Alternative Technologies for High Availability
However, we decided not to limit ourselves to these developments and look for an alternative cluster solution for x86. Thus, an internal project was initiated to test cluster configuration based on Pacemaker software.
Pacemaker is a opensource product that is included with many Linux distributions. The product supports a wide range of cluster topologies, various quorum strategies, starting order and dependencies between applications, parallel applications, etc. It does not have a licensing program, respectively, licenses do not need to be purchased, at the same time a solution can be supplied for support from a number of vendors, for example from Red Hat.
The main goal of the project was the development and expansion of the products and clustering technologies offered by us and the construction of High Availability Configuration, the formation of a more accessible alternative to the existing solutions.
')
We set ourselves the following tasks:
- to carry out a standout of typical configurations, to study the functionality and limitations of the solution, to work out the configurations, to gain skills of implementation and configuration;
- to determine the possibility and prospects of further promotion of solutions in our projects.
We defined the main success criteria for testing configurations. The first is that the configurations should provide the basic functions of ensuring high availability of services. Protection should be provided from the main types of hardware and software failures: server failure (hardware, OS), failure to connect to disk resources, failure to connect to the LAN, failure of the application service. Verification of the functions carried out according to the PMI.
The second criterion is that the product being tested should be commercially advantageous compared to Veritas Cluster Server.
The third is the presence of additional functionalities of the product, such as user-friendly GUI, monitoring tools and alerts.
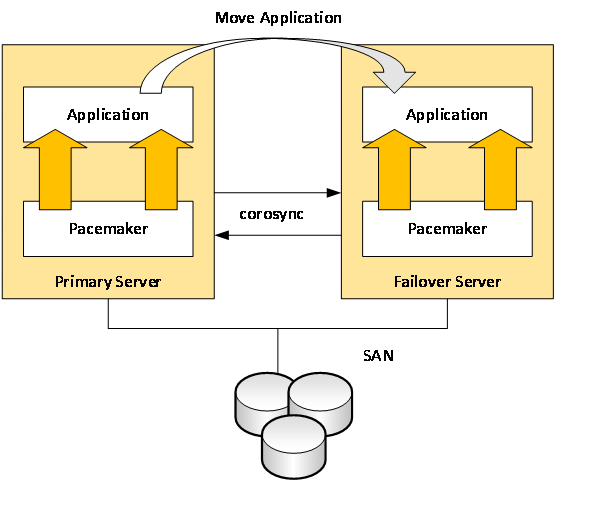
We have prepared a test bench, the general scheme of which is shown in Fig. one.
Fig. 1. Scheme of the test stand

To ensure the integrity of the configuration, each of the cluster nodes has 2 connections in the intercluster interaction network. In addition, to increase the availability of cluster nodes, each node has a duplicate connection to a public network segment intended for the transfer of application data.
The cluster configuration was built for an instance of Oracle Database 11g2. For system redundancy, a 1 + 1 scheme was used. It implies the use of the same type of equipment and the possibility of transferring the functionality of one of the servers in case of its failure to the backup node. The schematic diagram of the solution is shown in Fig. 2
Fig. 2. Solution scheme
The distribution of cluster resources between computing nodes is illustrated in Fig. 3
Fig. 3. Configuration of the distribution of cluster resources between computing nodes
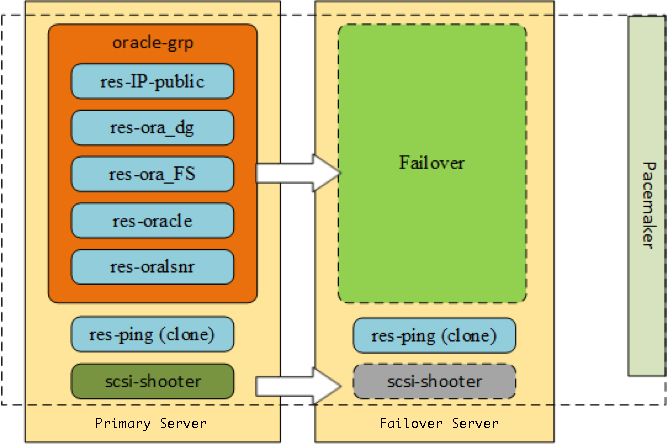
The oracle-grp group includes the following resources:
- res-IP public - IP address from public network (IPaddr2 agent)
- res-ora_dg - disk subsystem management resource (LVM agent)
- res-ora_FS - file system management resource (Filesystem agent)
- res-oracle - Oracle DBMS instance
- res-oralsnr - Oracle Listener instance
Resources outside the group:
- res-ping - network connection check resource (ping agent in clone configuration)
- scsi-shooter - fencing agent
The decision revealed some limitations. At the time of testing, the supported versions of Oracle DBMS for creating fail-safe configurations based on Pacemaker software were Oracle Database 10g and 11g. As mentioned above, testing was conducted with Oracle Database 11g2. Oracle Database 12c DBMS is not supported.
The prepared solution was subjected to a full test cycle. The main ones and the test results are presented in Table. one.
Tab. 1. Test cycle and their results
Item number | Requirements to be checked | Test result |
Pacemaker software based cluster validation technique | ||
| one. | Verification of the composition and configuration of hardware and software | Done |
| 2 | Verify network network reservation to the Public Network | Done |
| 3 | SAN reservation check | Done |
| four. | DBMS availability check | Done |
| five. | Connecting to the cluster management console | Done |
| 6 | Check Cluster Resource Status | Done |
| 7 | Checking the status of cluster nodes | Done |
| eight. | Cluster check | Done |
| 9. | Checking heartbeat condition | Done |
| ten. | Checking the status of IO Fencing | Done |
| eleven. | Check availability of services (Kernel Panic of the primary node of the cluster) | Done |
| 12. | Check availability of services (disabling all Ethernet connections of the primary node of the cluster) | Done |
| 13. | Check availability of services (disabling all FC connections of the primary node of the cluster) | Done |
| 14. | Check availability of services (kill process managed by cluster software) | Done |
| 15. | Checking the availability of services (reset by means of ILO of the main cluster node) | Done |
| sixteen. | Testing the fault tolerance mechanisms (disabling the main cluster node from one intercluster interaction network) | Done |
| 17 | Testing the fault tolerance mechanisms (disabling the main cluster node from all intercluster interaction networks) | Done |
| 18. | Established migration of services to the backup node | Done |
findings
The high availability configuration based on the Pacemaker software meets the basic requirements for fault tolerance and can be an alternative to VCS in productive applications with a number of the following limitations:
- Ethernet adapters redundancy (working out of the physical connection failure situation) must be provided with third-party software and application of the additional agent “ping” in the configuration, which is configured to periodically check the availability of specified targets in the network by IP address
- You must use the latest version of the cluster software;
- decision support by the vendor is limited to the basic composition of the software. Other agents are written by the community or by themselves. Support for these agents by the vendor is not covered.
The main directions of development solutions and vendor plans:
- documentation improvement;
- increase the number of resources in the cluster to 100;
- development of integration with containers;
- development of integration with RedHat 7.x.
- failure to further develop solutions based on cman & rgmanger
Ability to scale configurations: according to the documentation, it is possible to build a multi-node cluster based on Pacemaker (up to 16 nodes).
Ability to create DR configurations: building full-fledged DR-solutions based on Pacemaker software is impossible. A supported solution is a “stretched” cluster configuration with DRBD replication. Native integration with replication mechanisms from storage vendors is absent.
The main features of the Pacemaker software are:
- lack of a licensing program, i.e. the cost of licenses;
- cluster software integration with Linux system services;
- open source.
At the same time, a number of shortcomings of the tested solution were revealed:
- limit on the number of nodes in the cluster - a maximum of 16;
- application only on the Linux platform;
- small number of agents;
- non-functional GUI;
- lack of Disaster Recovery functionality;
- little flexibility in setting;
- instability of work in some software releases (software errors);
- lack of ability to manage multiple clusters from a single graphical management console;
- difficulty in setting up and operating;
- no consolidated documentation set.
Our experience with cluster solutions shows that using Veritas Cluster Server cluster software is more preferable from the point of view of availability, reliability and stability of the system, configuration flexibility and functionality, as well as vendor support. For this indicator, Pacemaker is inferior to Veritas.
However, in cases where price is a decisive factor, the use of Pacemaker software is possible subject to the nuances and limitations described above.
The article was prepared by Anton Goloschapov, the engineer-designer of computer systems of Jet Infosystems.
Source: https://habr.com/ru/post/308840/
All Articles