Identification of road network problems using Yandex.Probok. Lecture in Yandex
Yandex.Traffic and related functions in Navigator and Maps work thanks to the data on the speed of cars on different parts of the road. This is not at all new, but still an effective scheme. The question that has arisen as the traffic jams develop - can the specified data be used somehow else?
Cards analyst Leonid Mednikov told about the example of such use at the Yandex conference “Ways of Communication 2016”. Under the cut - the transcript of the report and most of the slides.
The theme of my story is to identify problem areas on the road using the data that we have. First, I’ll tell you why this is so important, and then we’ll see how easy it is with Yandex.Prob to find problem areas that create congestion in the city.
So let's start with the theory. Pretty simple.

Here we have a road, the roads consist of lanes, one lane in theory can not drive more than 1.5 thousand cars, about that, in an hour. This is due to the fact that they keep a distance of one after another for about two seconds. If we want to transport more people, either we need to put more people in one car, or we can put a bus in there for him to drive. It's great that public transport is evolving.
But if we are talking about motorists, then everything, 1.5 thousand cars and no more. The only problem is that there may be less. With this you want to do something.
What could be less cars? The first most common case - just so many cars there. Drives fewer cars, the roads are empty. Yandex.Navigator is struggling with this very well. If a road is empty, it will send all the drivers there so that they take it as soon as possible and drive around the existing traffic jam.
The problem is that just existing traffic jams is the second factor that reduces the capacity of the road. Maybe this is not a very obvious fact, that if we collected a traffic jam, then we now use this road less efficiently. I want to talk more about this on the example of the graph.

On the horizontal axis we see the speed in km / h, vertically - the number of cars that can travel if the flow rate is this.
What is important here? There is a zone of high speeds, where the capacity of the road varies little. This is an important practical fact. He says that if we have a permitted speed of 60 km / h, we can make it 100, 50 or 40 km / h, the capacity of the road will not change much. This is high speed.
But at speeds somewhere below 20 km / h, the situation is exactly the opposite. Here, every km / h takes up road capacity is very noticeable. If we reduced the speed from 60 km / h to 7 km / h for some reason, then we lost twice the road capacity. That is, built a two-lane road, and goes as if single-lane.
Demonstrate how this works. Suppose there is a stream of cars defined. If we have a speed above the border on this schedule, above 20 km / h, then the road calmly copes, the cars are going. If for some reason the cars slowed down, it means that the capacity has already become lower than that required from the road, and this means that the cars are starting to accumulate. In this case, we have 1,200 cars per hour, and only 1,000 can go at that speed. So, we collect 200 cars per hour, with a car length of 5 meters, this is a kilometer tube already.
Why speeds decrease? What can you do about it?
The first is when the whole flow stops by a traffic light or a speed bump, a broken road, for some reason there is a road, but everyone moves more slowly.
The second reason is the narrowing of the road due to design features, repairs and so on. In the second example, I want a little more to deal with the search for problem areas.

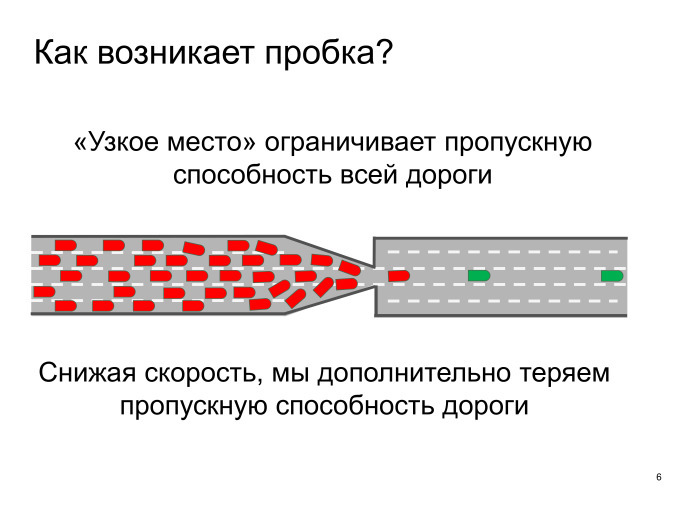
A typical picture, here it is a little hypertrophied, the road for some reason narrows. The problem is that the throughput of the entire road is determined by the place where it is the lowest. As the chain breaks along the weakest link, so here the throughput of the entire road is determined by one place. Before and after we have five lanes, they are useless. We really have one lane.
But the worst thing is that we don’t even have this one lane, because we just found out that if we move slowly at the narrowest point, here the road’s carrying capacity is lost. We see a five-lane road, in fact - 0.5 lanes. I would not want to allow such situations at all.
What can be done with this? What are some ideas? Everywhere make one lane. It would seem a paradox. Let's remove these lanes, or if this is some kind of temporary phenomenon, just ensure smooth road narrowing. Drivers should not be allowed to rebuild at the last moment, they lose speed at the narrowest point at this moment, this is unacceptable. It is necessary to give the possibility of a sufficient distance so that the cars change lanes and without losing speed pass a bottleneck.
It would seem a simple theory, but I will show a couple of examples of how it is used or not used.

This, thank God, is a historical picture in Moscow, but it had a place to be. Exit from the outside of the Moscow Ring Road on the Leningradskoe highway towards the area. I think many were there. Ram is now being reconstructed, after all, it is not quite so. What is important here that we especially see the island? This created a situation where cars are forced to slow down. Because three lanes crash into the main stream, it is impossible to do this non-emergency, if you are not alone in the middle of the night, that is, you are forced to slow down, other cars slow down, the road narrows and we get a reduction in speed in the narrowest spot in a difficult situation, we also get a decrease in throughput.

The second example is also a real snapshot from the same cosmos. The same situation: the main road is even narrower, at the congress we have not three lanes, but two, but what has been done? When a merger occurs, the machines, in principle, do not feel each other, two lanes in parallel stood up. One another does not interfere. And then they have half a kilometer until they take away one lane, and another half kilometer until they take the second lane. Just at speed, they have the opportunity to restructure. Of course, it is possible to submit such a flow of cars to such a denouement that it cannot cope, because the lanes are getting smaller, but up to a certain limit we won’t get a traffic jam here and let the road’s full traffic capacity work.

I want to summarize the first part. On the roads, there are so-called bottlenecks, bottlenecks, which determine the carrying capacity of the road, they create traffic jams, and if we want to do something about it, there are two conclusions. It should be treated here and no need to be treated anywhere else. Because if we remember the five-lane highway, we can expand it to 10 lanes in any other place, narrow down to two, invite repairmen — no problem, nothing will change.
But this one single bottleneck sets the parameters of the entire route.
My further story will be devoted to finding out where these places are. And the solution to the problem is not always expensive, it is not always necessary to build an extra denouement. Sometimes you need to take away the extra lane, or if there is a traffic light there - maybe reconfigure it forever or depending on the time of day. Solutions are not necessarily some kind of super-complicated and expensive.
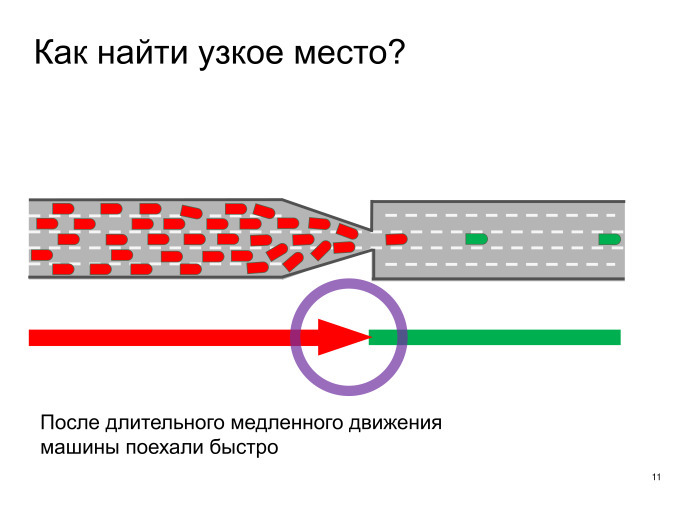
How do we find these bottlenecks? Simple enough. Yandex.Prob has no such data, how many lanes are there, what and how, but we can see the speed of movement, and it has a completely clear pattern: first, the cars drive slowly, then quickly. And seeing such a picture, especially if the traffic jam is large, we can say that there is some problem in this place. Which one? We must go to the place and study.

Let's see how you can find on real examples, where are the bottlenecks. This is the Enthusiasts Highway, one of the best routes to illustrate traffic jams in Moscow. Here are typical daily traffic jams, at the beginning of this traffic jam we must look at what is happening here.
An important practical nuance: we see that red turns into yellow, and then into green. Most likely, the problem is somewhere on the border of yellow and green. If we have two bottlenecks, if we run into the second, then it is useless to expand the first. We will expand the first one, and immediately the whole traffic will be transferred further, in this case to 100 meters, so we need to look at the second bottleneck, there is a traffic light, well, in general, for example, if we want to solve the traffic jams problem, and we know that somewhere the rough road, first of all, it should be leveled here. If we want to reconfigure the traffic light, we must first look here. If we want to see what's with the fences, first of all we need to look here, in a narrow place.
A similar situation in the opposite direction. Cork, easily determine the bottleneck, everything is the same.
Not only these questions can be answered through the search for bottlenecks.
In some cases, you can even answer the question of whether to build a road or not. This can be done not always, but sometimes it is possible.
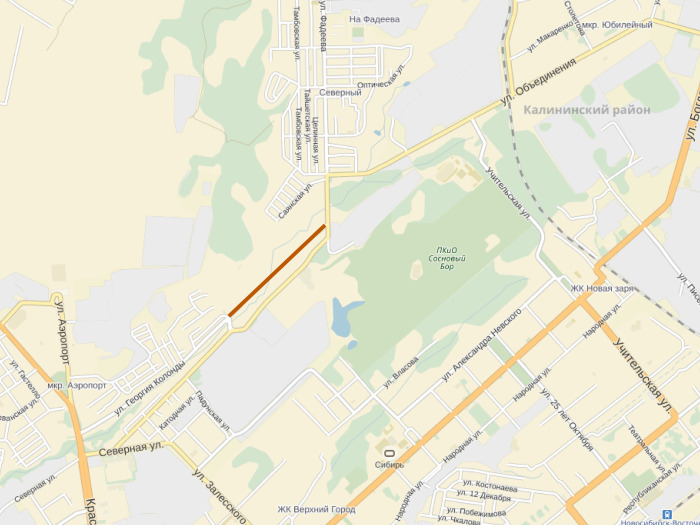
Here is an example from Novosibirsk. Here it was proposed to build a new road. The case is interesting in that it runs parallel to the existing one, so a fairly simple analyst is obtained.
Let's look at traffic jams in the morning and evening rush hour, where we have narrow places.
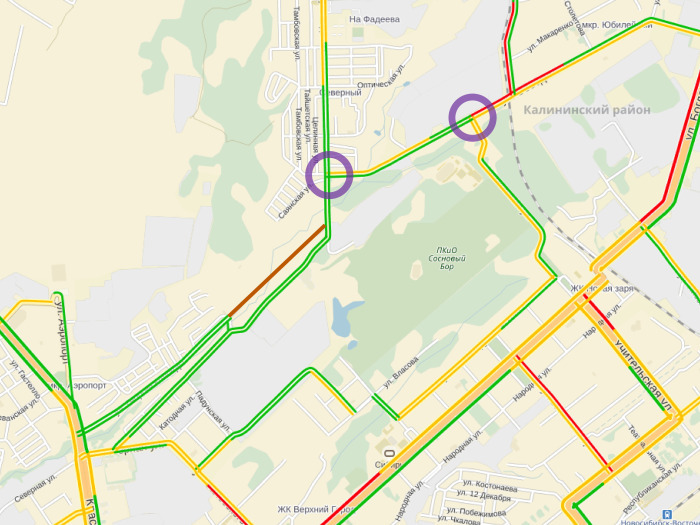
A typical picture of traffic jams in the morning rush hour. There is a difficulty that rests on this intersection. All go left - down in the south of the city center in the morning. Perhaps we should give more priority to those traveling south at this intersection during the morning rush hour.
The second problem here is an interesting example, which consists in the fact that the continuous yellow line goes almost to the center itself, which means that everything is already there, the problem can be unsolvable. When everyone runs into the center, you can’t expand it here, here again the glory of public transport, because when all traffic jams hit the center, the problem cannot be solved in this way. The road has nothing to do with it, it does not expand the bottleneck in any way, which means that the situation with traffic jams will not be affected. Maybe it will be more convenient for people to drive, faster, anything, in the sense of more comfortable to drive through this section, but it will not change traffic jams.

The picture in the evening rush hour, the same, bottlenecks, perhaps, should be given greater priority to people turning north from the center. There is a problem here, one can give priority to those traveling to the north, but the new road will not solve the problem of traffic jams. A simple analysis can be done on the service in five minutes.
Speaking about the service, in conclusion I want to remind you: see a typical map of traffic jams can be any person, enthusiast or mayor, just go to Yandex.Maps, turn on Jams, there is a secret button with a clock, it is a time machine, you switch to the statistics of jams, choose any day of the week, any time. Usually it is weekdays - 8:30 in the morning, the morning peak, and around 18:30 - the evening peak. And look at traffic jams.
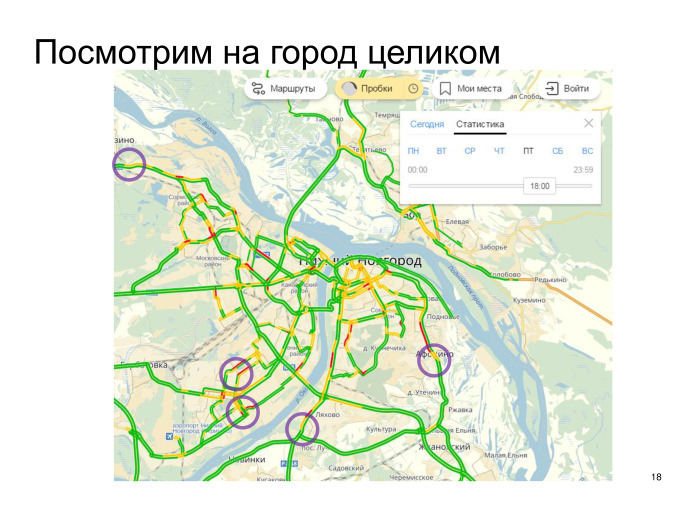
Here in Nizhny Novgorod, you can identify some of the main places on the road away from the city on Friday, where you can really solve the problem and help motorists to travel more easily.
Last practical trick on the example of a bottleneck:
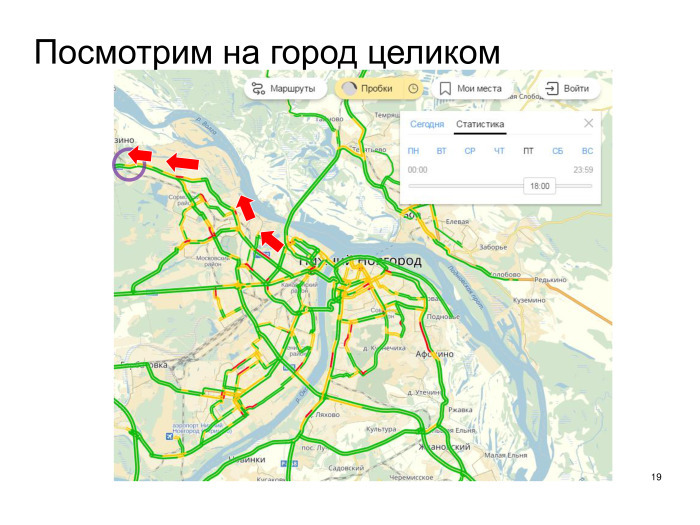
Those who leave the center actually go through a series of traffic jams. It is useless to solve the problem in the first traffic jam, we just send all motorists to extend the second one. Either it is necessary to solve everything, or if one by one, then it is necessary to solve with the latter, as it is here highlighted, because motorists will continue to travel free, but they will stand in the first three.
As an option, we can say that we are not solving the problem, it is so, there are too many difficulties so far. But to decide only the first and expect that we will improve something, unfortunately, is not necessary.
All this can be done independently, but if you are ready to influence the situation and study in more detail, then we are ready to help you with this. You can ask me through. We can not only with our eyes, but also automatically find bottlenecks and provide such data.

If you are ready to change the situation, we are ready to calculate the travel time during the day, the days of the week for these bottlenecks, and when any changes are made, it may be a change in the mode of traffic lights, to see what has become.
For those who really seriously want to dive into analytics, it is impossible to answer all questions only by studying the bottlenecks. There is Yandex Data Factory, this is a separate subdivision of Yandex, which is just engaged in paid analytics, you can come to them on a commercial basis for deeper analysis, for automatic reports and the like.
I have it all.
')
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/309652/
All Articles