New security features Android 7
 Google has already released Android 7. In the near future, owners of various devices running Android will receive a firmware update. One of the first new version will be users of branded devices Google Nexus 6P, 5X, 6, 9, Google Pixel C, Nexus Player, Android One. Since Google distributes Android updates in waves, not all users of these devices will be able to quickly receive the update. Android 7 will also be able to get the flagship device models of such vendors as Samsung (Galaxy S6 and S7), HTC (HTC 10, One A9 and One M9), Sony (Xperia Z3 +, Xperia Z4 Tablet, Xperia Z5, Xperia X), LG (V20 ), Huawei. The new version of Android has a number of new serious security features (security features), some of which we wrote in previous posts. The first was dedicated to the Direct Boot feature, which will make it easier for device owners to work with encryption. The second contained information about improvements to the security of the Linux kernel on which Android is based.
Google has already released Android 7. In the near future, owners of various devices running Android will receive a firmware update. One of the first new version will be users of branded devices Google Nexus 6P, 5X, 6, 9, Google Pixel C, Nexus Player, Android One. Since Google distributes Android updates in waves, not all users of these devices will be able to quickly receive the update. Android 7 will also be able to get the flagship device models of such vendors as Samsung (Galaxy S6 and S7), HTC (HTC 10, One A9 and One M9), Sony (Xperia Z3 +, Xperia Z4 Tablet, Xperia Z5, Xperia X), LG (V20 ), Huawei. The new version of Android has a number of new serious security features (security features), some of which we wrote in previous posts. The first was dedicated to the Direct Boot feature, which will make it easier for device owners to work with encryption. The second contained information about improvements to the security of the Linux kernel on which Android is based.The Direct Boot function is responsible for the timely preparation of the execution of the Android system files on the encrypted device. Since previous Android versions used the Full Disc Encryption (FDE) encryption method, i.e. the entire device memory encryption, the loader needed to know the device unlock code to decrypt system files (the Android unlock code uses the device unlock code as a component of the encryption key). In this scheme, the user had to enter the unlock code twice after rebooting the device: the first time to unlock the system files, and the second to unlock the device itself.
Its implementation of Direct Boot is due to the fact that Android 7 switched from using FDE encryption to per-file encryption, i.e. each individual file. This encryption scheme has long been used in iOS.
')
Under the hood, file-based encryption enables this improved user experience. For each system, it can be encrypted separately. If you use a device, it doesn’t need to have a full-disk encryption option. If you’re typing, you’ll be able to get the most out of it.
A source
Another security enhancement concerns the infamous system service called MediaServer. This component works with elevated rights and is responsible for playing various multimedia content. Vulnerabilities in it were regularly closed in Android security updates, which we wrote about in a blog. A security feature called overflow sanitization helps to close a whole class of Android vulnerabilities that were found in the libstagefright library. This library uses MediaServer. Another security improvement from MediaServer concerns the operation of the entire multimedia stack of components, each of which is now in isolation from its own sandbox environment.
First, by incorporating Clang's Undefined BeehaviorSanitizer, we’ve made it a matter of course. It is stopped. It is a modularization of sandboxes that have been modified. It is a great deal of effort to keep track of your body.
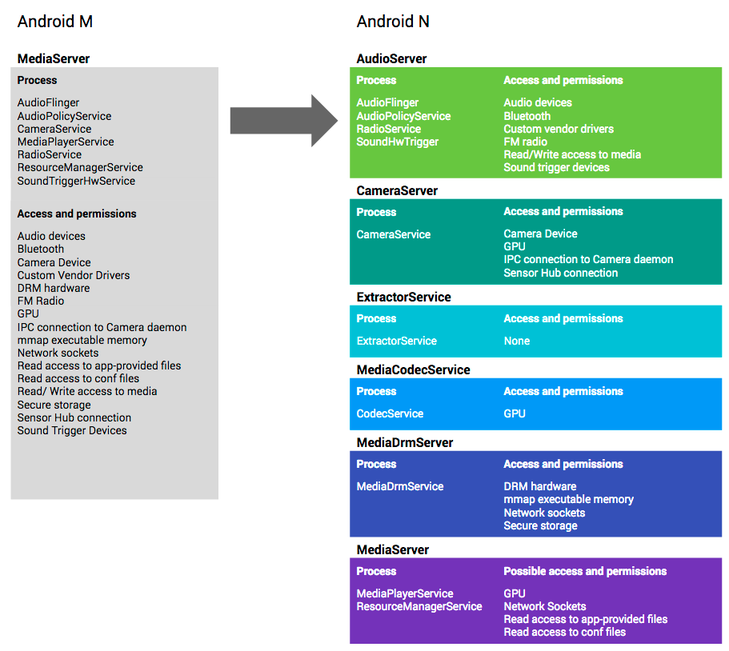
Fig. In Android 7, the MediaServer service is divided into various subsystems (multimedia stack) that work with limited rights and in a limited environment (sandbox). It can be seen that the new system of assigning rights to services is much more efficient from the point of view of security, because it allows the application to specify only the rights it needs. In the new version, the libstagefright library functions in the MediaCodecService service, which has minimal rights in the system. Thus, the exploitation of vulnerabilities in this component for Android 7 will not bring any results to the attacker.
The new feature Verified Boot strictly controls the integrity of the bootloader, preventing the device from loading if it is compromised. The Linux kernel's sandbox application, known as seccomp, has also been improved . In addition, SELinux security subsystem configuration settings have been improved. Both of these measures make it possible to completely close the sandbox security mechanism of applications, as well as reduce the risk of successful exploitation of other attack methods used by exploits.
We’ve written about improvements to the Android kernel security earlier . These include the implementation of DEP for kernel-mode virtual memory (Kernel DEP), a SMAP-type function that allows you to block access to user-defined virtual memory pages for kernel-mode code. Several new features relate to the technique known as Attack Surface Reduction (ASR), it can significantly reduce the success of the exploitation of a whole class of vulnerabilities. As part of the ASR. Android 7 supports removing default device debugging access, and also prohibits applications from using certain commands using the ioctl function.
Improved and has become a mechanism for updating Android 7 "over the air" (OTA update). Now the size of updates has become more compact, and the installation time has been significantly reduced. The reduction in installation time is also due to the fact that the new version will not have the “application preparation” stage, which took the most time during the update process in previous versions of Android.

be secure.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/309416/
All Articles