Getting Started with Intel Active Management (AMT)
This document provides information on how to get started with Intel Active Management Technology (Intel AMT). It contains an overview of the capabilities of this technology, information about system requirements, Intel AMT client configurations, and development tools available for building applications that support Intel AMT.

Intel AMT supports remote applications running under Microsoft Windows * or Linux *. Intel AMT 2.0 or later supports only local Windows applications. For a complete listing of system requirements , see the Implementation Guide and the Intel AMT Reference Guide .
To remotely manage an Intel AMT client or run examples from the SDK, use a separate system to remotely manage an Intel AMT device. For more information, see the Implementation Guide and the Intel AMT Reference Manual , located in the Docs folder in the Intel AMT SDK.
')
Intel AMT is part of the Intel vPro solution package. If the platform supports Intel AMT, then such platforms can be remotely controlled regardless of the state of the power supply and the presence or absence of the operating system.
The Intel AMT system is based on the core of the Converged Security and Manageability Engine (CSME). Intel AMT is a component of Intel vPro and uses a number of elements of the Intel vPro platform architecture. In fig. 1 shows the relationship between these elements.

Figure 1. Intel Active Management Technology Architecture 11
Note the network connection associated with the Intel Management Engine (Intel ME). The adapter used varies depending on the version of Intel AMT used.
Intel AMT stores the following information in flash memory (Intel ME data).
In fig. Figure 2 shows the steps to configure an Intel AMT device before using it.
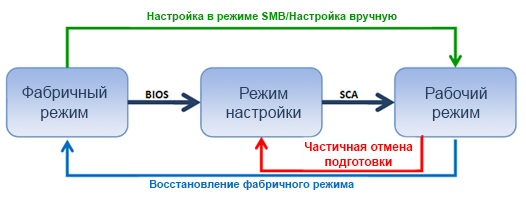
Figure 2. Setting progress
Before you configure an Intel AMT device in the Setup and Configuration Application (SCA), you must prepare it, having received the initial information, and put it into installation mode. The initial information will vary depending on the available components of the Intel AMT release and the platform settings applied by the OEM manufacturer. Table 1 lists installation and configuration procedures for different versions of Intel AMT.
Table 1. Installation methods depending on the version of Intel AMT
Intel Setup and Configuration Software (Intel SCS) 11 can be used to prepare systems for earlier versions up to Intel AMT 2.x. For more information about Intel SCS and training levels available for different versions of Intel AMT, see the website Download the latest Intel Setup and Configuration Service (Intel SCS) .
When setting up the platform manually, starting from version 6.0, there are no restrictions on the components, but certain features of the system behavior should be taken into account.
Starting with Intel AMT 10, some devices are shipped without a physical network adapter. These devices cannot be configured using existing USB solutions included with Intel SCS 11.
When enabled, the Intel AMT platform displays the BIOS startup screen, then processes the MEBx. During this process, you can access Intel MEBX, but this approach depends on the manufacturer of the BIOS. Some possible methods are:
After installing a device with Intel AMT 7.0 or later, it switches to one of two control modes.
There is also a configuration method that includes the procedure for changing the mode: from client mode to administrator mode. This procedure assumes that the Intel AMT device is in client control mode, and switches the device to administrator control mode.
In the administrator control mode, the Intel AMT functionality is not limited. This is due to a higher level of trust with this installation method.
Upon completion of the simple host-based configuration, the platform enters the client control mode, in which the following restrictions apply.
When you turn on the Intel AMT platform, the BIOS initial screen is displayed, then the BIOS extensions are processed. Logging into the Intel AMT extension in BIOS depends on the BIOS manufacturer.
When using the Intel AMT reference platform (SDS or SDP), you are prompted to press the <Ctrl + P> keys. After that, control passes to the main menu of the CSME.
In OEM systems, a one-time boot menu can be used, and logging into CSME is usually one of the boot options in this menu. The specific key combinations may vary depending on the OEM manufacturer, type of BIOS and model.
Many systems no longer have a physical connector for connecting to a wired LAN. You can configure and activate Intel ME, then use the web interface or some other method to configure your wireless settings.
Enter the default CSME password (admin).
Change the default password (required to continue). The new value must be a strong password. It must contain at least one uppercase letter, one lowercase letter, one digit and one special character, and its length must be at least eight characters. Using the management console, you can change the Intel AMT password without changing the CSME password.
An administrator with user rights can establish a remote connection to an Intel AMT device through a web interface. To do this, enter the URL of the device. The URL will vary depending on whether TLS is enabled.
To connect without TLS, you can also use a local connection and a host browser. You can specify localhost or 127.0.0.1 as the IP address. Example: 127.0.0.1 : 16992.
In addition to properly configuring the BIOS and CSME, an Intel AMT-compatible wireless network adapter is required. To manage a host's OS using Intel AMT, certain drivers and services are required.
To ensure that the drivers and Intel AMT services are loaded correctly, locate them in the device manager and in the "Services" section of the host OS. Regularly visit the OEM site for updated BIOS, firmware and driver versions.
Here are the drivers and services that should be displayed in the host OS.
* Versions of the network controller and wireless interface will vary depending on the generation of the Intel vPro platform.
** As part of the complete driver package for Intel MEI (chipset).
*** HID device drivers are required when connecting via Intel AMT KVM. There are usually no problems with the default drivers, but we encountered difficulties when using non-standard OS installations. If a connection is established to a device without HID drivers, the OS attempts to automatically install these drivers. After installation, re-establish the KVM connection.
Note. The driver version level must match the firmware and BIOS version level. If incompatible versions are installed, Intel AMT will not work with components that require these interfaces.
By default, all wireless vPro wireless platforms will have an Intel AMT-enabled wireless network card, such as the Intel AC 8260 dual-band adapter. Other wireless adapters other than Intel adapters will not support Intel AMT wireless connectivity. When using a wireless network adapter other than Intel AC 8260, you can use ark.intel.com to verify that this adapter is compatible with Intel AMT.
For remote control, device drivers are not required, but they are necessary for local data exchange with the firmware. OS discovery and configuration features require the Intel MEI driver, the SOL driver, the LMS service, and the Intel MSS application.
An Intel MEI is required to connect to the firmware. By default, the Intel MEI driver is automatically installed from Windows Update. The version level of the Intel MEI driver should be the same as that of the Intel MEBX.
The Intel MEI driver is displayed in the device manager in the "System devices" section called the Intel Management Engine Interface.
The SOL driver is used in the IDE redirection operation when connecting a remote CD-ROM drive.
The SOL driver is displayed in the device manager in the "Ports" section titled "Intel Active Management Technology - SOL (COM3)".
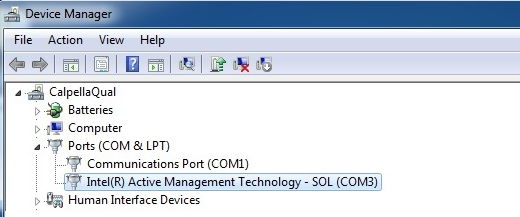
Figure 3. Serial LAN driver
The Local Manageability Service (LMS) runs locally on an Intel AMT device and enables local management applications to send requests and receive responses. The LMS responds to requests sent to the local Intel AMT host and sends them to Intel ME using the Intel MEI driver. The service installer is in the same package as the Intel MEI drivers on the OEM websites.
Please note that when installing Windows, Windows Update only installs the Intel MEI driver. IMSS and LMS are not installed. The LMS service communicates from an OS application with the Intel MEI driver. If the LMS service is not installed, go to the OEM website and download the Intel MEI driver, which is usually in the chipset driver category.
Figure 4. Intel Management Engine Interface Driver
LMS is a Windows service installed on Intel AMT 9.0 or later. Previously, in versions of AMT AMT from 2.5 to 8.1, the LMS service was called User Notification Service (UNS).
The LMS receives a set of alerts from an Intel AMT device. The LMS writes an alert to the Windows application event log. To view alerts, right-click Computer and select Computer Management> System Software> Event Viewer> Application .
You can open the Intel MSS application using the blue key icon in the Windows notification area.

Figure 5. Intel Management and Security Status icon in the notification area
The General tab in Intel MSS displays the status of the Intel vPro components available on this platform and the event log. Each tab provides additional information.

Figure 6. General tab in Intel Management and Security Status
Here, a local user can perform KVM and media redirection operations, use the help request and view the security status of the system.
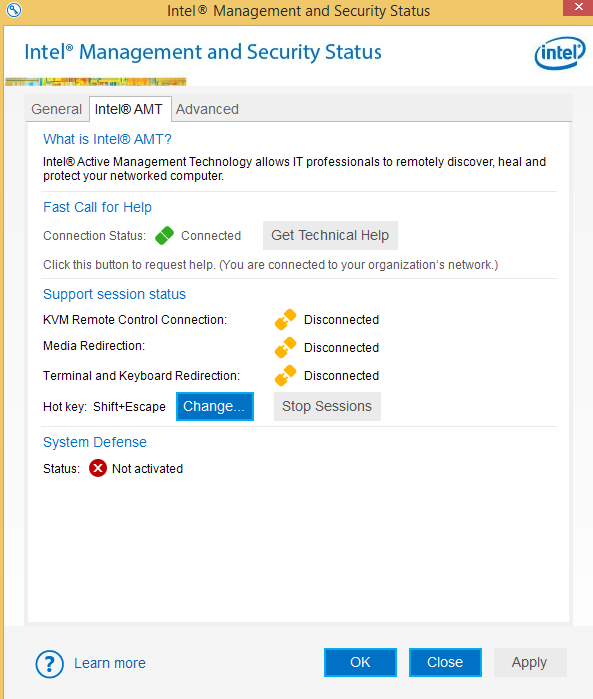
Figure 7. Intel AMT tab in Intel Management and Security Status
The Advanced tab in Intel MSS displays more detailed configuration information and Intel AMT components. In the screenshot shown in Fig. 8, it is clear that Intel AMT technology is configured on this system.
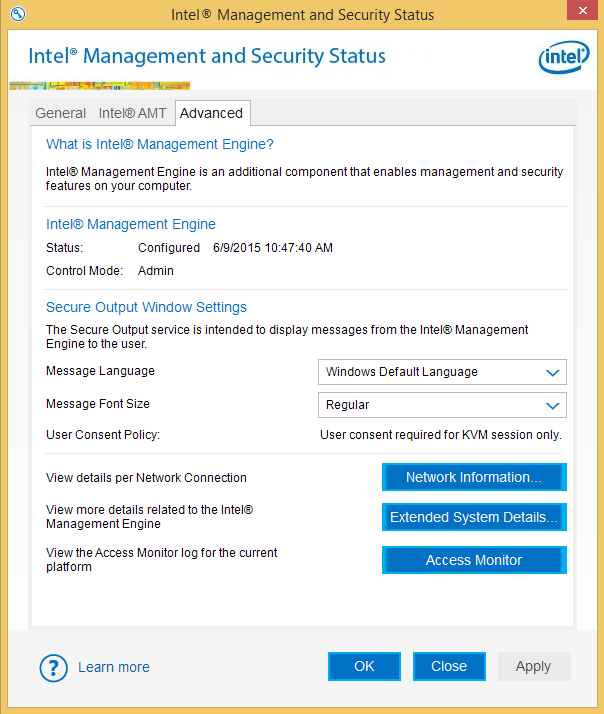
Figure 8. Advanced tab in Intel Management and Security Status
The Intel AMT Software Development Kit (SDK) provides low-level programming capabilities, so developers can create management applications that best use Intel AMT.
The package of tools for developing software based on Intel AMT is a sample code and a set of API interfaces that allow developers to quickly and easily add support for Intel AMT to applications. The SDK also includes a complete set of documentation in HTML format.
This software development toolkit supports C ++ and C # on Microsoft Windows and Linux operating systems. The user manual and Readme files in each directory contain important information about building examples.
An SDK is a collection of folders that can be copied to any location. In this case, the entire folder structure should be copied, this is due to the mutual dependence between the components. At the top level are three folders: DOCS (contains documentation for the SDK), as well as folders with code examples for Linux and Windows. For more information on how to get started and use the SDK, see the Implementation Guide and the Intel AMT Reference Guide .
For more information about system requirements and sample code building, see the "Using the Intel AMT SDK" section in the Implementation Guide and the Intel AMT Reference Guide. Documentation is available on the Intel Software Network: Intel AMT Based Software Development Kit (latest release) .
» Implementation Guide and Intel AMT Reference Guide
» Intel AMT SDK Downloadable File
»High-level API, article and downloadable file
»Intel Platform Solutions Manager, article and download
» Power Shell module, downloadable file
» KVM Application Developer Guide
» Redirect Library
» CIM C ++ Platform API
» CIM C # Platform API
» WMI Intel ME Provider
» System Status Check (NAP)
» Case Studies and Projects
The following table lists the features supported in Intel AMT versions 8 through 11.
For a description of all features and components, see the Intel AMT Implementation Guide and Reference Manual (in the "Intel AMT Components" section.)

Intel AMT supports remote applications running under Microsoft Windows * or Linux *. Intel AMT 2.0 or later supports only local Windows applications. For a complete listing of system requirements , see the Implementation Guide and the Intel AMT Reference Guide .
Getting started
To remotely manage an Intel AMT client or run examples from the SDK, use a separate system to remotely manage an Intel AMT device. For more information, see the Implementation Guide and the Intel AMT Reference Manual , located in the Docs folder in the Intel AMT SDK.
')
What is Intel Active Management?
Intel AMT is part of the Intel vPro solution package. If the platform supports Intel AMT, then such platforms can be remotely controlled regardless of the state of the power supply and the presence or absence of the operating system.
The Intel AMT system is based on the core of the Converged Security and Manageability Engine (CSME). Intel AMT is a component of Intel vPro and uses a number of elements of the Intel vPro platform architecture. In fig. 1 shows the relationship between these elements.

Figure 1. Intel Active Management Technology Architecture 11
Note the network connection associated with the Intel Management Engine (Intel ME). The adapter used varies depending on the version of Intel AMT used.
- The CSME firmware contains Intel AMT functionality.
- A flash image is stored in flash memory.
- To support the capabilities of Intel AMT, you can use the CSME kernel implemented by the OEM manufacturer of the platform. The remote application installs and configures the corporate system.
- After turning on the firmware is copied to the RAM.
- Firmware runs on an Intel processor with Intel ME and uses a small amount of RAM (slot 0) to store data at runtime. Therefore, for the firmware to work, it is necessary that the RAM module is installed in slot 0 and that this connector is enabled.
Intel AMT stores the following information in flash memory (Intel ME data).
- Parameters customizable by OEM:
- Settings such as passwords, network configuration, certificates, and access control lists.
- Other configuration data, such as alert lists and Intel AMT system security policies.
- The hardware configuration defined in the BIOS when the computer starts.
- Information about platforms in 2016 that support Intel vPro technology (release 11.x):
- Technological process 14 nm
- Platform (mobile devices and desktop computers)
- 6th generation Intel Core processor
- CPU: SkyLake
- Platform Controller Node: Sunrise Point
New features in the Intel Active Management Technology version 11.0 SDK
- CSME is a new Intel AMT 11 architecture. Prior to Intel AMT 11, the CSME core was called the Intel Management Engine BIOS Extension (Intel MEBx).
- MOFs and XSL files: MOFs and XSL files in the \ DOCS \ WS-Management folder and class reference materials in the documentation are for version 11.0.0.1139.
- New WS event fields and PET arguments: additional arguments added to CILA alerts provide a reason code for connecting the user interface and the host name of the device that issued the alert.
- Updated version of OpenSSL *: The version of OpenSSL is v1.0. Also updated library redirects.
- Updated version of Xerces: on Windows and on Linux, the Xerces version 3.1.2 library is used.
- HTTPS support for WS events: secure subscription to WS events is supported.
- Remote secure wipe using Intel AMT boot options: Among Intel AMT boot options, you can safely remove all data from the primary storage device.
- Signing DLLs with a strong name: The following DLLs are now signed with a strong name: CIMFramework.dll, CIMFrameworkUntyped.dll, DotNetWSManClient.dll, IWSManClient.dll and Intel.Wsman.Scripting.dll.
- HECI and agent monitoring modules enable automatic platform reboot: the ability to automatically restart when any HECI or agent monitoring modules report that the agent has expired.
- Replacing IDE-R storage redirection protocol: storage redirection works via USB-R protocol instead of IDE-R protocol.
- SHA Update: SHA1 certificates have been eliminated, a series of SHA256 certificates has been applied instead.
Setting up an Intel AMT client
Preparing an Intel AMT client for use
In fig. Figure 2 shows the steps to configure an Intel AMT device before using it.

Figure 2. Setting progress
Before you configure an Intel AMT device in the Setup and Configuration Application (SCA), you must prepare it, having received the initial information, and put it into installation mode. The initial information will vary depending on the available components of the Intel AMT release and the platform settings applied by the OEM manufacturer. Table 1 lists installation and configuration procedures for different versions of Intel AMT.
| Installation Method | Applicability to Intel AMT versions | additional information |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional mode | 1.0; versions 2.x and 3.x in traditional mode | Traditional installation and setup |
| SMB | 2.x, 3.x, 4.x, 5.x | Installation and configuration in SMB mode |
| Psk | From version 2.0 to Intel AMT 10, abolished in Intel AMT 11 | Install and configure using PSK |
| PKI | 2.2, 2.6, 3.0 and later versions | Install and configure using PKI (remote configuration) |
| Manually | 6.0 and later | Manual installation and setup (from version 6.0) |
| CCM, ACM | 7.0 and later | Client control mode and admin control mode Manually configure clients for Intel AMT 7.0 and later |
Intel Setup and Configuration Software (Intel SCS) 11 can be used to prepare systems for earlier versions up to Intel AMT 2.x. For more information about Intel SCS and training levels available for different versions of Intel AMT, see the website Download the latest Intel Setup and Configuration Service (Intel SCS) .
Manual Tips
When setting up the platform manually, starting from version 6.0, there are no restrictions on the components, but certain features of the system behavior should be taken into account.
- API methods will not return PT_STATUS_INVALID_MODE status, since only one mode is available.
- By default, the TLS protocol is disabled and must be enabled during configuration. This will always be the case during manual configuration, since it is not possible to set TLS parameters locally.
- The local platform clock will be used until the time over the network is set remotely. Automatic configuration will not succeed if network time is not set (and this can only be done after configuring TLS or Kerberos *). Enabling TLS or Kerberos after configuration will not work if network time has not been set.
- The web user interface is enabled by default in the system.
- The system defaults to SOL and IDE-R.
- The system disables the default redirection listener in Intel AMT, starting with version 10.
- If you enable KVM locally via CSME, it will still not work until the administrator activates it remotely.
Starting with Intel AMT 10, some devices are shipped without a physical network adapter. These devices cannot be configured using existing USB solutions included with Intel SCS 11.
Manual installation
When enabled, the Intel AMT platform displays the BIOS startup screen, then processes the MEBx. During this process, you can access Intel MEBX, but this approach depends on the manufacturer of the BIOS. Some possible methods are:
- Most BIOS makers add the ability to log in to the CSME in a one-time boot menu. Press the appropriate keys (usually use the keyboard shortcut Ctrl + P) and follow the prompts on the screen.
- On some OEM platforms, you are prompted to press the <Ctrl + P> keys after the start-up self-test procedure. When you press the <Ctrl + P> key combination, control goes to the Intel MEBx main menu (CSME).
- Some OEMs embed CSME in the BIOS (but this approach is relatively rare).
- Some OEMs provide the ability in the BIOS to show or hide an offer by pressing <Ctrl + P>, therefore. if the corresponding command is absent in the one-time boot menu, check the BIOS to enable the prompt.
Client control mode and admin control mode
After installing a device with Intel AMT 7.0 or later, it switches to one of two control modes.
- Client management mode. Intel AMT enters this mode after a simple host-based configuration (see “Host-based Configuration (Local)”). In this mode, the functionality of Intel AMT is limited, since a lower level of trust is sufficient for a host-based configuration.
- Admin control mode. After remote configuration, configuration using USB or manual configuration using CSME Intel AMT goes into administrator control mode.
There is also a configuration method that includes the procedure for changing the mode: from client mode to administrator mode. This procedure assumes that the Intel AMT device is in client control mode, and switches the device to administrator control mode.
In the administrator control mode, the Intel AMT functionality is not limited. This is due to a higher level of trust with this installation method.
Customer Management Restrictions
Upon completion of the simple host-based configuration, the platform enters the client control mode, in which the following restrictions apply.
- The system security feature is not available.
- Redirection actions (IDE-R and KVM, excluding starting a SOL session) and changing download parameters (including SOL loading) require additional user consent. In this mode, remote IT support staff can still troubleshoot end-user systems using Intel AMT.
- If an auditor is appointed, then auditor rights are not required to cancel training.
- A number of functions are blocked to prevent the untrusted user from accessing the platform.
Manually configure the Intel AMT 11.0 client
When you turn on the Intel AMT platform, the BIOS initial screen is displayed, then the BIOS extensions are processed. Logging into the Intel AMT extension in BIOS depends on the BIOS manufacturer.
When using the Intel AMT reference platform (SDS or SDP), you are prompted to press the <Ctrl + P> keys. After that, control passes to the main menu of the CSME.
In OEM systems, a one-time boot menu can be used, and logging into CSME is usually one of the boot options in this menu. The specific key combinations may vary depending on the OEM manufacturer, type of BIOS and model.
Configure Intel AMT 11.0 Clients Manually with Wi-Fi Only
Many systems no longer have a physical connector for connecting to a wired LAN. You can configure and activate Intel ME, then use the web interface or some other method to configure your wireless settings.
- Change the default password by setting a new value (this is required to continue). The new value must be a strong password. It must contain at least one uppercase letter, one lowercase letter, one digit and one special character, and its length must be at least eight characters.
- Log in to CSME at startup.
- Enter the default password (admin).
- Enter and confirm a new password.
- Select "Intel AMT Setup."
- Make sure the checkbox “Select Management Components” is checked.
- Select "Enable Network Access."
- Select "Y" to confirm the inclusion of the interface.
- Select "Network Setup".
- Select the Intel ME Network Name setting.
- Enter the node name.
- Enter the domain name.
- Select User Consent.
- The default is "KVM only". You can select “No” or “All”.
- The default is "KVM only". You can select “No” or “All”.
- Exit CSME.
- Set up a wireless connection using ProSet wireless drivers synchronization, a web interface, or another method.
Configuring Intel AMT 11.0 Clients Manually with Local Area Connection
Enter the default CSME password (admin).
Change the default password (required to continue). The new value must be a strong password. It must contain at least one uppercase letter, one lowercase letter, one digit and one special character, and its length must be at least eight characters. Using the management console, you can change the Intel AMT password without changing the CSME password.
- Select "Intel AMT Setup."
- Make sure the checkbox “Select Management Components” is checked.
- Select "Enable Network Access."
- Select "Y" to confirm the inclusion of the interface.
- Select "Network Setup".
- Select the Intel ME Network Name setting.
- Enter the node name.
- Enter the domain name.
- Select User Consent.
- The default is "KVM only". You can select “No” or “All”.
- The default is "KVM only". You can select “No” or “All”.
- Exit CSME.
Access to Intel AMT via a web interface
An administrator with user rights can establish a remote connection to an Intel AMT device through a web interface. To do this, enter the URL of the device. The URL will vary depending on whether TLS is enabled.
- Not TLS - http: // <IP address or FQDN>: 16992
- TLS - https: // <full domain name only>: 16993
To connect without TLS, you can also use a local connection and a host browser. You can specify localhost or 127.0.0.1 as the IP address. Example: 127.0.0.1 : 16992.
Requirements for Intel AMT support
In addition to properly configuring the BIOS and CSME, an Intel AMT-compatible wireless network adapter is required. To manage a host's OS using Intel AMT, certain drivers and services are required.
To ensure that the drivers and Intel AMT services are loaded correctly, locate them in the device manager and in the "Services" section of the host OS. Regularly visit the OEM site for updated BIOS, firmware and driver versions.
Here are the drivers and services that should be displayed in the host OS.
- Intel Ethernet Network Connection i218-LM *
- Intel AC 8260 Dual Band Wireless Network Adapter or equivalent *
- Intel Management Engine Interface Driver (Intel MEI)
- Local Area Network (SOL) Driver
- Intel Management and Security Status Local Management Service (Intel MSS) **
- Intel AMT Management and Security Status **
- HID device drivers (mouse and keyboard) ***
* Versions of the network controller and wireless interface will vary depending on the generation of the Intel vPro platform.
** As part of the complete driver package for Intel MEI (chipset).
*** HID device drivers are required when connecting via Intel AMT KVM. There are usually no problems with the default drivers, but we encountered difficulties when using non-standard OS installations. If a connection is established to a device without HID drivers, the OS attempts to automatically install these drivers. After installation, re-establish the KVM connection.
Note. The driver version level must match the firmware and BIOS version level. If incompatible versions are installed, Intel AMT will not work with components that require these interfaces.
Physical device - wireless Ethernet connection
By default, all wireless vPro wireless platforms will have an Intel AMT-enabled wireless network card, such as the Intel AC 8260 dual-band adapter. Other wireless adapters other than Intel adapters will not support Intel AMT wireless connectivity. When using a wireless network adapter other than Intel AC 8260, you can use ark.intel.com to verify that this adapter is compatible with Intel AMT.
Required software for Windows
For remote control, device drivers are not required, but they are necessary for local data exchange with the firmware. OS discovery and configuration features require the Intel MEI driver, the SOL driver, the LMS service, and the Intel MSS application.
Device Drivers - Intel Management Engine Interface
An Intel MEI is required to connect to the firmware. By default, the Intel MEI driver is automatically installed from Windows Update. The version level of the Intel MEI driver should be the same as that of the Intel MEBX.
The Intel MEI driver is displayed in the device manager in the "System devices" section called the Intel Management Engine Interface.
Device Drivers - LAN Serial Driver
The SOL driver is used in the IDE redirection operation when connecting a remote CD-ROM drive.
The SOL driver is displayed in the device manager in the "Ports" section titled "Intel Active Management Technology - SOL (COM3)".

Figure 3. Serial LAN driver
Service - Intel Active Management Technology LMS Service
The Local Manageability Service (LMS) runs locally on an Intel AMT device and enables local management applications to send requests and receive responses. The LMS responds to requests sent to the local Intel AMT host and sends them to Intel ME using the Intel MEI driver. The service installer is in the same package as the Intel MEI drivers on the OEM websites.
Please note that when installing Windows, Windows Update only installs the Intel MEI driver. IMSS and LMS are not installed. The LMS service communicates from an OS application with the Intel MEI driver. If the LMS service is not installed, go to the OEM website and download the Intel MEI driver, which is usually in the chipset driver category.

Figure 4. Intel Management Engine Interface Driver
LMS is a Windows service installed on Intel AMT 9.0 or later. Previously, in versions of AMT AMT from 2.5 to 8.1, the LMS service was called User Notification Service (UNS).
The LMS receives a set of alerts from an Intel AMT device. The LMS writes an alert to the Windows application event log. To view alerts, right-click Computer and select Computer Management> System Software> Event Viewer> Application .
Application - Intel Management and Security Status
You can open the Intel MSS application using the blue key icon in the Windows notification area.

Figure 5. Intel Management and Security Status icon in the notification area
General tab
The General tab in Intel MSS displays the status of the Intel vPro components available on this platform and the event log. Each tab provides additional information.

Figure 6. General tab in Intel Management and Security Status
Intel AMT tab
Here, a local user can perform KVM and media redirection operations, use the help request and view the security status of the system.

Figure 7. Intel AMT tab in Intel Management and Security Status
Advanced tab
The Advanced tab in Intel MSS displays more detailed configuration information and Intel AMT components. In the screenshot shown in Fig. 8, it is clear that Intel AMT technology is configured on this system.

Figure 8. Advanced tab in Intel Management and Security Status
Intel Active Management Technology Software Development Kit (SDK)
The Intel AMT Software Development Kit (SDK) provides low-level programming capabilities, so developers can create management applications that best use Intel AMT.
The package of tools for developing software based on Intel AMT is a sample code and a set of API interfaces that allow developers to quickly and easily add support for Intel AMT to applications. The SDK also includes a complete set of documentation in HTML format.
This software development toolkit supports C ++ and C # on Microsoft Windows and Linux operating systems. The user manual and Readme files in each directory contain important information about building examples.
An SDK is a collection of folders that can be copied to any location. In this case, the entire folder structure should be copied, this is due to the mutual dependence between the components. At the top level are three folders: DOCS (contains documentation for the SDK), as well as folders with code examples for Linux and Windows. For more information on how to get started and use the SDK, see the Implementation Guide and the Intel AMT Reference Guide .
For more information about system requirements and sample code building, see the "Using the Intel AMT SDK" section in the Implementation Guide and the Intel AMT Reference Guide. Documentation is available on the Intel Software Network: Intel AMT Based Software Development Kit (latest release) .
Other Intel AMT Resources
» Implementation Guide and Intel AMT Reference Guide
» Intel AMT SDK Downloadable File
»High-level API, article and downloadable file
»Intel Platform Solutions Manager, article and download
» Power Shell module, downloadable file
» KVM Application Developer Guide
» Redirect Library
» CIM C ++ Platform API
» CIM C # Platform API
» WMI Intel ME Provider
» System Status Check (NAP)
» Case Studies and Projects
application
The following table lists the features supported in Intel AMT versions 8 through 11.
For a description of all features and components, see the Intel AMT Implementation Guide and Reference Manual (in the "Intel AMT Components" section.)
| Component | Intel AMT 8 | Intel AMT 9 | Intel AMT 10 | Intel AMT 11 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware inventory | X | X | X | X |
| Persistent id | X | X | X | X |
| Remote on and off | X | X | X | X |
| SOL / IDE redirection | X | X | X | X |
| Event management | X | X | X | X |
| Third-party data warehouses | X | X | X | X |
| Embedded web server | X | X | X | X |
| Flash Protection | X | X | X | X |
| Firmware update | X | X | X | X |
| HTTP Digest / TLS | X | X | X | X |
| Static and dynamic IP addresses | X | X | X | X |
| System protection | X | X | X | X |
| Agent presence | X | X | X | X |
| Power management policies | X | X | X | X |
| Mutual authentication | X | X | X | X |
| Kerberos * | X | X | X | X |
| TLS-PSK | X | X | X | Abolished |
| Privacy icon | X | X | X | X |
| Wake on Intel Management Engine LAN | X | X | X | X |
| Remote setup | X | X | X | X |
| Wireless setup | X | X | X | X |
| EAC 802.1 | X | X | X | X |
| Power Packs | X | X | X | X |
| Environment detection | X | X | X | X |
| Scope of reading the event log | X | X | X | X |
| System Heuristic Protection | X | X | X | X |
| WS-MAN interface | X | X | X | X |
| VLAN settings for Intel AMT | X | X | X | X |
| Network interfaces | X | X | X | X |
| Quick Help Call (CIRA) | X | X | X | X |
| Access monitor | X | X | X | X |
| Microsoft NAP support * | X | X | X | X |
| Virtualization support for agent presence | X | X | X | X |
| PC alarm clock | X | X | X | X |
| KVM remote control | X | X | X | X |
| Synchronize wireless profiles | X | X | X | X |
| IPv6 support | X | X | X | X |
| Host based training | X | X | X | X |
| Proper shutdown | X | X | X | X |
| WS-Management API | X | X | X | X |
| SOAP commands | X | Abolished | Abolished | Abolished |
| InstantGo Support | X | |||
| Remote secure wipe | X |
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/310318/
All Articles