to a network request, then it sends messages again and again. When the network is overloaded in the New Year, many requests or responses are “lost”, and it turns out that we “flood” ourselves with repeated paging. Therefore, it is better to make a paging once. If you did not answer, then the person will simply reassign. But others will get through.
In recent years, on New Year's Eve, we observe the following trend: bursts of voice traffic and SMS are decreasing. People rarely call or send SMS immediately after the chiming clock. Now basically data transfer is growing. People congratulate each other in social networks and through messengers.
Although on the Red Square there are still overloads on New Year's Eve. But on the whole in Moscow there is no such work around as it was 10 years ago. So the New Year is passing pretty “boring” now.
Recall that in our first post, Andrey Vyacheslavovich told how our Center for the operational management of a mobile network in Krasnodar works. In the second post I answered your questions about the work of the center. Today, Andrei Vyacheslavovich will answer the question of concern to everyone, why the network of mobile operators sometimes falls.
Each subscriber, sooner or later, may encounter a situation when, with a good network signal level, it is impossible to make a call or download / send information. I propose to talk about the causes of this phenomenon in cellular networks and the ability of operators to minimize inconvenience for subscribers.
')
In the language of technical experts, this situation is called “local overload”. In our life, we also often encounter “local overloads” - whether on the road in the Friday traffic jam on the outskirts of the city or even in a shopping center in the queue for a new iPhone on the night of the start of sales. Bottlenecks may also appear on the network at some time or in some place.

Our network never falls at the level of switching or “on transport”, because there is always high bandwidth supported there. Problems arise, as a rule, on the radio subsystem. Here, for example, there is a tower with a base station far beyond the city, in an open field. Under normal circumstances, she has a load of 10 erlang (continuous use of the voice channel) - that is, 10 people always speak at the same time. This may be, for example, grandmothers from a neighboring village, summer residents, vacationers from a nearby boarding house, drivers of cars passing nearby, etc. In general, the base station can be designed for 28 calls simultaneously. And suddenly 50 people come to corporate events in this field or pension. And everyone starts to call at the same time. Naturally, they "overwhelm" this station. This will be comparable to the way in the subway 50 people at the same time try to squeeze through one door of the car.
By the way, since we are talking about the subway. Communication in the metro has an interesting feature. If you are traveling in a tunnel, and there is no network signal between the stations, then upon the arrival of the train at the station, your telephone, as well as the phones of hundreds more subscribers, will simultaneously begin to establish a connection with the appeared network. At this moment service signaling channels become a bottleneck. Due to the sudden overload, this does not allow for a short time to transmit / receive data or make calls.
After a while, the alarm avalanche subsides, and the Internet pages will start loading again, and the calls will reach subscribers. But as soon as the train leaves the station, the connection can be interrupted again.
What can an operator who cares about subscribers do in such situations?
In the subway, of course, it’s best to lay the radiating cable in the tunnel so that the radio coverage is continuous. This will eliminate the root cause of the problem. You can also deal with the consequences of the problem by increasing the number of signaling channels or selecting special parameters for base stations in the metro that reduce the signal load. All this is done depending on the technical capabilities and engineering difficulties.
But back to our topic. Naturally, in order to solve the problem of network overload, with the mass accumulation of subscribers, additional base stations are installed: directly in boarding houses, business and shopping centers, at sports stadiums, in entertainment complexes. These are the so-called indore base stations.
It is important to follow the development of the city or region proactively and to build all channels of communication and establish indor base stations even at the stage of building new facilities. It is also necessary to follow the planned major events: concerts, sports games, forums, congresses, etc., in order to assess in advance the possibilities of the network and have time to pull them up to the necessary level.
In general, this is already the usual, one might say, everyday work of each operator. Interestingly, in recent times, operators have begun to join forces to jointly build a high-capacity network in local areas. This is most clearly manifested in the provision of communications for new stadiums being built for the 2018 World Cup.
Son
A rather new and interesting technology implemented here in Moscow is SON (self-organizing network - self-organizing networks). Among the many useful functions of SON, there are functions that help to avoid the network “falling”. How it works? Suppose some base station has failed - what will the SON system do? She looks at the statistics - if the traffic is distributed between stations and the quality of coverage has suffered slightly, then, of course, she does nothing. If SON sees that the traffic has "sank" and a "hole" appeared in the coverage and that the subscribers from the station that turned off have not redistributed anywhere, then it increases the power, changes the antenna tilt angles of the neighboring stations to cover this area with a signal. "Wound" on the network is delayed. So SON can be called a “doctor” for the network.

Similarly, the function of the "doctor" SON can almost instantly change the parameters of base stations in order to reduce the load on one base station due to the resource of neighboring ones. The algorithm is similar to that described above, only it is used not when the BS fails, but when it is under excessive load.
New Year
New Year's Eve is a special example of network overload, which is hardly local. In the first hours of the New Year, the load on the network increases wherever there are subscribers meeting the New Year. It is worth noting that no one in the world expands base stations under such a surge of load.
At the same time on the New Year we introduce special network parameters that allow you to pass the increased load to the detriment of some minor functions. For example, we disable re-paging. What does it mean. If someone tries to reach you, the first thing the network does is search for you by sending paging messages. Whether you are in network coverage or not. If your phone does not respond to a network request, then it sends messages again and again. When the network is overloaded in the New Year, many requests or responses are “lost”, and it turns out that we “flood” ourselves with repeated paging. Therefore, it is better to make a paging once. If you did not answer, then the person will simply reassign. But others will get through.
In recent years, on New Year's Eve, we observe the following trend: bursts of voice traffic and SMS are decreasing. People rarely call or send SMS immediately after the chiming clock. Now basically data transfer is growing. People congratulate each other in social networks and through messengers.
Although on the Red Square there are still overloads on New Year's Eve. But on the whole in Moscow there is no such work around as it was 10 years ago. So the New Year is passing pretty “boring” now.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/310480/
All Articles